All issues

Volume 63, Issue 9
Displaying 1-15 of 15 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review
-
Hikaru Yanai2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 649-662
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe bis[(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl]methyl (Tf2CH; Tf=SO2CF3) group is known to be one of the strongest carbon acid functionalities. The acidity of such carbon acids in the gas phase is stronger than that of sulfuric acid. Our recent investigations have demonstrated that this type of carbon acids work as novel acid catalysts. In this paper, recent achievements in carbon acid chemistry by our research group, including synthesis, physicochemical properties, and catalysis, are summarized. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2404K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2404K) Full view HTML
Regular Articles
-
Tatsuo Koide, Yoshihisa Yamamoto, Toshiro Fukami, Noriko Katori, Haruh ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 663-668
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe aim of this study was to evaluate pharmaceuticals using a near-infrared chemical imaging (NIR-CI) technique for visualizing the distribution of ingredients in solid dosage forms of commercially available clarithromycin tablets. The cross section of a tablet was measured using the NIR-CI system for evaluating the distribution of ingredients in the tablet. The chemical images were generated by performing multivariate analysis methods: principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares (PLS) with normalized near-infrared (NIR) spectral data. We gained spectral and distributional information related to clarithromycin, cornstarch, and magnesium stearate by using PCA analysis. On the basis of this information, the distribution images of these ingredients were generated using PLS analysis. The results of PCA analysis enabled us to analyze individual components by using PLS even if sufficient information on the products was not available. However, some ingredients such as binder could not be detected using NIR-CI, because their particle sizes were smaller than the pixel size (approximately 25×25×50 µm) and they were present in low concentrations. The combined analysis using both PCA and PLS with NIR-CI was useful to analyze the distribution of ingredients in a commercially available pharmaceutical even when sufficient information on the product is not available.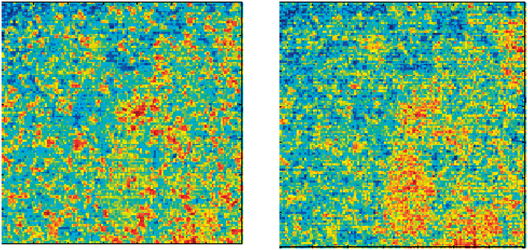 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6639K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6639K) Full view HTML -
Minkyu Kim, Yongseo Park, Won-Yoon Chung, Kwang-Kyun Park, Mankil Jung2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 669-677
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialNovel saponins that retain a free carboxyl group at the C-17 position and various sugars linked at the C-3 position of hederagenin aglycone were synthesized via stereospecific glycosylation. Since these natural products represented by Pulsatilla saponin D (PSD) were obtained in very small amounts, the total synthesis developed in this paper will resolve this problem of scarcity. The two types of synthesized arabinose- and rhamnose-cored saponins showed potent anticancer activity against a human lung cancer cell line (A549), and most disaccharide moiety saponins possessed more potent anti-lung cancer activity. Among the novel PSD analogues containing disaccharide saponins, compound 10i showed anti-lung cancer activity (6.6 µM) that was four-fold more potent than the clinical agent Iressa® (26.08 µM).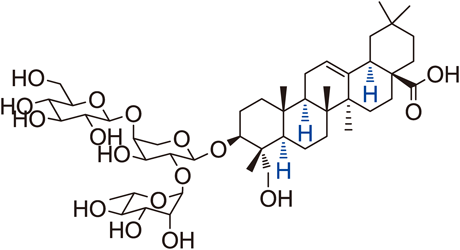 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1066K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1066K) Full view HTML -
Rafat Milad Mohareb, Nadia Youssef Megally Abdo2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 678-687
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of coumarin analogues bearing 4H-pyran rings 2a–d, 11a–d and 1,4-dihydropyridine rings 3a–d, 12a–d at position 3 were synthesized starting from either 3-acetyl coumarin (1) or the coumarin acetohydrazide derivative 4. Condensation of 3-acetylcoumarin (1) with 2-cyanoacetohydrazide afforded 2-cyano-N′-{1-[2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl]ethylidene}acetohydrazide (4). Reaction of compound 4 with elemental sulfur and either malononitrile or ethyl cyanoacetate afforded the thiophene derivatives 8 and 9, respectively. The structures of the newly synthesized compounds were confirmed on the basis of their spectral data and elemental analyses. All synthesized compounds were screened for their in vitro anticancer activity against six human cancer cell lines and normal fibroblasts. Several compounds showed potent inhibition with an IC50 value of ˂870 nM. Compound 3d exhibited equivalent cytotoxic effect as the standard CHS 828 against a breast cancer cell line (IC50 value=18 nM). Normal fibroblast cells (WI38) were affected to a much lesser extent (IC50 value >10000 nM). Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (992K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (992K) Full view HTML -
Bing Wang, Yiqiong Pu, Benliang Xu, Jiansheng Tao, Yuqin Wang, Tong Zh ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 688-693
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
