All issues

Volume 63, Issue 10
Displaying 1-14 of 14 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Communication to the Editor
-
Shota Asai, Yuki Yabe, Ryota Goto, Saori Nagata, Yasunari Monguchi, Ya ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 757-761
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe benzylic positions of the phthalan and isochroman derivatives (1) as benzene-fused cyclic ethers effectively underwent gold-catalyzed direct azidation using trimethylsilylazide (TMSN3) to give the corresponding 1-azidated products (2) possessing the N,O-acetal partial structure. The azido group of the N,O-acetal behaved as a leaving group in the presence of catalytic iron(III) chloride, and 1-aryl or allyl phthalan and isochroman derivatives were obtained by nucleophilic arylation or allylation, respectively. Meanwhile, a double nucleophilic substitution toward the 1-azidated products (2) occurred at the 1-position using indole derivatives as a nucleophile accompanied by elimination of the azido group and subsequent ring opening of the cyclic ether nucleus produced the bisindolylarylmethane derivatives. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (851K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (851K) Full view HTML
Regular Articles
-
Toshimasa Toyo’oka, Ruri Kikura-Hanajiri2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 762-769
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA reliable method using supercritical fluid chromatography with mass spectrometry (SFC-MS) was developed for cannabinoids using compressed carbon dioxide (CO2) and methanol as the mobile-phase. The cannabinoids, i.e., cannabicyclohexanol (CCH: cis-isomer), trans-CCH, 5-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)-2-[(1R,3S)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-phenol (CP-47497), 5-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)-2-[(1R,2R,5R)-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxypropyl)cyclohexyl]-phenol (CP-55940), 3-(1,1′-dimethylheptyl)-6aR,7,10,10aR-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-6,6-dimethyl-6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-9-methanol (HU-210), 2-[1R-3-methyl-6R-(1-methylethenyl)-2-cyclohexen-1-yl]-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol (CBD), (1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-naphthalenyl-methanone (JWH-018), (1-butyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-1-naphthalenyl-methanone (JWH-073) and 1-(1-pentyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-ethanone (JWH-250), were determined within 12 min using a conventional column (2-EP) for SFC. Furthermore, two optical isomers of CCH and trans-CCH were completely and rapidly separated by a chiral stationary phase column (AMY1). A highly sensitive detection (0.002–3.75 ppb) was also obtained by these methods using 2-EP and AMY1 columns. These methods were applied to the qualitative and quantitative determination of cannabinoids in dried plant products. Although the concentration and species were different in the products, JWH-018, JWH-073 and CCH, including the cis-isomer, trans-isomer and the optical isomers, were detected in the products. Therefore, the proposed SFC-MS method seems to be useful as an alternative method to GC-MS and LC-MS for illegal drugs, such as cannabinoids. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1069K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1069K) Full view HTML -
Tomonobu Uchino, Yasunori Miyazaki, Tomoyo Ohkawa, Takuto Yamazaki, Yo ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 770-779
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe aim of this study was to characterize protein aggregation during reconstitution of a highly concentrated solution of lyophilized L-asparaginase (L-ASP). The effect of the preparation method on L-ASP aggregation using siliconized or non-siliconized syringes and the effect of storage after preparation were evaluated by far-UV circular dichroism spectroscopy, Raman microscopy, flow cytometry, and flow particle image analysis. To investigate the effect of syringe type in combination with shaking and headspace air on L-ASP aggregation, four kinds of L-ASP in 5% glucose solutions were prepared (in the presence or absence of silicon oil and headspace air). Slight differences in L-ASP secondary structure were observed between the siliconized and non-siliconized syringe systems before shaking. Large numbers of sub-visible (0.1–100 µm) and submicron (0.1–1 µm) particles were formed by preparation with siliconized syringes and the combination of shaking and headspace air. The number of aggregated particles was not decreased with increased storage time. The Raman microscopy, flow cytometry and flow particle image results suggested that L-ASP interacted with silicone oil, which induced aggregation. Nevertheless, sub-visible and submicron particles were also formed with non-siliconized syringes. However, using non-siliconized syringes, the number of aggregated particles decreased with storage. No changes in particle character were observed before or after shaking with headspace air in non-siliconized syringes, indicating that soluble aggregates formed and dissolved with storage. Silicone oil in syringes, in combination with shaking and headspace air, strongly affected the aggregation of lyophilized L-ASP formulations during preparation. