All issues

Volume 33, Issue 11
Displaying 1-20 of 20 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Call for Papers
-
Article type: Call for Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1207
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (219K)
Highlights
-
Hajime MIZUNOArticle type: Highlights
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1209
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (868K)
Original Papers
-
Nataporn WIJIT, Sukon PRASITWATTANASEREE, Sugunya MAHATHEERANONT, Pete ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1211-1217
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA quantitative structure–retention relationship (QSRR) study was applied for an estimation of retention times of secondary volatile metabolites in Thai jasmine rice. In this study, chemical components in rice seed were extracted using solvent extraction, then separated and identified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). A set of molecular descriptors was generated for these substances obtained from GC-MS analysis to numerically represent the molecular structure of such compounds. Principal component analysis (PCA) and principal component regression analysis (PCR) were used to model the retention times of these compounds as a function of the theoretically derived descriptors. The best fitted regression model was obtained with R-squared of 0.900. The informative chemical properties related to retention time were elucidated. The results of this study demonstrate clearly that the combination of molecular weight and autocorrelation functions of two dimensional interatomic distance, which are molecular polarizability, atom identity, sigma charge, sigma electronegativity and polarizability, can be considered as comprehensive factors for predicting the retention times of volatile compounds in rice. View full abstractDownload PDF (550K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (550K) -
Biljana NIGOVIC, Ivona MILANOVICArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1219-1223
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe electrooxidation of xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat was investigated on a boron-doped diamond electrode in aqueous solution. The oxidation of the drug molecule was irreversible and exhibited a diffusion-controlled form. A green electroanalytical method for simple and fast measurements of febuxostat was developed at the unmodified electrode surface. The analyses were performed using square-wave voltammetric peak current at 1.38 V. The linear response was obtained in the range of 7.5 × 10−7 – 2.0 × 10−5 M with the detection limit of 9.5 × 10−8 M. The practical analytical value of the method is demonstrated by quantitative determination of febuxostat in film-coated tablets with excellent recovery of 99.6%. Interference studies reveal that uric acid shows a well-developed voltammetric response at +0.64 V. In view of this, the electroanalytical performances of the boron-doped diamond electrode can open up new possibilities for development of the method for simultaneous clinical analysis of febuxostat and uric acid.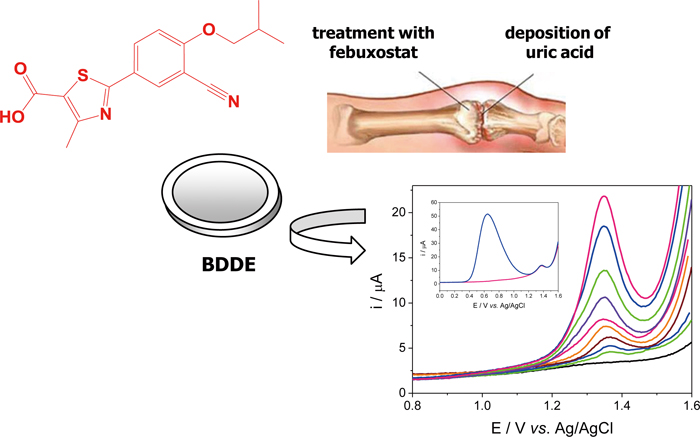 View full abstractDownload PDF (680K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (680K) -
Min LI, Lu ZHANG, Xiaolong YAO, Xingyu JIANGArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1225-1230
