
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Kazuma Ogawa2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 897-903
Kazuma Ogawa2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 897-903
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe word “theranostics,” a portmanteau word made by combining “therapeutics” and “diagnostics,” refers to a personalized medicine concept. Recently, the word, “radiotheranostics,” has also been used in nuclear medicine as a term that refer to the use of radioisotopes for combined imaging and therapy. For radiotheranostics, a diagnostic probe and a corresponding therapeutic probe can be prepared by introducing diagnostic and therapeutic radioisotopes into the same precursor. These diagnostic and therapeutic probes can be designed to show equivalent pharmacokinetics, which is important for radiotheranostics. As imaging can predict the absorbed radiation dose and thus the therapeutic and side effects, radiotheranostics can help achieve the goal of personalized medicine. In this review, I discuss the use of radiolabeled probes targeting bone metastases, sigma-1 receptor, and αVβ3 integrin for radiotheranostics.
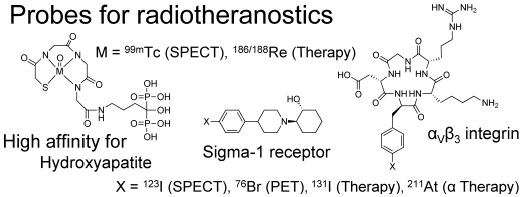 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickRadiotheranostics means the integration between diagnosis and therapy using radioisotopes. In the radiotheranostics, the diagnostic probe and corresponding therapeutic probe should show similar biodistribution. Thus, imaging using diagnostic probes before therapy can predict therapeutic and side effects of corresponding therapeutic probes. The author has developed radiolabeled probes with controlled pharmacokinetics for use in radiotheranostics. In this article, bone-seeking probes, sigma-1 targeted probes, and αVβ3 integrin targeted probes containing RGD peptide for cancer diagnosis and therapy are introduced as radiotheranostic probes.
Download PDF (1578K) Full view HTML
-
Kunikazu Moribe, Etsuo Yonemochi2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 904-905
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (178K) Full view HTML
-
Kenjirou Higashi, Keisuke Ueda, Kunikazu Moribe2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 906-914
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymer, Eudragit® E (EUD-E), has gained tremendous attention as a solid dispersion carrier because it efficiently stabilizes drugs in the amorphous state. Furthermore, EUD-E remarkably enhances drug dissolution in water. This review focuses on the interaction between drugs and EUD-E in solution, which contributes to the enhancement of drug concentration. Studies examining interactions between acidic drugs and EUD-E in organic solvents have revealed that the interaction occurs predominantly by electrostatic interaction, including hydrogen bonding and dipolar interactions. Other studies on interactions in aqueous solution found evidence for strong electrostatic interactions between acidic drugs and EUD-E in ion exchange experiments. 1H-NMR studies using high-resolution magic-angle spinning, nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy, diffusion, and relaxation time measurements successfully identified the interaction site and strength in aqueous solution. Hydrophobic and ionic interactions occurred between drugs and EUD-E. The conformation of EUD-E, which was affected by the ionic strength and pH of the aqueous media, also influenced the interaction. The knowledge discussed in this review will be helpful in designing solid dispersion formulations with EUD-E, which will efficiently enhance drug concentration and subsequent absorption into the body.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1589K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1589K) Full view HTML -
Daisuke Iohara, Makoto Anraku, Kaneto Uekama, Fumitoshi Hirayama2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 915-920
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLControlling drug crystallization is one of the important issues in pre-formulation study. In recent years, advanced approaches including the use of tailor-made additives have gathered considerable attention to control crystallization behavior of drugs. This review focuses on the use of hydrophilic cyclodextrins (CDs) as additives for controlling drug crystallization. CDs affect the crystallization of drugs in solution and in solid state based on a host–guest interaction. For example, 2,6-di-O-methyl-β-CD and 2-hydroxybutyl-β-CD suppressed solution-mediated transition of drugs during crystallization by the host–guest interaction; as a result, metastable forms selectively precipitated in solution. The use of CDs in crystal engineering provided an opportunity for the detection of a new polymorph by changing the crystallization pathway. It was also possible to modify crystal morphology (i.e., crystal habit) by selective suppression of crystal growth on a certain direction based on the host–gust interaction. For solid formulation, stable amorphous drug/CDs complex under humid conditions was prepared using two different CDs. An overview of some recent progress in the use of CDs in crystal engineering and in amorphous formulation is described in this review.