
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Kounosuke Oisaki2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 907-919
Kounosuke Oisaki2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 907-919
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
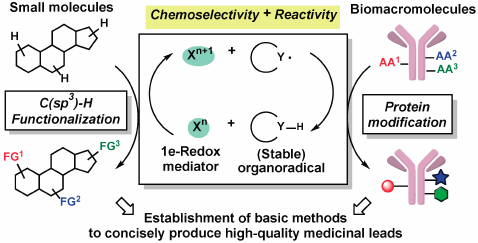
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo conduct organic synthesis in the field of pharmaceutical science, methodologies that can easily and quickly supply compounds with high drug-likeness are highly desirable. Based on the original catalyst design concept “Radical-Conjugated Redox Catalysis (RCRC)” established during my research, various C(sp3)–H functionalizations and protein modifications have been developed, taking advantage of the high reactivity and chemoselectivity of the single-electron transfer process. This review focuses on the eight-year research efforts by my collaborators and me, from conception to results.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickFor organic synthesis in the field of pharmaceutical sciences, methodologies that can easily and quickly supply compounds with high drug-likeness is highly desirable. Based on the original catalyst design concept "Radical-Conjugated Redox Catalysis (RCRC)" established during author's research, various C(sp3)-H functionalizations and protein modifications have been developed, taking advantage of high reactivity and chemoselectivity of single-electron transfer process. This review will focus on the research concept and efforts over eight years of the author and his collaborators.
Download PDF (4755K) Full view HTML
-
 Tomoki Niwa, Kiyoshi Ujiie, Hitomi Sato, Hiromichi Egami, Yoshitaka Ha ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 920-922
Tomoki Niwa, Kiyoshi Ujiie, Hitomi Sato, Hiromichi Egami, Yoshitaka Ha ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 920-922
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAsymmetric fluorination of cyclic tetrasubstituted alkenes with a pendant amide group was investigated under dianionic phase-transfer catalysis. Fluorination proceeded with high face selectivity, affording the corresponding allylic fluorides with a chiral tetrasubstituted carbon center with up to 97% enantiomeric excess (ee). It should be noted that deprotonative fluorination occurred mainly in preference to intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the amide group.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickAllylic fluoride is a useful synthetic intermediate for the preparation of various organofluorine compounds. The authors demonstrated a highly enantioselective fluorination of cyclic tetrasubstituted alkenes with a pendant amide group using their dianionic phase-transfer catalyst. The deprotonative fluorination mainly proceeded in preference to the intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the amide group, and the corresponding allylic fluorides with a chiral tetrasubstituted carbon center were obtained with up to 97% ee.
Download PDF (463K) Full view HTML
-
Narender Malothu, Umasankar Kulandaivelu, Malathi Jojula, Shravan Kuma ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 923-931
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo series of 3-substituted-7-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[4′,3′:4,5] thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (6a–k) and 3-substituted-7,2-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropyrido[4′,3′:4,5]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one (7a–k) derivatives were synthesized and characterized using spectral data i.e., IR, 1H-, 13C-NMR, Mass and CHN elemental analyses. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for antibacterial activity against each of two strains of Gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae) bacteria and antimycobacterial activity screened against two strains i.e., Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) H37Rv and an isoniazid-resistant clinical sample. Further to validate potentiality of our design was analyzed using molecular docking studies by taking crystal structure of MTB pantothenate synthetase (MTB-PS) (PDB: 3IVX). In this study, some compounds 6k (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC): MIC-22 µM), 7d (MTB: MIC-22 µM) and 7k (MTB: MIC-11 µM) showed potential antibacterial and antimycobacterial activities.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (577K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (577K) Full view HTML -
Masanori Kobayashi, Daisuke Shinozuka, Hiromu Kondo, Kazuhiro Sako, Ka ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 932-938
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIt is well known that high-pressure carbon dioxide (CO2) lowers the glass transition temperature (Tg) of polymers. We therefore investigated whether Tg depression of high-pressure CO2 results in interparticle bridging of a polymer and the tablet characteristics that makes the manufacture of an orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) possible. Copolyvidone (Kollidon®) and polyvinyl caprolactam–polyvinyl acetate–polyethylene glycol graft copolymer (Soluplus®) were examined and found to exhibit a large Tg depression. Placebo ODTs were prepared and hardness, disintegration rate, porosity, and change in thickness and appearance were evaluated before and after the high-pressure CO2 treatment. This enabled the establishment of the optimal conditions for pressure, temperature, and treatment time under pressure. Experimental results showed that it was possible to manufacture ODTs comprising Kollidon® as a water-soluble polymer with CO2 treatment under the suitable conditions such as temperature at 45°C, pressure lower than 8 MPa, and a treatment time shorter than 30 min, which is a new ODT manufacturing process called “Carbon Dioxide Assisted Tablet Formation Scheme” (CATS). In comparison to the conventional processes, which require high temperatures or humidity, CATS is expected to be applicable to drugs that are unstable at high temperature and humidity, and to functional drug particles used for bitter taste masking, sustained release, and other uses.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1781K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1781K) Full view HTML -