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe emerging membrane introduction mass spectrometry technique has been successfully used to detect benzene, toluene, ethyl benzene and xylene (BTEX), while overlapped spectra have unfortunately hindered its further application to the analysis of mixtures. Multivariate calibration, an efficient method to analyze mixtures, has been widely applied. In this paper, we compared univariate and multivariate analyses for quantification of the individual components of mixture samples. The results showed that the univariate analysis creates poor models with regression coefficients of 0.912, 0.867, 0.440 and 0.351 for BTEX, respectively. For multivariate analysis, a comparison to the partial-least squares (PLS) model shows that the orthogonal partial-least squares (OPLS) regression exhibits an optimal performance with regression coefficients of 0.995, 0.999, 0.980 and 0.976, favorable calibration parameters (RMSEC and RMSECV) and a favorable validation parameter (RMSEP). Furthermore, the OPLS exhibits a good recovery of 73.86 – 122.20% and relative standard deviation (RSD) of the repeatability of 1.14 – 4.87%. Thus, MIMS coupled with the OPLS regression provides an optimal approach for a quantitative BTEX mixture analysis in monitoring and predicting water pollution. View full abstractDownload PDF (1175K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1175K) -
Hisanori IWAIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1231-1236
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTo maintain performance related to fuel consumption and maneuverability, the bottom of ships are painted with antifouling paint that contains Cu2O as a biocidal pigment. However, in enclosed coastal areas around dockyards, some of the Cu(II) contained in the paint is eluted into the surrounding water. The present study examined the removal of Cu from seawater by co-precipitation with humic acids (HAs). After precipitating the HA in seawater, the amount of Cu(II) in the supernatant was colorimetrically measured by a colorimetry using bathocuproine. The removal efficiency (RE%) for micromolar Cu(II) increased with increasing initial concentrations of HAs. An RE of 90% was obtained using an HA derived from hardwood bark compost. Aromatic components in the HA that contained highly substituted acidic functional groups appeared to enhance the removal of Cu(II). The findings reported herein indicate that HAs represent a useful material for removing trace levels of Cu from seawater.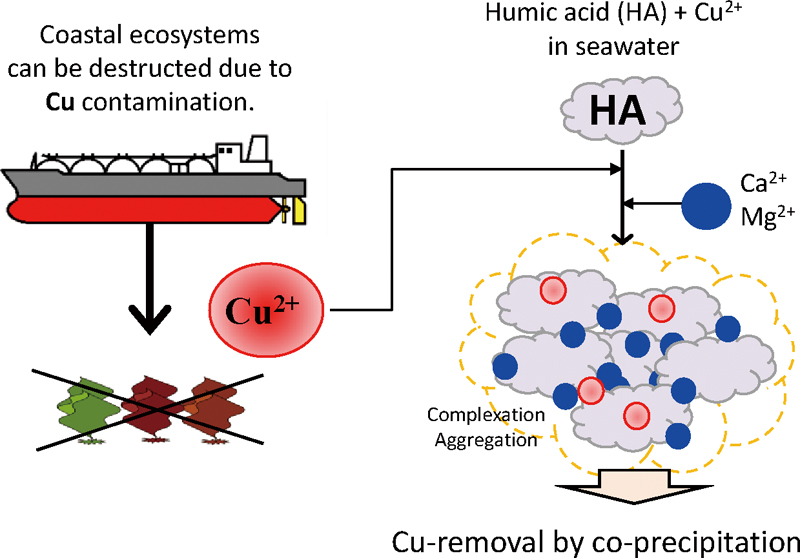 View full abstractDownload PDF (1217K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1217K) -
Lin BAO, Xuan-Yu SHA, Hang ZHAO, Si-qin-gao-wa HAN, Wu-Li-Ji HASIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1237-1240
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) was used to measure scopolamine hydrobromide. First, the Raman characteristic peaks of scopolamine hydrobromide were assigned, and the characteristic peaks were determined. The optimal aggregation agent was potassium iodide based on a comparative experimental study. Finally, the SERS spectrum of scopolamine hydrobromide was detected in aqueous solution, and the semi-quantitative analysis and the recovery rate were determined via a linear fitting. The detection limit of scopolamine hydrobromide in aqueous solution was 0.5 μg/mL. From 0 – 10 μg/mL, the curve of the intensity of the Raman characteristic peak of scopolamine hydrobromide at 1002 cm−1 is y = 4017.76 + 642.47x. The correlation coefficient was R2 = 0.983, the recovery was 98.5 – 109.7%, and the relative standard deviation (RSD) was about 5.5%. This method is fast, accurate, non-destructive and simple for the detection of scopolamine hydrobromide. View full abstractDownload PDF (1275K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1275K) -
Megumi KATO, Taichi YAMAZAKI, Hisashi KATO, Noriko YAMANAKA, Akiko TAK ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1241-1245
