All issues

Volume 30, Issue 12
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Yuma ITO, Kumiko SAKATA-SOGAWA, Makio TOKUNAGAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1103-1106
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMany research programs focus on the molecular dynamics of living cells. This research requires cells to be adhered to a substrate while retaining the innate motility of their surface molecules. Lipid bilayer-based systems fulfill this requirement, although current methods are complicated and their utility is limited. We developed a simple and rapid method for reproducible preparation of homogeneous glass-supported lipid bilayers. Our method provides a facile means for bioimaging and analysis of molecular dynamics in living cells. View full abstractDownload PDF (569K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (569K)
Original Papers
-
Arisa KURODA, Yuri ISHIGAKI, Mats NILSSON, Kiichi SATO, Kae SATOArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1107-1112
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn situ padlock/rolling circle amplification (RCA) is a method used to amplify, visualize, and quantify target DNA molecules in cells. However, the multiple reaction steps involved make this technique costly and cumbersome. We developed a novel, simplified, automated microfluidic system for RCA, and demonstrated its effectiveness by counting amplified mitochondrial DNA fragments in HeLa cells. After optimizing the volume of the reaction solutions and washing buffer composition, the product yield was equal to that obtained by the conventional manual method. The required volume of reagents was reduced to 10 μL, which is less than half the volume used in the conventional method. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of an automated microfluidic method for in situ padlock/RCA, which can be useful for making highly efficient pathological diagnoses. View full abstractDownload PDF (571K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (571K) -
Tomoko IMASAKA, Totaro IMASAKAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1113-1120
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialExcitation energies, oscillator strengths, and vacuum-ultraviolet/deep-ultraviolet absorption spectra were calculated for nerve agents, such as sarin, soman, VX, tabun, mustard gas, and analogs. We used time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) methods that included B3LYP combined with basis sets of cc-pVDZ and cc-pVTZ, and ωB97XD with cc-pVTZ. The vertical ionization energies were also calculated for these compounds, in order to collect additional information relative to the optimal pathways for multiphoton ionization in mass spectrometry. View full abstractDownload PDF (1223K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1223K) -
Mariela F. RAZUC, Marcos GRÜNHUT, Mariano GARRIDO, Beatriz S. FER ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1121-1127
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSOn-line photodegradation and spectrophotometric analysis assisted by multivariate curve resolution-alternating least squares (MCR-ALS) was developed the simultaneous determination of ciprofloxacin (CIP) and dexamethasone (DEX) in ophthalmic suspensions using an automated flow-batch analysis (FBA) system. CIP and DEX have strongly overlapped UV spectra. Overcoming this lack of selectivity involves augmenting data dimensionality. This could be performed by adding information about the sample photodegradation to obtain the so-called second order advantage. Commercial sample analysis was successfully performed and no statistical differences (α = 0.05) with respect to pharmacopeia methods were obtained. The proposed method offers several advantages over the methods developed to date. In agreement with the principles of green chemistry, only water was used as solvent, low amounts of waste were generated and on-line waste treatment was included in the system. Moreover, the cost per analysis was significantly reduced compared to methods that employ separative techniques. View full abstractDownload PDF (1308K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1308K) -
Sirinya SIRAWATCHARIN, Amornrat SAITHONGDEE, Anusak CHAICHAM, Boosayar ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1129-1134
