All issues

Volume 29, Issue 10
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Rapid Communications
-
Hiroshi SHIIGI, Yusuke MURANAKA, Yojiro YAMAMOTO, Tsutomu NAGAOKAArticle type: Rapid Communications
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 937-939
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA single-step strategy has been developed for synthesizing a micrometer-sized structure by using the raspberry-like hybrid as a building block comprising a repeated sequence of a three-dimensional gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-aniline oligomer-AuNP arrangement. The hybrid holds a high density of highly dispersible AuNPs without any contact with each other, and therefore the microstructure has many nanometer-sized gaps between the adjacent AuNPs for both electrical and optical sensing. We have discussed how the formation mechanism of the microstructure is based on using the hybrid.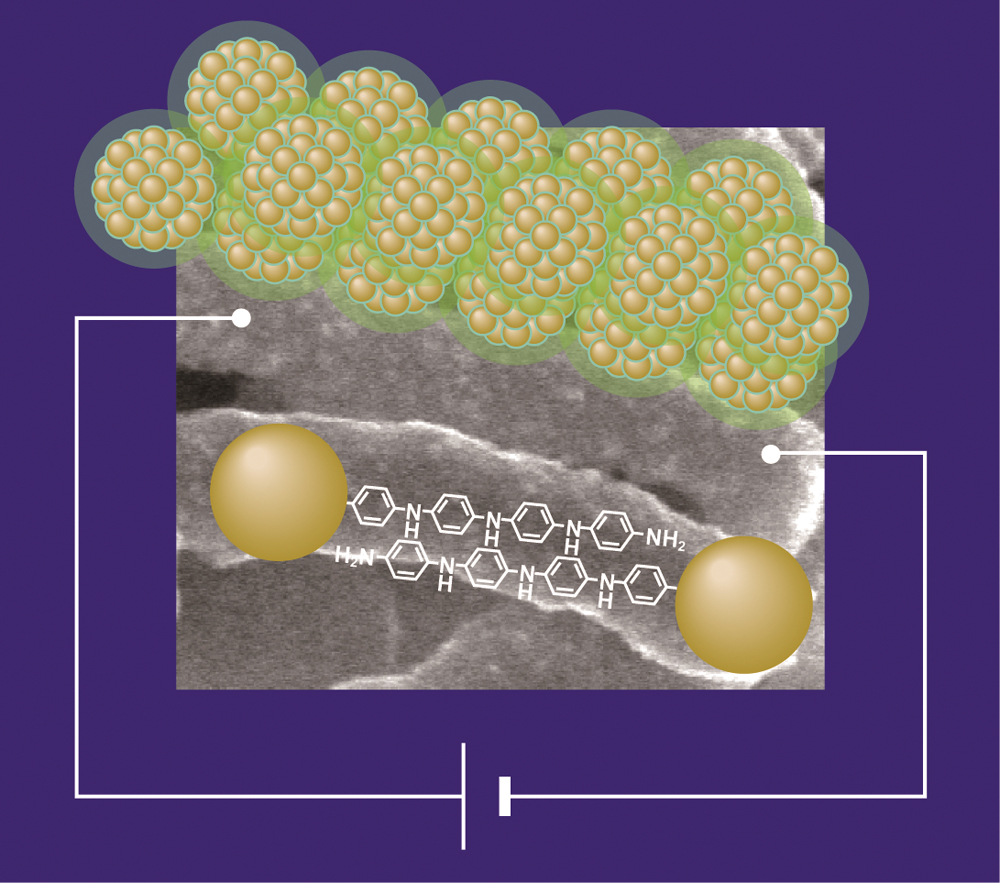 View full abstractDownload PDF (808K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (808K)
Original Papers
-
Tomoko OHTA, Yasunori MAHARA, Takumi KUBOTA, Toshifumi IGARASHIArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 941-947
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSWe measured 134Cs and 137Cs in the surface soil of the Kanto loam in the eastern Tokyo metropolitan area and the Nishiyama loam in Nagasaki, Japan. The observed 137Cs deposition in the Kanto loam from the Fukushima nuclear power plant (NPP) accident ranged from 4.0 to 77 kBq m−2, which corresponds to 0.3 – 5 times of that in the Nishiyama loam. The 137Cs retardation factor in the Kanto loam obtained seven months after the Fukusima NPP accident and in the Nishiyama loam after 36 and 38 years from the detonation of the Pu atomic bomb (A-bomb) ranged from 180 to 260 and 2000 to 10000, respectively. This difference in the retardation factors is attributed to an aging effect that corresponds to seven months and 36 to 38 years after the deposition of 137Cs occurred on the soil minerals. View full abstractDownload PDF (15266K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (15266K) -
Hitoshi MIZUGUCHI, Kentaro NUMATA, Chiaki MONMA, Masamitsu IIYAMA, Kaz ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 949-954
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA new flow-injection/anodic stripping voltammetry has been demonstrated to assess ultra-trace mercury(II) using track-etched microporous membrane electrodes. The electrodes were prepared by the sputtering of gold or platinum onto both sides of a membrane filter with a smooth flat surface and with cylindrical pores having uniform diameter. The deposition of mercury from a mercury(II) solution was performed while the sample solution flowed through the membrane electrodes. After the deposition step, an anodic stripping voltammogram was obtained by sweeping the potential from 0 to +0.8 V vs. Ag/AgCl. In this case, the sample solution flowed through the pores of the 10-μm-thick membrane filters. Efficient electrolysis occurred during passage of the sample solution through the electrode, of which the pore size was 0.4 μm. In this study, the voltammetry described above was demonstrated using an FIA system. The continuous-flow mode showed a detection limit of 0.04 μg L−1 when the experimental conditions of the flow rate and the deposition time were set at 0.5 mL min−1 and 180 s. In the sample-injection mode equipped with a 1-mL sample loop, a linear relation was found for 0.5 – 4.0 μg L−1 of a mercury(II) standard solution (r = 0.995). The detection limit was 0.05 μg L−1. This method was applied to the ultra-trace determination of mercury(II) in river-water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1158K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1158K) -
Mirna DAYE, Baghdad OUDDANE, Jalal HALWANI, Mariam HAMZEArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 955-961