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTo prepare metrologically traceable amino acid mixed standard solutions, it is necessary to determine the stability of each amino acid present in the mixed solutions. In the present study, we prepared amino acid mixed solutions using certified reference standards of 17 proteinogenic amino acids, and examined the stability of each of these amino acids in 0.1 N HCl. We found that the concentration of glutamic acid decreased significantly during storage. LC/MS analysis indicated that the instability of glutamic acid was due to the partial degradation of glutamic acid to pyroglutamic acid in 0.1 N HCl. Using accelerated degradation tests, we investigated several solvent compositions to improve the stability of glutamic acid in amino acid mixed solution, and determined that the change of the pH by diluting the mixed solution improved the stability of glutamic acid. View full abstractDownload PDF (598K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (598K) -
Shoma AKI, Kenji SUEYOSHI, Hideaki HISAMOTO, Tatsuro ENDOArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1247-1251
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe investigated the origin of the optical responses of a two-dimensional photonic crystal (2D-PhC) optode membrane ion sensor based on plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) containing lipophilic dye. We previously developed a highly sensitive potassium ion sensor. However, the contributions of various factors to the sensor’s optical response could not be distinguished. Here, we synthesized a lipophilic dye with spectral changes that do not overlap with those of propagated light in the PhC. Using this synthesized dye excluded the contribution of light absorption by the dye to the peak intensity change of the ion sensor. In refractive index standard solutions, the bulk refractive index change upon ion extraction contributed negligibly. The contribution of diffracted light scattering by optical transparency change of the plasticized PVC upon ion extraction accounted for approximately 45% of the ion sensor’s total response. These findings are important for the development of highly sensitive plasticized PVC-based 2D-PhC ion sensors. View full abstractDownload PDF (4746K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (4746K) -
Rong LU, Takayuki HONDA, Meesook SUNG, Jaekook JUNG, Tetsuo MIYAKOSHIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1253-1257
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe chemical structure of fresh lacquer sap collected from a lacquer tree growing in Nago City of Okinawa, Japan, was analyzed by gas chromatography/mass-spectrometry (GC/MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). The results showed that Nago lacquer is laccol lacquer and its major components are 3-(heptadeca-10Z,13E,15E-trienyl)catechol, 3-(heptadeca-10Z,13E-dienyl)catechol, 3-(heptadeca-14Z-enyl)catechol, and 3-(heptadeca-12Z-enyl)catechol, which are similar to the components of Vietnamese lacquer. It showed higher laccase activity at pH 5 – 8 and better low temperature adaptability than Vietnamese lacquer. The Nago lacquer reached a dust free dry (DF) condition after 6 h, but Vietnamese lacquer did not. However, both were able to achieve harden dry (HD) in 24 h at 25°C, 80% relative humidity. In order to identify the lacquer provenance, the strontium isotope ratio was analyzed. The strontium isotope ratio (87Sr/86Sr) of Nago lacquer was 0.7110, which is different from the 0.7450 of Vietnamese lacquer.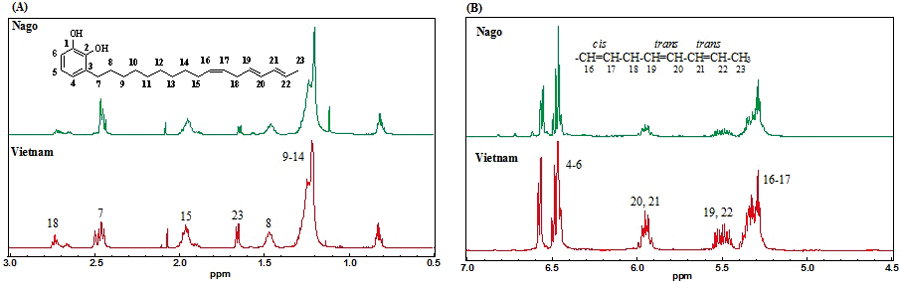 View full abstractDownload PDF (1685K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1685K) -
Manzoor AHMED, Muhammad ASGHAR, Mohammad YAQOOB, Nusrat MUNAWAR, Farkh ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1259-1263
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDiperiodatoargentate(III) (DPA)/silver(III) complex, [Ag(HIO6)2]5−, in sulfuric acid medium has been used to determine hyoscine butylbromide (HBB) by flow injection (FI) coupled with chemiluminescence (CL) detector. A linear standard curve between the CL intensity and concentration range from 0.005 to 20 mg L−1 was obtained. The determination coefficient (R2), limit of detection (3s × blank), relative standard deviation (RSD) for 0.5 mg L−1 HBB and analytical throughput were 0.9992 (n = 8), 5 × 10−4 mg L−1, 1.5% (n = 10) and 160 injections