Mohammed K. Abd elhameid, Noha Ryad, Al-Shorbagy MY, Manal R. mohammed ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 939-952
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
Advance online publication: August 14, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA new series of pyridine and pyrimidine derivatives is designed and synthesized as potential antitumor molecules. The tested compounds show promising in vitro cytotoxic activity against HL-60 cell line as eight compounds: 4, 6, 11, 13, 14, 15, 18 and 21 exhibit potent cytotoxic activity in sub-micromolar concentration higher than the combretastatin A4 (CA-4). Compound 21 shows a cytotoxic activity 5-fold more potent than CA-4 on HL-60 cells. DNA-Flow cytometry cell cycle analysis and annexin-V assay on HL-60 cells show that compounds 4, 18 and 21 exhibit potent cell growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and pro-apoptotic inducing activities. The percentage inhibition assay of β-tubulin polymerization on HL-60 cells shows that the antitumor activity of the tested compounds appears to correlate well with its ability to inhibit β-tubulin polymerization. In addition, enzyme-linked immunosorbene assay (ELlSA) measurement for compound 21 shows apoptotic inducing activities through significant up regulation of p53, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 proteins parallel to down regulation of the level of survivin proteins.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1436K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1436K) Full view HTML -
Suhair H. Jasim, Ghassan M. Abu Sheikha, Haneen M. Abuzaid, Tariq M. A ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 953-958
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA new series of imidazole-5-carboxamide derivatives were prepared and tested for their anti-hyperlipidemic activity in Triton-WR-1339-induced hyperlipidemic Wistar rats. The purpose of this research was to improve benzophenone carboxamides water solubility maintaining at the same time the antihyperlipidemic activity. Compounds 4, 6, 10, and 11 were synthesized through a coupling reaction between imidazoles-5-carbonyl chloride and amino benzophenones. The tested animals (n=48) were divided into six groups: the first group (hyperlipidemic control group; HCG) received an intraperitoneal injection (i.p.) of (300 mg/kg) Triton WR-1339. The second group received i.p. injection of Triton WR-1339 followed by an intra-gastric administration of bezafibrate (100 mg/kg) (bezafibrate; BF). The third, fourth, fifth, and sixth groups received i.p. injection of Triton WR-1339 followed by an intra-gastric administration of (30 mg/kg) of compounds 4, 6, 10, and 11, respectively. At a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight compounds 4, 6, 10, and 11 significantly (p<0.0001) decreased the plasma level of triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and total cholesterol (TC) levels after 18 h of treatment. Additionally, compounds 4, 6, 11 and bezafibrate (100 mg/kg) significantly (p<0.0001) increased the plasma level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, which is known for its preventive role against atherogenesis. These results demonstrate the possibility of pharmacokinetic properties improvement maintaining the biological and pharmacological profile of these compounds.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (424K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (424K) Full view HTML -
Hiroaki Todo, Mai Tamura, Takashi Uchida, Miyuki Kurumada, Anzu Motoki ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 959-966
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlthough many in silico models were reported to predict the skin permeation of drugs from aqueous solutions, few studies were founded on the in silico estimation models for the skin permeation of drugs from neat oil formulations and o/w emulsions. In the present study, the cumulative amount of a model lipophilic drug, flurbiprofen (FP), that permeated through skin was determined from 12 different kinds of ester oils (Qoil) and an in silico model was developed for predicting the skin permeation of FP from these ester oils. Thus, the obtained Qoil values were well predicted with the FP solubility in the oils (Soil), the amount of FP uptake into the stratum corneum (SCoil) and molecular descriptors of dipolarity/polarizability (π2H) and molecular density. This model suggests that the thermodynamic activities of FP both in the formulations and skin are the key factors for predicting the skin permeation of FP from the ester oils. In addition, a high linear relationship was observed in the double-logarithm plots between the Qoil and the cumulative amount of FP permeated through skin from 20% ester oil in water emulsion (Qemul20%). Furthermore, the skin permeations of FP from 5 and 10% ester oil in water emulsions, Qemul5% and Qemul10%, respectively, were also predicted by the horizontal translation of the y-axis intercept of the liner equation for the relation between the Qoil and Qemul20%. These prediction methods must be helpful for designing topical oily and/or o/w emulsion formulations having suitable and high skin permeation rate of lipophilic drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (967K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (967K) Full view HTML -
