
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Ikuro Abe2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 823-831
Ikuro Abe2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 823-831
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
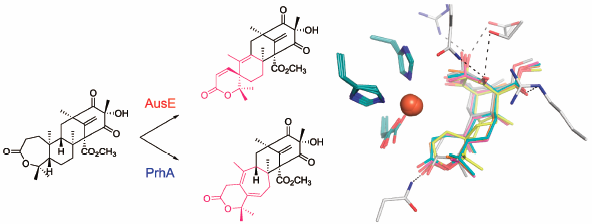
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis review summarizes the recent progress in research on the non-heme Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, which are involved in the biosynthesis of pharmaceutically important fungal meroterpenoids. This enzyme class activates a selective C–H bond of the substrate and catalyzes a wide range of chemical reactions, from simple hydroxylation to dynamic carbon skeletal rearrangements, thereby significantly contributing to the structural diversification and complexification of the molecules. Structure–function studies of these enzymes provide an excellent platform for the development of useful biocatalysts for synthetic biology to create novel molecules for future drug discovery.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe fungal meroterpenoid biosynthetic pathways exhibit an abundance of unusual chemistries and interesting enzyme reactions, including those of the multi-functional non-heme Fe(II)- and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases that perform selective C–H activation/functionalization with unusual substrate promiscuity and catalytic versatility. Structure–function studies of these remarkable enzymes provide an excellent platform for the development of useful biocatalysts for synthetic biology to create novel molecules for drug discovery.
Download PDF (5020K) Full view HTML
-
 Akinari Abe, Hiromichi Suzuki, Miyuki Saito, Hiroaki Todo, Kenji Sugib ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 832-836
Akinari Abe, Hiromichi Suzuki, Miyuki Saito, Hiroaki Todo, Kenji Sugib ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 832-836
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLRubbing actions are often conducted to apply topical formulations onto the skin. Although rubbing was found to increase the skin permeation of drugs, few reports have revealed whether rubbing enhanced either drug permeation through the stratum corneum (SC) or hair follicles (HFs) pathways, or through both. In the present study, we investigated the effects of rubbing on caffeine (CAF) distribution in the SC and HFs. The effect of rubbing direction on the skin penetration of CAF was also investigated. The skin concentration of CAF and its cumulative permeation amount were increased clearly by rubbing. More than six times higher CAF concentrations in the viable epidermis and dermis were observed 5 min after rubbing application compared with no rubbing. On the other hand, slightly increased CAF concentrations were observed in the SC, suggesting that CAF was delivered through the HF pathway by rubbing. Rubbing against the natural hair direction provided the highest skin permeation as well as skin concentrations. Changes in the morphology of the HF opening area might be related to the enhancement effect. These results may provide useful information to understand the effect of rubbing on the skin permeation of applied drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickRubbing actions are often conducted to apply topical formulations onto the skin. However, few studies have reported the reasons for the acceleration of drug permeation through skin after topical application with or without rubbing. In addition, no studies observed the effect of rubbing direction on the skin penetration-enhancement effects. In this paper, the authors investigated the effects of rubbing direction on the skin permeation and disposition of a model hydrophilic drug, caffeine. This paper provides useful information on the effect of rubbing action and rubbing direction on the skin permeation of topically applied drugs.