h−1, respectively. The developed method was applied for the determination of HBB in pharmaceutical formulations with recoveries from 92 ± 4 to 108 ± 3%. For comparison, a spectrophotometric method was used and the results obtained by both methods were in good agreement at a 95% confidence level. The effect of key chemical and physical variables (reagent concentration, flow rate, sample volume, PMT voltage) and interfering species (pharmaceutical excipients and inorganic ions) on the determination of HBB was examined. The possible CL mechanism of HBB on silver(III) complex in sulfuric acid medium was also discussed in brief. View full abstractDownload PDF (772K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (772K) -
Shuhua HE, Mumei CHEN, Zheng LI, Haixia CONG, Lan ZHANG, Qinnuan LIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1265-1270
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFor the determination of μg-mg L−1 of FPs in 100 g L−1 of thorium matrix with HCl medium, a method, including anion-exchange pre-separation, evaporation and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) measurement, was developed. The procedure parameters, such as the matrix effect of thorium, the acidity of separation, the elution curve of thorium and FPs and the temperature of evaporation were optimized by batch equilibration, column elution and evaporation experiments. It was found that the average recovery of the FPs was in the range 80 – 110%, and the RSD values were in the range 2 – 15% utilizing prior anion exchange separation of FPs from thorium samples. Furthermore, the detection limit of the method was also investigated.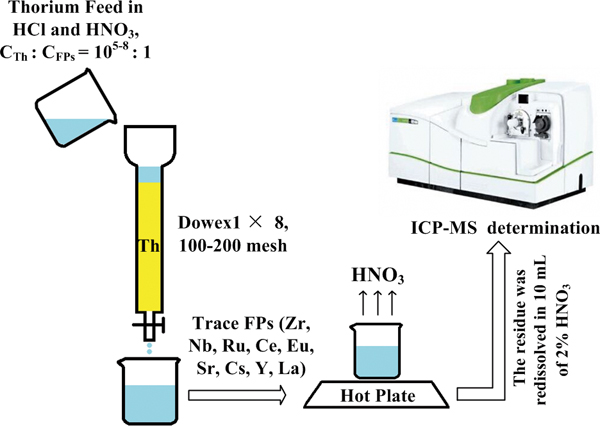 View full abstractDownload PDF (790K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (790K) -
Fengjiang ZHANG, Hao DONG, Xuanlang ZHANG, Jin GUO, Yunqing LIU, Cheng ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1271-1277
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPropofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) is widely used in total intravenous anesthesia. An unknown drug concentration in blood always leads to some side effects in patients with propofol injection. However, the drug concentration in the blood is hard to be continuously measured since invasive sampling causes a loss of blood at each measurement. Here, we introduced a virtual surface acoustic wave sensor array (VSAWSA) to non-invasively detect the propofol concentration in blood through exhaled gases. Calibration was conducted by a parallel test using gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS) with solid-phase micro-extraction (SPME) for preconcentration. The limit of detection of VSAWSA reached 0.15 nmol/L for propofol. Six cases of clinical trials was conducted to compare the exhaled propofol concentrations to the plasma concentrations controlled by target-controlled infusion (TCI). The calibration by GC-MS ensured the feasibility, reliability, and accuracy of the VSAWSA (R = 0.9904, p <0.001). The clinical monitoring data by VSAWSA showed an excellent consistency with TCI. View full abstractDownload PDF (2118K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (2118K) -
Yanbei ZHU, Kazumi NAKANO, Yasuyuki SHIKAMORIArticle type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1279-1284
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe analysis of fluorine was carried out by measuring BaF+ ions with an inductively coupled plasma tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer (ICP-QMS/QMS). After optimization, a radio frequency power of 1300 W was found to benefit for the production of BaF+ ions while suppressing the production of BaOH3+ ions. After optimization of the reaction cell gas, it was found that the best performance for measuring BaF+ could be achieved at a flow rate of O2 in the range from 0.65 to 0.75 mL min−1. The signal intensity of BaF+ depended linearly on the concentration