All issues

Volume 31, Issue 6
Displaying 1-17 of 17 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 461-462
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (865K)
Original Papers
-
Taichi YAMAZAKI, Takuro WATANABE, Satoe NAKAMURA, Kenji KATOArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 463-468
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAcetaldehyde is regulated as a toxic substance in various fields, and the method for monitoring or analysis of acetaldehyde is important. However, handling is difficult because of the high reactivity and low boiling point of acetaldehyde. Therefore, a reference material for high purity acetaldehyde with high accuracy was not available. Although the measuring method of acetaldehyde as a reagent is published in the Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) where the specification of acetaldehyde purity is more than 80%, the analytical method described in JIS is not enough for an accuracy purity determination method. In this research, the high precision purity determination method for development of a certified reference material (CRM) of acetaldehyde was examined. By controlling the volatility and reactivity of acetaldehyde, we established the purity determination method of acetaldehyde with a relative standard uncertainty of less than 0.3%. Furthermore, this method was applied to develop a high purity acetaldehyde CRM with an expanded uncertainty of 0.005 kg kg−1 (k = 2).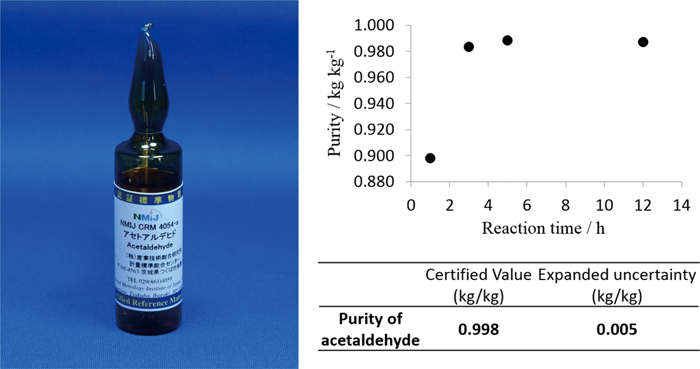 View full abstractDownload PDF (583K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (583K) -
Li Juan LI, Xue TIAN, Xiang Juan KONG, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 469-473
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA G-quadruplex-based, label-free fluorescence assay was demonstrated for the detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). A double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), hybridized by ATP-aptamer and its complementary sequence, was employed as a substrate for ATP binding. SYBR Green I (SG I) was a fluorescent probe and exonuclease III (Exo III) was a nuclease to digest the dsDNA. Consequently, in the absence of ATP, the dsDNA was inset with SG I and was digested by Exo III, resulting in a low background signal. In the presence of ATP, the aptamer in dsDNA folded into a G-quadruplex structure that resisted the digestion of Exo III. SG I was inserted into the structure, showing high fluorescence. Owing to a decrease of the background noise, a high signal-to-noise ratio could be obtained. This sensor can detect ATP with a concentration ranging from 50 μM to 5 mM, and possesses a capacity for the sensitive determination of other targets.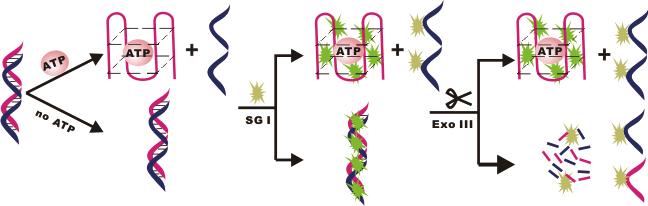 View full abstractDownload PDF (2424K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2424K) -
Yawen MU, Hao XIE, Yakun WANArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 475-479
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNeutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a candidate diagnostic biomarker for acute kidney injury (AKI). Since there is no specific treatment to reverse AKI, a good biomarker such as NGAL can increase the performance of clinical care. Therefore, a timely, specific and sensitive assay for detecting NGAL is critical for clinical determination. In this study, we established a solid-phase proximity ligation assay for the detection of NGAL using polyclonal antibodies conjugated with a pair of oligonucleotides. The data are read out as the Ct value via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Our results demonstrate that this new assay performs with good specificity and sensitivity for detection of NGAL spiked in buffer or serum, which indicates that the solid-phase proximity ligation technique is a promising tool for diagnostics in clinical decisions. View full abstractDownload PDF (839K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (839K) -