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3626K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3626K) Full view HTML
-
Satoshi Tanida, Aika Yoshimoto, Miyabi Yoshida, Hiromasa Uchiyama, Kaz ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 921-928
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe studied the possibility of using ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) as an excipient to create an amorphous composite that can be administered to animals in preclinical studies of experimental drugs. Three UDCA-based amorphous samples composed of nifedipine (NIF), indomethacin (IND), and naproxen (NAP) were found by screening. The UDCA-based formulations were adjudged amorphous by solid-state analysis using X-ray powder diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry. In addition, amorphous samples of NIF–UDCA, IND–UDCA, and NAP–UDCA did not crystallize while in 1% methyl cellulose (MC) solution for 120 min, although an amorphous solid dispersion of NIF–poly(vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) crystallized rapidly. The low hygroscopicity of UDCA helps NIF maintain an amorphous state in 1% MC solution. The UDCA-based amorphous composites can be administered as suspended formulations to animals in preclinical studies.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1948K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1948K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Hoshino, Motoshige Azuma, Yuki Yamada, Varin Titapiwatanakun, M ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 929-934
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe investigated the water contents in commercial semi-solid preparations used for pressure ulcer (PU) treatment using near-IR spectroscopy (NIRS) and compared the results with those measured using the Karl Fischer (KF) method. The aim of this study was to determine a standard method and select the appropriate topical preparation with the optimal moisture for PU treatment. The water absorption properties of bases and formulations were evaluated with a time-dependent factor using Transwell as the model membrane. KF and NIRS were applicable as measurement methods of the water content in semi-solid formulations. NIRS was shown to be a useful, simple, nondestructive tool that is more advantageous than the KF method. The water absorption characteristics tested using Transwell revealed that the rate of and capacity for water absorption are determined not only by the absorption ability of the polymer base but also by other factors, such as the osmotic pressure exerted by additives. KF and NIR measurements can be used to choose external skin preparations to control the amount of water in PU treatment.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (833K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (833K) Full view HTML -
Yasunori Iwao, Hitoshi Ishida, Shin-ichiro Kimura, Toshiyuki Wakimoto, ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 935-939
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChafuroside A and chafuroside B are flavone C-glycosides isolated from oolong tea leaves. They have a number of beneficial pharmacological activities related to antiinflammation at various concentrations. However, no crystallographic study of chafurosides has yet been reported. In the present study, the crystal structures of chafuroside A and chafuroside B were investigated using single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The asymmetric unit of the chafuroside A crystal consists of one chafuroside A and two water molecules, and that of chafuroside B contains one chafuroside B and one water molecule. The flavone moiety of chafuroside A is curved, i.e., the angle between the best-fit planes of the chromene and phenyl rings is 18.9°, whereas the chafuroside B flavone moiety is relatively flat. A comparison of the curvatures of the flavone moieties of various C-glycosides showed that the curvature of chafuroside A is significantly larger than those of the others. This structural feature might contribute to the differences between the strengths of the pharmacological activities of chafurosides A and B.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1679K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1679K) Full view HTML -