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2355K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2355K) Full view HTML -
Wenhai Huang, Wenhua Wei, Yewei Yang, Tao Zhang, Zhengrong Shen2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 780-791
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEstrogen receptor α (ERα) and estrogen receptor β (ERβ) regulate different sets of gene expression, and have different ligand responses, which make the estrogen tissue-specific. Thus, the estrogen receptor (ER) subtype-selective ligands can improve the target-site selectivity and decrease the off-target effect. In order to discover the selective ER subtype ligands with novel scaffolds, in this work three-dimensional (3D) pharmacophore models of the ERα ligands (Hypo 1) and the ERβ ligands (Hypo 2) were established (correlation coefficients were 0.959 and 0.966) and validated (R=0.936 and 0.879; enrichment factors (EFs) at 2% were 16.2 and 8.4; areas under the concentration–time curve (AUC) of the receiver operating curve (ROC) were 0.88 and 0.91) using the Discovery Studio 4.0 software package. Hypo 1 and Hypo 2 were then employed for virtual screening and ten hits were found as potential candidate leads. Based on their ERα/ERβ binding affinity results by fluorescence polarization technology, two of these leads, AH-262/34334025 (AH) and AG-670/08803023 (AG) with novel scaffolds were identified as selective ERα ligands. A molecular docking study was also performed, which provided the explanation for the ER subtype preferences for AH and AG. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2867K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2867K) Full view HTML -
Jeong-Woong Seo, Kyung-Jin Kim, Su-Hyeon Kim, Kyu-Mok Hwang, Su Hyun S ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 792-798
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe objectives of this study were to prepare itraconazole (ITZ) nanoparticles using a Shirasu porous glass (SPG) membrane and to characterize the effects of diverse preparation parameters on the physical stability of nanoparticles. SPG membrane technology was used for the antisolvent precipitation method. The preparation of nanoparticles was carried out over a wide range of continuous-phase factors (type of surfactant, surfactant concentration), dispersed-phase factors (solvent type, solvent volume used to dissolve ITZ), and technical factors (pressure, membrane pore size, stirring speed in the continuous phase, temperature). Improved physical stability of nanoparticles was observed when surfactant with a lower molecular weight and higher hydrophilic segment ratio was used. The water miscibility of the solvent also had an effect on the physical stability. N,N-Dimethylacetamide contributed to creating a well-rounded shape and narrow size distribution due to high miscibility. Concentration of the surfactant and solvent volume used for dissolving ITZ were related to instability of nanoparticles, resulting from depletion attraction and Ostwald ripening. In addition to these factors, technical factors changed the environment surrounding ITZ nanoparticles, such as the physicochemical equilibrium between surfactant and ITZ nanoparticles. Therefore, the appropriate continuous-phase factors, dispersed-phase factors, and technical factors should be maintained for stabilizing ITZ nanoparticles.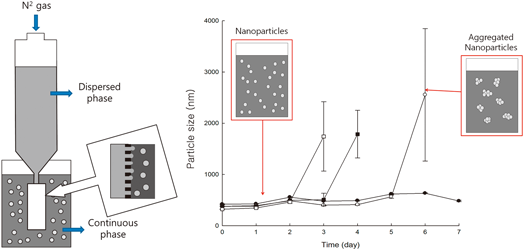 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1602K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1602K) Full view HTML -
Kyohei Yamada, Yasunori Iwao, Ahmad Bani-Jaber, Shuji Noguchi, Shigeru ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 799-806