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis work presents a new colorimetric method that is simple, rapid and cost effective for the determination of arsenic(III) in water samples. The method is based on changes in the absorbance of difluoroboron-curcumin (BF2-curcumin), prepared by the reaction of borontrifluoride diethyletherate ((C2H5)2OBF3) and curcumin. The BF2-curcumin was dissolved in 60% ethanol, which yielded an orange solution with the maximum absorbance at 509 nm. Upon the addition of arsenic(III), the color of the BF2-curcumin solution changed from orange to blue and the absorbance was measured by UV-visible spectrometry at 632 nm. The BF2-curcumin was applicable in both solution and coated resin. Under the optimal conditions, the detection limits achieved by means of UV-visible spectrometry, naked-eye detection with BF2-curcumin solution and naked-eye detection with BF2-curcumin-coated resin were found to be 0.26, 25 and 30 μM, respectively. View full abstractDownload PDF (5434K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5434K) -
Kei OKAMURA, Hideshi KIMOTO, Takuroh NOGUCHI, Mayumi HATTA, Hiroaki KA ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1135-1141
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA colorimetric pH measurement of seawater samples using a light source comprising a three light-emitting diodes (TLED) detector and meta-cresol purple (mCP) as an indicator was investigated. The molar absorption ratios (e1, e2, and e3/e2) for mCP using the TLED detector at 25°C were determined to be 0, 1.9994, and 0.1010, respectively. Next, the pH values of 2-amino-2-hydroxymethyl-1,3-propanediol (TRIS) and 2-aminopyride (AMP) seawater buffers were determined. Notably, the raw pH of TRIS buffer (∼8.1) agreed with the reference value, while that for the AMP buffer (∼6.8) had an error of +0.004 due to the small absorption ratio (R) and being out of the lower adequate pH range (> 7.2) for mCP. pHT measurements obtained for seawater samples using the present colorimetric method agreed with those obtained using a glass electrode. These results demonstrate that this low-cost TLED detection system with a short cell length, 5 cm, can be used for seawater pHT analysis.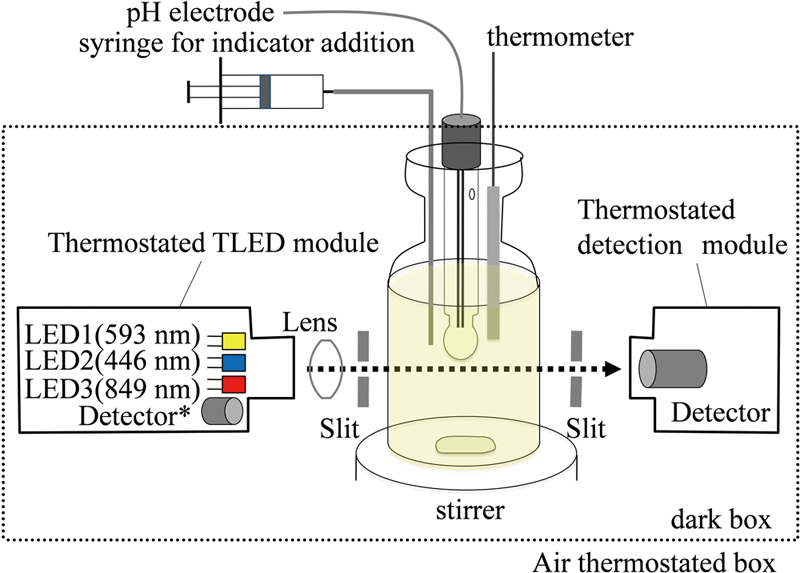 View full abstractDownload PDF (471K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (471K) -
Arunas RAMANAVICIUS, Jaroslav VORONOVIC, Tatiana SEMASHKO, Raisa MIKHA ...Article type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1143-1149
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe properties of amperometric glucose biosensors based on three different glucose oxidases and various redox mediators were evaluated. Glucose oxidases (GOx) from Penicillium adametzii, Penicillium funiculosum and Aspergillus niger and artificial redox mediators, such as ferrocene, ferrocenecarboxaldehyde, α-methylferrocene methanol and ferrocenecarboxylic acid, were used for modifying the graphite rod electrode and amperometrical reagent-less glucose detection. The obtained results were compared using N-methylphenazonium methyl sulphate in the solution. Taking into account the experimental kinetic parameters and the stability of the tested enzymatic electrodes, GOx from Penicillium funiculosum proved to be more suitable for glucose biosensor design in comparison with other evaluated enzymes. View full abstractDownload PDF (677K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (677K) -
Xintong LI, Lianjuan FU, Qianfeng WENG, Jinxiang LIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1151-1156
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA miniaturized transverse flow gating interface (μ-TFGI) is presented for the on-line coupling of solid-phase extraction with capillary electrophoresis (SPE-CE). The fabrication and operation procedures of the μ-TFGI are described in detail. After the operation conditions were investigated and selected, the μ-TFGI was evaluated on an SPE-CE-UV setup using clenbuterol (CLB) as the test analyte. The preconcentration factors obtained with the SPE-CE-UV system and the SPE-UV part were 600 and 620, respectively. The plate numbers obtained within 3 min were 100000 and 80000 for automatic injection via the μ-TFGI and manual direct injection, respectively. The precisions were 2.4 – 6.8% (RSD, %, n = 9) and 3.1% (RSD, %, n = 27) for the recovery (94.3 – 101.9%) and migration time of CLB spiked in urine samples, respectively. These results demonstrate that the μ-TFGI has the ability to exactly and reproducibly transfer nanoliters of fractions from SPE onto CE with no degradation of the efficiencies of SPE and CE. View full abstractDownload PDF (708K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (708K) -
