
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Takeo Kawabata2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 466-484
Takeo Kawabata2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 466-484
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA strategy for symmetric synthesis based on dynamic chirality of enolates (memory of chirality) has been developed. Asymmetric alkylation, conjugate addition, aldol reaction, and arylation via C–N axially chiral enolate intermediates are described. Asymmetric alkylation and conjugate addition via C–O axially chiral enolate intermediates with a half-life of racemization as short as approx. 1 s. at −78 °C have been accomplished. Organocatalysts for asymmetric acylation and site-selective acylation have been developed. Kinetic resolution of racemic alcohols via remote asymmetric induction by the catalyst is shown. Catalyst-controlled site-selective acylation of carbohydrates and its application to total synthesis of natural glycoside are described. Chemo-selective monoacylation of diols and selective acylation of secondary alcohols with reversal of inherent reactivity are also discussed. Geometry-selective acylation of tetrasubstituted alkene diols is achieved, where acylation takes place independent from the steric environments of the substrates.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickTwo topics on novel synthetic strategy are shown. The first topic concerns enolate chemistry. The enolate structure has been long believed to be achiral because all four substituents are in the same enolate plane. From the viewpoint of dynamic chirality, however, the enolate can exist as an axially chiral form or a planar chiral form in a limited time scale. The author demonstrated that these chiral enolates can be employed as reliable intermediates for asymmetric synthesis. The second topic concerns catalyst function. 4-pyrrolidinopyridine (PPY) had been known to be the most active catalyst for acylation. Based on the PPY skeleton, strategies for enantio- and site-selective catalysis were proposed. The latter opened up a new way to total syntheses of natural glycosides in extremely short overall steps.
Download PDF (3121K) Full view HTML
-
 Seikou Nakamura2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 485
Seikou Nakamura2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 485
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEditor's pickThis “Current Topics” contains one review and four regular articles describing the latest research on natural product chemistry that have been contributed by young researchers. These contents include computer science technology in natural products research, isolation of biological constituents from medicinal plants, evaluation of the biological activity of natural products, and synthesis of biological constituents from medicinal plants. These findings could be useful for the development of effective medicines from natural medicinal resources.
Download PDF (188K) Full view HTML
-
Keiko Ogawa, Daiki Sakamoto, Rumiko Hosoki2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 486-494
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLComputational approaches to drug development are rapidly growing in popularity and have been used to produce significant results. Recent developments in information science have expanded databases and chemical informatics knowledge relating to natural products. Natural products have long been well-studied, and a large number of unique structures and remarkable active substances have been reported. Analyzing accumulated natural product knowledge using emerging computational science techniques is expected to yield more new discoveries. In this article, we discuss the current state of natural product research using machine learning. The basic concepts and frameworks of machine learning are summarized. Natural product research that utilizes machine learning is described in terms of the exploration of active compounds, automatic compound design, and application to spectral data. In addition, efforts to develop drugs for intractable diseases will be addressed. Lastly, we discuss key considerations for applying machine learning in this field. This paper aims to promote progress in natural product research by presenting the current state of computational science and chemoinformatics approaches in terms of its applications, strengths, limitations, and implications for the field.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1181K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1181K) Full view HTML
-
Takahiro Matsumoto, Hayato Yoshikawa, Takahiro Kitagawa, Daisuke Imaho ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 495-501
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe isolated the new sesquiterpenes, valerianaterpenes IV and V, and the new lignans valerianalignans I–III from the methanol extracts of the rhizomes and roots of Valeriana fauriei and elucidated their structures based on chemical and spectroscopic findings. The absolute configuration of valerianaterpene IV and valerianalignans I–III were established by comparing experimental and predicted electronic circular dichroism (ECD) data. Among the isolated compounds, valerianalignans I and II exerted anti-proliferative activity against human astrocytoma cells (U-251 MG) and their cancer stem cells (U-251 MG CSCs). Interestingly, valerianalignans I and II notably exerted anti-proliferative activities at lower concentrations against CSCs than non-CSCs, and the absolute configurations of these compounds affected their activities.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (868K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (868K) Full view HTML -
Seikou Nakamura, Sachiko Sugimoto, Taichi Yoneda, Akari Shinozaki, Moe ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 502-507
