
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Makoto Nakajima2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 594
Makoto Nakajima2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 594
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEditor's pickMolecular space chemistry is an important concept for the design of novel functional materials and catalysts. The research group “Molecular space chemistry for the chemical conversion” was established by the member who advocate that the organic integration of supramolecular chemistry and catalytic chemistry enables flexible chemical conversion in multi-component molecular ensembles. It is noteworthy that most of the member got a position of full professor (or similar position) in these few years. To this volume of Chem. Pharm. Bull., four of the members, who have deep connection with the Pharmaceutical Society of Japan, contribute their cutting-edge results.
Download PDF (198K) Full view HTML
-
Taiga Karimata, Shinya Adachi, Masakatsu Shibasaki, Naoya Kumagai2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 595-598
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAn iterative hydride reduction/oxidation process was promoted under ambient conditions by a quasi-planar iminium cation rigidified by two concatenated quinoline units. The iminium proton was fixed by hydrogen bonding from neighboring quinoline nitrogen atoms, rendering the imine highly susceptible to hydride reduction with weak reductants, e.g., 1,4-dihydropyridines. The thus-formed amine was readily oxidized by molecular oxygen to regenerate the quasi-planar iminium cation under ambient conditions. This process was exploited for catalytic oxidation of 1,4-dihydropyridines as well as 9,10-dihydroacridine to highlight an intriguing rigidity-driven catalysis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1754K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1754K) Full view HTML
-
Ryuichi Nishiyori, Ken Okuno, Bun Chan, Seiji Shirakawa2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 599-604
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary material1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol (BINOL)-derived chiral bifunctional sulfide and selenide catalysts that possess a hydroxy group are known to be effective catalysts for enantioselective bromolactonizations. When applied to asymmetric iodolactonizations of 4-pentenoic acids, these catalysts yield chiral γ-butyrolactone products that are important compounds in medicinal chemistry. Although chiral bifunctional selenides have shown good catalytic performances in enantioselective iodolactonizations, reactions with BINOL-derived chiral sulfide catalysts unexpectedly gave iodolactonization products in nearly racemic forms. The roles of chalcogenide moieties and hydroxy groups on bifunctional catalysts were investigated, and the importance of both a selenide moiety and a hydroxy group on chiral bifunctional selenide catalysts to achieve enantioselective iodolactonizations was clarified. An optimized chiral bifunctional selenide catalyst was applied to the asymmetric synthesis of chiral γ-butyrolactones and phthalides. Furthermore, the utility of chiral bifunctional selenides was also demonstrated in the catalytic enantioselective desymmetrizing iodolactonization of α,α-diallyl carboxylic acids.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (906K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (906K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Murai, Shohei Hamada, Yusuke Kobayashi, Takahiro Sasamori, Taku ...2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 605-615
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe preparation, optical resolution, and structural investigations of a series of axially chiral biaryl dicarboxylic acids bearing oxygen, sulfur, and selenium atoms were carried out. The crystal structures of sulfur- and selenium-containing derivatives revealed that the carboxy groups of these compounds are located in a co-planar geometry with the fused aromatic rings including the chalcogen atoms. These conformational controls were found to be achieved by chalcogen-bonding interactions between chalcogen atoms in the aromatic rings and oxygen atoms in the carboxy groups. Even in the case of a binaphthofuran derivative, in which the formation of chalcogen-bonding interactions was expected to be negligible, the carboxy groups were also found to be located in a co-planar geometry toward its fused cyclic rings. Natural bond orbital (NBO) analyses of these dicarboxylic acids indicated the formation not only for the chalcogen-bonding interactions for S and Se derivatives, but also the tetrel-bonding interactions between the oxygen atoms in the carboxy groups and the carbon atoms in the fused cyclic rings for all biaryl dicarboxylic acids. These tetrel-bonding interactions were thought to contribute to conformational control in the binaphthofuran derivative. Physical and chiroptical properties such as the racemization barriers and circular dichroism (CD) spectra of these biaryl dicarboxylic acids were also revealed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (4253K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4253K) Full view HTML -
Yoshihiro Sohtome, Mikiko Sodeoka2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 616-623
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialControlling catalytic asymmetric space has received increasing attention for the on-demand synthesis of chiral molecules of interest. However, the identification of the key parameters controlling the stereo-determining step in transition metal catalysis is challenging and involves the thorough characterization of the rate- and stereo-determining transition state(s). In this paper, we describe the computational analysis of the (3 + 2) cycloaddition of Ni(II)–enolate with cyclic (E)-nitrone to provide a comprehensive analysis of how the bond-forming processes are regulated in the two-electron manifold in the triplet state. Our molecular orbital analysis, in particular, reveals the occurrence of the singly occupied molecular orbital–highest occupied molecular orbital (SOMO–HOMO) level inversion in the Ni(II)–enolate. Further, distortion and interaction analysis are also used to explain the substrate-dependent diastereodivergence in this reaction by alternating the structure of the nitrone. Using a range of computational analyses, we show that the rate- and stereo-determining step in the (3 + 2) cycloaddition of (E)-nitrone is regulated integrally by (1) isomerism of the octahedral Ni(II) complex, (2) E/Z isomerism of the Ni(II)–enolate, and (3) steric repulsion between the reactants and ligand.
