
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Katsumi Matsuzaki2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 1-9
Katsumi Matsuzaki2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 1-9
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBiomembranes composed of various proteins and lipids play important roles in cellular functions, such as signal transduction and substance transport. In addition, some bioactive peptides and pathogenic proteins target membrane proteins and lipids to exert their effects. Therefore, an understanding of dynamic and complex intermolecular interactions among these membrane constituents is needed to elucidate their mechanisms. This review summarizes the major research carried out in the author’s laboratory on how lipids and their inhomogeneous distributions regulate the structures and functions of antimicrobial peptides and Alzheimer’s amyloid β-protein. Also, how to detect transmembrane helix–helix and membrane protein–protein interactions and how they are modulated by lipids are discussed.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickA combination of biophysical techniques revealed various complex molecular interactions in membranes. Antimicrobial peptides form toroidal pores with surrounding lipids, followed by translocation into the cytosol. Amyloid β-protein recognizes clusters of monosialoganglioside GM1 on neuronal membranes, forming toxic amyloid fibrils containing 2-residue-shifted antiparallel β-sheets. The coiled–coil labeling method enables a quantitative analysis of membrane protein associations. The introduction of a GXXXG motif drives the formation of an otherwise unfavorable parallel dimer of a model transmembrane helix.
Download PDF (1180K) Full view HTML
-
 Naoya Kishikawa2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 10-11
Naoya Kishikawa2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 10-11
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEditor's pickThese current topics introduce the latest research on the liquid chromatographic techniques utilized in food analysis. These liquid chromatographic techniques are based on various detection methods including UV detection, fluorescence detection, electrochemical detection and MS. These methods incorporate innovations that go beyond simple chromatography, such as derivatization to improve detectability of analyte, effective separation from matrices by fluorous chemistry, multidimensional chromatography to separate a wide range of polar compounds, and the use of methylated reference for the determination without calibration curves using single reference liquid chromatography. The contents of the topics would provide useful suggestions to improve analysis of important ingredients in food samples.
Download PDF (186K) Full view HTML
-
Yoshio Muguruma, Mari Nunome, Koichi Inoue2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 12-18
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDue to the globalization of food production and distribution, the food chain has become increasingly complex, making it more difficult to evaluate unexpected food changes. Therefore, establishing sensitive, robust, and cost-effective analytical platforms to efficiently extract and analyze the food-chemicals in complex food matrices is essential, however, challenging. LC/MS-based metabolomics is the key to obtain a broad overview of human metabolism and understand novel food science. Various metabolomics approaches (e.g., targeted and/or untargeted) and sample preparation techniques in food analysis have their own advantages and limitations. Selecting an analytical platform that matches the characteristics of the analytes is important for food analysis. This review highlighted the recent trends and applications of metabolomics based on “foodomics” by LC-MS and provides the perspectives and insights into the methodology and various sample preparation techniques in food analysis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (558K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (558K) Full view HTML
-
Shimba Kawasue, Yohei Sakaguchi, Reiko Koga, Tadashi Hayama, Hideyuki ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 19-24
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCasein is one of the allergen proteins present in milk. Therefore, a quantification method for the selective analysis of casein using fluorous derivatization with LC-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was developed. After two allergen proteins (αS1-casein and β-casein) extracted from baked sugar cookies were tryptic digested, the obtained phosphorylated peptides were selectively derivatized by β-elimination with Ba(NO3)2 under basic condition and Michael addition with perfluoroalkylthiol (1H,1H,2H,2H-perfluorooctanethiol, PFOT). In this study, YKVPQLEIVPN(pSer)AQQR (104–119 fragment from αS1-casein) and FQ(pSer)EEQQQTEDELQDK (33–48 fragment from β-casein) obtained by tryptic digestion were selected as target peptides. The phosphorylated serine residue in each peptide was converted to a perfluoroalkyl group by derivatization. The obtained fluorous-derivatized peptides were analyzed by LC-MS/MS, to which a fluorous LC column was connected. Therefore, it was possible to analyze casein without being affected by the matrix components in the baked food sample. When the present method was applied to cookies with arbitrary amounts of αS1-casein and β-casein, the obtained quantification values were in good agreement with the arbitrary amounts spiked. The quantification limits of αS1- and β-casein in cookie analysis were 246 and 152 ng/g, respectively. Hence, this method can be used to analyze trace amounts of allergen proteins present in the baked food.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (888K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (888K) Full view HTML -
Miki Takahashi, Koji Morimoto, Yuzo Nishizaki, Naoko Masumoto, Naoki S ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 25-31
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe report on the recommendation of the simple and versatility of methylated reference (MR) to improve applications in the single reference (SR)-LC based on relative molar sensitivity (RMS). Three curcuminoids (Curs) such as curcumin, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin in turmeric products were determined using authentic standards and methylated curcumin. In addition, high-speed countercurrent chromatography (HSCCC) purification is necessary to separate Curs for indicating the RMS. For HSCCC separation, a biphasic solvent system was used to obtain these fractions, which were then subjected to 1H quantitative NMR to determine their contents in each test solution. Using these solutions, the RMS of Curs are calculated from slopes ratios of calibration curves (three ranges from 0–100 µmol/L, r2 > 0.998). The averaged RMS of Curs were 8.92 (relative standard deviation (RSD), 1.17%), 8.97 (2.18%), and 9.61 (0.77%), respectively. Cur concentrations in turmeric products can be determined using RMS, peak area, and MR content added in these samples. This proposed method, which is based on chemical methylation and the SR-LC assay has been successfully applied for the simple and reliable estimation of Curs in turmeric products.
