
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Kentaro Takayama2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 413-419
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe enhancement of basic research based on biomolecule-derived peptides has the potential to elucidate their biological function and lead to the development of new drugs. In this review, two biomolecules, namely “neuromedin U (NMU)” and “myostatin,” are discussed. NMU, a neuropeptide first isolated from the porcine spinal cord, non-selectively activates two types of receptors (NMUR1 and NMUR2) and displays a variety of physiological actions, including appetite suppression. The development of receptor-selective regulators helps elucidate each receptor’s detailed biological roles. A structure–activity relationship (SAR) study was conducted to achieve this purpose using the amidated C-terminal core structure of NMU for receptor activation. Through obtaining receptor-selective hexapeptide agonists, molecular functions of the core structure were clarified. Myostatin is a negative regulator of skeletal muscle growth and has attracted attention as a target for treating atrophic muscle disorders. Although the protein inhibitors, such as antibodies and receptor-decoys have been developed, the inhibition by smaller molecules, including peptides, is less advanced. Focusing on the inactivation mechanism by prodomain proteins derived from myostatin-precursor, a first mid-sized α-helical myostatin-inhibitory peptide (23-mer) was identified from the mouse sequence. The detailed SAR study based on this peptide afforded the structural requirements for effective inhibition. The subsequent computer simulation proposed the docking mode at the activin type I receptor binding site of myostatin. The resulting development of potent inhibitors suggested the existence of a more appropriate binding mode linked to their β-sheet forming properties, suggesting that further investigations might be needed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (839K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (839K) Full view HTML
-
 Nuttapon Apiratikul, Kanlayanee Sriklung, Kulvadee Dolsophon, Pattamap ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 420-426
Nuttapon Apiratikul, Kanlayanee Sriklung, Kulvadee Dolsophon, Pattamap ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 420-426
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 26, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCationic liposomal formulations of the telomeric G-quadruplex stabilizing ligand, 13-(2-naphthylmethoxy)berberine bromide (1), have been developed with the purpose of delivering 1 into the nucleus of cancer cells for potential telomere targeting. Berberine derivative 1 was encapsulated in various cationic lipids 2–4 by the thin film evaporation method; these lipids are cationic after amine protonation. The most appropriate liposomal berberine formulation was that of 1 and the cholesterol derived cationic lipid 4 in a weight ratio of 1 : 20 with 76.5% encapsulation efficiency of 1. Cellular uptake studies in the HeLa and HT-29 cancer cells lines showed that the liposomal berberine derivative uptake in the cells was higher and more stable than for berberine derivative 1 alone while free 1 was completely decomposed in the cells within 60 min exposure to the cells. Anticancer activity of the liposomal berberine derivative 1 based on 4 was greater than that for the free berberine derivative 1 in the MCF-7, HeLa and HT-29 cell line by 2.3-, 4.9- and 5.3-fold, respectively, and also, interestingly, superior to the anticancer drug doxorubicin against the HT29 cancer cell line.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThis paper reports the successful use of a cationic liposomal-encapsulated novel 13-substituted berberine derivative for the targeted cell uptake and delivery to the cancer cell nucleus. Additionally the liposome also assists with stabilization of the selectively toxic anticancer berberine derivative with respect to oxidative cleavage in solution. Liposomes derived from a cholesterol-based lipid with a polar side chain which would become cationic after amine protonation, were of particular interest. Enhanced cancer cell toxicity was seen in vitro with the cationic liposomal formulation of the berberine derivative possibly via inhibitory interactions with the cell’s telomere/telomerase system.
