
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Ken-ichi Izutsu, Tatsuo Koide, Noriyuki Takata, Yukihiro Ikeda, Makoto ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1421-1430
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: June 18, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLRecent active research and new regulatory guidance on pharmaceutical cocrystals have increased the rate of their development as promising approaches to improve handling, storage stability, and bioavailability of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). However, their complex structure and the limited amount of available information related to their performance may require development strategies that differ from those of single-component crystals to ensure their clinical safety and efficacy. This article highlights current methods of characterizing pharmaceutical cocrystals and approaches to controlling their quality. Different cocrystal regulatory approaches between regions are also discussed. The physical characterization of cocrystals should include elucidating the structure of their objective crystal form as well as their possible variations (e.g., polymorphs, hydrates). Some solids may also contain crystals of individual components. Multiple processes to prepare pharmaceutical cocrystals (e.g., crystallization from solutions, grinding) vary in their applicable ingredients, scalability, and characteristics of resulting solids. The choice of the manufacturing method affects the quality control of particular cocrystals and their formulations. In vitro evaluation of the properties that govern clinical performance is attracting increasing attention in the development of pharmaceutical cocrystals. Understanding and mitigating possible factors perturbing the dissolution and/or dissolved states, including solution-mediated phase transformation (SMPT) and precipitation from supersaturated solutions, are important to ensure the bioavailability of orally administrated lower-solubility APIs. The effect of polymer excipients on the performance of APIs emphasizes the relevance of formulation design for appropriate use.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (397K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (397K) Full view HTML -
 Toshihide Takeuchi, Shiroh Futaki2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1431-1437
Toshihide Takeuchi, Shiroh Futaki2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1431-1437
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLArginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) including Tat, Penetratin and oligoarginine peptides are a series of short peptides that can be efficiently internalized into cells and have been widely used as carriers for intracellular delivery of bioactive molecules. In the early phase of the study, CPPs, as well as their conjugates, were thought to rapidly enter cells by direct penetration through membranes, which was later found to be an experimental artifact that was concluded from observations in fixed cells. Although re-evaluation using living unfixed cells revealed that endocytosis has a major role in internalization of these peptides, there are a number of studies reporting that, even if fixation is avoided, direct translocation across plasma membranes and cytosolic distribution of arginine-rich CPPs are still observed in cells without membrane perturbation. In addition, amphiphilic counteranions such as pyrenebutyrate dramatically accelerate direct translocation of these peptides into cells. These results suggest that there are at least two pathways, i.e., endocytosis and direct translocation, both of which would contribute to cellular internalization of arginine-rich CPPs. In this review, we first introduce the story of fixation artifact, which indeed led to the critical progress in CPP study, and then summarize the current understanding for direct translocation of arginine-rich CPPs. Comprehensive understanding of direct translocation of these peptides and its mechanistic elucidation would provide useful knowledge for developing methodologies that would enable efficient intracellular delivery.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn the review, the authors summarize recent reports on direct translocation of arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) through cell membranes, including counteranion-assisted delivery method, and discuss its mechanism, which would provide insight into highly efficient intracellular delivery.
Download PDF (574K) Full view HTML
-
Practical Synthesis of Axially Chiral Dicarboxylates via Pd-Catalyzed External-CO-Free CarbonylationHideyuki Konishi, Fumika Hoshino, Kei Manabe2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1438-1441
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: August 03, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe have developed a safe and practical synthetic method for preparing axially chiral diphenyl dicarboxylates using Pd-catalyzed external-CO-free carbonylation with phenyl formate as a CO surrogate. Optimized conditions consisted of axially chiral [1,1′-binaphthalene]-2,2′-diyl ditriflate and its congeners, each easily prepared from commercially available enantiomerically pure diols, Pd(OAc)2, 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane, ethyldiisopropylamine, and no solvent. To demonstrate the potential utility of these products, this method was conducted on gram-scale and the phenyl ester products were converted to other useful compounds, and both processes were carried out without difficulty.