Reiko Teraoka, Toshiro Fukami, Takayuki Furuishi, Hiromasa Nagase, Har ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 940-944
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe photostability of three types of furosemide (FUR) cocrystal (FUR-caffeine, FUR-urea, and FUR-nicotinamide cocrystals) was studied under irradiation with a D65 fluorescent lamp. The coloration of the FUR-urea pellets was significantly faster than that of the intact FUR, whereas the coloration of FUR-nicotinamide was suppressed compared with that of intact FUR and the other cocrystals. In the case of FUR-urea, the chemical degradation of FUR increased by approximately 6.6% after irradiation for 90 d. On the other hand, FUR-nicotinamide showed better chemical stability, with only 1.3% of FUR degraded, which was significantly lower than the other cocrystals. The FUR-urea pellets showed a UV-Visible absorption spectrum similar to that of intact FUR, while the absorption range of FUR-nicotinamide shifted to a shorter wavelength. The light sensitivity of FUR-nicotinamide was improved because of the much lower emission of the D65 fluorescent lamp in the absorption range of the cocrystal.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (712K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (712K) Full view HTML -
Akihito Kiguchiya, Reiko Teraoka, Toshiyasu Sakane, Etsuo Yonemochi2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 945-952
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSalt and cocrystal formulations are widely used as techniques to improve physicochemical properties of compounds. Some spectrometric techniques to distinguish cocrystals from salts have been reported; however, it has not been possible to adapt these formulations with many compounds, because of limitations, high difficulty, and exceptions. Therefore, we focused on the possibility of UV spectrometry, which had not been reported as a classification technique for salts and cocrystals. The integration values of solid-state UV/visible (Vis) spectra of indomethacin salts were larger than those of physical mixtures of indomethacin and counter molecules, while that of indomethacin cocrystal was not large compared with that of the physical mixture. From these results, differences between a salt and a cocrystal were observed in their solid-state UV/Vis absorption spectra for indomethacin complexes. Therefore, it is suggested that solid-state UV/Vis absorption spectra can be used as a new technique to classify salts and cocrystals.
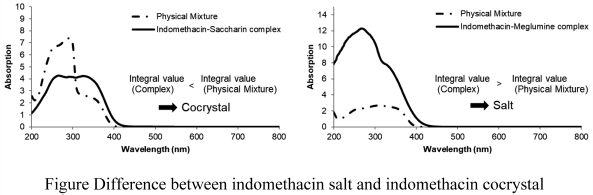 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1353K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1353K) Full view HTML
-
 Atsushi Nakayama, Hideo Sato, Shuji Nagano, Sangita Karanjit, Hiroshi ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 953-958
Atsushi Nakayama, Hideo Sato, Shuji Nagano, Sangita Karanjit, Hiroshi ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 953-958
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAsymmetric total syntheses of dihydropyran containing natural products, (+)-eurotiumide F and (+)-eurotiumide G have been described. These total syntheses revealed the absolute configuration of eurotiumide F and G, and confirmed the reported structure of eurotiumide F and revised the reported structure of eurotiumide G. Highlight of these syntheses is thermal rearrangement with 4-methoxyisochroman-1-one derivative having propargyl ether on phenolic ether under thermal condition to construct dihydropyran ring. X-Ray crystallographic analysis of (+)-eurotiumide G clarified the stereochemistry at the C1-position.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickDetermining the stereochemistry of a cyclic acetal moiety is sometimes difficult because it is hard to observe NOESY correlations depending on the substitution pattern and the conformation. While the X-ray crystallographic analysis is a powerful method for structure determination, many natural products are often difficult to form single crystals because of their limited availability. The authors accomplished the first asymmetric total syntheses of (+)-eurotiumide F and (+)-eurotiumide G having such a cyclic acetal moiety, and through their total syntheses, they succeeded to measure the X-ray crystallographic analysis of eurotiumide G and revised the relative configuration between H1 and H4.