Download PDF (3700K) Full view HTML -
Liu Han, Jiahuan Liu, Yuxin Yang, Huifeng Zhang, Liancong Gao, Yawei L ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 427-434
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: April 13, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn the present study, four novel ginsenosides fatty acid and aromatic acid derivatives were designed and synthesized, and their cytotoxic effects on human ovarian carcinoma cells (SKOV3) were assessed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The results demonstrated that all derivatives inhibited SKOV3 cell growth, and Compound 3 showed the most outstanding anti-proliferative effect on SKOV3 cells. The IC50 value of Compound 3 was 33.8 ± 2.21 µM, less than half of that of cis-platinum (70.1 ± 7.64 µM). Subsequent analysis revealed that Compound 3 could promote SKOV3 cell apoptosis, and the percentage of apoptotic cell population increased with increasing Compound 3 concentrations. In addition, the expression ratios of Bax/Bcl-2, cleaved-Caspase-3/Caspase-3 and cleaved-Caspase-9/Caspase-9 were gradually elevated in Compound 3-treated SKOV3 cells compared with control cells. Furthermore, translocation of Bax to mitochondria was associated with the release of Cytochrome C. Molecular docking analysis revealed three hydrogen-bonds existed in Compound 3 with poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) receptor (PDB code: 5DSY), which may be the target of the anti-ovarian cancer effect of Compound 3. Altogether, our study indicates that Compound 3 induces SKOV3 cell apoptosis via reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent mitochondrial pathway, and can serve as an anti-cancer agent for treating ovarian carcinoma.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (8111K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (8111K) Full view HTML -
 Kazutada Ikeuchi, Shota Haraguchi, Hidetoshi Yamada, Keiji Tanino2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 435-442
Kazutada Ikeuchi, Shota Haraguchi, Hidetoshi Yamada, Keiji Tanino2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 435-442
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPicrotoxinin, coriamyrtin, and tutin are representative natural products classified as picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes and they function as strong neurotoxins. Because they possess a cis-fused 5,6-ring skeleton with a highly congested functionalization, organic chemistry researchers have pursued the development of a stereoselective synthesis method for such skeleton. This study aims to stereoselectively synthesize the cis-fused 5,6-ring skeleton with two tetrasubstituted carbons at both angular positions using a model compound. The results revealed that the desymmetrization of the 2-methyl-1,3-cyclopentanedione moiety via the DL-proline-mediated intramolecular aldol reaction of a pentanal derivative bearing an isopropenyl group and the five-membered ring at the 3- and 5-position, respectively, provided the desired cis-fused skeleton. This reaction can construct four contiguous stereogenic centers of the bicyclic skeleton with the two angular positions in good yield with high stereoselectivity. Further, this reaction was applied to the kinetic resolution of the racemate using L-proline, providing the enantiomeric pure aldol product with the desired skeleton. This method can be utilized for total synthesis of picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes.
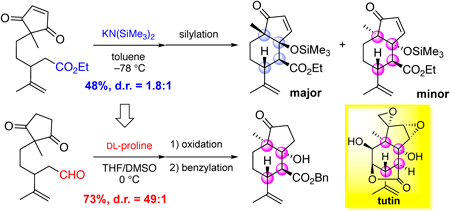 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes a stereoselective synthesis of a cis-fused 5,6-ring skeleton in picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes. This bicyclic skeleton is a synthetic challenging structure because of the presence of multiple consecutive stereocenters including two tetrasubstituted carbons at the angular positions. The authors developed a synthetic method of the core structure via DL-proline-mediated intramolecular aldol reaction accompanied with the desymmetrization of the 2-methyl-1,3-cyclopentanedione moiety and the construction of four contiguous stereocenters. This reaction can be also applied to the kinetic resolution using L-proline, implying that the established method would be useful for the synthesis of natural products classified as picrotoxane-type sesquiterpenes.
Download PDF (827K) Full view HTML -
Shinya Kimura, Sota Mori, Masashi Yokoya, Masamichi Yamanaka2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 443-447
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLUrea derivatives 1 and 2, synthesized from adenosine, were designed as low-molecular-weight gelators. Hydrophobic groups have been introduced into all or part of the hydroxy groups of the hydrophilic ribose moiety of 1 and 2 to control the solvophilicity of the molecules and their aggregates. Compound 2 selectively formed supramolecular gels in halogenated solvents such as chloroform and 1,2-dichloroethane. The supramolecular gel of 2 and chloroform was thermally stable and its gel-to-sol phase transition temperature was higher than the boiling point of chloroform. The physical properties of the supramolecular gel were investigated by determining its viscoelastic properties using a rheometer. The supramolecular gel realized multiple stimuli-responsive reversible gel–sol phase transitions. The supramolecular gel showed reversible phase transition by repeated warming–cooling cycles accompanying with the gel–sol transitions. The supramolecular gel could undergo five repeated mechano-responsive gel–sol transitions. Gel-to-sol phase transition could also be achieved by adding various anions to the supramolecular gel, such as tetrabutylammonium fluoride. Regelation was realized by adding boron trifluoride etherate to the fluoride ion containing sol. Addition of methanol to the supramolecular gel also induced gel-to-sol phase transition. Regelation was realized by adding molecular sieves 4 Å to the suspension.
