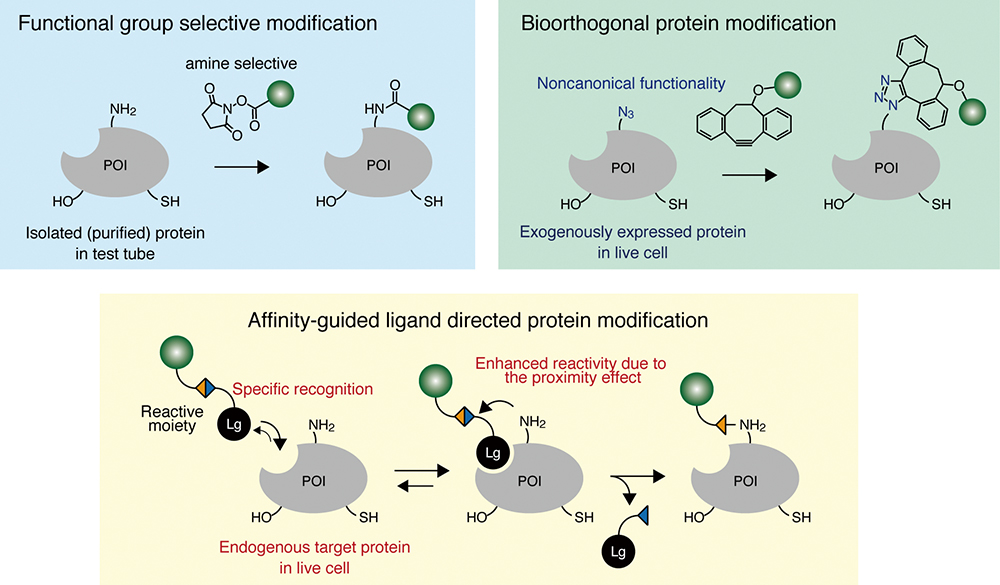
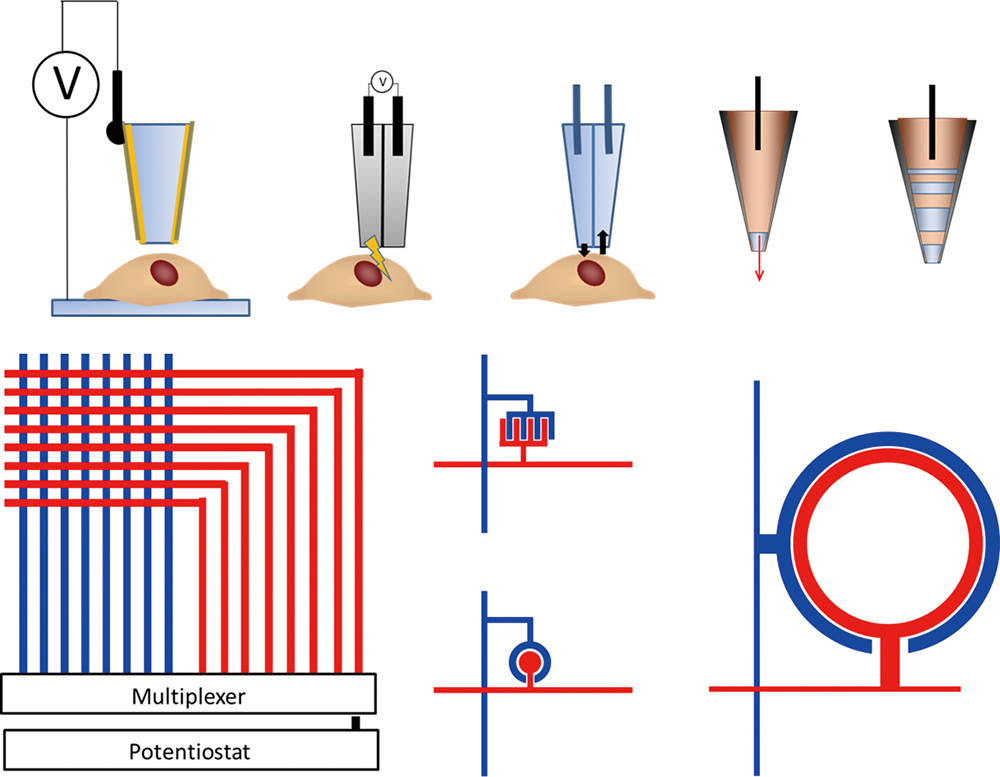
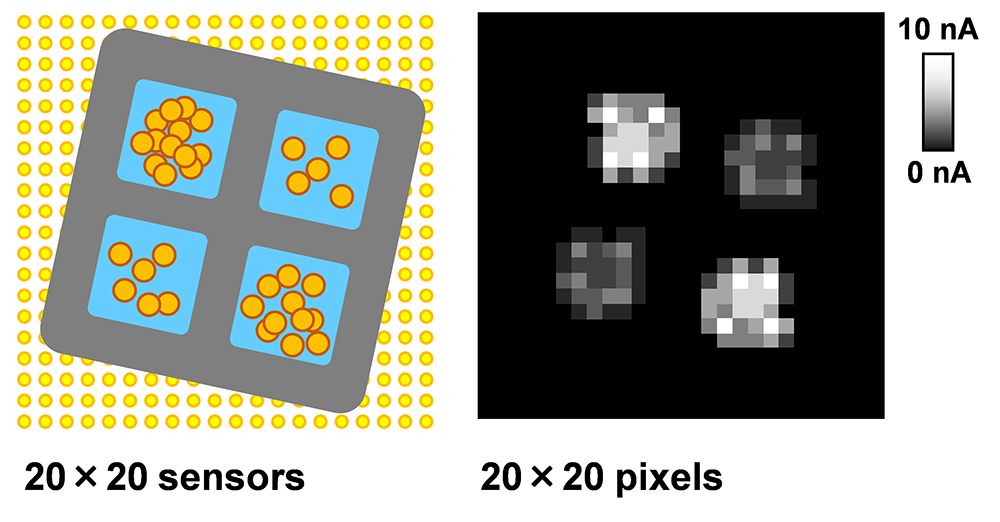
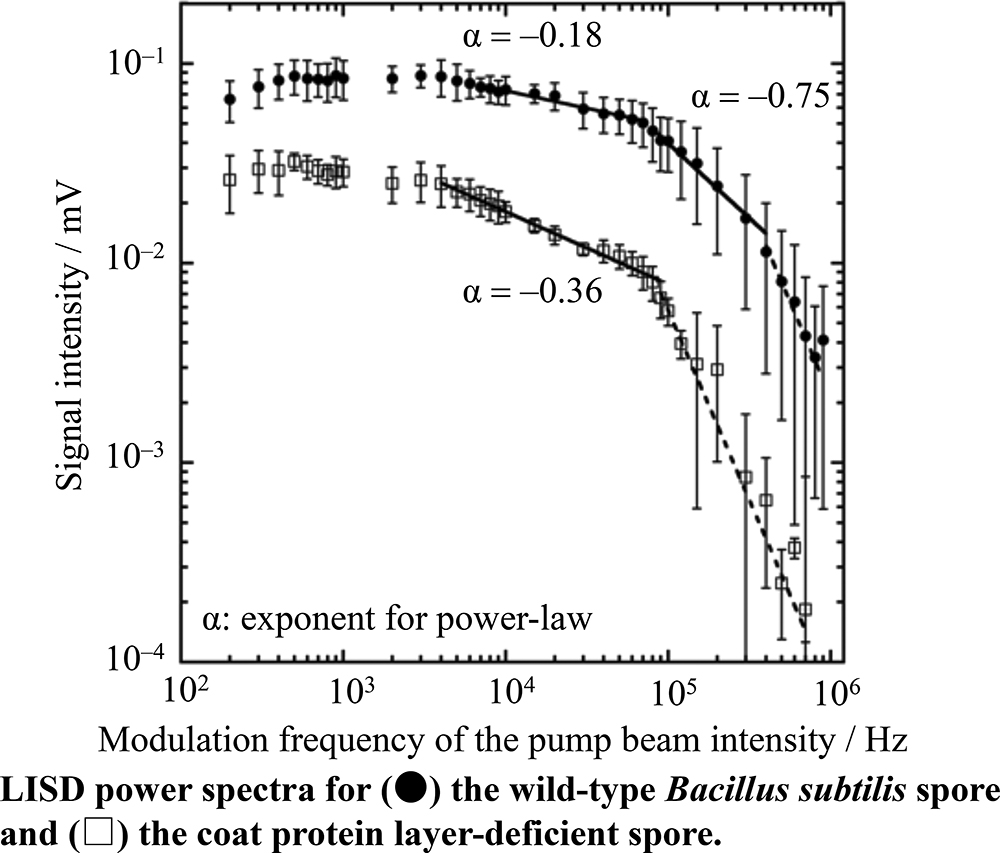
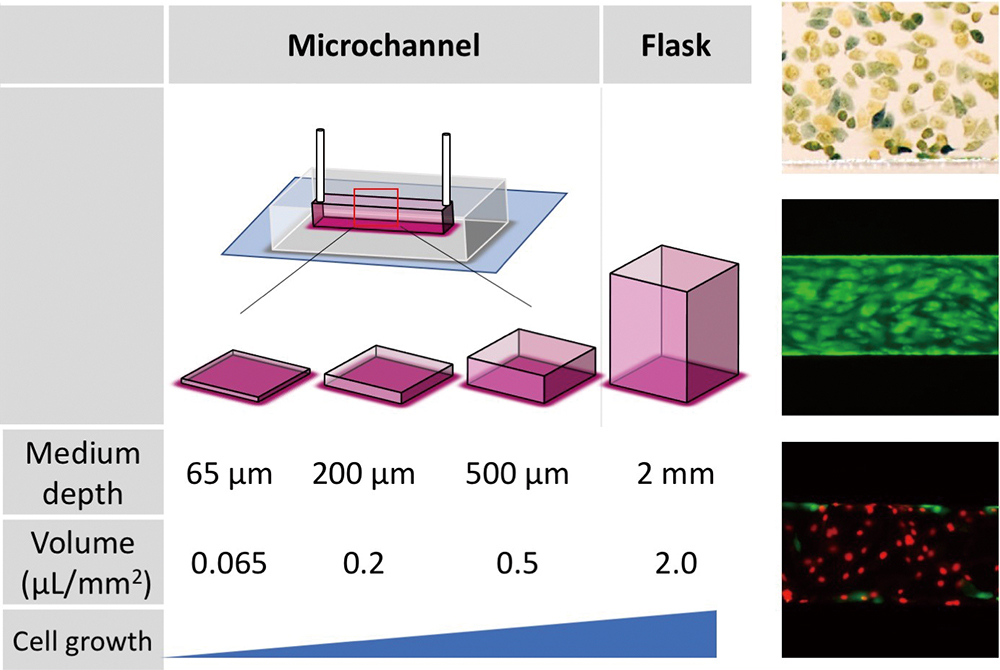
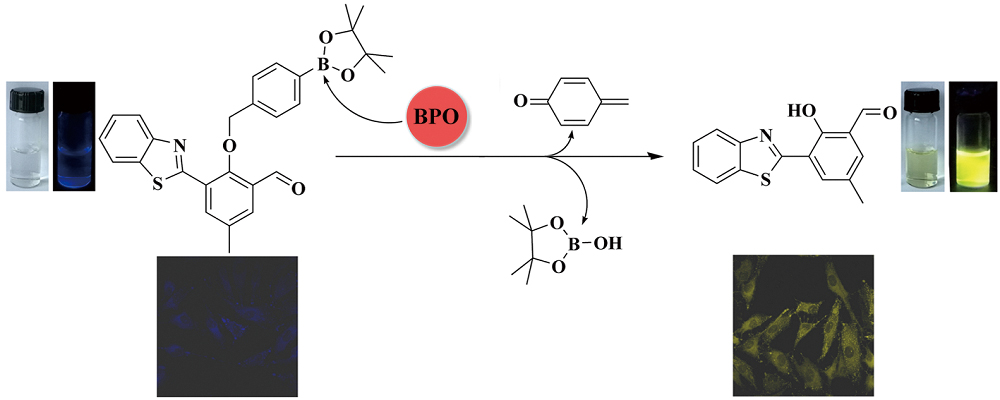
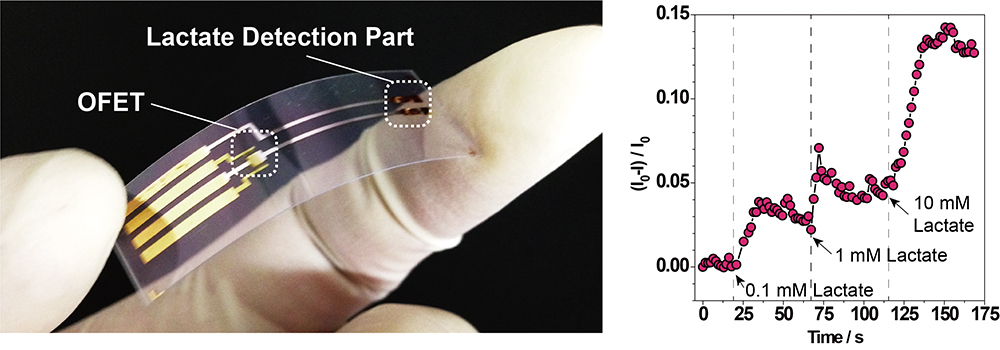
Volume 35, Issue 1
Displaying 1-18 of 18 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 1-2
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Download PDF (78K)
Guest Editorial
-
Article type: Guest Editorial
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 3
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Download PDF (23K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 5-27
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 12, 2018Download PDF (4337K) -
Article type: Reviews
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 29-38
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 23, 2018Download PDF (900K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 39-43
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: September 28, 2018Download PDF (1251K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 45-48
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018Download PDF (625K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 49-56
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 23, 2018Download PDF (3420K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 57-63
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (7096K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 65-69
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (1215K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 71-78
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 30, 2018Download PDF (782K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 79-83
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 16, 2018Download PDF (522K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 85-90
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 02, 2018Download PDF (1877K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 91-97
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: November 09, 2018Download PDF (923K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 99-102
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: May 25, 2018Download PDF (605K) -
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 103-106
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: August 24, 2018Download PDF (3925K) -
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 107-111
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Advance online publication: October 05, 2018Download PDF (934K) -
Article type: Notes
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 113-116
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Download PDF (264K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2019Volume 35Issue 1 Pages 117
Published: January 10, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: January 10, 2019
Download PDF (1724K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|