Download PDF (803K) Full view HTML -
Liang Qu, Satoshi Fudo, Katsumi Matsuzaki, Tyuji Hoshino2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 959-965
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFibrillated aggregation of amyloid β (Aβ) peptides is a potential factor causing toxic amyloid deposition in neurodegenerative diseases. A toxic fibril formation of Aβ is known to be enhanced on the ganglioside-rich lipid membrane containing some amounts of cholesterol and sphingomyelin. This ganglioside-rich membrane is supposed to provide a hydrophobic environment that promotes the formation of Aβ fibrils. Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to investigate the structure of Aβ complex in the hydrophobic solution composed of dioxane and water molecules. The Aβ conformation was contrasted to that in the aqueous condition by executing multiple computational trials with the calculation models containing one, four, or six Aβ peptides. The conformation was also compared between the calculations with the 42-mer (Aβ42) and 40-mer (Aβ40) peptides. The simulations for Aβ42 demonstrated that Aβ peptides had a tendency to stretch out in the hydrophobic environment. In contrast, Aβ peptides were closely packed in the aqueous solution, and the motions of Aβ peptides were suppressed significantly. The N-terminal polar domains of Aβ peptides tended to be positioned at the inside of the Aβ complex in the hydrophobic environment, which supported the C-terminal domains in expanding outward for inter-molecular interaction. Since Aβ peptides were not tightly packed in the hydrophobic environment, the total surface area of the Aβ complex in the hydrophobic solution was larger than that in the aqueous one. The simulation for Aβ40 peptides also showed a difference between the hydrophobic and aqueous solutions. The difference was compatible with the results of Aβ42 in the structure of the Aβ complex, while the C-terminal outward expansion was not so distinct as Aβ42 peptides.
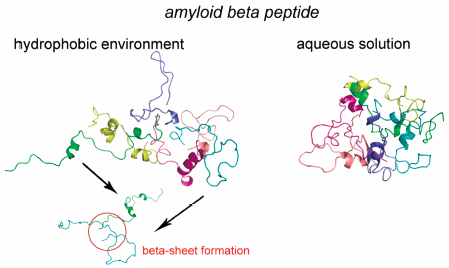 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2238K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2238K) Full view HTML -
San-ha Lee, Xiang Fei, Chaelin Lee, Hien Thi Thu Do, Inmoo Rhee, Seung ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 966-976
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
Advance online publication: June 28, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHonokiol, a biphenolic neolignan isolated from Magnolia officinalis, was reported to have a promising anti-inflammatory activity for the treatment of various diseases. There are many efforts on the synthesis and structure–activity relationship of honokiol derivatives. However, regioselective O-alkylation of honokiol remains a challenge and serves as a tool to provide not only some derivatives but also chemical probes for target identification and mode of action. In this study, we examined the reaction condition for regioselective O-alkylation, in which C2 and C4′-alkylated analogs of honokiol were synthesized and evaluated for inhibitory activity on nitric oxide production and cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Furthermore, we successfully synthesized a potential photoaffinity probe consisting of biotin and benzophenone based on a C4′-alkylated derivative.
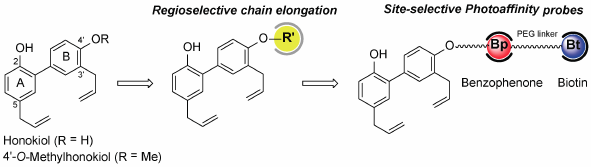 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1232K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1232K) Full view HTML -
Hui Liu, Xiaoning Zhao, Shan Liang, Linlan Fan, Zhaojun Li, Yun Zhang, ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 977-984
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEndomorphin-1 (Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2, EM-1), an endogenous μ-opioid receptor ligand with strong antinociceptive activity, is not in clinical use because of its limited metabolic stability and membrane permeability. In this study, we develop a short-peptide self-delivery system for brain targets with the capability to deliver EM-1 without vehicle. Two amphiphilic EM-1 derivatives, C18-SS-EM1 and C18-CONH-EM1, were synthesized by attaching a stearyl moiety to EM-1 via a disulfide and amide bond, respectively. The amphiphilicity of EM-1 derivatives enabled self-assembling into nanoparticles for brain delivery. The study assessed morphology, circular dichroism, and metabolic stability of the formulations, as well as their pharmacodynamics and in vivo distribution, directly monitored by near-IR fluorescence imaging in mouse brains. In aqueous solution, the C18-SS-EM1 derivative self-assembled into spherical nanostructures with a diameter of 10–20 nm. Near-IR fluorescence analysis visualized the accumulation of the peptides in the brain. Importantly, the analgesic effect of C18-SS-EM1 nanoparticles was significantly stronger as compared to that of unmodified EM-1 or C18-CONH-EM1 nanoparticles. An in vitro release study demonstrated that self-assembled C18-SS-EM1 nanoparticles possessed reduction-responsive behavior. In summary, self-assembling C18-SS-EM1 nanoparticles, which integrate the advantages of lipidization, nanoscale characteristics and, labile disulfide bonds, represent a promising strategy for brain delivery of short peptides.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3606K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3606K) Full view HTML -