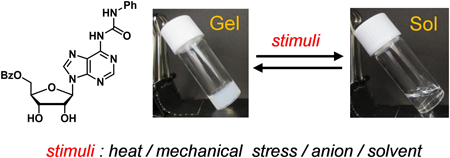 View full abstractDownload PDF (1137K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1137K) Full view HTML -
 Nguyen Phu Quy, Bui Thi Buu Hue, Kiep Minh Do, Ha Thi Kim Quy, Tran Qu ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 448-453
Nguyen Phu Quy, Bui Thi Buu Hue, Kiep Minh Do, Ha Thi Kim Quy, Tran Qu ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 448-453
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo series of 2-substituted benzimidazole conjugated 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivatives were designed, synthesized and evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against the three human cancer cell lines (cervical cancer (HeLa), breast cancer (MCF-7) and lung cancer (A549)). As the results 14 compounds demonstrated consistent to stronger cytotoxicities compared to the control 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) towards the tested cell lines including 4c (HeLa); 4b, 4e, 4h, 7i–j, 7m–n, 7s (MCF-7); 7b (MCF-7, A549); 7h (HeLa, MCF-7); and 4d, 4i, 7c (HeLa, MCF-7, A549), with the IC50 ranging from 2.7 to 38 µM. Notably, compound 4b illustrated almost 5-fold activity against the MCF-7 while 4d, 4i were 9- and 8-fold (HeLa), 4.5- and 13-fold (MCF-7), 4.7- and 4-fold (A549) increase in activity compared to 5-FU, respectively, and were found as lead compounds. These findings suggest that compounds 4b, 4d and 4i merit further characterization and can serve as promising scaffolds in the discovery of new potent anticancer agents.
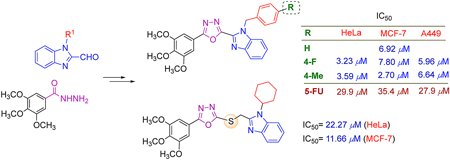 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickMany drugs being used in chemotherapy of cancer has nitrogen-containing heterocyclic moieties as their basic structure, and the authors extensively focused on the 1,3,4-oxadiazole and benzimidazole scaffolds. In this article, two series of novel hybrids combining the 1,2-disubstituted benzimidazole and 1,3,4-oxadiazole or thioether linked 1,3,4-oxadiazole were designed and successfully synthesized. The in vitro cytotoxicity bioassays came up with the discovery of three lead compounds which displayed 4.5-13 fold increase in activity compared to 5-FU against the three human cancer cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7, A549), meriting further characterization and serving as promising scaffolds in the discovery of new potent anticancer agents.
Download PDF (1134K) Full view HTML
-
Natsumi Hashimoto, Shigeru Tatsuta, Hisashi Kitamura, Misa Katsuyama, ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 6 Pages 454-457
Published: June 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 19, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBoth iontophoresis (IP) and electroporation (EP) can be utilized to increase the penetration of relatively high molecular pharmaceutical and/or cosmeceutical compounds into the stratum corneum (SC), the uppermost layer of the skin. However, few reports exist on which molecular weights are capable of penetrating the SC, although low molecular compounds of less than 500 Da have been found to readily permeate the skin barrier. In our investigation, we applied fluorescein amine-labeled sodium hyaluronate to porcine aural skin after treatment by IP alone or EP + IP. Each layer of the SC was then tape stripped several times. The stripped SC sheets were observed using a confocal laser scanning microscope to determine the relative amounts of sodium hyaluronate present. The results confirmed that the molecular weight of sodium hyaluronate that penetrated the SC was higher with EP + IP than with IP alone. A high correlation was also established between the quantity of sodium hyaluronate that penetrated and its molecular weight following combined EP + IP treatment.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1098K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1098K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|