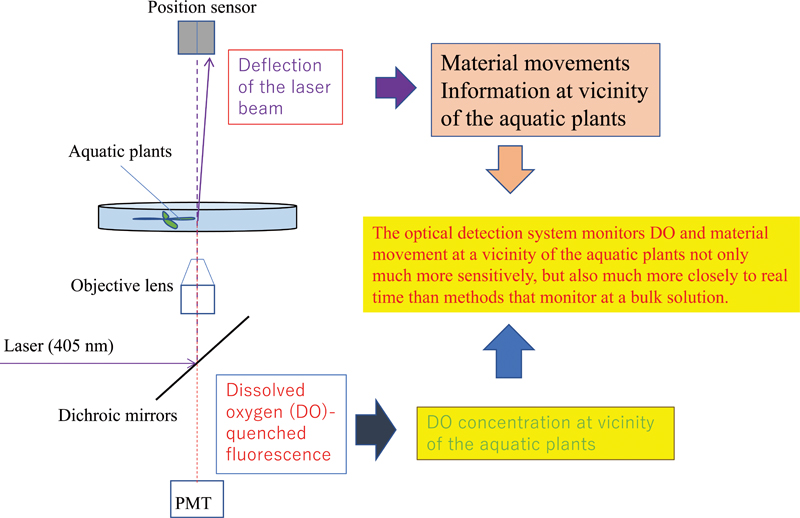
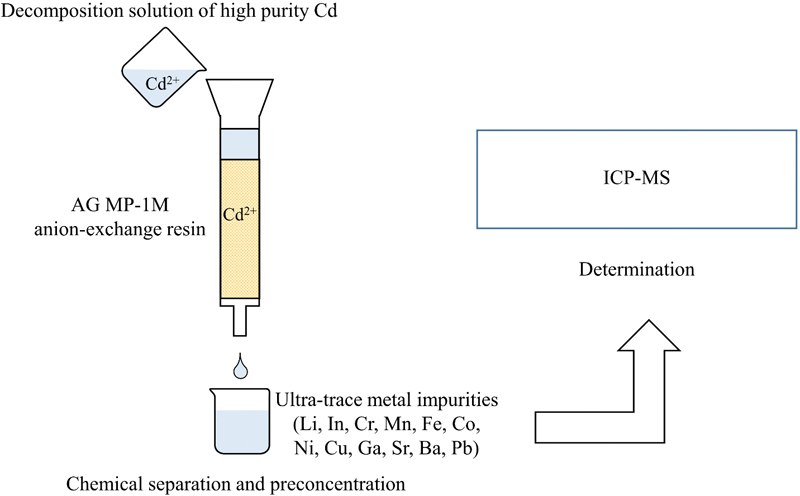
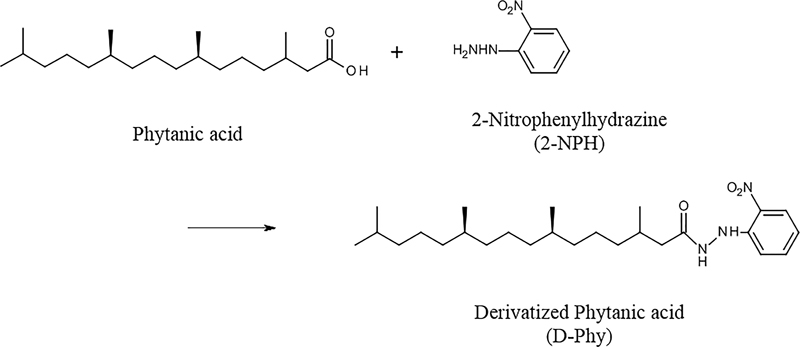
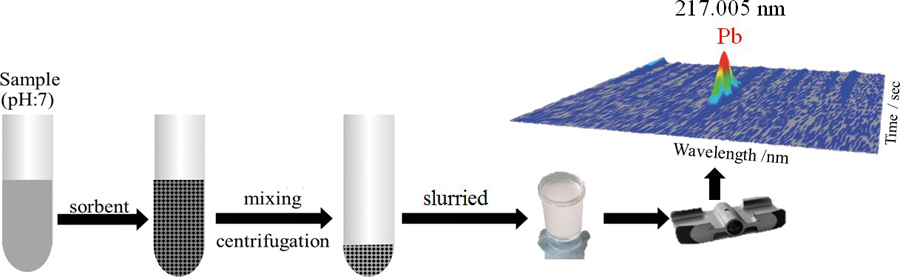
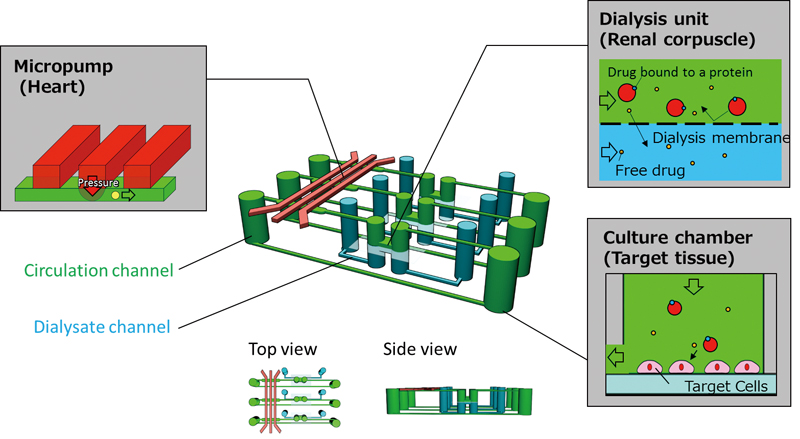
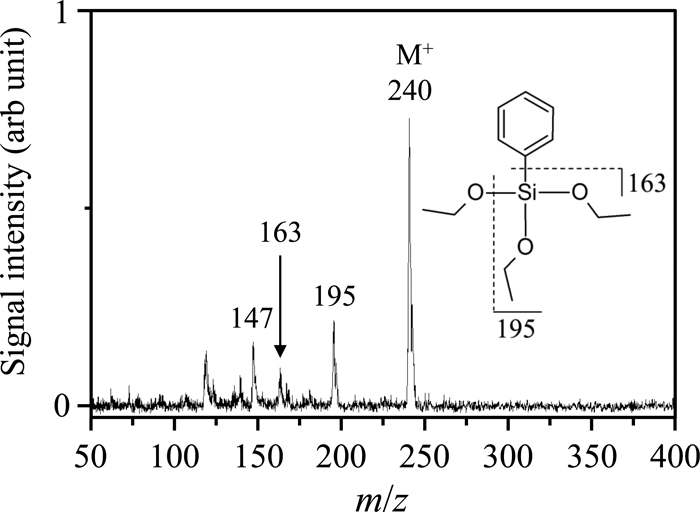
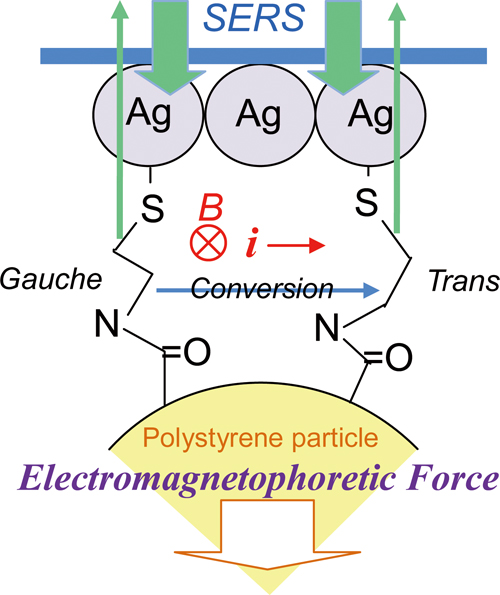
Volume 33, Issue 3
Displaying 1-25 of 25 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 259
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (210K)
Reviews
-
Article type: Reviews
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 261-274
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1887K)
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 275-279
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (747K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 281-285
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1488K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 287-292
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (920K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 293-298
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (744K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 299-305
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (744K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 307-311
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (747K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 313-319
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (702K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 321-325
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1906K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 327-333
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (3352K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 335-341
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (2302K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 343-349
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1873K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 351-357
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (2342K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 357-363
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (767K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 365-368
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (698K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 369-373
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (431K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 375-380
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (824K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 381-385
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1465K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 387-390
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (569K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 391-394
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (839K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 395-397
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (649K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 399-401
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (1036K) -
Article type: Notes
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 403-407
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (410K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017Volume 33Issue 3 Pages 409
Published: March 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: March 10, 2017
Download PDF (3122K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|