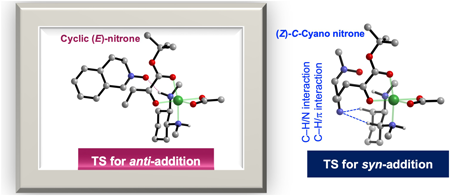 View full abstractDownload PDF (2380K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2380K) Full view HTML
-
Ayako Tabuchi, Fumihiko Ogata, Megumu Toda, Masashi Otani, Takehiro Na ...2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 624-627
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we evaluate the desorption or recovery capacity of chromium(VI) ions using desorption solutions containing sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or sodium sulfate (Na2SO4). A complex hydroxide of nickel–aluminum–zirconium (NAZ) was prepared as the adsorbent for the removal of chromium(VI) ions. The results from repeated adsorption/desorption experiments on chromium(VI) ions using NAZ complex hydroxide were evaluated. The desorption percentage of chromium(VI) ions increased with the increase in the concentration of NaOH or Na2SO4 in the desorption solution. The determined optimal concentration of NaOH or Na2SO4 in the desorption solution was 10 mmol/L under the used experimental conditions. After three adsorption–desorption cycles, the recovery percentages of chromium(VI) ions using NaOH and Na2SO4 were 60% (total amounts adsorbed and desorbed were 102 and 61 mg/g, respectively) and 75% (total amounts adsorbed and desorbed were 96 and 72 mg/g, respectively), respectively. Additionally, we confirmed the existence of chromium on the surface of the NAZ complex hydroxide. After three adsorption/desorption cycles, the crystal structure of the NAZ complex hydroxide was maintained. These results indicated the potential of the NAZ complex hydroxide using a desorption solution containing NaOH or Na2SO4 for the recovery of chromium(VI) ions.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1252K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1252K) Full view HTML
-
The Effect of Cellulose Nanofibers on the Manufacturing of Mini-Tablets by Direct Powder CompressionShohei Nakamura, Mizuno Nakura, Takatoshi Sakamoto2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 628-636
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMini-tablets (MTs) contain a small amount of active pharmaceutical ingredients in one small tablet. MTs are advantageous because they can be fine-tuned according to the age and weight of pediatric patients and they are easy for children and the elderly to swallow. However, there are manufacturing concerns such as the difficulty in achieving both hardness and disintegration of a small tablet and it is difficult to keep the tablet weight and drug content consistent in MTs because the mold used for its production is special. In this study, we aimed to determine if an additive such as cellulose nanofibers (CNF), which has been studied in various fields in recent years, could be used to manufacture MTs without difficulties. In this study, an MT was manufactured using a rotary tableting press with a compression force of 2, 5, and 8 kN, and the weight variation, drug content variation, tensile strength, friability, disintegration time, and drug dissolution were evaluated. Of note, the tensile strength of MTs produced with a compression force of ≥5 kN was ≥1.3 MPa, which was comparable to that of an ordinary tablet with an 8 mm diameter and a hardness of ≥30 N. The disintegration time of the MT which was 20–30% CNF was ≤30 s at any compression force. MTs with CNF showed similar disintegration to MTs with other common disintegrants. Therefore, we found that CNF is a functional additive capable of manufacturing MTs by direct powder compression which has both strength and disintegration.
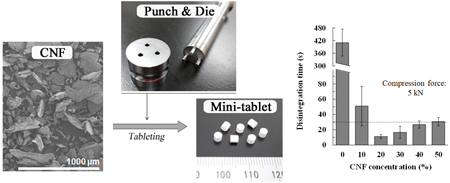 View full abstractDownload PDF (1835K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1835K) Full view HTML -
Jing Wang, Liwei Huang, Xi Chen, Yangchen Yuan, Juan Sun, Meng Yang2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 637-641
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHuman epidermal growth factor (EGFR) is an important target for antitumor drug research. A series of novel quinazolinone derivatives were synthesized and developed as potent inhibitors of EGFR. The results showed that most of the aimed compounds had potential anti-tumor cell proliferation activities. Some compounds were tested for their EGFR inhibitory activity. Especially, compound 6d showed the most potent antitumor activity with IC50 values of 1.58 µM against human breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines and exhibited the most potent EGFR inhibitory activity with IC50 of 0.77 µM. Docking simulation was performed to position compound 6d into the EGFR active site to determine the probable binding conformation.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2924K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2924K) Full view HTML -
Xiang Li, Qing Wang, Dianwen Zhang, Di Wu, Ning Liu, Tianli Chen2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 642-649
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: July 12, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialEpilepsy treatment with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is usually requires for many years. Q808 is an innovative antiepileptic chemical. It exerts effective antiepileptic effect against various epilepsy models. Exploring the gene transcriptomic profile of long-term treatment of Q808 is necessary. In the present study, hippocampus RNA-sequencing was performed to reveal the transcriptome profile of rats before and after treatment of Q808 for 28 d. Results confirmed 51 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between Q808 and healthy control groups. Gene cluster analysis showed that most upregulated DEGs linked to response to drug and nucleus, most downregulated DEGs linked to locomotory, neuronal cell body, and drug binding. Most of DEGs were enriched in the signaling transduction, substance dependence, nervous system, and neurodegenerative disease pathways. Furthermore, quantitative real-time PCR analysis confirmed that Q808 significantly increased the expression of neuroprotective genes, such as Mdk, and decreased the mRNA levels of Penk, Drd1, and Adora2a, which are highly expressed in epilepsy models. In addition, Q808 decreased the mRNA expression of Pde10A and Drd2, which are known to be closely associated with schizophrenia. Our study may provide a theoretical basis to explore the effect of Q808 on the susceptibility to epilepsy and other neurological diseases.
