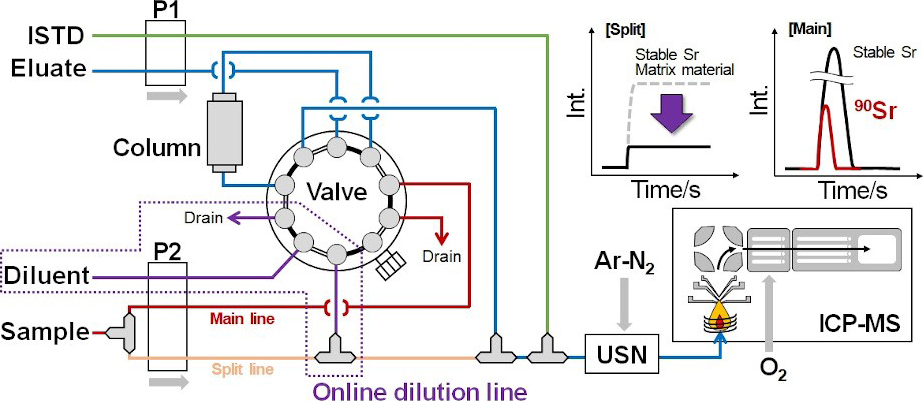
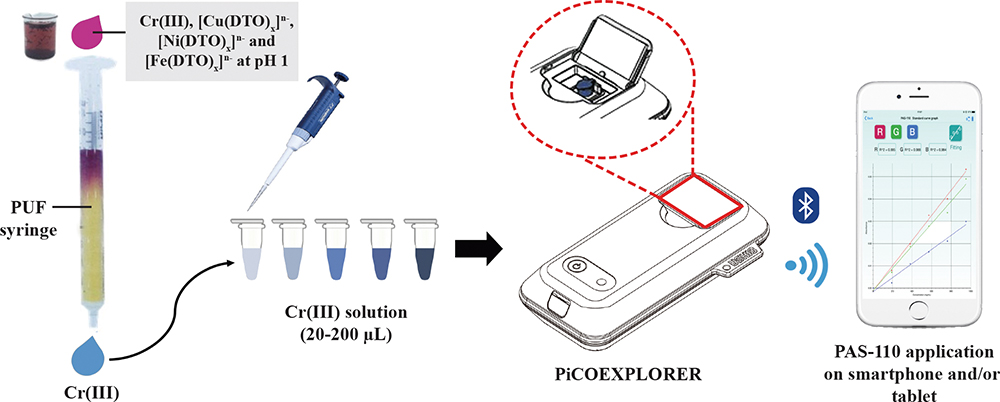
Volume 36, Issue 9
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Highlights
-
Article type: Highlights
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1023-1024
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Download PDF (165K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1025-1030
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: January 17, 2020Download PDF (2420K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1031-1038
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 14, 2020Download PDF (964K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1039-1043
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020Download PDF (1834K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1045-1051
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020Download PDF (650K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1053-1057
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: February 28, 2020Download PDF (930K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1059-1064
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020Download PDF (1328K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1065-1070
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 03, 2020Download PDF (198K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1071-1074
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (1536K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1075-1079
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (485K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1081-1089
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (5619K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1091-1097
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (849K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1099-1104
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (413K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1105-1111
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (1816K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1113-1118
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: May 01, 2020Download PDF (990K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1119-1124
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Download PDF (2172K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1125-1129
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (715K) -
Article type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1131-1135
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (301K) -
Article type: Notes
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1137-1140
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 24, 2020Download PDF (562K)
Advancements in Instrumentation
-
Article type: Advancements in Instrumentation
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1141-1144
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Advance online publication: April 17, 2020Download PDF (3675K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2020 Volume 36 Issue 9 Pages 1145
Published: September 10, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 10, 2020
Download PDF (152K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|