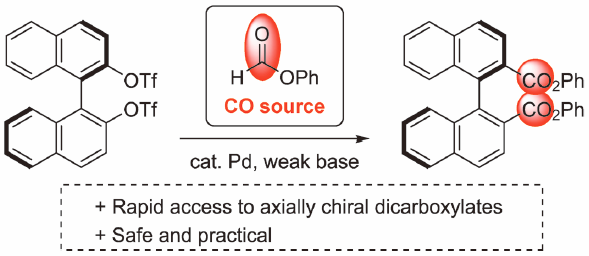 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (451K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (451K) Full view HTML -
Kohei Harada, Noriyuki Tezuka, Keiichi Hirano, Kazunori Miyamoto, Tats ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1442-1444
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe have developed an efficient Rh-catalyzed (perfluoroalkyl)olefination reaction of acetanilides, which provides a versatile synthetic entry to a range of perfluoroalkylated compounds.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (482K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (482K) Full view HTML
-
Su Hyun Seok, Seung-Yeob Kang, Jeong-Woong Seo, Su-Hyeon Kim, Kyu-Mok ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1445-1449
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe aims of this study were to improve in vitro dissolution property of poorly water-soluble everolimus (EVR) for enhanced bioavailability without using organic solvents and characterize the effects of microfluidization and freeze-drying on physicochemical properties of EVR nanosuspension and nanoparticle, respectively. EVR nanosuspension was prepared using microfluidization with various types and concentrations of stabilizers. After that, it was solidified into nanoparticle using freeze-drying with various concentrations of xylitol, a cryoprotectant. The particle size, zeta potential, physical stability, and chemical stability of EVR nanosuspension and nanoparticle were measured. In vitro release of EVR nanoparticle was also measured and compared with that of physical mixture. Zero point five percent (w/w) poloxamer 407 (P407) was chosen as the stabilizer considering particle size, zeta potential, and yield of EVR nanosuspension. Freeze-drying with 1% (w/w) xylitol improved both physical and chemical stability of EVR nanoparticle. In vitro release test showed improved dissolution property compared to that of physical mixture, implying enhanced bioavailability.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (483K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (483K) Full view HTML -
Yoshihiro Hishikawa, Yukari Kakino, Hoshi Tsukamoto, Kohei Tahara, Ris ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1450-1457
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOral gel formulations are known as easy to administer drug products for patients who have problems taking drugs including those with conditions such as dysphagia. In addition, there are numerous commercially available oral gel products, most of which are immediate-release formulation that release their pharmaceutical ingredient content by diffusion. This study is focused on developing oral gel formulations that reduce the dosing frequency and dosage compared to the conventional types. This is with the aim of facilitating the use of gel formulations for producing pharmaceutical agents with different dose regimens, thereby enhancing patient convenience. Here, we used naturally derived high-molecular-weight agar (Ag), xanthan gum (Xa), and locust bean gum (Lo) as gel bases to prepare a variety of gel membranes, and evaluated the diffusion coefficient of the model substances. The result revealed that the Ag content in the Xa–Lo combination gel concentration-dependently increased the diffusion coefficient. Moreover, these findings were applied in an attempt to mask the taste of intensely bitter levofloxacin. The results indicated that the Xa–Lo combination gel exhibited a significantly superior masking effect to that of the Ag gel. This study demonstrates the feasibility of using oral gel formulations to modulate the controlled-release functionality of pharmaceutical agents.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (911K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (911K) Full view HTML -
Yan Sun, Jiao Fan, Dong Chai, Minghua Zhang2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1458-1465
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: August 04, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe hypothesis that oxidative stress contributes to renal dysfunction in sinoaortically denervated (SAD) rats was investigated. Rats were sinoaortically denervated and received treatment with tempol (0.5 mmol/L in drinking water) for 8 weeks. Although the tempol treatment of the SAD rats had no significant effect on blood pressure or blood pressure viability, it significantly ameliorated the renal dysfunction as indicated by increases in renal blood flow (RBF) and the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and reductions in plasma creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), the urine albumin excretion rate (UAE), and the glomerular sclerosis score (GSS). The SAD rats treated with tempol exhibited decreased plasma and renal malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and reduced renal formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide (O2−), peroxynitrite (OONO−) and 3-nitrotyrosine. Treatment with tempol suppressed the nuclear concentration of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and reduced the renal levels of macrophage chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). The tempol-treated SAD rats exhibited decreased renal advanced glycation end product (AGE) levels and decreased receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) protein expression. The tempol treatment of the SAD rats restored mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate (ATP) formation, DNA content, membrane integrity and the renal oxygen consumption rate. Additionally, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), glutathione S epoxide transferase (GST), and catalase were decreased, and the activities of xanthin oxidase (XO) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase were enhanced in the kidneys of the SAD rats. In conclusion, our work firstly provided direct evidence that oxidative stress played an important role in the renal dysfunction of SAD rats.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1441K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1441K) Full view HTML -