Kotaro MORITA, Akane KOBAYASHI, Hirohisa NAGATANI, Hisanori IMURAArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 481-485
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA photoluminescent detection method for nitrite with high selectivity and sensitivity using carbon nanodots (CNDs) is demonstrated. The selectivity of nitrite is accomplished by a highly specific diazotization reaction between nitrite and p-phenylenediamine (p-PDA). In the presence of nitrite, p-PDA easily reacts to form the diazonium cation in the acidic aqueous solution. By alkalization of the reaction mixture, diazonium cation of p-PDA was converted to an aryl radical to form aggregated CNDs, which causes the change in the photoluminescent intensity of CNDs. In the present method, nitrite can be selectively detected down to 1 μM over several anions, such as nitrate, perchlorate, sulfate, fluoride, chloride, and bromide at mM levels. View full abstractDownload PDF (654K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (654K) -
Takamasa KINOSHITA, Dung Quang NGUYEN, Tomoaki NISHINO, Hidenobu NAKAO ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 487-493
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, we examined raspberry-shaped organic/inorganic hybrid structure for potential development of a nanoantenna system capable of detecting and labeling biomolecules. The structure is characterized by a high density of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) separated by closely packed aniline oligomers that serve as a linkage between adjacent particles. In particular, the structure was based on repeated sequences of AuNP-aniline oligomer-AuNP in a three-dimensional arrangement, which enabled the creation of optical hot spots that can hold multiple molecules. We examine the expression of such features by focusing on the structure and characteristics of the hybrid. We demonstrate that these optical hot spots enhance the dye fluorescence without quenching. As a result, we were able to create a nanoantenna structure enabling the efficient use of light. View full abstractDownload PDF (2004K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2004K) -
Nobuo UEHARA, Yoshikuni NUMANAMI, Toru OBA, Noriyuki ONISHI, Xiaomao X ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 495-501
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThermoresponsive immunonephelometry was achieved with biotinylated poly(acrylate) and thermoresponsive gold nanocomposites composed of 13-nm gold nanoparticles and thermoresponsive polymers containing triethylenetetramine and biotin groups. The avidin–biotin interaction was used to model an immunoreaction in order to demonstrate thermoresponsive immunonephelometry. In the absence of avidin, positively charged gold nanocomposites electrostatically interacted with biotinylated poly(acrylate) to form binary complexes, in which the charges canceled each other out. The charge cancelation resulted in the binary complexes precipitating when the