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo new diterpenes named trichoterpene I (1) and trichoterpene II (2) were isolated from the extract from the leaves of Isodon trichocarpus together with 19 known diterpenes. Their chemical structures were elucidated on the basis of chemical and physicochemical properties. Among them, oridonin (3), effusanin A (4), and lasiokaurin (9) with the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety showed antiproliferative activities against breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and human astrocytoma U-251 MG cells [i.e., non-cancer stem cells (non-CSCs)] and their cancer stem cells (CSCs) isolated by sphere formation. In particular, compound 4 (IC50 = 0.51 µM) showed a higher antiproliferative activity against MDA-MB-231 CSCs than against MDA-MB-231 non-CSCs. The antiproliferative activity toward CSCs of compound 4 was equal to adriamycin (positive control, IC50 = 0.60 µM).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (758K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (758K) Full view HTML -
Tomoe Ohta, Momoka Inoha, Chiaki Kawahara, Saori Toshimitsu, Yukihiro ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 508-514
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe root of Rehmannia glutinosa Liboschitz forma hueichingensis HSIAO has been used as a tonic and treatment for urinary and skin disorders in Japanese Kampo medicine. Phytochemical investigation of the root has been well reported, but that of the leaves is limited. To explore the potential value of R. glutinosa leaves, we focused on the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory activity. The leaf extract exhibited ACE-inhibitory activity, and the inhibitory potency of leaves was stronger than that of roots. Using this activity as an indicator, we isolated linaride (1), 6-O-hydroxybenzoyl ajugol (2), acteoside (3), leucosceptoside A (4), martynoside (5), luteolin (6), apigenin (7), and chrysoeriol (8) by separating and purifying the extract. We then examined the ACE-inhibitory activities of 1–8, catalpol (9), aucubin (10), ajugol (11), and echinacoside (12). Among them, 3, 6, and 12 displayed the most potent inhibitory activity. A simultaneous analytical method was also developed using compounds contained in R. glutinosa leaves and roots, and their contents were compared. The method consisted of extraction with 50% aqueous methanol under sonication for 60 min and LC/MS measurement. R. glutinosa leaves tended to have higher levels of majority of the analytes than the roots, including 3 and 6, which had higher ACE-inhibitory activity. These results suggest that 3 and 6 contribute to the ACE-inhibitory activity of R. glutinosa leaves, which may represent a useful medicinal resource for hypertension.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (735K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (735K) Full view HTML -
Hiroki Iwasaki, Mari Ikemoto, Haruka Shibata, Yuka Shima, Erina Himeno ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 515-519
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHere, we report a regioselective, samarium(II) diiodide mediated intramolecular radical ipso-substitution cyclization. Through the use of a methoxy group as a leaving group, it was possible to regulate the regioselectivity of the reaction by changing the temperature and additives. We applied the developed reaction to the synthesis of four Amaryllidaceae alkaloids and have shown that the present reaction successfully overcomes regioselectivity issues encountered with other cyclization methods.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (768K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (768K) Full view HTML
-
Wenping Wang, Honami Kojima, Ming Gao, Xingbin Yin, Takahiro Uchida, J ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 520-527
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLItraconazole, a commonly used antifungal drug in the clinic approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), has been gradually found to have anti-tumor, angiogenesis inhibition and other pharmacological activities. However, its poor water solubility and potential toxicity limited its clinical application. In order to improve the water solubility and reduce the side effects caused by the high concentration of itraconazole, a novel preparation method of itraconazole sustained release microspheres was established in this study. Firstly, five kinds of polylactic acid-glycolic acid (PLGA) microspheres loaded with itraconazole were prepared by oil/water (O/W) emulsion solvent evaporation and then characterized by infrared spectroscopy. Then the particle size and morphology of the microspheres were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). After that, the particle size distribution, drug loading rate, entrapment efficiency, and drug release experiments were evaluated. Our results showed the microspheres prepared in this study had uniform particle size distribution and good integrity. Further study found that the average drug loading of the five kinds of microspheres prepared with PLGA 7505, PLGA 7510, PLGA 7520, PLGA 5020 and PLGA 0020 were 16.88, 17.72, 16.72, 16.57, and 16.64%, respectively, and the encapsulation rate all reached about 100%. More surprisingly, the release experimental results showed that the microspheres prepared with PLGA 7520 did not show sudden release, showing good sustained release performance and high drug release rate. To sum up, this study optimized the preparation method of sustained-release microspheres without sudden release, which provides a new solution for the delivery of itraconazole in the clinic.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2996K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2996K) Full view HTML -
A Facile Raman Spectroscopy Method for Online Monitoring of Crystal Plane Orientation of FavipiravirShiyi Tang, Rui Feng, Yanlei Kang, Jianbo Cheng, Jianguang Zhou2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 528-533