Download PDF (1427K) Full view HTML -
Panpan Wang, Hui Huang, Bing Chen, Ya Su, Peiying Shi, Hong Yao2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 837-847
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialDengzhan Xixin injection (DZXXI), a herbal product prepared from a Chinese herb called Erigeron breviscapus, is a classical and traditional therapeutic for cadiovascular diseases (CVDs), including coronary heart disease (CHD), angina, and stroke, etc. However, its potential pharmacology mechanism against CVDs remains unclear. In this paper, a systems pharmacology-based strategy is presented for predicting drug targets and understanding therapeutic mechanisms of DZXXI against CVDs. The main ingredients were identified by HPLC-diode array detector (DAD). The target fishing was performed on the PharmMapper Server (http://lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/). Potential targets were confirmed by two molecular docking tools, Sybyl-X 1.3 and Ledock to ensure the accuracy. The resulting target proteins were applied as baits to fish their related diseases and pathways from the molecular annotation system (MAS 3.0, http://bioinfo.capitalbio.com/mas3/) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). Network generation and topological analysis were performed in Cytoscape 3.6.0. 15 main ingredients from DZXXI were identified. Forty five putative drug targets and 50 KEGG pathways, which have highly relevance to the therapeutic effects of DZXXI against CVDs, were then obtained. The systems analysis suggested that DZXXI could attenuate cardiac fibrosis, regulate cardiac contractility, and preserve heart function in adverse cardiac remodeling; meanwhile DZXXI also could have the function of activating blood circulation and dilating blood vessels. DZXXI exerts its therapeutic effects on CVDs possibly through multi-targets including CMA1, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase (PAH), SRC, F7, etc., and multi-pathways including Focal adhesion, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, complement and coagulation cascades, Wnt signaling pathway, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, Renin-angiotensin system, etc.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5495K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5495K) Full view HTML -
Koichi Saito, Nami Hagiwara, Miho Sakamoto, Daigo Wakana, Rie Ito, Tom ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 848-854
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe degradation behavior of eight tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs; amitriptyline, amoxapine (AMX), imipramine, clomipramine, desipramine, doxepin, dothiepin, and nortriptyline) in artificial gastric juice was investigated to estimate their pharmacokinetics in the stomach. As a result, among the eight TCAs, only AMX was degraded in artificial gastric juice. The degradation was a pseudo first-order reaction; activation energy (Ea) was 88.70 kJ/mol and activation entropy (ΔS) was −80.73 J/K·mol. On the other hand, the recovery experiment revealed that the degradation product did not revert to AMX and accordingly, this reaction was considered to be irreversible. In the AMX degradation experiment, peaks considered to be degradation products A (I) and B (II) were detected at retention times of around 3 min and 30 min in LC/UV measurements, respectively. Structural analysis revealed that compound (I) was [2-(2-aminophenoxy)-5-chlorophenyl]-piperazin-1-yl-methanone, a new compound, and compound (II) was 2-chlorodibenzo[b,f][1,4]oxazepin-11(10H)-one. As for the degradation behavior, it was estimated that AMX was degraded into (II) via (I), i.e., (II) was the final product. The results are expected to be useful in clinical chemistry and forensic science, including the estimation of drugs to be used at the time of judicial dissection and suspected drug addiction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1045K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1045K) Full view HTML -
Keita Yaginuma, Shuichi Tanabe, Takuya Miyano, Hiroshi Nakagawa, Satos ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 855-863
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn-line monitoring of granule water content during fluid bed granulation is important to control drug product qualities. In this study, a practical scale-free soft sensor to predict water content was proposed to cope with the manufacturing scale changes in drug product development. The proposed method exploits two key ideas to construct a scale-free soft sensor. First, to accommodate the changes in the manufacturing scale, the process parameters (PPs) that are critical to water content at different manufacturing scales were selected as input variables. Second, to construct an accurate statistical model, locally weighted partial least squares regression (LW-PLSR), which can cope with collinearity and nonlinearity, was utilized. The soft sensor was developed using both laboratory (approx. 4 kg) data and pilot (approx. 25 kg) scale data, and the prediction accuracy in the commercial (approx. 100 kg) scale was evaluated based on the assumption that the process was scaled-up from the pilot scale to the commercial scale. The developed soft sensor exhibited a high prediction accuracy, which was equivalent to the commonly used near-infrared (NIR) spectra-based method. The proposed method requires only standard instruments; therefore, it is expected to be a cost-effective alternative to the NIR spectra-based method.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1013K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1013K) Full view HTML -
 Masashi Tsuda, Ryui Makihara, Masayuki Tsuda, Takeyuki Suzuki2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 864-867
Masashi Tsuda, Ryui Makihara, Masayuki Tsuda, Takeyuki Suzuki2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 864-867
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo new macrolides, iriomoteolides-14a (1) and 14b (2) have been isolated from the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium species (strain KCA09057). Compounds 1 and 2 are 15-membered macrolides, which are structural analogs of amphidinolides O (3) and P (4). The structures of 1 and 2 were assigned on the basis of detailed NMR analyses and chemical conversion studies. Compounds 1 and 2 showed moderate cytotoxic activity against human cervix adenocarcinoma HeLa cells.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickMarine dinoflagellates are well known as rich sources of biologically active compounds possessing unique chemical structures. This paper deals isolation and structure elucidation of two new cytotoxic 15-membered macrolides, iriomoteolodes-14a and 14b, from the marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium species collected off Iriomote Island, Okinawa. The structures including the absolute stereochemistry of eight stereocenters were determined on basis of spectroscopic data and chemical conversion method. These compounds are analogous to known macrolides, amphidinolides O and P, and the biosynthetic relationships for four compounds are also described.