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlthough chitosan (CS) has been recognized as a good material for colon-specific drug delivery systems, an overcoating with an enteric coating polymer on the surface of CS is absolutely necessary because CS is soluble in acidic conditions before reaching the colon. In the present study, to improve its stability in the presence of acid, a newly developed CS-laurate (CS-LA) material was evaluated as a coating dispersion for the development of colon-specific drug delivery systems. Two types of CS with different molecular weights, CS250 and CS600, were used to prepare CS-LA films by the casting method. The CS250-LA films had smooth surfaces, whereas the surfaces of the CS600-LA films were rough, indicating that the CS250-LA dispersion could form a denser film than CS600-LA. Both of these CS-LA films maintained a constant shape over 22 h in a pH 1.2 HCl/NaCl buffer, where the corresponding CS films rapidly disintegrated. In addition, the CS250-LA film showed specific colon degradability in a pH 6.0 phosphate buffered solution containing 1.0% (w/v) β-glucosidase. As a result of tensile strength and elongation at the break, both CS-LA films were found to have flexible film properties. Finally, the release of acetaminophen from disks coated with CS250-LA dispersions was significantly suppressed in fluids at pH 1.2 and 6.8, whereas disks coated with CS solution rapidly released the drug in pH 1.2 fluids. Taken together, this study shows that LA modification could be a useful approach in preparing CS films with acid stability and colonic degradability properties without requiring overcoating. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1194K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1194K) Full view HTML -
Hwangseo Park, Hye Seon Lee, Seung Jun Kim2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 807-811
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlthough VH1-related member Y (VHY) phosphatase is responsible for the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory diseases, no small-molecule inhibitor of VHY has been reported so far. Here we first report eight VHY inhibitors identified from molecular docking-based virtual screening and subsequent enzyme inhibition assays. These inhibitors exhibit good biochemical potencies against VHY, with associated IC50 values ranging from 1 to 9 µM. Because all these inhibitors were also screened in silico for having desirable physicochemical properties as a drug candidate, they deserve further investigation by structure–activity relationship studies to develop new medicines for the treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. The structural features of VHY-inhibitor interactions relevant to the micromolar-level inhibitory activity are addressed in detail.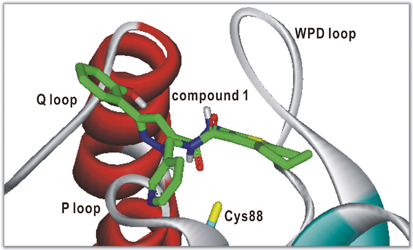 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (921K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (921K) Full view HTML -
Magdy Mohamed Hemdan, Heba Kamal Abd El-Mawgoude2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 812-818
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe reaction of lauroyl isothiocyanate with ethyl 2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylate gave ethyl 2-(3-dodecanoylthioureido)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[b]thiophene-3-carboxylate 3. Compound 3 could serve as a main building block in synthesis of the target heterocyclic systems like thieno[2,3-d]-pyrimidine, thieno[2′,3′:4,5]pyrimido[1,2-a][1,3,5]triazine, thieno[2,3-d]-1,3-thiazine and 1,2,4-triazole systems attached to the lauryl group. The structures of the synthesized target heterocyclic compounds were confirmed by microanalytical and spectral data. The antimicrobial activity of some of the synthesized compounds was tested. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (612K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (612K) Full view HTML -
Koji Morimoto, Ryosuke Ogawa, Daichi Koseki, Yusuke Takahashi, Toshifu ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 819-824
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe facile and clean oxidative coupling reaction of pyrroles with azoles has been achieved using the recyclable hypervalent iodine(III) reagents having adamantane structures. These iodine(III) reagents could be recovered from the reaction mixtures by a simple solid–liquid separation, i.e., filtration, for reuse.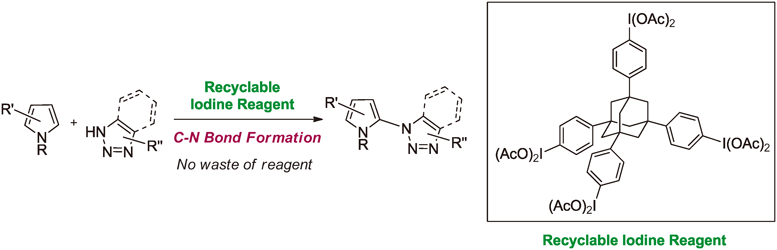 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (684K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (684K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
Bitoku Takahashi, Hideaki Funami, Makoto Shibata, Hiroshi Maruoka, Mak ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 825-832
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLStructural optimization of 2-aminonicotinamide derivatives as ghrelin receptor inverse agonists is reported. So as to avoid mechanism-based inactivation (MBI) of CYP3A4, 1,3-benzodioxol ring of the lead compound was modified. Improvement of the main activity and lipophilicity was achieved simultaneously, leading to compound 18a, which showed high lipophilic ligand efficiency (LLE) and low MBI activity. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K) Full view HTML -