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: April 26, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe efficiency of pharmacotherapy is significantly influenced by the crystal habit and polymorphic form of the drugs. Especially due to the anisotropy of different facets in crystalline material, crystal habit impacts the physicochemical properties and behaviors of a drug, which has been rarely reported. This paper describes a facile method for online monitoring of crystal plane orientation of favipiravir (T-705) by Raman spectroscopy. Firstly, we investigated the synergy of multiple physicochemical fields (solvation, agitated flow fields, etc.), and then prepared favipiravir crystals with different orientations in a controllable manner. Secondly, to establish the connection between crystal planes and Raman spectra, the favipiravir crystals were theoretically analyzed at the molecular and structural levels using density functional theory (DFT) and three dimensional (3D) visualization tools. Finally, we based on standard samples and applied it to 12 actual samples to evaluate the crystal habit of favipiravir. The results are similar to the classical X-ray diffraction (XRD) method. Additionally, the XRD method is difficult to be monitored online, while the Raman method is non-contact, fast, and requires no sample preparation, showing a great application prospect in the pharmaceutical process.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1642K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1642K) Full view HTML -
Shishir Chourey, Rui Wang, Qiuji Ye, Chintam Nagendra Reddy, Shiyu Sun ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 534-544
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML5-Oxo-6,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-ETE) is the most potent eosinophil chemoattractant among lipid mediators, and its actions are mediated by the selective oxoeicosanoid (OXE) receptor. Our group previously developed a highly potent indole-based OXE antagonist, S-C025, with an IC50 value of 120 pM. S-C025 was converted to a number of metabolites in the presence of monkey liver microsomes. Complete chemical syntheses of authentic standards enabled us to identify that the four major metabolites were derived by the oxidation at its benzylic and N-methyl carbon atoms. Herein we report concise syntheses of the four major metabolites of S-C025.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1042K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1042K) Full view HTML -
Yoshimi Ichimaru, Koichi Kato, Rina Nakatani, Risa Isomura, Kirara Sug ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 545-551
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe designed and synthesized a chiral ligand N-(anthracen-9-ylmethyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)ethanamine (APPE) DNA photocleavage agent to investigate the effects of chirality of bis(2-picolyl)amine on the DNA photocleavage activity of metal complexes. The structures of ZnII and CoII complexes in APPE were analyzed via X-ray crystallography and fluorometric titration. APPE formed metal complexes with a 1 : 1 stoichiometry in both the crystalline and solution states. Fluorometric titration was used to show that the ZnII and CoII association constants of these complexes (log Kas) were 4.95 and 5.39, respectively. The synthesized complexes were found to cleave pUC19 plasmid DNA when irradiated at 370 nm. The DNA photocleavage activity of the ZnII complex was higher than that of the CoII complex. The absolute configuration of the methyl-attached carbon did not affect DNA cleavage activity and, unfortunately, an achiral APPE derivative without the methyl group (ABPM) was found to perform DNA photocleavage more effectively than APPE. One reason for this may be that the methyl group suppressed the structural flexibility of the photosensitizer. These results will be useful for the design of new photoreactive reagents.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1262K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1262K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Iwasaki, Ryosuke Uchiyama, Kazuto Nosaka2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 552-557
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBenzalkonium chloride (BAC) is a useful preservative for ophthalmic solutions but has some disadvantageous effects on corneal epithelium, especially keratinocytes. Therefore, patients requiring the chronic administration of ophthalmic solutions may suffer from damage due to BAC, and ophthalmic solutions with a new preservative instead of BAC are desired. To resolve the above situation, we focused on 1,3-didecyl-2-methyl imidazolium chloride (DiMI). As a preservative for ophthalmic solutions, we evaluated the physical and chemical properties (absorption to a sterile filter, solubility, heat stress stability, and light/UV stress stability), and also the anti-microbial activity. The results indicated that DiMI was soluble enough to prepare ophthalmic solutions, and was stable under severe heat and light/UV conditions. In addition, the anti-microbial effect of DiMI as a preservative was considered to be stronger than BAC. Moreover, our in vitro toxicity tests suggested that DiMI is safer to humans than BAC. Considering the test results, DiMI may be an excellent candidate for a new preservative to replace BAC. If we can overcome manufacturing process issues (soluble time and flushing volume) and the insufficiency of toxicological information, DiMI may be widely adopted as a safe preservative, and immediately contribute to the increased well-being of all patients.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML -
Keiji Nishiwaki, Shinya Nakamura, Kenji Yoshioka, Eri Nakagawa, Shiori ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 558-565