solution was heated above the phase-transition temperature. However, adding avidin formed ternary sandwich complexes through the avidin–biotin interaction. The ternary complexes remained sufficiently soluble above the phase-transition temperature because of the spatial isolation of the positive and negative charges. The transmittance of the solution containing the thermoresponsive gold nanocomposites and biotinylated poly(acrylate) at 37°C increased as the avidin concentration increased. A sigmoidal profile was observed from 10−6.5 to 10−5.5 mol/L. The concentration of avidin spiked in bovine serum was determined by our method.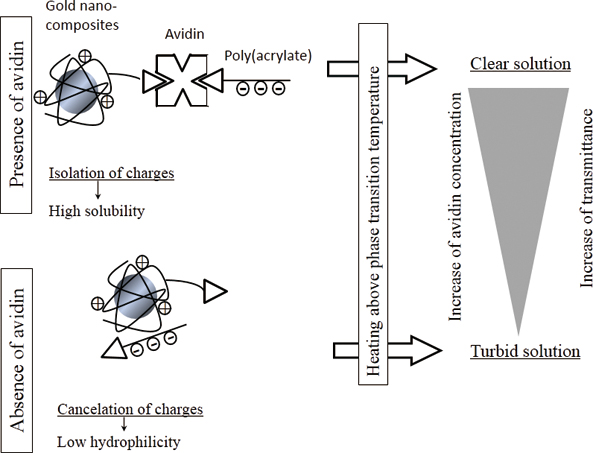 View full abstractDownload PDF (2765K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2765K) -
Kazuaki WAGATSUMAArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 503-511
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes several interesting excitation phenomena occurring in a microwave-induced plasma (MIP) excited with Okamoto-cavity, especially when a small amount of oxygen was mixed with nitrogen matrix in the composition of the plasma gas. An ion-to-atom ratio of iron, which was estimated from the intensity ratio of ion to atomic lines having almost the same excitation energy, was reduced by adding oxygen gas to the nitrogen MIP, eventually contributing to an enhancement in the emission intensities of the atomic lines. Furthermore, Boltzmann plots for iron atomic lines were observed in a wide range of the excitation energy from 3.4 to 6.9 eV, indicating that plots of the atomic lines having lower excitation energies (3.4 to 4.8 eV) were well fitted on a straight line while those having more than 5.5 eV deviated upwards from the linear relationship. This overpopulation would result from any other excitation process in addition to the thermal excitation that principally determines the Boltzmann distribution. A Penning-type collision with excited species of nitrogen molecules probably explains this additional excitation mechanism, in which the resulting iron ions recombine with captured electrons, followed by cascade de-excitations between closely-spaced excited levels just below the ionization limit. As a result, these high-lying levels might be more populated than the low-lying levels of iron atom. The ionization of iron would be caused less actively in the nitrogen–oxygen plasma than in a pure nitrogen plasma, because excited species of nitrogen molecule, which can provide the ionization energy in a collision with iron atom, are consumed through collisions with oxygen molecules to cause their dissociation. It was also observed that the overpopulation occurred to a lesser extent when oxygen gas was added to the nitrogen plasma. The reason for this was also attributed to decreased number density of the excited nitrogen species due to collisions with oxygen molecule.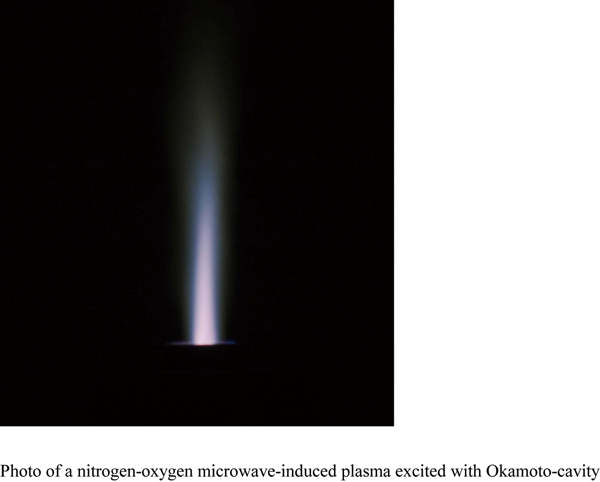 View full abstractDownload PDF (1514K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1514K) -
Yeong Hee AHN, Yeon Jung LEE, Sung Ho KIMArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 513-520