Hyun jin An, Yonghwa Lee, Lichao Liu, Seulbi Lee, Jae duk Lee, Yongsub ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 985-991
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
Advance online publication: July 04, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChemically stable ester derivatives of taxifolin have become a focus of interest for their role in the satisfactory effects on human health. Accordingly, the aim of this study was to evaluate the physical and chemical stability of different formulations containing 0.02% taxifolin tetra-octanoate, which was proved to possess higher inhibitory effect on tyrosinase activity compared with taxifolin in a cell-free system. In the studies of physical stability, a Brookfield viscometer was used to determine rheological behavior of formulations containing taxifolin tetra-octanoate, and a portable pH meter was used to determine pH change. Moreover, chemical stability was determined by HPLC with UV detection. Formulations were evaluated for 12 weeks stored at 25 and 40°C. Results showed that storage time had no significant influence on viscosity of the formulations containing taxifolin tetra-octanoate, and pH value was relatively stable, which was within the limits of normal skin pH range. In the chemical stability studies, taxifolin tetra-octanoate in the essence formulation was most unstable at 40°C with about 81% degradation in 12 weeks of storage, however, the percentage of remaining taxifolin tetra-octanoate in cream formulation stored for 12 weeks at 25°C was the highest, about 93%. The results in this study may contribute to the development of more stable formulations containing taxifolin tetra-octanoate.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML -
Shin-ichiro Kimura, Taichi Ishikawa, Yasunori Iwao, Shigeru Itai, Hiro ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 992-999
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA three-dimensional (3D) printer is a powerful tool that can be used to enhance personalized medicine. A fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printer can fabricate 3D objects with different internal structures that provides the opportunity to introduce one or more specific functionalities. In this study, zero-order sustained-release floating tablet was fabricated using FDM 3D printer. Filaments comprising poorly water-soluble weak base drug, itraconazole (ITZ) and polymers (hydroxypropyl cellulose and polyvinylpyrrolidone) were prepared, and tablets with a hollow structure and different outside shell thicknesses were fabricated. In the 3D printed tablets, ITZ existed as an amorphous state and its solubility improved markedly. As the outside shell thickness of the tablet increased, drug release was delayed and floating time was prolonged. In the tablets with 0.5 mm of the upper and bottom layer thickness and 1.5 mm of the side layer thickness, holes were not formed in the tablets during the dissolution test, and the tablets floated for a long period (540 min) and showed nearly zero-order drug release for 720 min. These findings may be useful for improving the bioavailability of several drugs by effective absorption from the upper small intestine, with floating gastric retention system.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2975K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2975K) Full view HTML -
Mayuko Hatai, Shizuyo Horiyama, Noriko Yoshikawa, Eriko Kinoshita, Sat ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 1000-1005