Advance online publication: June 18, 2015JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML20(S)-Protopanaxadiol (20(S)-PPD) is one type of sapogenin of protopanaxadiols and has a variety of pharmacological activities. In order to improve the dissolution of 20(S)-PPD as well as its oral bioavailability, a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) was utilized for 20(S)-PPD preparation. Following the preparation of the 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS, its dissolution, stability, and intestinal absorption in rats were studied, and the pharmacokinetics and optimal dosage after oral administration were evaluated. The dissolution tendency of the SMEDDS in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 0.1 M HCl and distilled water was consistent. SMEDDS was stable under a condition of high temperature (40°C), high humidity or with strong light irradiation, or within 6 h in artificial digestive tracts. 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS was well-absorbed in all intestinal segments in rats. When the drug concentration was higher than 200 µg/mL or the perfusion flow was faster than 0.5 mL/min, passive diffusion of drug in the duodenum reached a saturated level. In addition, P-glycoprotein inhibitor did not affect the intestinal absorption of 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS. Pharmacokinetic study showed that Tmax in male rats was shortened significantly, while Cmax and area under the curve (AUC(0–t)) were remarkably increased. The relative oral bioavailability of 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS was increased approximately three fold compared with the 20(S)-PPD carboxy methyl cellulose (CMC). 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS (100 mg/mL) was administered by gastric infusion to both mice and rats for 14 d. SMEDDS improved the oral bioavailability of 20(S)-PPD and reduced the necessary drug dosage. 20(S)-PPD SMEDDS could become a promising clinical alternative as an anti-tumor or antidepressant drug. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (487K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (487K) Full view HTML -
Stefania-Felicia Barbuceanu, Constantin Draghici, Florica Barbuceanu, ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 694-700
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the present study, a series of new heterocyclic condensed systems with bridgehead nitrogen from the thiazolo[3,2-b][1,2,4]triazoles class was synthesized starting from some 4-(4-X-phenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thioles 1a–c (X=H, Cl, Br). The intermediates of S-alkylated 1,2,4-triazoles, 2-(5-(4-(4-X-phenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-2H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylthio)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethanones 2a–c, were obtained by treatment of triazoles 1a–c with 2-bromo-4′-fluoroacetophenone. The 2-(4-(4-X-phenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-6-(4-fluorophenyl)thiazolo[3,2-b][1,2,4]triazoles 3a–c were obtained by cyclization of S-alkylated 1,2,4-triazoles 2a–c in sulfuric acid media, at 0°C. For the synthesis of 2-(4-(4-X-phenylsulfonyl)phenyl)-5-(4-fluorobenzylidene)-thiazolo[3,2-b][1,2,4]triazol-6(5H)-ones 4a–c, the triazoles 1a–c were treated with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde, chloroacetic acid and anhydrous sodium acetate, in the presence of acetic acid and acetic anhydride. The structures of the newly synthesized compounds have been confirmed by elemental analysis and spectral methods (IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MS). The antimicrobial activity of all new compounds has been screened against some bacteria and yeasts. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (520K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (520K) Full view HTML -
Norikazu Sakakibara, Junsuke Igarashi, Maki Takata, Yosuke Demizu, Tak ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 701-709
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSix novel carbocyclic oxetanocin A analogs (2-chloro-C.OXT-A; COA-Cl) with various hydroxymethylated or spiro-conjugated cyclobutane rings at the N9-position of the 2-chloropurine moiety were synthesized and evaluated using human umbilical vein endothelial cells. All prepared compounds (2a–f) showed good to moderate activity with angiogenic potency. Among these compounds, 100 µM cis–trans-2′,3′-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutyl derivative (2b), trans-3′-hydroxymethylcyclobutyl analog (2d), and 3′,3′-bis(hydroxymethyl)cyclobutyl derivative (2e) had greater angiogenic activity, with relative tube areas of 3.43±0.44, 3.32±0.53, and 3.59±0.83 (mean±standard deviation (S.D.)), respectively, which was comparable to COA-Cl (3.91±0.78). These data may be important for further development of this class of compounds as potential tube formation agents. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1749K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1749K) Full view HTML -
Chihiro Tsukano, Sho Yamamoto, Yoshiji Takemoto2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 710-719