En-bo Cai, Li-min Yang, Cai-xia Jia, Wei-yuan Zhang, Yan Zhao, Wei Li, ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1466-1473
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: July 06, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe use of arctigenin (ARG), a traditional medicine with many pharmacological activities, has been restricted due to its poor solubility in water. Five amino acid derivatives of ARG have been synthesized using glycine, o-alanine, valine, leucine, and isoleucine, which have t-butyloxy carbonyl (BOC) as a protective group. In this study, we examined the effects of removing these protective groups. The results showed that the amino acid derivatives have better solubility and nitrite-clearing ability than ARG. Among the compounds tested, the amino acid derivatives without protective group were the best. Based on these results, ARG and its two amino acid derivatives without protective group (ARG8, ARG10) were selected to evaluate their anti-tumor activity in vivo at a dosage of 40 mg/kg. The results indicated that ARG8 and ARG10 both exhibit more anti-tumor activity than ARG in H22 tumor-bearing mice. The tumor inhibition rates of ARG8 and ARG10 were 69.27 and 43.58%, which was much higher than ARG. Furthermore, the mice treated with these compounds exhibited less damage to the liver, kidney and immune organs compared with the positive group. Furthermore, ARG8 and ARG10 improved the serum cytokine levels significantly compared to ARG. In brief, this study provides a method to improve the water solubility of drugs, and we also provide a reference basis for new drug development.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (504K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (504K) Full view HTML -
Shinji Harada, Kexin Li, Ryuto Kino, Takuya Takeda, Chia-Hsien Wu, Shi ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1474-1483
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: July 22, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe have developed a new method for synthesizing chiral isotwistane and homoisotwistane skeletons as well as aminocyclitols in a highly stereoselective manner. These results were achieved through the use of a common intermediate, which was derived from the ytterbium-catalyzed asymmetric Diels–Alder reaction of Danishefsky diene.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (824K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (824K) Full view HTML -
Kuniharu Utsuno, Hiroyuki Kono, Emika Tanaka, Nozomi Jouna, Yohichiro ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1484-1491
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPolyethylenimine (PEI) is one of the most versatile non-viral vectors used in gene therapy, especially for delivering plasmid DNA to human cells. However, a good understanding of PEI binding to DNA, the fundamental basis for the functioning of PEI as a vector, has been missing in the literature. In this study, PEI (branched, 600 Da) binding to DNA was examined by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) and a complementary set of analysis tools. We demonstrated that a separation between the binding heat and the condensation heat is needed and that the excluded site model should be used for PEI binding stage in the ITC analysis. The equilibrium constant for PEI binding to DNA was determined to be 2.5×105 M−1 from the ITC analysis, and as 2.3×105 M−1 from the QCM analysis. Additionally, we suggested that the 600 Da branched PEI binds to the major groove of DNA and the rearrangement of PEI on DNA may be difficult to occur because of the small dissociation rate. The binding analysis presented here can be employed to improve our understanding of the functioning of PEI and PEI-like non-viral vectors.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1258K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1258K) Full view HTML -
Susumu Kawakami, Masanori Inagaki, Katsuyoshi Matsunami, Hideaki Otsuk ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1492-1498
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFrom the stems of Croton cascarilloides, further crotofolane-type diterpenoids, named crotocascarins L–Q (1–6), and a rearranged one (7), named neocrotocascarin were isolated. Their structures were elucidated from spectroscopic evidence. Also, the structures of crotocascarin O (4) and neocrotocascarin (7) were determined by X-ray crystallographic analyses. As a result, neocrotocascarin (7) was found to possess a new carbon framework. A plausible mechanism for the formation of neocrotocascarin (7) is also discussed.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (902K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (902K) Full view HTML -
Koichi Takao, Takayuki Saito, Daisuke Chikuda, Yoshiaki Sugita2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1499-1504
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of 2-azolylchromone derivatives were synthesized and their monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B inhibitory activities were evaluated. Of the synthesized compounds, compounds 1b, 2b, 4a–c, 5b and 7b showed potent inhibitory activities against MAO-A (IC50 values, 1b: 0.32 µM; 2b: 0.14 µM; 4a: 0.11 µM; 4b: 0.023 µM; 4c: 0.15 µM; 5b: 0.59 µM; 7b: 0.19 µM) and 4a, c, 5a, c, 6c and 8c for MAO-B (IC50 values, 4a: 0.028 µM; 4c: 0.019 µM; 5a: 0.73 µM; 5c: 0.28 µM; 6c: 0.28 µM; 8c: 0.27 µM). These data suggest that 6-methoxy substitution favors MAO-A inhibition and 7-methoxy substitution favors MAO-B inhibition. In addition, compound 4b was the most potent inhibitor for MAO-A, and compound 4c for MAO-B. This is the first report identifying 2-azolylchromone derivatives as potent monoamine oxidase inhibitors. These results suggest that the 2-triazolylchromone structure may be a useful scaffold for the design and development of novel monoamine oxidase inhibitors, as evidenced by the activities of 4a–c and 5a–c.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (519K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (519K) Full view HTML