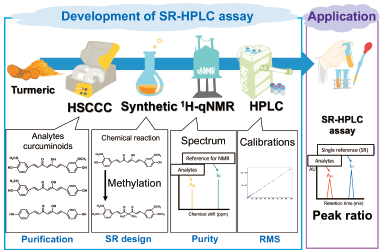 View full abstractDownload PDF (832K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (832K) Full view HTML -
Mizuho Fukuda, Naoya Kishikawa, Taketo Samemoto, Kaoru Ohta, Kaname Oh ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 32-36
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe have developed an HPLC-UV method for the determination of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), which utilizes a redox-based colorimetric reaction. In the proposed colorimetric reaction, the redox reaction between PQQ and dithiothreitol generates superoxide anion radicals that can convert 2-(4-iodophenyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride (INT) to formazan dye. After PQQ separation on an octadecyl silica column, it was mixed online with dithiothreitol and INT, and the formed formazan dye was monitored by absorbance at 490 nm. The detection limit (S/N = 3) of the proposed method was 7.6 nM (152 fmol/injection). The proposed method could selectively detect PQQ in food products without any clean-up procedures.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (946K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (946K) Full view HTML -
Makoto Takada, Masashi Sakamoto, Haruna Yamada, Naoya Kishikawa, Junpe ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 37-42
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEugenols (Eugs) such as eugenol (Eug), methyleugenol (MeEug), and linalool (Lin) in basil product are the main bioactive components of basil products and have a terminal double-bond. A sensitive HPLC-fluorescence method for Eugs derivatized with 4-(4,5-diphenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl)iodobenzene (DIBI) was developed. Good separation of DIB-Eugs was achieved within 20 min on an Atlantis T3 column (50 × 2.1 mm i.d., 3 µm) with a mobile phase of methanol-water. The calibration curves obtained with Eug standards showed good linearities in the range of 0.1–50 µM (r ≥ 0.999). The limits of detection at a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) = 3 for Eug, MeEug, and Lin were 1.0, 6.0, and 4.8 nM, respectively. The limits of quantitation (S/N = 10) of the Eugs were lower than 19.9 nM. The accuracies for the Eugs were within 96.8–104.6%. The intra- and inter-day precisions as relative standard deviations for the Eugs were less than 1.2 and 9.6% (n = 3). The recoveries of Eug, MeEug, and Lin were 99.0 ± 0.1, 98.0 ± 0.2, and 96.0 ± 0.4% (n = 3), respectively. The DIB-Eugs were confirmed to be stable for 2 h (>90%) at room temperature and 24 h (>95%) at 4 °C. These parameters of the proposed method were useful for the simultaneous determination of Eugs in basil products. Therefore, the developed method may be a powerful tool for the quality evaluation of dried commercially available basil products.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (681K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (681K) Full view HTML -
Yuwen Sun, Akira Kotani, Koichi Machida, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Hideki Hak ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 43-49
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFor the quantitative analysis of phenolic compounds in beverage samples, a three-flow channel isocratic HPLC with electrochemical detection (3LC-ECD) system was devised using a column-switching technique. Phenolic compounds with significantly different hydrophobicity (the range of calculated log P: −0.77 to 3.02) were simultaneously measured to draw three chromatograms by the 3LC-ECD; the peaks of gallic acid (GA), protocatechuic acid (PCA), and gallocatechin (GC) were observed at electrochemical detector 1 (D1) within 42 min, the peaks of procyanidin B3 (B3), epigallocatechin (EGC), catechin (C), epicatechin (EC), procyanidin B2 (B2), ethyl gallate (Eg), and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg) were observed at D2 within 50 min, and the peaks of epicatechin gallate (ECg), gallocatechin gallate (GCg), catechin gallate (Cg), propyl gallate (Pg), and resveratrol (RVT) were observed at D3 within 70 min. The relationships between the phenolic compound concentrations and their chromatographic peak heights gave good linearity with correlation coefficients of more than 0.998. The detection limits of the phenolic compounds by the 3LC-ECD ranged from 0.6 to 3.0 µg/L. Further, the phenolic compound concentrations of commercially available teas and wines were determined with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 4.9% (n = 6), and their recoveries ranged from 91 to 109%. These results indicate that the 3LC-ECD system provided an accurate, precise, and specific determination of the phenolic compounds in beverages without affecting the matrices derived from these samples.
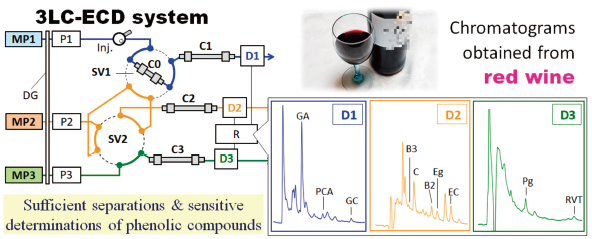 View full abstractDownload PDF (2546K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2546K) Full view HTML
-
Chihiro Takei, Kenji Mori, Takeshi Oshizaka, Kenji Sugibayashi2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 50-51
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFerrofluids are colloidal liquids with fine magnetic particles. They change shape and fluidity depending on the magnitude and direction of the external magnetic field. The magnetic field-responsive pulsatile release of a model drug, lidocaine hydrochloride (LID·HCl), was determined using a depot-type injection containing white petrolatum and/or hydrophilic cream with a magnetic fluid in various proportions. Drug release was confirmed using a self-made diffusion cell and the application of a moving magnet at the bottom of the preparation. Magnetic field-responsive LID release was observed only when using the white petrolatum preparation and depended on the concentration of the magnetic fluid. Magnetic field responsiveness was not observed in the preparation with only the hydrophilic cream. A greater magnetic field-responsive release was observed with a combination of white petrolatum and hydrophilic cream than with white petrolatum alone. These results may lead to the development of an injectable formulation that enables pulsatile administration of macromolecular drugs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (365K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (365K) Full view HTML
-
Yoshiyuki Miyasaka, Kaname Hashizaki, Yumi Kono, Hiroyuki Taguchi, Mak ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 52-56
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLLecithin reverse wormlike micelles (LRWs) have been studied recently for dermal application dosage use but the effects of the physicochemical properties of oils on the formation and rheological properties of LRWs have not been investigated. We studied the effect of oil on the formation of LRWs using 5 types of liquid paraffin (LP) with kinematic viscosities ranging from 4.00 to 88.0 mm2/s. Partial phase diagrams of lecithin/water/LP systems indicated that LPs with low molecular weights could form LRWs with only a small amount of water, but LPs with high molecular weights could not form LRWs, regardless of the water concentration. The solubility of lecithin in LPs was higher for low molecular weight LPs, thus possibly affecting the formation of LRWs. The zero-shear viscosity and relaxation time of LRWs initially increased with increasing water concentration, and then decreased. The water concentration providing the maximum value was dependent on the molecular weight of the LP, whereas the maximum amount and length of the LRWs were independent of the water concentration. Our results indicate that the molecular weight of LP affects the ease of formation and the viscoelasticity of LRWs.