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLProtein kinase CK2 (CK2) is involved in the suppression of gene expression, protein synthesis, cell proliferation, and apoptosis, thus making it a target protein for the development of therapeutics toward cancer, nephritis, and coronavirus disease 2019. Using the solvent dipole ordering-based method for virtual screening, we identified and designed new candidate CK2α inhibitors containing purine scaffolds. Virtual docking experiments supported by experimental structure–activity relationship studies identified the importance of the 4-carboxyphenyl group at the 2-position, a carboxamide group at the 6-position, and an electron-rich phenyl group at the 9-position of the purine scaffold. Docking studies based on the crystal structures of CK2α and inhibitor (PDBID: 5B0X) successfully predicted the binding mode of 4-(6-carbamoyl-8-oxo-9-phenyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-purin-2-yl) benzoic acid (11), and the results were used to design stronger small molecule targets for CK2α inhibition. Interaction energy analysis suggested that 11 bound around the hinge region without the water molecule (W1) near Trp176 and Glu81 that is frequently reported in crystal structures of CK2α inhibitor complexes. X-ray crystallographic data for 11 bound to CK2α was in very good agreement with the docking experiments, and consistent with activity. From the structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies presented here, 4-(6-Carbamoyl-9-(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-8-oxo-8,9-dihydro-7H-purin-2-yl) benzoic acid (12) was identified as an improved active purine-based CK2α inhibitor with an IC50 of 4.3 µM. These active compounds with an unusual binding mode are expected to inspire new CK2α inhibitors and the development of therapeutics targeting CK2 inhibition.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1538K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1538K) Full view HTML -
Yusuke Imayoshi, Shuji Ohsaki, Hideya Nakamura, Satoru Watano2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 566-575
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
Advance online publication: April 22, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA rotary tableting machine is used for the continuous tableting process. Tableting conditions often result in capping, leading to serious problems during production. Several studies have been conducted to predict the tablet capping tendency. However, as most previous studies were conducted using a compaction simulator, there is a lack of technology that can be readily applied during actual production. Therefore, the present study aimed to develop a novel method for predicting tablet capping in a rotary tableting machine. We hypothesized that capping occurs when residual stress of the tablet inside a die exceeds the critical stress immediately before ejection. Residual stress was evaluated by measuring the in-line die-wall pressure in a rotary tableting machine. Additionally, critical stress was estimated from the tablet strength inside the die using the Rumpf’s equation. The critical and residual stresses were compared to determine the capping tendency to some extent. The findings of this study will substantially contribute to the rapid detection of tablet capping during tablet production.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1859K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1859K) Full view HTML -
 Takahiro Tsuji, Takashi Ono, Hiromu Taguchi, Kok Hoong Leong, Yoshihir ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 576-583
Takahiro Tsuji, Takashi Ono, Hiromu Taguchi, Kok Hoong Leong, Yoshihir ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 576-583
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
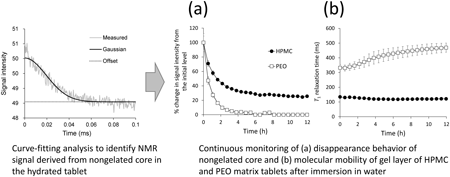
Supplementary materialTime-domain NMR (TD-NMR) was used for continuous monitoring of the hydration behavior of hydrophilic matrix tablets. The model matrix tablets comprised high molecular weight polyethylene oxide (PEO), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), and polyethylene glycol (PEG). The model tablets were immersed in water. Their T2 relaxation curves were acquired by TD-NMR with solid-echo sequence. A curve-fitting analysis was conducted on the acquired T2 relaxation curves to identify the NMR signals corresponding to the nongelated core remaining in the samples. The amount of nongelated core was estimated from the NMR signal intensity. The estimated values were consistent with the experiment measurement values. Next, the model tablets immersed in water were monitored continuously using TD-NMR. The difference in hydration behaviors of the HPMC and PEO matrix tablets was then characterized fully. The nongelated core of the HPMC matrix tablets disappeared more slowly than that of the PEO matrix tablets. The behavior of HPMC was significantly affected by the PEG content in the tablets. It is suggested that the TD-NMR method has potential to be utilized to evaluate the gel layer properties, upon replacement of the immersion medium: purified (nondeuterated) water is replaced with heavy (deuterated) water. Finally, drug-containing matrix tablets were tested. Diltiazem hydrochloride (a highly water-soluble drug) was employed for this experiment. Reasonable in vitro drug dissolution profiles, which were in accordance with the results from TD-NMR experiments, were observed. We concluded that TD-NMR is a powerful tool to evaluate the hydration properties of hydrophilic matrix tablets.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe hydration behavior of hydrophilic matrix tablets is a crucial process for the in vitro release of highly water-soluble drugs. This article presented a novel method for continuous monitoring of the hydration behavior by using time-domain nuclear magnetic resonance (TD-NMR). TD-NMR has an ability to identify the NMR signals corresponding to the nongelated core remaining in the sample from the measured T2 relaxation curves. The authors succeeded in characterizing fully the hydration behaviors of the model matrix tablets. The TD-NMR method is powerful to evaluate the hydration properties of hydrophilic matrix tablets.