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simple and cheap analytical technique was developed for the measurement of total mercury in river water samples using inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). It is based on the direct complexation of mercury ions using iodide and a cationic surfactant in water for its subsequent solid-phase extraction. Mercury ions are retained on the silica phase as ion pairs in the presence of iodide ions and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide. Parameters having influential influence on the retention of Hg(II) were investigated: sample flowrate, eluent type, sample volume, iodide and surfactant concentrations. The retained mercury ions are stripped off from silica phase using 10 mL of 8 mol L−1 HNO3 and quantified by ICP-MS. An enrichment factor of 50 was achieved with a maximum adsorption capacity of 718 μg Hg(II) g−1. The limit of detection of Hg(II) was 8 pg mL−1. The developed method was applied for the determination of total mercury in river and tap-water samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (918K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (918K) -
Shingo TERAKADO, Naoya OHMURA, Seok-Un PARK, Seung-Min LEE, Thomas R. ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 963-969
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDevelopment and modifications are described that expand the application of an immunoassay from the detection of Kanechlors (Japanese technical PCBs mixtures) to the detection of Aroclors (U. S. technical PCB mixtures, used in Korea) in contaminated Korean transformer oil. The first necessary modification was the development of a new antibody with a reactivity profile favorable for Aroclors. The second modification was the addition of a second column to the solid-phase extraction method to reduce assay interference caused by the Korean oil matrix. The matrix interference is suspected to be caused by the presence of synthetic oils (or similar materials) present as contaminants. The modified assay was validated by comparison to high-resolution gas chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis, and was shown to be tolerant of up to 10% of several common synthetic insulating oils. Finally the screening performance of the modified assay was evaluated using 500 used transformer oil samples of Korean origin, and was shown to have good performance in terms of false positive and false negative rates. This report provides evidence for the first establishment of immunoassay screening for Aroclor based PCB contamination in Korean transformer oil. View full abstractDownload PDF (927K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (927K) -
Kazuko MATSUMOTO, Hiroko KIMURA, Nobuko KON, Ken-ichi YOSHIDA, Mitsuru ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 971-977
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialA novel peroxidase activity assay was developed for horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), in which substrate Eu2+ was catalytically oxidized to Eu3+, and the Eu3+ luminescence was enhanced by the addition of sensitizer 4,4′-bis(1″,1″,1″,2″,2″,3″,3″-hepatafluoro-4″,6″-hexanedione-6″-yl)chlorosulfo-o-terphenyl (BHHCT) for time-resolved measurement of the BHHCT-Eu3+ complex. Since BHHCT-Eu3+ has a long lifetime (more than 500 μs), typical of Eu3+ oxidation state, and the emission wavelength (615 nm) is totally different from those of Eu2+ complexes, time-resolved luminescence measurement of the Eu3+ complex enabled suppressed background and high signal/background ratio. The present method was successfully applied to monitor the oxidative stress level, which is closely associated with peroxidase activity level, in rat heart muscle homogenates. Notable parallel temporal change was observed for peroxidase activity and 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) concentration after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection for induction of oxidative stress in rats. Such a relation does not contradict the oxidative stress mechanism that HNE is produced via lipid peroxidation, which is caused by the •OH radical generated by peroxidase activity. View full abstractDownload PDF (794K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (794K) -