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis study describes an MS-based analysis method for monitoring changes in polymer composition during the polyaddition polymerization reaction of toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and ethylene glycol (EG). The polymerization was monitored as a function of reaction time using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI TOF MS). The resulting series of polymer adducts terminated with various end-functional groups were precisely identified and the relative compositions of those series were estimated. A new MALDI MS data interpretation method was developed, consisting of a peak-resolving algorithm for overlapping peaks in MALDI MS spectra, a retrosynthetic analysis for the generation of reduced unit mass peaks, and a Gaussian fit-based selection of the most prominent polymer series among the reconstructed unit mass peaks. This method of data interpretation avoids errors originating from side reactions due to the presence of trace water in the reaction mixture or MALDI analysis. Quantitative changes in the relative compositions of the resulting polymer products were monitored as a function of reaction time. These results demonstrate that the mass data interpretation method described herein can be a powerful tool for estimating quantitative changes in the compositions of polymer products arising during a polymerization reaction. View full abstractDownload PDF (12551K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (12551K) -
Tomohiro NARUKAWA, Eri MATSUMOTO, Tsutomu NISHIMURA, Akiharu HIOKIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 521-527
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNew measurement conditions for arsenic speciation analysis of rice flour were developed using HPLC-ICP-MS equipped with a reversed phase ODS column. Eight arsenic species, namely, arsenite [As(III)], arsenate [As(V)], monomethylarsonic acid (MMAA), dimethylarsinic acid (DMAA), trimethylarsine oxide (TMAO), tetramethylarsonium (TeMA), arsenobetaine (AsB) and arsenocholine (AsC), were separated and determined under the proposed conditions. In particular, As(III) and MMAA and DMAA and AsB were completely separated using a newly proposed eluent containing ammonium dihydrogen phosphate. Importantly, the sensitivity changes, in particular those of As(V) and As(III) caused by coexisting elements and by complex matrix composition, which had been problematical in previously reported methods, were eliminated. The new eluent can be applied to C8, C18 and C30 ODS columns with the same effectiveness and with excellent repeatability. The proposed analytical method was successfully applied to extracts of rice flour certified reference materials.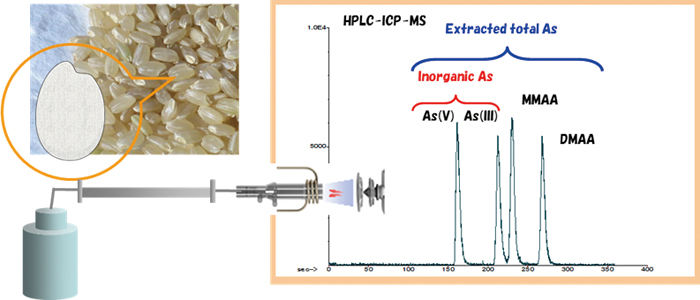 View full abstractDownload PDF (529K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (529K) -
Anastasiia PETROVA, Andrey BULATOV, Andrey VISHNIKIN, Leonid MOSKVIN, ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 529-533
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA novel micro-stepwise injection analyzer (μSWIA) has been developed for the automation and miniaturization of spectrophotometric analysis. The main unit of this device is a mixing chamber (MC) connected to the atmosphere. This part of the μSWIA provides rapid and effective homogenization of the reaction mixture components and completion of the reaction by means of gas bubbling. The μSWIA contained a rectangular labyrinth channel designed in way allowing one to eliminate bubbles by moving a solution from the MC to an optical channel. The light-emitting diode (LED) was used as a light emitter and the analytical signal was measured by a portable spectrophotometer. Fluid movement was attained via the use of a computer-controlled syringe pump. The μSWIA was successfully used for the spectrophotometric determination of cysteine in biologically active supplements and fodder by using 18-molybdo-2-phosphate heteropoly anion (18-MPA) as the reagent. View full abstractDownload PDF (994K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (994K) -