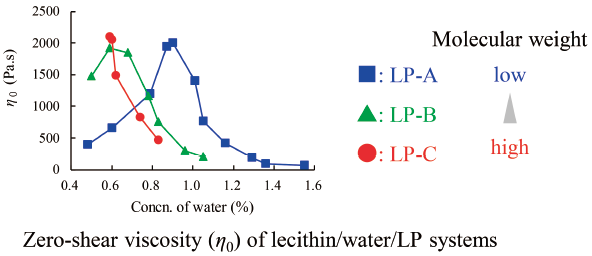 View full abstractDownload PDF (805K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (805K) Full view HTML -
 Nobuyuki Takayama, Tetsuya Yoneda, Kenji Takebayashi, Masaru Ogasawara ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 57-65
Nobuyuki Takayama, Tetsuya Yoneda, Kenji Takebayashi, Masaru Ogasawara ...2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 57-65
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialOsmium is defined in the international council for harmonization (ICH-Q3D) guidelines as an element whose concentration can be determined by validated methods including microwave-assisted nitric acid digestion and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. However, microwave digestion using nitric acid is known to result in osmium recoveries higher than the theoretical values in spiked tests because of the formation of highly volatile osmium tetroxide in an oxidation reaction. To stabilize osmium, the addition of thiourea as a complexing agent has been tested and proved its utility. It remains unclear whether other compounds can prevent the over-recovery of osmium. In this study, we investigated four compounds, thiourea, ascorbic acid, sodium sulfite, and potassium metabisulfite, that could reduce the overestimation of osmium isotopes. The minimum amounts of thiourea, ascorbic acid, sodium sulfite, and potassium metabisulfite required to stabilize 10 ng/mL osmium in blank matrix were 1.0, 1.0, 2.5, and 2.5 g/L, respectively. The relative standard deviations obtained from 12 analyses for each stabilization solution were less than 3.3% in thiourea, 12.7% in ascorbic acid, 9.0% in sodium sulfite, and 10.6% in potassium metabisulfite. The stabilization solutions were investigated in a digested tablet matrix and were found to be effective. The impact of adding stabilization solutions on the determination of all ICH-Q3D element concentrations was also evaluated. As stabilization solutions had a small or significant impact on the determination of some elements, it was concluded that osmium determination should be conducted independently.
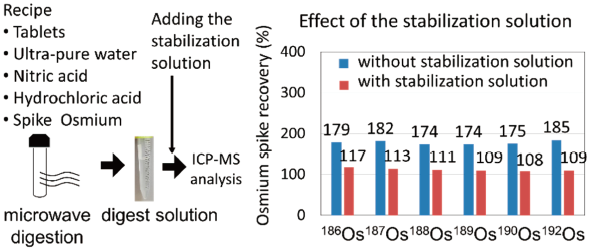 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe overestimation of osmium is often observed in spike recovery test by ICP-MS. This is because osmium formed the highly volatile osmium tetroxide in an oxidation reaction when microwave digestion. The authors investigated the methods to stabilize osmium by using four compounds, thiourea, ascorbic acid, sodium sulfite, and potassium metabisulfite, that could reduce the overestimation of osmium isotopes. All compounds were useful for stabilizing osmium and showed good spike recovery results. The influence of adding compounds against other elements defined by Q3D was also investigated.
Download PDF (951K) Full view HTML -
Li Han, Aimei Chen, Ling Liu, Fang Wang2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 66-73
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDespite the precise mechanisms for renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) are poorly understood, nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathways were considered as the important targets. Leonurine (LEO) is a special alkaloid extracted from Chinese motherwort (Leonurus japonicus Houtt), which has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces oxidative stress. We conducted the study to explore the efficacy of LEO against I/R-induced AKI in rats and further investigated the underlying mechanisms. Ischemic renal injury was induced by temporary vascular clamping for 45 min. We have measured the levels of inflammation-related biomarkers and antioxidative stress markers. Next, Western blot analysis and Real-time PCR were performed to analyze whether the Nrf2 and TLR4/nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) pathways were involved in this process. We found that LEO pretreatment remarkably decreased serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in I/R rats and attenuated acute tubular damage. In addition, LEO markedly increased the expression of antioxidant proteins and decreased the levels of inflammatory factors. Further study revealed that LEO promoted Nrf2 into the nucleus, promoted the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO-1), and suppressed the TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway in kidney tissues of ischemic AKI rats. The study reveals that LEO has a protective effect to prevent ischemic AKI through activation of Nrf2 nuclear translocation resisting oxidative stress injury and inhibition of the TLR4/NF-κB pathway mediated inflammatory gene expression.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2909K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2909K) Full view HTML -
 Keita Yaginuma, Shuichi Tanabe, Manabu Kano2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 74-81
Keita Yaginuma, Shuichi Tanabe, Manabu Kano2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 74-81