Shingo NORIMOTO, Seiya MORIMINE, Takafumi SHIMOAKA, Takeshi HASEGAWAArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 979-984
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe coverage of a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of octadecyl silane on a silicon surface is analyzed by infrared external-reflection spectrometry via molecular orientation analysis. A commercially available octadecyl trimethoxy silane (ODS) solution is employed, which readily reacts with an oxidized surface of Si(100) prepared by a UV/ozone treatment in an ambient condition to yield a highly reproducible SAM. With the present technique, a very flat surface with no holes is obtained in the entire area of the SAM. IR external-reflection spectra of the SAM apparently indicate that the alkyl chains are highly ordered having the all-trans zigzag conformation, and the molecular orientation agrees with that of a Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) monolayer film of octadecanoic acid. Since the orientation analysis is based on an assumption that the surface is fully covered by the SAM as the LB film, the agreement of the orientation confirms that the surface coverage of the present SAM on Si(100) is on the same level as the LB film. View full abstractDownload PDF (810K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (810K) -
Yan ZHANG, Xiaoyan HUANG, Wenfang LIU, Zeneng CHENG, Chuanpin CHEN, Li ...Article type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 985-990
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIllegal chemicals, which could cause unpredictable side effects, may be added into traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for a rapid healing effect. In this report, a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) analysis method for five kinds of illegally added drugs (rosiglitazone maleate, phenformin hydrochloride, metformin hydrochloride, pioglitazone hydrochloride and sibutramine hydrochloride) in Chinese traditional patent medicine (CTPM) has been demonstrated, including simultaneous detections of drug mixtures with CTPM. Silver colloidal, prepared by a sodium citrate reaction, was used as a SERS substrate. The optimum pH condition for each drug has also been explored because of its combined effect on protonation, surface charge, repulsion of an analyte and nanoparticles. Furthermore, the simultaneous detection of two or three kinds of these chemicals has been carried out. Characteristic peaks are employed for qualitative analysis. This is the first research using SERS for the analysis of drug mixtures in CTPM without any separation process. View full abstractDownload PDF (5016K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5016K) -
Hai-Ying QIAO, Mei-Lan HONG, Xue TIAN, Li-Jiao HUANG, Xia CHUArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 991-996
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn this work, we developed a label-free, homogeneous surface-enhanced Raman-scattering (SERS) platform for the rapid, simple and sensitive detection of Ag+ by using the unmodified gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). It utilizes the different absorption properties of single-strand DNA (ssDNA) and double-strand DNA (dsDNA) on citrate-coated AuNPs and specific interactions between Ag+ and cytosine–cytosine pairs. In the presence of Ag+, the structure of ssDNA containing rich cytosine will form a duplex, resulting in the salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles; the corresponding SERS signal transduction can be observed due to the plasmonic coupling of metallic nanoparticles. The assay possesses a superior signal-to-background ratio as high as ∼35.8 with a detection limit of 15 nM. This approach is not only rapid and convenient in operation, but also shows excellent selectivity, which makes it possible to detect Ag+ in actual samples. View full abstractDownload PDF (1234K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1234K) -
Qiuyu SHI, Heya WANG, Chao DU, Weiguo ZHANG, He QIANArticle type: Original Papers
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 997-1002