Wenjing DAI, Lihua HU, Lifang JI, Jing LI, Kaishun BI, Qing LIArticle type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 535-541
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA method of quality evaluation by a single standard to determine multi-components (SSDMC), fingerprint and high-performance thin layer-chromatography (HPTLC) was developed for traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), and validated with dry Houttuyniae Herba (HH). In quantitative analysis, an SSDMC method involving nine components has been established with the desirable linearity (r2 ≥ 0.9998), precision (RSD < 2.7%), accuracy (97.4 – 103.1%) and ruggedness. Compared with the results obtained using the external standard method (ESM), this alternative SSDMC method was found to have no statistically significant differences. In fingerprint analysis, nine of fourteen peaks were identified. Simultaneously, 15 HH samples from different origins were classified by similarity analysis and hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA). Additionally, the HPTLC method with three flavonoid markers was firstly established. The combination of SSDMC with the fingerprint and HPTLC method has been verified in the quality control of HH both quantitatively and qualitatively, and will provide a new quality evaluation pattern for TCMs.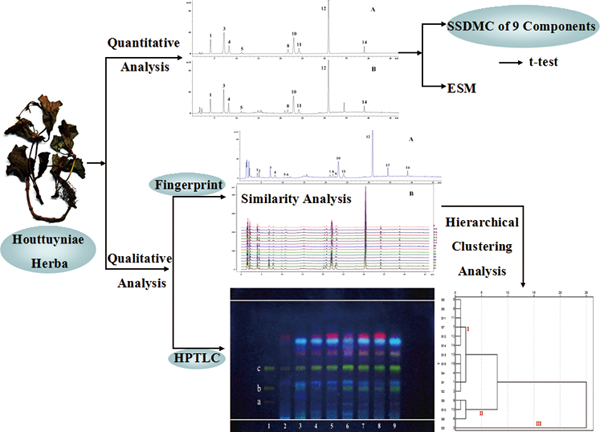 View full abstractDownload PDF (920K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (920K) -
Huiqing YANG, Lin CHEN, Menglin GUO, Yabin DENG, Ping HUANG, Donghui L ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 543-549
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe conventional spectrophotometric method that is often applied to determine ribonuclease (RNase) has disadvantages that include cumbersome manipulation, time-consuming processing and a lack of linear range. We had found that a low concentration of RNA could induce cationic aluminum phthalocyanine (tetra(trimethylammonio)aluminum phthalocyanine (TTMAAlPc)), which emitted strong red fluorescence to aggregate in neutral media, resulting in an almost complete quenching of fluorescence from the cationic aluminum phthalocyanine. The RNA is degraded through hydrolysis by RNase, which destroys the induced aggregation of TTMAAlPc on RNA and releases free TTMAAlPc, leading to a significant fluorescence recovery of the reaction system. Based on this new finding, a method to detect RNase by enhanced fluorescence was established using the TTMAAlPc-RNA association complex as a new fluorogenic substrate of RNase. The optimal conditions were determined, and the interfering foreign substances were investigated. Under optimal conditions, the linear range was 0.05 – 50 μg/L, and the detection limit was 0.02 μg/L. This method was applied for the analysis of ribonuclease in urine specimens from normal adults, and the results were consistent with those determined by conventional spectrophotometric methods. The developed method is easy to operate and highly sensitive, and has a wide linear range, thus solving issues with conventional methods. This study applied, for the first time, cationic phthalocyanine as a fluorescent probe in the detection of nuclease, which provides new applications of phthalocyanine as a fluorescent probe emitting at the red wavelength region. View full abstractDownload PDF (1356K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1356K) -