Abdelsattar M. Omar, Tamer M. Abdelghany, Mohamed S. Abdel-Bakky, Abdu ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 967-975
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
Advance online publication: July 25, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe 2-styryl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one might be considered as a system with isosteric properties similar to trans-cinnamaldehyde (styrylaldehyde), a safe natural compound that exhibited interesting activities against various cancers. We synthesized a series of compounds that differ structurally in having different alkyl, aryl and heterocyclic substituents at the N3 position of the 2-styryl-4-imidaolone pharmacophore. The compounds were assayed for their cytotoxicity against both cancer and normal cell lines. In addition, their cellular mechanism of action as reactive oxygen species (ROS) inducers were investigated. Many of the synthesized compounds showed higher activities on colon, breast and hepatic cancer cell lines than the parent trans-cinnamaldehyde. Compounds 3a and 3e showed selective antiproliferative activity against cancer cell lines at low micromolar to sub-micromolar IC50 value. Compounds were extremely less toxic on normal cell lines baby hamster kidney fibroblasts (BHK) and human lung tissue fibroblast (WI-38). Similar to trans-cinnamaldehyde, the colon cancer cell cycle analysis indicated cell cycle changes consistent with increased oxidative stress leading to apoptosis. Compound 3e caused elevation of all cell oxidative indicators of ROS such as a decrease in reduced glutathione, increased malondialdehyde and suppression of catalase and superoxide dismutase activities. Dihydroethidium staining, nuclear fragmentation and increased caspase-3 further confirmed extensive apoptotic induction due to ROS accumulation upon treatment of human colon adenocarcinoma (HCT116) cells with compounds 3a and 3e. Changes in human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF7) cells were less revealing for ROS induction and increased oxidative stress. Conclusion: The compounds represent an example of efficient rescaffolding of a natural compound to a highly potent drug-like analogues.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2735K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2735K) Full view HTML -
Shoko Hara, Yasumasa Hara, Midori A. Arai, Yoko Kusuya, Hiroki Takahas ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 976-982
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA new aminocyclitol derivative, designated nabscessin C (1), was isolated from Nocardia abscessus IFM 10029T. Nabcessin C is an isomer of nabscessins A (2) and B (3) with different positioning of the acyl group. Absolute configuration of nabscessin A was determined by conversion into the 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosamine pentaacetyl derivative (4) by hydrolysis and acetylation of 2. The biosynthetic pathway of nabscessins is proposed based on gene expression analysis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (692K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (692K) Full view HTML -
SiPeng Wu, Ning Wang, Qun He, GuoJie Chang, Sai Wang Seto, Dennis Chan ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 983-991
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA novel strategy for screening active components in traditional Chinese medicines (TCM) using living cells and HPLC and GC analysis are proposed. The hypothesis is that when cells are incubated with the extract of Tongqiao Huoxue Decoction (TQHXD), a famous ancient prescription in TCM, the potential active components in the TQHXD should selectively combine with the cells, and the cell-combining components would be detectable in the extract of denatured cells. The identities of the cell-combining components could be determined by HPLC and GC analysis. Using the proposed approach, two characteristic active ingredients binding to the membrane of the PC12 cells are indicated. In the fingerprint of HPLC, there are two characteristic peaks. One active ingredient with its retention time was at around 70 min had been identified as muscone by HPLC, GC, which came from Moschus herb, the other active ingredient may come from the Allium fistulosum, its structure needs further research. Also, the protective effect of muscone on PC12 cells induced by Oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) had been explored. These results show that the pretreatment with muscone on PC12 cells observably increased cell viability, reduced the release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and cell apoptosis. Combined with the pharmacodynamic study of muscone on neuroprotective effect, it could be identified as one of the effective components in TQHXD.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2401K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2401K) Full view HTML -
Heba Kamal Abd El-Mawgoud, Saad Ramadan Atta-Allah, Magdy Mohamed Hemd ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 992-998
