
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hao Chen, Yi Huang, Hong Liu, Ming Yang, Hengli Tong, Feipeng Gong, Li ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 827-838
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
Advance online publication: September 17, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSini Decoction (SND) is the main prescription for treating Shaoyin disease in Zhang Zhongjing’s Treatise on Typhoid diseases in Han Dynasty. It is composed of Aconitum carmichaeli Debeaux, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch ex DC and Zingiber officinale Roscoe. It has the effects of warming middle-jiao to dispel cold and revive the yang for resuscitation. Nowadays, it is mainly used in diseases in cardiovascular system, nervous system, digestive system and so on. In this paper, the effect and mechanism of the compatibility of Aconitum carmichaelii, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch ex DC and Zingiber officinale Roscoe in SND were described. The results showed that SND performed remarkbly on strengthening heart, promoting blood circulation as well as inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis, anti-inflammatory and anti-hypothyroidism. The toxic effect of Aconitum carmichaelii was relieved by the combination of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch ex DC and Zingiber officinale Roscoe. The mechanism of increasing efficiency and reducing toxicity after the compatibility of medicines in SND was discussed from the perspective of changes in biological effects and chemical compositions. In terms of biological effects, the mechanism of SND in treating heart failure, myocardial ischemia, myocardial hypertrophy and hypothyroidism and protecting cell injury were discussed. As to chemical composition changes, most studies have compared the changes of main components in Aconitum carmichaelii, Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch ex DC and Zingiber officinale Roscoe with the whole prescription, drug pair and single Decoction, which further confirmed the effect of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch ex DC on the detoxification of Aconitum carmichaelii and the significance of compatibility efficiency of SND. For the application of differently processed varieties of Aconitum carmichaelii in SND, the treatment of different diseases has siginificant tendencies and differences in the selections of Aconitum carmichaelii processed varieties. This paper will lay a foundation on clarifying the mechanism of drug compatibility of SND and in the future, provide a reference for the proper selection of differently processed products of Aconitum carmichaelii in SND in order to exert better effects in clinical practices.
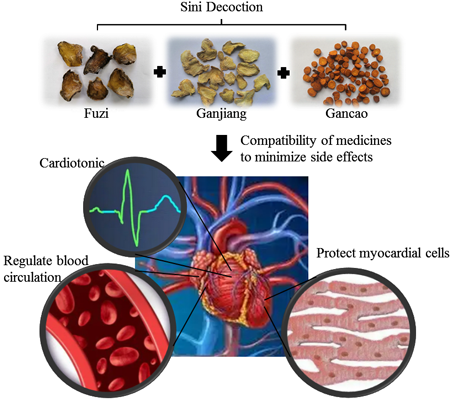 View full abstractDownload PDF (4791K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4791K) Full view HTML
-
Takuro Maruyama2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 839
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (196K) Full view HTML
-
Yuto Goto, Taichi Fujii, Yasumasa Takao, Takashi Tsuchida, Mikako Sone ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 840-847
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn order to investigate the relationship between the chemical composition of essential oils and haplotypes of the psbA-trnH intergenic spacer region of chloroplast DNA (psbA-trnH) in Valerianae Fauriei Radix (Japanese Valerian; JV), we analyzed the DNA sequence and GC-MS metabolome of JV from Japanese markets and of herbal specimens from related species. DNA analysis revealed that JV products from Japan consisted of three haplotypes, namely AH-1, -2 and -5 reported in our previous study. The GC-MS metabolome revealed five chemotypes (J1, J2, C, K and O), of which J1, J2 and C were detected in the JV products from Japan. Chemotypes J1 and J2, with kessyl glycol diacetate (KGD) as the main volatile component, were found in the products of Japanese origin whereas chemotype C, with 1-O-acetyl-2,10-bisaboladiene-1,6-diol (ABD), was found in the products of Chinese and Korean origin. The haplotypes were correlated with the chemotypes: haplotype AH-1 for chemotype J1, AH-2 for chemotype J2 and AH-5 for chemotype C, suggesting that the chemical diversity of JV is not attributed to the environmental factors rather to the genetic factors. Since KGD and ABD were reported to have sedative effects and nerve growth factor (NGF)-potentiating effects, respectively, understanding the chemotypes and selecting an appropriate one would be important for the application of JV. The psbA-trnH haplotypes could be useful DNA markers for the quality control and standardization of JV.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1845K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1845K) Full view HTML -
Hiroyuki Fuchino, Naoko Anjiki, Sayaka Murase, Hirotaka Matsuo, Shigek ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 848-858
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we investigated the correlation between the cultivation conditions and chemical composition of Ephedra sinica and E. sp. (denoted EP-13, which has been grown at the National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health, and Nutrition for many years). The total contents of ephedrine and pseudoephedrine are specified in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia; therefore, we investigated the changes in their content under different cultivation conditions, including varying soil conditions and fertilization or the lack of fertilization. Poor growth due to low soil nutrition and lack of sunlight caused decrease of the alkaloid content. As expected, the plants accumulated proline, although the proline content varied considerably with cultivation location. The proline concentration correlated with the content of methanoproline. Moreover, a new compound, namely N,N-dimethyl-p-hydroxyphenylethylamine-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside], was isolated from E. sinica but was absent in EP-13. This study on the correlation between cultivation methods and the alkaloid content in Ephedra is expected to assist in the future production of quality Ephedra herb.