-
Qi-Tong Feng, Guo-Yuan Zhu, Wei-Na Gao, Zifeng Yang, Nanshan Zhong, Ji ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1505-1508
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPhytochemical investigation of the root of Baphicacanthus cusia (NEES) BREMEK afforded two new alkaloids, baphicacanthin A (1) and baphicacanthin B (2), along with 28 known compounds. The chemical structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of one and two dimensional (1D/2D)-NMR and high resolution (HR)-MS spectral evidence.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (568K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (568K) Full view HTML -
Kota Sasaki, Tomohiro Ito, Hirotada G. Fujii, Shingo Sato2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1509-1513
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe hybrid compounds 1–5 comprised of five nitroxides with ibuprofen were synthesized and their reduction rate for ascorbic acid (AsA) and methyl radicals were measured in comparison with 3-hydroxy-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl (PROXYL) 6. The rate constants in reduction reaction with 200-fold excess of AsA were determined in following order: 1 (0.42±0.06), 3 (0.17±0.06), 2 (0.10±0.05), and 6 (0.09±0.02 M−1s−1). The remaining two sterically shielded nitroxides 4 and 5 scarcely reacted with AsA. In the reaction with the more reactive methyl radicals, produced by 200-fold excess of Fenton’s reagent, the reduction rates of 2, 4, and 5 were in the following decreasing order: 2 (1.1±0.2), 4 (0.76±0.09), and 5 (0.31±0.03 M−1s−1).
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (464K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (464K) Full view HTML -
Shiro Nakai, Akito Nakai, Takashi Michida2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1514-1518
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMicrometer-sized polymer particles encapsulated ascorbic acid (vitamin C; VC) were successfully prepared by the three types of the self-assembling method, those are, phase separation and self-assembly of added polymer at the oil–water interface in emulsion, microsuspension polymerization utilizing the self-assembling of phase separated polymer (SaPSeP) method, and their hybrid method. In the stability study at 50°C for 2 months, the three kinds of capsule particles exhibited effective protection of VC from the interaction with other components in cosmetic consisting of water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion. The encapsulated VC was easily released from the capsule particles by an excess of water. These encapsulation methods will be useful for the stabilization of water-soluble substances in cosmetic consisting of W/O emulsion.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2127K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2127K) Full view HTML -
Tsung-Chang Tsai, Yu-Ting Huang, Shih-Kai Chou, Ming-Cheng Shih, Ching ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1519-1522
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
Advance online publication: August 03, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA new 10-demethylated steroid, nephtheasteroid A (1), a new 19-oxygenated steroid, nephtheasteroid B (2) as well as five known steroids 3–7 were isolated from the organic extract of a Taiwanese soft coral Nephthea erecta. The structure was determined by means of IR, MS, and NMR techniques. Among these metabolites, 1 is rarely found in steroids possessing a 19-norergostane skeleton. In vitro cytotoxicity study using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay revealed that compounds 3 and 4 exhibited cytotoxicity against human chronic myelogenous leukemia (K562), human acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Molt-4), human T lymphoblastoid (Sup-T1), and human leukemic monocyte lymphoma (U937), with IC50 of 6.5–14.0 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (384K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (384K) Full view HTML -
Tran Thi Hong Hanh, Le Thi Vien, Le Ba Vinh, Nguyen Van Thanh, Nguyen ...2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1523-1527
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialEight highly hydroxylated steroids (1−8), including three new compounds as sodium salts of (24S)-5α-cholestane-3β,4β,5,6α,7β,8,14,15α,24-nonaol 6-sulfate (1), (24E)-5α-cholest-24-ene-26-yde-3β,6α,8,14,15α-pentaol 15-sulfate (2), and 5α-cholest-3β,6α,8,14,15α,24,25,26-octaol 15-sulfate (3), were isolated and elucidated from the methanol extract of the Vietnamese starfish Archaster typicus. The structure elucidation was done by spectroscopic methods including one and two dimensional (1D-, 2D-)NMR and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR)-MS. The isolated compounds can be used as chemical markers for taxonomic identification of the starfish A. typicus.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (656K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (656K) Full view HTML -
Satoshi Yokoshima, Masatsugu Ishikawa, Youko Beniyama, Tohru Fukuyama2016Volume 64Issue 10 Pages 1528-1531
Published: October 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChemical transformation of an early intermediate in our synthesis of huperzine A provided a diverse array of molecules in which a variety of functional groups could be embedded.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|