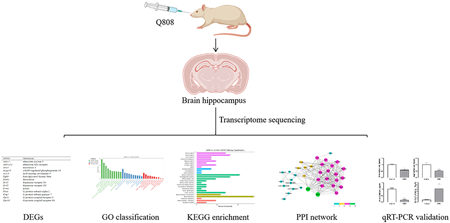 View full abstractDownload PDF (3635K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3635K) Full view HTML -
 Takeo Sakai, Rina Takenaka, Yumika Koike, Atsunori Hira, Yuji Mori2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 650-661
Takeo Sakai, Rina Takenaka, Yumika Koike, Atsunori Hira, Yuji Mori2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 650-661
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe acetamide moiety is a general functional group present in many natural and pharmaceutical products. Herein, we report two new reagents, p-methoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (PM-BENAC-K) and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (2,4-DM-BENAC-K), which are refined versions of the benzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (BENAC-K). These compounds, which we reported as simple equivalents of N-acetamide nucleophiles, are stable and easy-to-handle powders that react with a variety of alkyl halides and sulfonates to afford substituted products in good yields. The products were transformed into N-alkylacetamides after p-methoxybenzyloxycarbonyl (Moz) or 2,4-dimethoxybenzyloxycarbonyl (Dmoz) cleavage under mild acidic conditions. The acetyl groups in the substituted products of PM- and 2,4-DM-BENAC-Ks were removed using K2CO3 in methanol to afford Moz- and Dmoz-protected amines, respectively. Hence, the new BENAC-Ks acted as versatile equivalents of both N-acetamide and Moz/Dmoz-protected nitrogen nucleophiles and can be used in synthetic studies of natural and pharmaceutical products.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThis report describes the synthesis of novel dual-purpose reagents, p-methoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (PM-BENAC-K) and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl N-acetylcarbamate potassium salt (2,4-DM-BENAC-K). The BENAC-Ks were stable colorless powders synthesized via a simple three-step procedure without column chromatography, which can be easily scaled-up. The BENAC-Ks reacted with various alkyl halides and sulfonates to form substituted products that were converted to N-alkylacetamides via acid-mediated deprotection. Simultaneously, p-methoxybenzyl and 2,4-dimethoxybenzyl carbamates were obtained via base-mediated deacetylation. Thus, the BENAC-Ks are worth remembering as simple reagents for synthesis of acetamides and benzyl carbamates.
Download PDF (2471K) Full view HTML -
 Jukiya Sakamoto, Mariko Kitajima, Hayato Ishikawa2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 662-668
Jukiya Sakamoto, Mariko Kitajima, Hayato Ishikawa2022Volume 70Issue 9 Pages 662-668
Published: September 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA number of alkaloids found in Mitragyna species belonging to the Rubiaceae family have been shown to have potent biological activity such as analgesic properties. Here, we report the asymmetric total syntheses of mitragynine, speciogynine, and 7-hydroxymitragynine, which are classified as corynantheine-type monoterpenoid indole alkaloids, isolated from Mitragyna speciosa. These syntheses were accomplished within 12 steps and in >11% total yield from commercial 3-(trimethylsilyl)propanal using an organocatalytic anti-selective Michael reaction and bioinspired transformations.
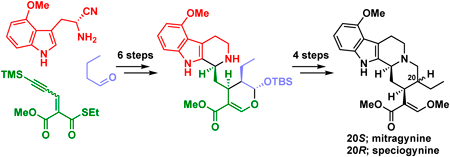 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickMitragyna speciosa, which belongs to the Rubiaceae family, contains several corynantheine-type monoterpenoid indole alkaloids that exhibit potent biological activity, including analgesic activity. In this article, the authors reported the asymmetric total syntheses of such Mitragyna alkaloids mitragynine, speciogynine, and 7-hydroxymitragynine. These syntheses were accomplished via asymmetric organocatalytic Michael reaction, diastereoselective Pictet-Spengler cyclization, and biogenetically inspired chemical transformations within 12 steps and in >11% overall yield from commercially available materials. These syntheses will strongly promote the structure-activity relationship study of Mitragyna alkaloids.
Download PDF (746K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|