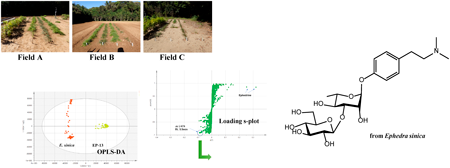 View full abstractDownload PDF (3346K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3346K) Full view HTML -
Yoshinori Ueno, Ryuichiro Suzuki, Masashi Kitamura2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 859-862
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe root of Paeonia lactiflora (PAEONIAE RADIX) is a constituent of the traditional Japanese medicines (Kampo) and is known to have various effects. Peony roots cultivated in Japan and China are available in the Japanese market for medicinal use. In this study, the chemical diversity of ten available peony roots in the market that differed in their cultivation area was investigated using 1H-NMR metabolomics techniques. Principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis of the 1H-NMR spectra of the peony roots methanolic extracts revealed a clear difference between the metabolic profiles of Japanese and Chinese peony roots. By preparative procedures using chromatography based on 1H-NMR spectra measurements, oxypaeoniflorin and (+)-catechin were found to be specific compounds for Japanese peony root. All peony roots used in this study were listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. Therefore, the differences in the constituents of these peony roots might be attributed to growing conditions than differences in species. Cultivation conditions also influence the quality of natural medicines.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1028K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1028K) Full view HTML -
Tatsuya Shirahata, Asuna Kanazawa, Marina Uematsu, Hiroyuki Fuchino, N ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 863-867
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialApricot and Peach Kernels are commercial crude drugs used in many formulas of traditional Japanese medicine, Kampo. Although their applications are quite different, it is difficult to distinguish them using conventional methods such as HPLC. The study aimed at near-infrared (NIR) metabolic profiling to discriminate Apricot and Peach Kernels (Armeniacae Semen and Persicae Semen) collected from Japanese markets. A fast, simple, non-destructive, and robust NIR measurement of kernel surface with no sample pre-treatment was achieved in situ. Principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) models showed discrimination between the two crude drugs with good fitting and prediction values. These results indicate that NIR metabolic profiling is useful for discriminating Apricot and Peach Kernels based on their chemical constituents using a simple and non-destructive procedure.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1314K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1314K) Full view HTML
-
Takahiro Suzuki, Kanae Sato, Tomohiro Seki, Toshinobu Seki2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 868-875
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe investigated polymer nanofilm (PNF) for use in high-throughput screening (HTS) to promote the development of transdermal therapeutic systems (TTS). The drug permeability of PNF with a 1 : 1 weight mix ratio of poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) and poly(methylhydrosiloxane) (PMHS) (PLLA/PMHS (1/1) PNF) and Strat-M® of the transdermal diffusion test membrane, was evaluated using 12 kinds of drugs with the logarithmic value of n-octanol/water partition coefficients of −4.70 to 3.86. The lag time of PLLA/PMHS (1/1) PNF made via polymer alloying was significantly shorter than that of Strat-M® for 10 drug types, and the formation of a highly diffusible PMHS-rich phase accompanying the formation of a sea–island structure was suggested as a contributing factor. Additionally, a high correlation was confirmed between the measured value for the logarithm of the apparent permeability coefficient of PLLA/PMHS (1/1) PNF and the literature values for the logarithm of the apparent permeability coefficient of human skin (r = 0.929). This study shows that PLLA/PMHS (1/1) PNF can reliably predict drug permeability in human skin and can potentially be used in HTS for developing TTS.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3004K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3004K) Full view HTML -