Download PDF (729K) Full view HTML -
 Masaya Ikubo, Akiharu Uwamizu, Luying Chen, Sho Nakamura, Misa Sayama, ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 584-615
Masaya Ikubo, Akiharu Uwamizu, Luying Chen, Sho Nakamura, Misa Sayama, ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 584-615
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialOur group has reported various derivatives of lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS) as potent and subtype-selective agonists for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). However, the ester linkage between the glycerol moiety and fatty acid or fatty acid surrogate is present in all of them. In order to develop these LysoPS analogs as drug candidates, appropriate pharmacokinetic consideration is essential. Here, we found that the ester bond of LysoPS is highly susceptible to metabolic degradation in mouse blood. Accordingly, we examined isosteric replacement of the ester linkage with heteroaromatic rings. The resulting compounds showed excellent retention of potency and receptor subtype selectivity, as well as increased metabolic stability in vitro.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe authors have reported various derivatives of lysophosphatidylserine (LysoPS) as potent and selective agonists for each LysoPS receptor subtype. In order to further develop these LysoPS analogs to drug candidates, appropriate pharmacokinetic consideration is essential. They found that the ester bond of LysoPS is highly susceptible to metabolic degradation in mouse blood and examined isosteric replacement of the ester linkage with heteroaromatic rings. The resulting compounds showed excellent retention of potency and receptor subtype selectivity, as well as increased metabolic stability. This work provides a molecular basis for the design of phospholipid-based agonists with improved metabolic stability.
Download PDF (6216K) Full view HTML
-
Momo Shimekake, Masahiro Komeno, Manawo Taguchi, Shoo Katsumoto, Yuna ...2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 616-619
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe developed a simple and sensitive analytical HPLC method for the determination of acetylated hyaluronic acid (AcHA) in moisturizing and milk lotions. AcHA with different molecular weights was separated as a single peak using a C4 column and detected through post-column derivatization using 2-cyanoacetamide. The limits of detection and quantification were 60 and 200 ng, respectively. We found that AcHA in water was successfully extracted into a strong anion exchange (SAX) spin column with a recovery rate of AcHA was 63.8 ± 1.8%. Although the supernatant from acetone precipitation of lotions could pass through the spin column, the recovery rate (%) and accuracy of AcHA were affected by the viscous properties of cosmetics and acidic and acetone-soluble ingredients. Upon conducting analytical methods in this study, the concentration of AcHA in nine lotions was found to have ranged from 7.50 to 83.3 µg/mL. These values are comparable to the concentration range of AcHA in emulsions that have been previously evaluated for their superior effects. We believe that the analytical and extraction method is useful for the qualitative analysis of AcHA in moisturizing and milk lotions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (645K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (645K) Full view HTML -
Marina Tsuzaki, Shin Ando, Tadao Ishizuka2023 Volume 71 Issue 7 Pages 620-623
Published: July 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn this study, we developed mild conditions for the synthesis of an aryl thioether via aromatic substitution using aryl halides, which is a process that has rarely been studied. Aromatic substrates such as aryl fluorides activated with a halogen substituent are difficult to use for substitution reactions, but by using 18-crown-6-ether as an additive, these were successfully converted to their corresponding thioether products. Under the conditions we established, in addition to a wide variety of thiols, less-toxic and odorless disulfides could be used directly as nucleophiles at 0 to 25 °C.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (634K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (634K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|