Hiroyuki Fuchino, Aya Yazawa, Fumiyuki Kiuchi, Nobuo Kawahara, Yutaka ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 833-836
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFour new monoterpene lactones, 5-(2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-4-hydroxy-4-methyldihydrofuran-2(3H)-one (1), 5-(2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-4-methylfuran-2(5H)-one (2), 8-hydroxy-4,7,7-trimethyl-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]non-3-en-2-one (3) and 8-hydroxy-4,7,7-trimethyl-1,6-dioxaspiro[4.4]non-3-en-2-one (4), were isolated from the methanolic extract of the fruit of Cinnamomum inunctum, a folk medicine in Myanmar, together with a known compound, 3-hydroxy-4,4-dimethyl-4-butyrolactone (5). Their chemical structures were determined by spectral methods. Among these, 3 and 4 possessed unique spirolactone moieties. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (655K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (655K) Full view HTML -
Ki Hyun Kim, Eunjung Moon, Joon Min Cha, Seulah Lee, Jae Sik Yu, Chung ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 837-842
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAs part of our ongoing search for bioactive constituents of natural Korean medicinal resources, we found in a preliminary study that the methanol (MeOH) extract from the trunks of Tilia amurensis RUPR. showed an inhibitory effect on nitric oxide (NO) production in an activated murine microglial cell line. A bioassay-guided fractionation and chemical investigation of the MeOH extract resulted in the isolation and identification of a new isoflavonoid glycoside, orobol 4′-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (1) and 16 known compounds (2–17). The structure of the new compound was determined by spectroscopic methods, i.e., one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D)-NMR techniques and high resolution (HR)-MS, and chemical methods. The antineuroinflammatory activities of the isolated compounds were determined by measuring NO levels in the medium using murine microglial BV-2 cells. Among them, 12 compounds, including compound 1 (most active with an IC50 value of 23.42 µM), inhibited NO production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 cells. Moreover, compounds 1–4 showed moderate antiproliferative activities against the SK-MEL-2 cell line, with IC50 values ranging from 12.31 to 19.67 µM. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML -
Dongguk Min, Moon Hi Han, Seulki Lee, Mankil Jung2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 843-847
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
Advance online publication: August 01, 2015JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe first total synthesis for large-scale production and anticancer activity of novel aminophenylpyridinium-5-(hydroxybenzoyl)hydrazonomethyl-2-oxothiazol-3-ide (PBHT) (1) and its derivatives are reported. The chemical structure of PBHT was unambiguously determined by utilization of the two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) technique. The anticancer activity against human colon adenocarcinoma (HCT15) cells of all synthesized compounds was approximately four-fold greater than that of 5-fluorouracil, with IC50 values ranging from 10.1 to 14.2 µM. The three structural determinants of hydroxybenzoyl, hydrazinylidene, and pyridinium oxothiazole in the synthesized compounds could be indispensable for exhibiting anticancer activity. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (671K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (671K) Full view HTML -
Toshihiro Nohara, Yukio Fujiwara, Jian-Rong Zhou, Jun Urata, Tsuyoshi ...2015 Volume 63 Issue 10 Pages 848-850
Published: October 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIt has been shown that commercial tomato juice packaged in 900 g plastic bottles contains rare, naturally occurring steroidal solanocapsine-type tomato glycosides in which the saponins consist of esculeosides B-1 (2) and B-2 (3) in 0.041% as major components lacking esculeoside A. We suggest that these saponins are derived from esculeoside A (1) when the juice in plastic bottles is prepared by treatment with boiling water, similar to the process used in preparing canned tomatoes. Herein, the obtained tomato saponins (2) and (3) provided sapogenols esculeogenin B1 (4) and B2 (5), respectively, by acid hydrolysis. The former was identical to esculeogenin B previously reported, and the latter was a new sapogenol characterized to be (5α,22S,23S,25S)-22,26-epimino-16β,23-epoxy-3β,23,27-trihydroxycholestane. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (523K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (523K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|