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe synthesis of α-acyloxyketones via the migration of a propargylic ester followed by the intramolecular nucleophilic addition of the resulting allene was achieved using a cationic platinum catalyst. The optimized conditions for this transformation were determined to be 3 mol% of Pt(cod)Cl2, 3 mol% of AgNTf2, and 3 eq of water in toluene at 100°C, and these conditions were successfully applied to the synthesis of a wide variety of α-aryl-α-acyloxyketones. The mechanism of this reaction was evaluated in detail based on the results of isotope labeling experiments using H218O.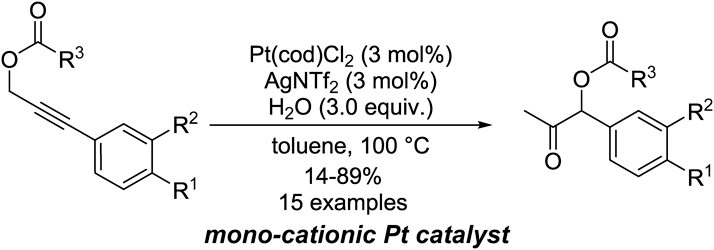 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (898K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (898K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
Handan Gokben Sevindik, Ufuk Ozgen, Alptug Atila, Handan Ozturk Er, Ca ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 720-725
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThymus praecox ssp. grossheimii (RONNIGER) JALAS var. grossheimii (Lamiaceae) is used as an herbal tea for cold, stomachache, cough, and infections in Turkey. There are no phytochemical studies on this species. We performed phytochemical studies and quantitative analysis of rosmarinic acid and luteolin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside in the methanol extract of the plant. Several chromatographic methods were used for the isolation of major compounds. HPLC methods were applied for quantitative analysis of rosmarinic acid and luteolin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside in the methanol extract. In this study, ursolic acid (1), oleanolic acid (2), methyl rosmarinate (3), ethyl rosmarinate (4), rosmarinic acid (5), luteolin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), and thymoquinol 2,5-O-β-diglucopyranoside (7) were isolated from the aerial parts of the plant. The relative contents of rosmarinic acid and luteolin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside in the extract were 15.2 and 57.8 mg/g of dry weight, respectively. Compounds isolated from this plant and the contents of rosmarinic acid and luteolin 5-O-β-D-glucopyranoside provided reasonable evidence for the traditional usages of this plant. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (838K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (838K) Full view HTML -
Tatsuru Goto, Yoshimasa Amano, Motoi Machida, Fumio Imazeki2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 726-730
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, introduction of acidic functional groups onto a carbon surface and their removal were carried out through two oxidation methods and outgassing to investigate the adsorption mechanism of aromatic compounds which have different polarity (benzene and nitrobenzene). Adsorption experiments for these aromatics in aqueous solution and n-hexane solution were conducted in order to obtain the adsorption isotherms for commercial activated carbon (BAC) as a starting material, its two types of oxidized BAC samples (OXs), and their outgassed samples at 900°C (OGs). Adsorption and desorption kinetics of nitrobenzene for the BAC, OXs and OGs in aqueous solution were also examined. The results showed that the adsorption of benzene molecules was significantly hindered by abundant acidic functional groups in aqueous solution, whereas the adsorbed amount of nitrobenzene on OXs gradually increased as the solution concentration increased, indicating that nitrobenzene can adsorb favourably on a hydrophilic surface due to its high dipole moment, in contrast to benzene. In n-hexane solution, it was difficult for benzene to adsorb on any sample owing to the high affinity between benzene and n-hexane solvent. On the other hand, adsorbed amounts of nitrobenzene on OXs were larger than those of OGs in n-hexane solution, implying that nitrobenzene can adsorb two adsorption sites, graphene layers and surface acidic functional groups. The observed adsorption and desorption rate constants of nitrobenzene on the OXs were lower than those on the BAC due to disturbance of diffusion by the acidic functional groups. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (485K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (485K) Full view HTML -
Yuka Funakoshi, Yasunori Iwao, Shuji Noguchi, Shigeru Itai2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 731-736
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPreviously, we developed lipid nanoparticles (LNs) containing poorly water-soluble drugs using two types of phospholipids, a neutral phospholipid (hydrogenated soybean phosphatidylcholine) and a negatively-charged phospholipid (dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol), with mean particle sizes of less than 100 nm. Here, we studied the effects of alkyl chain length and unsaturation of neutral and negatively-charged phospholipids on the physicochemical properties of LNs. Three neutral phospholipids, dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine and distearoylphosphatidylcholine, having different alkyl chain lengths, were compared. The mean particle size of the LNs increased with the alkyl chain length, while the concentration of the drug entrapped in the LNs decreased. The particle size of all of the LNs could be maintained at less than 100 nm for 1 month in cool and dark conditions, with the LNs with longer alkyl chain lipids showing greater stability. In the unsaturated phospholipids, the double bond in the alkyl chain of dioleoylphosphatidylcholine and dierucoylphosphatidylcholine did not affect the physicochemical properties of the LNs. The negatively-charged phospholipids dipalmitoylphosphatidylglycerol and distearoylphosphatidylglycerol were also compared; LNs with longer alkyl chain lipids had larger particle sizes and lower drug concentrations, similar to the results for neutral phospholipids. We concluded that although some changes in physicochemical properties were observed among LNs with different phospholipid alkyl chain lengths, this methodology was general. LNs with suitable physicochemical properties could be prepared irrespective of the type of phospholipids used. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (741K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (741K) Full view HTML -