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSoft sensors are powerful tools for the implementation of process analytical technology (PAT). They are categorized into white-box (first-principle), black-box (statistical), and gray-box models. Gray-box models integrate white-box and black-box models to address each drawback, i.e., prediction accuracy and intuitiveness. Although they have been applied to various industrial processes, their applicability to water content monitoring in fluidized bed granulation has not been reported. In this study, we evaluated three types of gray-box models, i.e., parallel, serial, and combined gray-box models, in terms of prediction accuracy using real operating data on a commercial scale with two formulations. The gray-box models were constructed by integrating the heat and mass balance model (white-box model) and locally weighted partial least squares regression (LW-PLSR) model (black-box model). LW-PLSR was utilized to cope with collinearity and nonlinearity. In the serial gray-box models, LW-PLSR models adjusted the fitting parameters of the white-box model depending on the process parameters for each query. In the parallel gray-box or combined gray-box models, LW-PLSR models compensated for the output error of the white-box or serial gray-box models, respectively. The results demonstrated that all three types of gray-box models improved the prediction accuracy of the white-box models regardless of the formulation. Besides, we proposed the assessment method based on Hotelling’s T2 and Q residual for gray-box models using LW-PLSR, which contributes decision support to select gray-box or white-box model. The accurate and descriptive gray-box models are expected to enhance process understanding and precise quality control in fluidized bed granulation.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe authors developed accurate and descriptive three types of gray-box models to enhance process understanding and precise quality control in fluidized bed granulation. These gray-box models were constructed by integrating the heat and mass balance model (white-box model) and locally weighted partial least squares regression (LW-PLSR) model (black-box model). Their applicability was demonstrated using real operating data on a commercial scale with two formulations. Furthermore, the authors proposed the assessment method based on Hotelling’s T2 and Q residual for gray-box models using LW-PLSR, which contributes decision support to select gray-box or white-box model.
Download PDF (1579K) Full view HTML -
Taka Sawazaki, Youhei Sohma, Motomu Kanai2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 82-84
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialKnoevenagel condensation, an olefin-forming reaction from active methyl/methylene-containing compounds and aldehydes, is a fundamental and useful synthetic method. Benzothiazoles are, however, out of the scope of Knoevenagel condensation. Here, we report that Knoevenagel condensation between aldehydes and 2-methyl-thiazolo[4,5-b]pyrazines (MeTPy), a fused ring structure comprising pyrazine and thiazole, proceeded smoothly, despite minor structural differences from benzothiazoles. This finding will be useful for short synthesis of MeTPy-containing functional molecules, such as a tau probe analog 1.
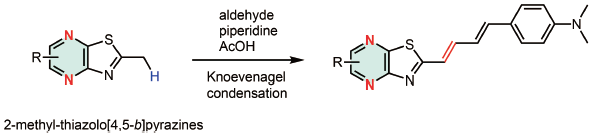 View full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (475K) Full view HTML
-
Hikaru Fujita, Takanari Arai, Munetaka Kunishima2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 85-88
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe electrophilic amination of nitrogen-based nucleophiles, including strong organic bases, was conducted in an Et2O solvent using O-(mesitylenesulfonyl)hydroxylamine. Aliphatic tert-amines and N,N,N′-(trialkyl)amidines rapidly formed precipitates of the corresponding aminated salts in high yields. The amination of the highly basic and sterically hindered N,N,N′,N′,N″-(pentaalkyl)guanidines was achieved under modified conditions, although the yields were moderate because of a competing side reaction caused by the acid–base equilibrium.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (533K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (533K) Full view HTML -
Keita Komine, Riki Ninomiya, Hayato Fukuda, Jun Ishihara2022Volume 70Issue 1 Pages 89-93
Published: January 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2022
Advance online publication: November 02, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSamarium diiodide (SmI2)-mediated desymmetrization of a meso-cyclic 1,3-dione pinacol coupling is described. The reaction proceeds with high stereoselectivity to provide fused carbocyclic compounds with three contiguous stereogenic centers featuring an all-carbon quaternary center and a cis-1,2-diol moiety.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (525K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (525K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|