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe major carotenoids (β-carotene, γ-carotene, torulene, and torularhodin) were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography, with torulene present in the largest amount (167.0 μg/g), followed by torularhodin (113.4 μg/g), β-carotene (52.1 μg/g) and γ-carotene (15.4 μg/g). In addition, cis/trans torulene isomers were further identified by developing an HPLC-DAD coupled with an atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization (APCI) MS method, following isolation and purification torulene from crude pigments by column chromatography. A total of 8 torulene geometrical isomers were resolved within 60 min by employing a YMC C30 column and a binary gradient mobile phase consisting of methanol–methyl tert–butyl ether–water, (50:47.5:2.5, v/v/v) (A) and methanol–methyl tert–butyl ether–water, (8:90:2, v/v/v) (B). Geometrical carotenoid isomers behave differently with respect to bioavailability; therefore, it is of great importance to expand our knowledge on their biological roles to determine the appropriate method to separate torulene cis/trans isomers.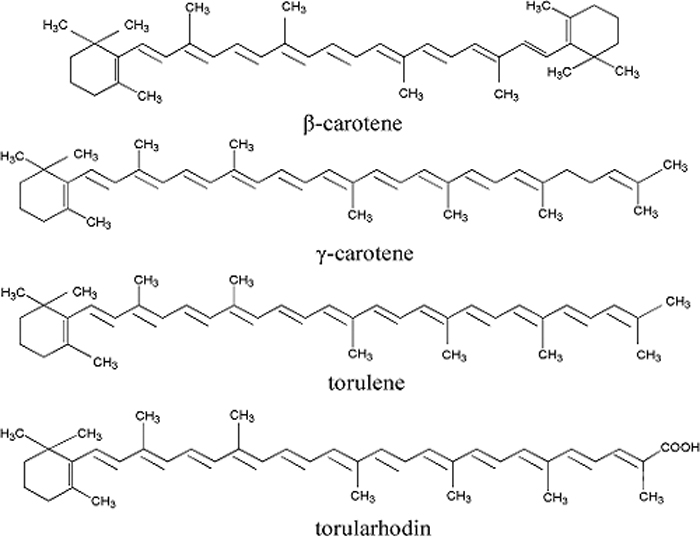 View full abstractDownload PDF (542K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (542K)
Notes
-
Kei NISHIYAMA, Masaharu MURATA, Masahiko HASHIMOTO, Kazuhiko TSUKAGOSH ...Article type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 1003-1008
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe tube radial distribution of ternary solvents (water–hydrophilic/hydrophobic organic mixture) fed into bent and wound microchannels in a microchip was examined by fluorescence observations of dyes dissolved in the solvents under laminar flow conditions. Four kinds of microchips incorporating bent microchannels were used, together with a microchip with a straight channel. The microchannels had different bending times (2, 4, or 12 times), bending radii (0.8, 2.3, or 3 mm), and total channel lengths (80, 120, 200, or 500 mm). A water–acetonitrile (hydrophilic)–ethyl acetate (hydrophobic) mixture containing relatively hydrophilic Eosin Y (green) and hydrophobic perylene (blue) was delivered into the bent microchannels in the microchips. The fluorescence of the green and blue dyes enabled us to observe the specific radial distribution behavior of the ternary solvents in the bent micro channels at 0°C, including liquid–liquid interfaces. Further, the radial distribution pattern of the solvents was clearly observed in the wound microchannel (bending radius, ca. 0.1 mm; real total channel length, 500 mm; and apparent straight channel length, 40 mm) at 20°C (room temperature) as well as 0°C. It was found that the radial distribution behaviors of the solvents were successfully generated in even specific microchannels including various types of curves under the present conditions. View full abstractDownload PDF (1493K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (1493K) -
Yingli ZHU, Guobin SHEN, Feifang ZHANG, Bingcheng YANGArticle type: Notes
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 1009-1011
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSA simply way was proposed to prepare solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber with cation-exchange functional groups by the thermally initiated radical polymerization of poly(butadiene-maleic acid) (PBMA) copolymer onto a silica capillary. The capacity of the fiber coating could be easily controlled by fabricating successive layers of PBMA. The performance of the fiber combined with ion chromatography was evaluated by choosing Mg2+ and Ca2+ as model analytes; ∼13 and ∼51-fold enrichment factors for Mg2+ and Ca2+ were obtained, respectively.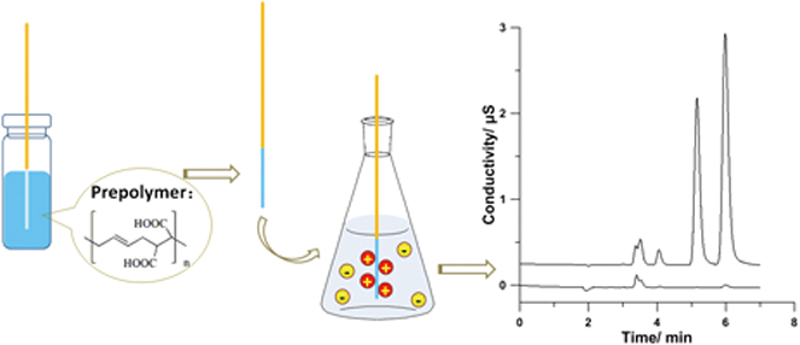 View full abstractDownload PDF (309K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (309K)
Announcements
-
Article type: Announcements
2013 Volume 29 Issue 10 Pages 1013
Published: October 10, 2013
Released on J-STAGE: October 10, 2013
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (1651K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|