Hidekazu Kawashima, Hiroyuki Kimura, Yuta Nakaya, Kenji Tomatsu, Kenji ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 737-740
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA new radiolabeling method using a microreactor was developed for the rapid synthesis of [11C]raclopride. A chip bearing a Y-shaped mixing junction with a 200 µm (width)×20 µm (depth)×250 mm (length) flow channel was designed, and the efficiency of O-[11C]methylation was evaluated. Dimethyl sulfoxide solutions containing the O-desmethyl precursor or [11C]CH3I were introduced into separate injection ports by infusion syringes, and the radiochemical yields were measured under various conditions. The decay-corrected radiochemical yield of microreactor-derived [11C]raclopride reached 12% in 20 s at 25°C, which was observed to increase with increasing temperature. In contrast, batch synthesis at 25°C produced a yield of 5%: this indicates that this device could effectively achieve O-[11C]methylation in a shorter period of time. The microreactor technique may facilitate simple and efficient routine production of 11C-labeled compounds via O-[11C]methylation with [11C]CH3I. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML -
Reiko Yutani, Reiko Teraoka, Shuji Kitagawa2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 741-745
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe examined the phase behavior of various polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester (polysorbates)/ethanol/isopropyl myristate (IPM)/150 mM NaCl solution (NaClaq) systems in order to prepare a microemulsion containing a low ratio of ethanol, which is more suitable for in vivo application. Using polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate (Tween 85), which has a large lipophilic moiety, as a surfactant component, single-phase domain of the phase diagram was the largest of all the polysorbates examined, and in particular a large oil-rich single-phase domain was obtained. When the ratio of Tween 85 to ethanol was changed from 1 : 1 to 3 : 1, the oil-rich single-phase domain further expanded, which led to a reduced ethanol concentration in the preparation. Thus, we determined the composition of the microemulsion to be Tween 85 : ethanol : IPM : NaClaq=30 : 10 : 53 : 7, and used it for skin delivery of resveratrol. Microemulsion gel was also prepared by adding 6.5% Aerosil® 200 into the microemulsion for ease of topical application. When applied with each vehicle, delivery of resveratrol into guinea pig skin in vitro was significantly enhanced compared with that by IPM, and resveratrol incorporated into the skin by microemulsion gel decreased lipid peroxidation to 29.5% compared with that of the control. Pretreatment of guinea pig dorsal skin with the microemulsion gel containing resveratrol almost completely prevented UV-B-induced erythema formation in vivo. These findings demonstrate that the microemulsion using Tween 85 containing a minimal concentration of ethanol enhanced the skin delivery of resveratrol and the incorporated resveratrol exhibited a protective effect against UV-induced oxidative damage. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3167K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3167K) Full view HTML -
Hye Mi Kim, Byeol Ryu, Jin Su Lee, Jung-Hye Choi, Dae Sik Jang2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 746-751
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFour new dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan glucosides, schisandrosides A–D (1–4), as well as two known rare nortriterpenoids, micrandilactone C (5) and propindilactone Q (6), were isolated from the roots of Schisandra chinensis BAILLON (Schisandraceae). The structure of compounds 1–4 were elucidated by physical and spectroscopic data interpretation. To the best of our knowledge, schisandrosides A–D (1–4) represent the first example of a dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan glycoside. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (608K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (608K) Full view HTML -
Chen-Ting Yin, Zhi-Hong Wen, Yu-Hsuan Lan, Yu-Chia Chang, Yang-Chang W ...2015Volume 63Issue 9 Pages 752-756
Published: September 01, 2015
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTwo new norcembranoids, sinumerolide A (1) and its epimer, 7E-sinumerolide A (2), were isolated from the ethyl acetate extract of the soft coral Sinularia numerosa. The structures of compounds 1 and 2 were established using spectroscopic methods. In the in vitro anti-inflammatory effect test, norcembranoids 1 and 2 were found to inhibit the accumulation of the pro-inflammatory inducible nitric oxide synthase protein of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophage cells significantly. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (759K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (759K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|