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialα,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds readily form adducts with SH or NH2 residues, which are nucleophilic agents, by Michael addition. Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide that contains an SH residue and functions as an antioxidant. We demonstrated previously that acrolein (ACR), crotonaldehyde (CA), and methyl vinyl ketone (MVK) are present in nicotine- and tar-removed cigarette smoke extract (CSE) and reacted with GSH in B16-BL6 mouse melanoma cells to form GSH-ACR, GSH-CA, and GSH-MVK adducts, suggesting a possible mechanism for CSE-induced cytotoxicity. In this study, we searched for novel α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds other than ACR, CA, and MVK. We selected candidate compounds in CSE based on accurate mass values generated using LC/MS analysis of products formed between CSE and GSH, and identified these using GC/MS analysis and library screening. As a result, we isolated trans-2-methyl-2-butenal, 2-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, 3-methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, and furfural, which were poorly reactive with GSH and only very weakly inhibited growth of Colon-26 mouse carcinoma cells and BALB/3T3 clone A31 mouse normal cells. We also isolated 2-cyclopenten-1-one, trans-2-pentenal, 3-methyl-2-butenal and ethyl vinyl ketone, which were highly reactive with GSH and significantly inhibited the growth of both cell lines. Our data suggest that the reactivity of compounds in CSE with GSH may be positively correlated with the effect on inhibiting cell growth. Notably, trans-2-pentenal showed marked inhibition of carcinoma cells growth, whereas this compound exhibited little inhibitory effect on normal cells. trans-2-Pentenal may be a potent candidate or seed for antitumor agents.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (931K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (931K) Full view HTML -
Pan Yu, Chao-Jie Xia, Dong-Dong Li, Zhenzhong Wang, Wei Xiao, Lin-Guo ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 1006-1014
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialChlorogenic acid (CGA) has been considered as one of important active components in a number of medicinal herbs. Recently our group demonstrated that caffeoyl salicylate scaffold derived from CGA can be employed for the development of novel anti-inflammatory agents. The most active compound D104 can be a very promising starting point for the further structural optimization. A series of novel caffeoyl salicylate analogs were designed, synthesized, and evaluated by preliminary biological evaluation. The obtained results showed that the two compounds B12 and B13 can not only inhibit production of nitric oxide (NO) in RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) effectively, but also have high safety in in vitro cytotoxic test, which could be comparable with D104. Molecular docking study on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) protein revealed that compounds B12 and B13 can follow the same binding mode with D104, and the carboxyl group of caffeoyl salicylate scaffold might play a key role in the interaction with protein target, which implied the carboxyl group should be retained in the further optimization.
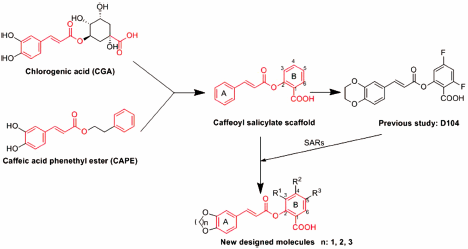 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2009K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2009K) Full view HTML
-
Yuta Ito, Akihiro Touyama, Minako Uku, Hiromichi Egami, Yoshitaka Hama ...2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 1015-1018
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThiocyanation of aromatic compounds has been investigated using the combination of 1-chloro-1,2-benziodoxol-3-(1H)-one (1) and (trimethylsilyl)isothiocyanate (TMSNCS). The reaction with electron rich aromatic compounds proceeded smoothly to provide the thiocyanated products in high yield, while electron deficient heteroaromatic compounds were not suitable for this reaction. In these reactions, the regioselectivity was generally high. Transformations of the products were also investigated to demonstrate the utility of the reaction. Based on NMR experiments, we propose that thiocyanogen chloride is generated in situ as an active species.
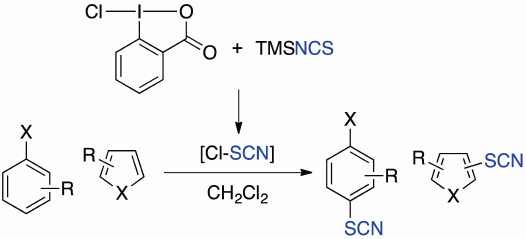 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML -
Kenji Sugimoto, Miyu Oshiro, Ryuhei Hada, Yuji Matsuya2019Volume 67Issue 9 Pages 1019-1022
Published: September 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA novel catalyst system—a combination of the readily available 2,2′-biphenol with the inexpensive, nontoxic, and eco-friendly B(OH)3—promoted the Nazarov cyclization of activated and inactivated divinyl ketones to afford the corresponding cyclopentenones up to 96% yield under, in a cis-selective manner. Compared with the conventional harsh conditions with hazardous reagents, user-friendly method was established with bench-stable and easy-to-handle reagents.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (723K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (723K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|