of Ba when it was not higher than 100 mg kg−1. The co-existence of metallic cations, such as Na in the sample, might suppress the generation of BaF+ ions in the plasma, while anions might not cause such a kind of interferences. The background equivalent concentration (BEC) and the lower detection limit (LDL) of fluorine were 0.4 and 0.06 mg kg−1, respectively, by adjusting the samples to a 10 mg kg−1 Ba matrix. The concentration of fluorine in a certified reference material (ERM-CA015a) was determined with the present method, for which the observed value was (1.36 ± 0.05)mg kg−1, which agreed with the certified value (1.3 ± 0.1)mg kg−1, where both values were shown as (mean value ± expanded uncertainty) with a coverage factor of (k = 2) for calculating the expanded uncertainty giving a level of confidence of approximately 95%. The present method was applied to the analysis of a tap water sample collected in the laboratory, for which the results of recovery tests gave a recovery around 100% with good reproducibility. View full abstractDownload PDF (1056K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1056K) -
Mayara FERREIRA BARBOSA, Danielle SILVA DO NASCIMENTO, Marcos GRÜ ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1285-1289
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new simple, rapid and inexpensive analytical method was developed to determine the biodiesel percentage in biodiesel/diesel blends through simple digital images of samples obtained by scanning with a commercial scanner. Soybean biodiesel and petroleum diesel samples were acquired from refineries currently in operation. There were prepared several mixtures within the range 1.5 to 12.0% of biodiesel in diesel oil, using the same procedure as is done in industry. The analytical signals were images recorded with a scanner. This data was decomposed with different color systems: RGB, HSV, HLS, CMYK and Grayscale. Chemometrics models based on color signals obtained from different mixtures of biodiesel/diesel were built. The quantification by using partial least squares (PLS) resulted in a RMSEP value for biodiesel of 0.9% (w/w); this load approximately 10-times smaller than the corresponding calibration range, with a correlation of 0.96 between predicted and reference values. View full abstractDownload PDF (534K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (534K) -
Zijian WAN, Longjie ZHONG, Yuxiang PAN, Hongbo LI, Quchao ZOU, Kaiqi S ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1291-1296
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA microplate method provides an efficient way to use modern detection technology. However, there are some difficulties concerning on-site detection, such as being non-portable and time-consuming. In this work, a novel portable microplate analyzer with a thermostatic chamber based on a smartphone was designed for rapid on-site detection. An analyzer with a wide-angle lens and an optical filter provides a proper environment for the microplate. A smartphone app-iPlate Monitor was used for RGB analyze of image. After a consistency experiment with a microtiter plate reader (MTPR), the normalized calibration curves were y = 0.7276x + 0.0243 (R2 = 0.9906) and y = 0.3207x + 0.0094 (R2 = 0.9917) with a BCA protein kit as well as y = 0.182x + 0.0134 (R2 = 0.994) and y = 0.0674x + 0.0003 (R2 = 0.9988) with a glucose kit. The times for obtaining the detection requirement were 15 and 10 min for the BCA protein kit and the glucose kit at 37°C; in contrast, it required more than 30 and 20 min at ambient temperature. Meanwhile, it also showed good repeatability for detections.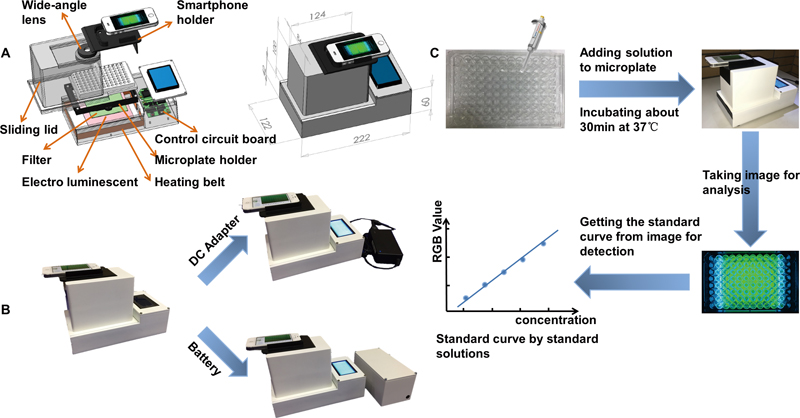 View full abstractDownload PDF (3060K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3060K) -
Rojeet SHRESTHA, Ken-ichi HIRANO, Akira SUZUKI, Satoshi YAMAGUCHI, Yus ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1297-1303
