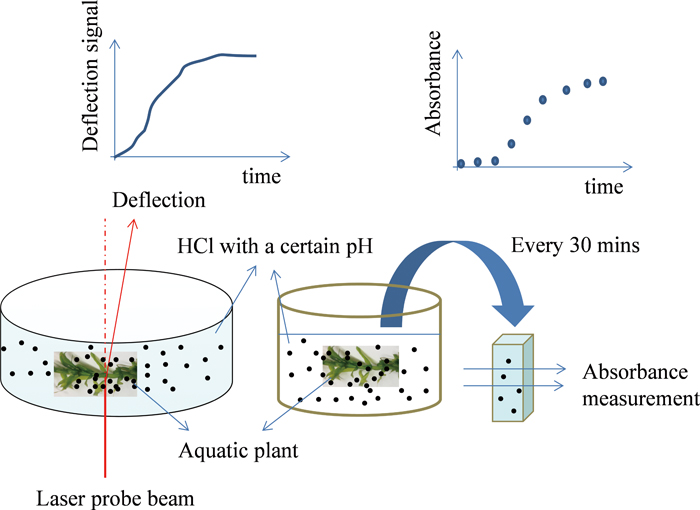
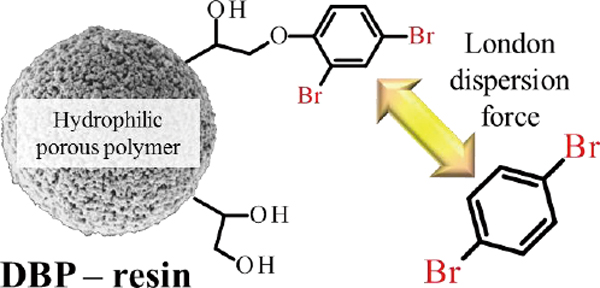
Volume 31, Issue 8
Displaying 1-21 of 21 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Original Papers
-
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 743-749
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (821K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 751-756
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (793K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 757-761
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (1849K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 763-768
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (630K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 769-772
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (512K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 773-780
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (854K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 781-785
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (3319K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 787-791
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (1577K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 793-798
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (6332K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 799-803
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (1409K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 805-814
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (554K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 815-822
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (6228K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 823-830
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (2229K) -
Article type: Original Papers
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 831-835
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (528K)
Notes
-
Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 837-840
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (7739K) -
Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 841-845
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (448K) -
Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 847-850
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (592K) -
Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 851-854
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (451K) -
Article type: Notes
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 855-858
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (7392K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 859
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (2707K)
Errata
-
Article type: Errata
2015 Volume 31 Issue 8 Pages 864
Published: August 10, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: August 10, 2015
Download PDF (126K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|