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe reaction of thiophene-2-carbonyl isothiocyanate 2 with thioglycolic acid gave 2-(thiophene-2-carbonylcarbamothioylthio)acetic acid 3. Compound 3 was subjected to some selected reactions with sulphuric acid as well as benzaldehyde, piperonal and isatin under different reaction conditions. The products obtained were new derivatives of thiazole and annulated thiazole derivatives bearing thiophene moiety in some cases. The structures of the new synthesized compounds were confirmed on the basis of their microanalytical and spectral properties. Some compounds were tested for their antimicrobial activity against six selected microorganisms using the standard antibacterial Gentamycin and antifungal Ketoconazole as references.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (483K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (483K) Full view HTML -
 Tsuyoshi Katayama, Shinya Uchida, Chiaki Kamiya, Shimako Tanaka, Yasuh ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 999-1005
Tsuyoshi Katayama, Shinya Uchida, Chiaki Kamiya, Shimako Tanaka, Yasuh ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 999-1005
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe examined the amlodipine dissolution from orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) in vivo in the human oral cavity. Additionally, 5 different in vitro short dissolution test methods (Tricorptester, magnetic stirrer, rotating injection syringe, paddle apparatus, shaking) were used to evaluate dissolution and the results were compared to those obtained with the human volunteers. Various amlodipine ODTs with different levels of physical masking effectiveness were manufactured using the RACTAB® technique. Quantitative findings showed that amlodipine dissolution from ODT was dependent on time in the oral cavity and the amount of coating applied for physical masking. We also found that dissolution in the oral cavity was best correlated to that in in vitro short dissolution tests with a time period of 30 s. For more detailed evaluations, mean prediction error, mean absolute error, and root mean square error values were calculated, each of which was lowest with the Tricorptester method among all of the investigated test methods. Our results indicate that mimicking of the inside of the human oral cavity is accurate with a testing time of 30 s, while the Tricorptester method was the most preferable of all in vitro tests investigated in this study.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe amlodipine dissolution from orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) in vivo in the human oral cavity was examined. Various amlodipine ODTs with different levels of physical masking effectiveness were manufactured. The present results are the first to show that drug dissolution from ODT is dependent on time in the oral cavity and coating amount. The mimicking of the inside of the human oral cavity is accurate with a testing time of 30 s, while the Tricorptester method was the most preferable of all in vitro short dissolution test methods investigated in this study.
Download PDF (703K) Full view HTML -
 Shinji Kitagaki, Shunsuke Murata, Kisaki Asaoka, Kenta Sugisaka, Chisa ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 1006-1014
Shinji Kitagaki, Shunsuke Murata, Kisaki Asaoka, Kenta Sugisaka, Chisa ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 1006-1014
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCentrally chiral bisoxazolines connected directly to a planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophane backbone were synthesized and evaluated as asymmetric ligands in Cu-catalyzed intermolecular ethanolic O–H insertion reactions of α-diazo esters. The reactivities and enantioselectivities of Cu complexes of the synthesized bisoxazoline ligands were lower than those of ligands without central chirality. However, planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophane-based bisoxazoline ligands with an inserted benzene spacer that had a sterically demanding isopropyl substituent showed good enantioselectivities in inter- and intramolecular aromatic O–H insertion reactions, without the aid of central chirality.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes the development of the planar chiral [2.2]paracyclophane-based bisoxazoline (PCP-Box) ligands for Cu-catalyzed O-H insertion reactions of α-diazo esters. C2-symmetric PCP-Box ligands, in which the achiral oxazoline unit is located at the meta-position of the benzene spacer having a bulky substituent at the para-position, gave better levels of enantioselectivity in ethanolic O-H insertion than the spacer free PCP-Boxes with or without central chirality of the oxazoline rings. The former also showed good enantioselectivities in inter- and intramolecular aromatic O-H insertions.
Download PDF (1298K) Full view HTML
-
Taeho Lee, Hong Seop Moon, Seon Woong Kim, Jitendra Shrestha, Sang Mi ...2018Volume 66Issue 10 Pages 1015-1018
Published: October 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFTY720 is employed for the treatment of multiple sclerosis and exerts apoptotic effects on various cancers through protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activation. In compound 4, the dihydroxy head group of FTY720 was modified into dihydroxy phenyl group. The cell survival in compound 4 treated colorectal and gastric cancer cells was significantly reduced as compared with control, 34.6 and 25.1%, respectively. The docking study of compound 4 showed that the aromatic head group effectively binds to PP2A.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1897K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1897K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|