Yugo Uematsu, Fumihiko Ogata, Kyohei Nishida, Yuri Mizuno, Masashi Yan ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 876-884
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo verify the interaction between sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS) and its concomitant drugs, we elucidated the capability of potassium ions and concomitant drugs to adsorb onto SPS and the effect of their coexistence on the amount adsorbed. We identified 14 drugs used concomitantly with SPS from 2017–2019 in our investigation, and 5 drug preparations used in the clinical setting were used for the experiments. In the artificial intestinal juice, SPS adsorbed 39.05–69.77 mEq/g of potassium ions. Amlodipine besylate and nifedipine were well-adsorbed, while azosemide and febuxostat were did not adsorb well onto SPS. Our results and the results of a previous study suggest that additives in drug preparations affect the adsorption of drugs onto SPS. The adsorption kinetics onto SPS of drugs conformed to the pseudo-second order model. However, the adsorption of amlodipine besylate completely may not be fitted to the pseudo-second order model. The amount of amlodipine besylate adsorbed under the coexistence of potassium ions decreased compared to when potassium ions were absent. The amount of nifedipine and potassium ions adsorbed remained constant, regardless of whether potassium ions were present or not. These results might be due to the differences in their mechanisms of adsorption onto SPS and to the characteristics of the drugs. In a clinical setting, SPS is used concomitantly with various oral drugs. The interaction between SPS and its other concomitant drugs need to be elucidated more to obtain enough evidence for pharmacists to propose the appropriate prescription.
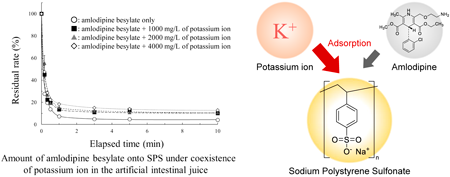 View full abstractDownload PDF (1905K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1905K) Full view HTML -
 Kazuki Fujii, Yasumasa Hara, Midori A. Arai, Samir K. Sadhu, Firoj Ahm ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 885-891
Kazuki Fujii, Yasumasa Hara, Midori A. Arai, Samir K. Sadhu, Firoj Ahm ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 885-891
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA new coumarin derivative (1) and 30 known compounds were isolated from Mammea siamensis and Andrographis paniculata, guided by B cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion region 1 (BMI1) promoter inhibitory activity. Among the isolated compounds, 15 compounds showed BMI1 promoter inhibitory activity, and five compounds were found to be cytotoxic. 14-Deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide (18) was highly cytotoxic to DU145 cells with an IC50 value of 25.4 µM. Western blotting analysis of compound 18 in DU145 cells suggested that compound 18 suppresses BMI1 expression.
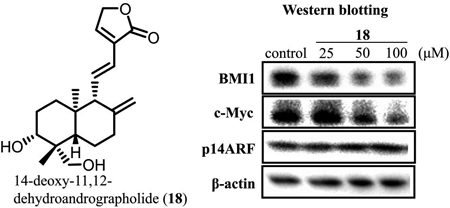 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickB cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion region 1 (BMI1) is known to be highly expressed in cancer stem cells that contribute to cancer recurrence and metastasis. The authors isolated a new coumarin derivative (1) and 30 known compounds from two plants (Mammea siamensis and Andrographis paniculata), guided by BMI1 promoter inhibitory activity. Among the isolated compounds, 15 compounds showed BMI1 promoter inhibitory activity, and five compounds were found to be cytotoxic against cancer cells. 14-Deoxy-11,12-dehydroandrographolide (18) was highly cytotoxic to DU145 cells. Western blotting analysis of compound 18 in DU145 cells suggested that compound 18 suppresses BMI1 expression.