Yuya SASAKI, Natsuki YAMAMOTO, Yasutada SUZUKI, Ikuo UETA, Susumu KAWA ...Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 551-555
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCadmium-catalyzed complexation of zinc with 5,10,15,20-tetraphenyl-21H,23H-porphinetetrasulfonic acid (TPPS) was monitored spectrophotometrically. A kinetic parameter for the determination was obtained under kinetic consideration. Absorbance of zinc-TPPS at a fixed reaction time was proportional to the concentration of cadmium at pH 8 and 25°C. Tolerable concentration of interfering ions were 200, 200, 2000, 50, 500 and 1 μg L−1 for Mg(II), Al(III), Ca(II), Fe(III), Zn(II) and Hg(II), respectively, in the determination of 20 μg L−1 of cadmium, indicating Ca(II) and Mg(II) interferes with the analysis of natural fresh water. Such interference became tolerable at 5 mg L−1 by the addition of an excess Ca(II) (50 mg L−1) in the reacting solution of sample and cadmium standards. A calibration curve of Cd(II) was linear up to 100 μg L−1 with a detection limit of 2 μg L−1. The reliability of the proposed method was confirmed by the recovery test of cadmium spiked into tap, river and reservoir water samples.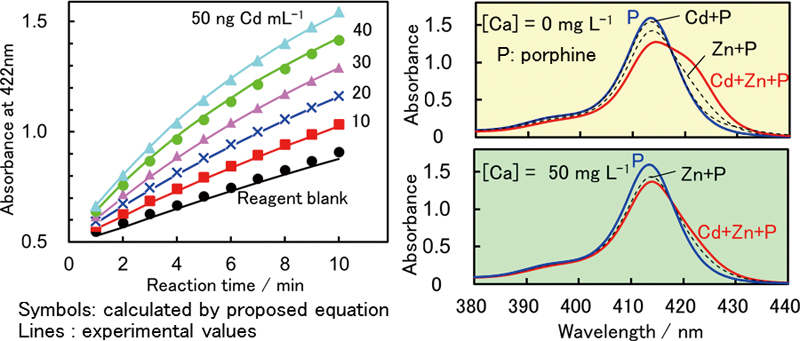 View full abstractDownload PDF (632K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (632K)
Notes
-
Kiyoharu NAKATANI, Emi MATSUTAArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 557-560
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe release mechanism of coumarin 102 from a single ODS-silica gel microparticle into the water phase in the presence of Triton X-100 was investigated by confocal fluorescence microspectroscopy combined with the single microparticle injection technique. The release rate significantly depended on the Triton X-100 concentration in the water phase and was not limited by diffusion in the pores of the microparticle. The release rate constant was inversely proportional to the microparticle radius squared, indicating that the rate-determining step is the external diffusion between the microparticle and the water phase. View full abstractDownload PDF (533K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (533K) -
Yasumi ANAN, Genki NAKAJIMA, Yasumitsu OGRAArticle type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 561-564
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe demonstrated the complementary use of inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-Q-TOF-MS) for the analysis of Se-containing compounds, such as selenate, selenomethionine (SeMet), and trimethylselenonium ion (TMSe), found in biological samples. The sensitivity of ESI-Q-TOF-MS for Se-containing compounds was strongly dependent on the chemical species. ICP-MS exhibited higher sensitivity than ESI-Q-TOF-MS, and had no species dependency. On the other hand, ESI-Q-TOF-MS enabled easy and robust identification of Se-containing compounds.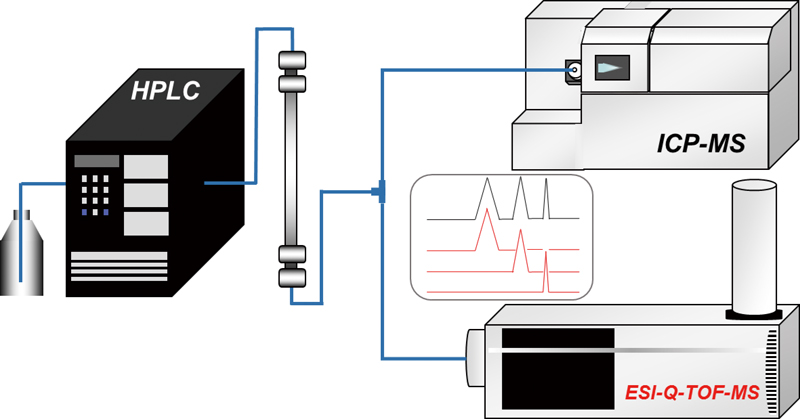 View full abstractDownload PDF (581K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (581K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 6 Pages 565
Published: June 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: June 10, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (2765K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|