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe studied change in the plasma total, esterified and non-esterified capric acid (FA10:0) and its effect on longer fatty acid concentrations during the short-term oral administration of synthetic tricaprin in dogs. We administered 150 and 1500 mg tricaprin/kg body weight per day orally to dogs for 7 consecutive days. Blood samples were collected at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h on the 1st and 7th days for measuring the total-, esterified- and non-esterified-FA10:0. The total-FA10:0 concentration increased in a dose-dependent manner, reaching a peak at 1 h on the 1st day and at 2 to 4 h on the 7th day; it then mostly disappeared within 24 h. The mean esterified FA10:0 concentration was found be 75.5 and 60.3% of total-FA10:0 in dogs fed 150 and 1500 mg of tricaprin/kg body weight, respectively. The plasma level of FA10:0 depends on the duration and dose of tricaprin administration, but are rapidly cleared from circulation within several hours. View full abstractDownload PDF (803K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (803K) -
Hirokazu NARITA, Motoki MAEDA, Chiharu TOKORO, Tomoya SUZUKI, Mikiya T ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1305-1309
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialUsing N,N,N′,N′-tetra-2-ethylhexyl-thiodiglycolamide (TEHTDGA) in n-dodecane as the extractant, we compared the percentages of Pd(II) extracted from HCl and HBr solutions, and analyzed the structures of the Pd(II)–extractant complexes. For comparison, similar experiments were performed with di-n-hexyl sulfide (DHS), a well-known sulfide-type extractant. TEHTDGA extracted Pd(II) from both HCl and HBr solutions much faster than DHS. The Pd(II)/(TEHTDGA or DHS) stoichiometry in the organic phase was 1:2. For TEHTDGA, the extractability of Pd(II) from HBr solution was inferior to that from HCl solution, whereas the opposite was true for DHS. However, FT-IR spectroscopy and EXAFS measurements indicated that the inner-sphere structure of Pd(II) in the TEHTDGA complex was almost the same as that in the DHS system: in both cases, two of the halide ions in the tetrachloro- or tetrabromopalladate(II) ion were replaced by the sulfur atoms of two extractant molecules.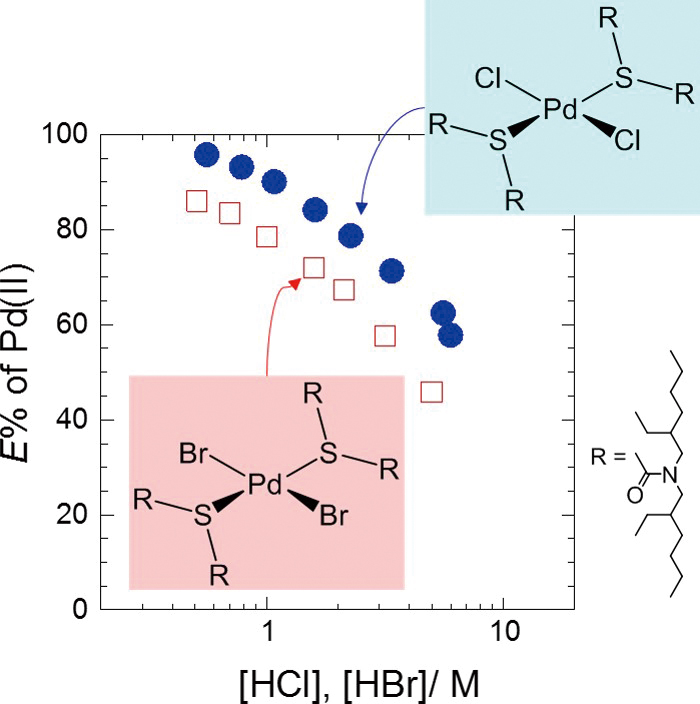 View full abstractDownload PDF (660K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (660K) -
Takuya KUBO, Shunsuke ARIMURA, Toyohiro NAITO, Tomoharu SANO, Koji OTS ...Article type: Original Papers
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1311-1315
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe report on a molecularly imprinted hydrogel for the selective fluorescent detection of a targeting protein. To achieve the fluorescent detection of proteins, a fluorescent functional monomer was synthesized with fluorescein isothiocyanate and allylamine. The monomer (FITC-AA) provided a gradable alteration of the absorption spectrum, and a decrease of the fluorescent intensity due to an interaction with the model protein, lysozyme. Also, the imprinted hydrogel (PI-gel) was simply prepared with FITC-AA, the anionic functional monomers, poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate, and lysozyme by radical photo polymerization. The PI-gel showed selective adsorption for lysozyme and the imprinting factor reached to 2.7. Additionally, the PI-gel indicated a gradual decrease of the fluorescent intensity corresponding to the lysozyme concertation similar to a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detection. View full abstractDownload PDF (12605K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (12605K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2017 Volume 33 Issue 11 Pages 1317
Published: November 10, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: November 10, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (3979K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