Huali LIAO, Qing LI, Ran LIU, Jingjing LIU, Kaishun BIArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1157-1163
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method employing high performance liquid chromatography–diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) has been developed to evaluate the quality of Saposhnikoviae Radix (SR) comprehensively through fingerprint analysis and multi-ingredient determination. In the fingerprint analysis, 12 out of 15 common peaks were identified with high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric (HPLC-MS/MS) and related references. To discriminate the 15 batches of samples collected from different origins, similarity analysis and principal component analysis (PCA) were performed. Meanwhile, the simultaneous quantification of four chromones was achieved by firstly applying a method of using a single standard to determine multiple components (SSDMC) with conversion factor. The method has the advantage of feasibility, economy and simplicity compared with traditional external standard method (ESM). The method possessed desirable linearity (R2 ≥ 0.9997), precision (RSD <4.0%), accuracy (97.4 – 106.6%) and robustness. This study indicated that the method of fingerprint analysis integrated with multi-ingredient determination using the HPLC technique was reliable for the overall quality evaluation of SR. View full abstractDownload PDF (1171K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1171K) -
Isao KOJIMA, Kazutoshi KAKITAArticle type: Original Papers
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1165-1168
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA Monte Carlo approach has been applied to investigate the statistical properties of data analysis methods for proficiency testing, namely, the median-nIQR, Q-method, Algorithm A and Classical method. Simulations were carried out by using a population consisting of two normal distributions, a main population without bias and a sub-population with bias. The difference for robustness among the methods has been discussed. An actual PT for a dioxin isomer was well interpreted by using the population model employed in this study.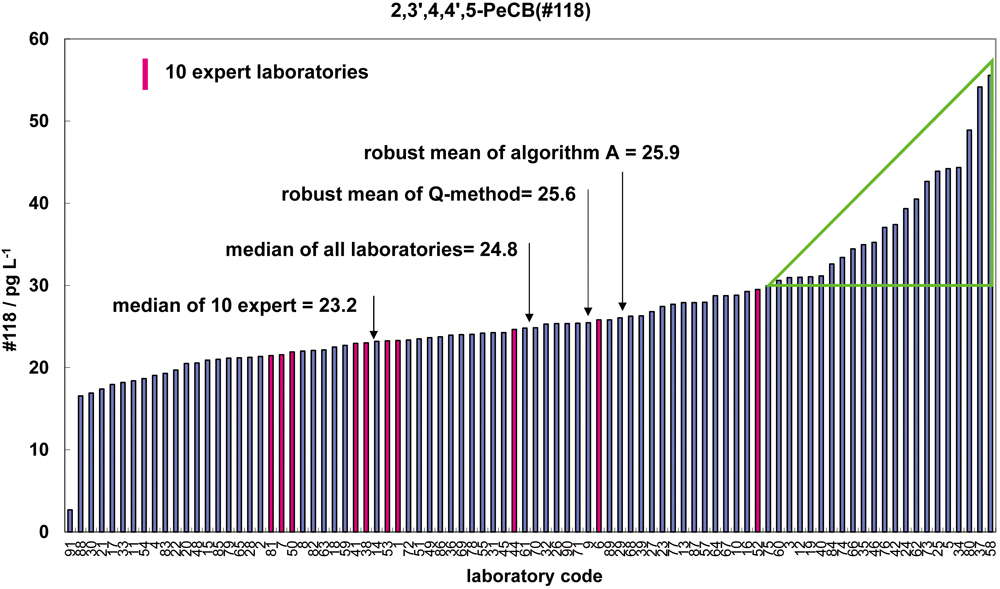 View full abstractDownload PDF (1858K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1858K)
Notes
-
Yasuo INOSHIMA, Naotaka ISHIGUROArticle type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1169-1173
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA portable cordless incubator was developed for on-site visual diagnosis of parapoxvirus infection on farms and in areas with no electricity or laboratory equipment. The battery-powered thermoregulator can maintain a stable temperature for more than 1 h. The incubator successfully amplified parapoxvirus DNA isolated from sheep and wild Japanese serows (Capricornis crispus) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Although different absorbance values were obtained for the LAMP reactions performed using the same sample on the incubator and the turbidimeter, visual assessments of whether the results were positive or negative were the same irrespective of the platform used to perform the LAMP reaction. Consequently, using the portable cordless incubator in conjunction with the LAMP assay is considered to be a powerful tool for on-site visual diagnosis of parapoxvirus infection on farms with no electricity. View full abstractDownload PDF (653K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (653K) -
Masanobu MORI, Keiko MISAWA, Hideyuki ITABASHIArticle type: Notes
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1173-1176
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTrace Cu2+ was detected with high selectivity using specific complexation with bathocuproinesulfonate (BCS) through flow-injection electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (FI-ESI-MS), which separates Cu2+ from coexisting metal ions by forming a Cu–BCS complex with a high mass number. Here, only [CuI(BCS)2]3− was obtained with a high ion count. Its calibration curve was linear from 1.0 × 10−8 to 1.0 × 10−5 M. This method was applied to determine the Cu-complexing capacities of humic acid solution and river water samples by adding traces of Cu2+. View full abstractDownload PDF (609K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (609K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2014 Volume 30 Issue 12 Pages 1177
Published: December 10, 2014
Released on J-STAGE: December 10, 2014
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2614K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|