Download PDF (902K) Full view HTML -
 Nahoko Uchiyama, Kohei Kiyota, Junko Hosoe, Takanori Komatsu, Naoki Su ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 892-900
Nahoko Uchiyama, Kohei Kiyota, Junko Hosoe, Takanori Komatsu, Naoki Su ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 892-900
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
Advance online publication: October 12, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialQuantitative 1H-NMR (1H-qNMR) is useful for determining the absolute purity of organic molecules; however, it is sometimes difficult to identify the target signal(s) for quantitation because of their overlap and complexity. Therefore, we focused on the 31P nucleus because of the simplicity of its signals and previously reported 31P-qNMR in D2O. Here we report 31P-qNMR of an organophosphorus compound, sofosbuvir (SOF), which is soluble in organic solvents. Phosphonoacetic acid (PAA) and 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)benzene-d4 (1,4-BTMSB-d4) were used as reference standards for 31P-qNMR and 1H-qNMR, respectively, in methanol-d4. The purity of SOF determined by 31P-qNMR was 100.63 ± 0.95%, whereas that determined by 1H-qNMR was 99.07 ± 0.50%. The average half bandwidths of the 31P signal of PAA and SOF were 3.38 ± 2.39 and 2.22 ± 0.19 Hz, respectively, suggesting that the T2 relaxation time of the PAA signal was shorter than that of SOF and varied among test laboratories. This difference most likely arose from the instability in the chemical shift due to the deuterium exchange of the acidic protons of PAA, which decreased the integrated intensity of the PAA signal. Next, an aprotic solvent, dimethyl sulfoxide-d6 (DMSO-d6), was used as the dissolving solvent with PAA and sodium 4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentanesulfonate-d6 (DSS-d6) as reference standards for 31P-qNMR and 1H-qNMR, respectively. SOF purities determined by 31P-qNMR and 1H-qNMR were 99.10 ± 0.30 and 99.44 ± 0.29%, respectively. SOF purities determined by 31P-qNMR agreed with the established 1H-qNMR values, suggesting that an aprotic solvent is preferable for 31P-qNMR because it is unnecessary to consider the effect of deuterium exchange.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pick31P-qNMR in organic solvents was performed by using an organophosphorus compound, sofosbuvir (SOF) with phosphonoacetic acid (PAA) as the qNMR reference standard. In a protic solvent, methanol-d4, the purity of SOF determined by 31P-qNMR was 1.6% higher than that by 1H-qNMR. This difference most likely arose from the instability in the chemical shift due to the deuterium exchange of the acidic protons of PAA. In an aprotic solvent, DMSO-d6, the purity determined by 31P-qNMR agreed with the 1H-qNMR one, suggesting that an aprotic solvent is preferable for 31P-qNMR because it is unnecessary to consider the effect of deuterium exchange.
Download PDF (1188K) Full view HTML -
 Susumu Kawakami, Chieko Kanagawa, Liva Harinantenaina Rakotondraibe, M ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 901-906
Susumu Kawakami, Chieko Kanagawa, Liva Harinantenaina Rakotondraibe, M ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 12 Pages 901-906
Published: December 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFrom the less polar fraction of the MeOH extract of the leaves and twigs of Omphalea oppositifolia, five new ent-rosane-type diterpenoids, named omphalines A–E (1–5), were isolated together with one known compound, 7-keto-ent-kaurane-16β,17-diol (6), by a combination of various kinds of chromatography. The structure of omphaline A (1) was elucidated to be 19-nor-ent-rosane-4,15-diene-2β,6α-diol-3-one. Omphalines B (2), C (3), D (4), and E (5) possessed two double bonds at 5- and 15-positions, and hydroxy functional groups at 3β-, 2α,3α-, 2α,3β-, and 2α,19-positions, respectively. The absolute configuration of 1 was determined by the comparison of the experimental electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectrum and calculated ECD spectra.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickMany species of flora and fauna in Madagascar were independently developed from other regions of the world. Thus, about 80% of 15,000 species of plants growing there is endemic and the editor very much appreciates that Omphalea oppositifolia (Euphorbiaceae) was collected by the authors’ own expedition to Madagascar. From the leaves and twigs of O. oppositifolia, one new ent-nor-rosane and four new ent-rosane-type diterpenoids were isolated. Rosane-type diterpenoids are rarely found in nature. Their structures were elucidated by the spectroscopic analyses and the absolute configuration was determined by the comparison of experimental and calculated ECD spectra.
Download PDF (1135K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|