Download PDF (528K) Full view HTML -
 Toru Miura, Naoki Sugimoto, Sitaram Bhavaraju, Taichi Yamazaki, Yuzo N ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 868-878
Toru Miura, Naoki Sugimoto, Sitaram Bhavaraju, Taichi Yamazaki, Yuzo N ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 868-878
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
Advance online publication: June 19, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNMR spectroscopy has recently been utilized to determine the absolute amounts of organic molecules with metrological traceability since signal intensity is directly proportional to the number of each nucleus in a molecule. The NMR methodology that uses hydrogen nucleus (1H) to quantify chemicals is called quantitative 1H-NMR (1H qNMR). The quantitative method using 1H qNMR for determining the purity or content of chemicals has been adopted into some compendial guidelines and official standards. However, there are still few reports in the literature regarding validation of 1H qNMR methodology. Here, we coordinated an international collaborative study to validate a 1H qNMR based on the use of an internal calibration methodology. Thirteen laboratories participated in this study, and the purities of three samples were individually measured using 1H qNMR method. The three samples were all certified via conventional primary methods of measurement, such as butyl p-hydroxybenzoate Japanese Pharmacopeia (JP) reference standard certified by mass balance; benzoic acid certified reference material (CRM) certified by coulometric titration; fludioxonil CRM certified by a combination of freezing point depression method and 1H qNMR. For each sample, 1H qNMR experiments were optimized before quantitative analysis. The results showed that the measured values of each sample were equivalent to the corresponding reference labeled value. Furthermore, assessment of these 1H qNMR data using the normalized error, En-value, concluded that statistically 1H qNMR has the competence to obtain the same quantification performance and accuracy as the conventional primary methods of measurement.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickQuantitative nuclear magnetic resonance is a powerful tool in quantitative determination of the main component and impurities in a drug substance or a drug product because of its high accuracy, precision and efficiency. This method has the potential to establish metrological traceability easily and expected to be widely utilized for some compendial guidelines and official standards. In this study, the authors conducted an inter-laboratory comparison for qNMR methodology and confirmed that statistically qNMR has the competence to obtain the same quantification performance and accuracy as the conventional reliable methods.
Download PDF (866K) Full view HTML -
Tomonori Hayashi, Hinako Kawaguchi, Tsumugi Eifuku, Hiroshi Matsuoka, ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 879-884
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe percutaneous absorption of a fentanyl (FEN)-patch is affected by various external factors including the volume of sebum secretion, which causes changes in the skin surface environment. In this study, we prepared a lard-based sebum-like secretion (SLS), and applied it to investigate the effect of different skin surface conditions on the drug penetration of a FEN-patch. In vitro work to test drug release using the Franz diffusion cell indicated that drug release was significantly suppressed by treatment with 5% SLS, which is equivalent to the amount of daily human sebum secretion. Conversely, in ex vivo experiments using rat skin, the amount of FEN that accumulated in the skin tissue of the 5% SLS-treated rats was higher in comparison with the non-SLS treated group. Furthermore, in vivo experiments indicated that the plasma FEN concentration in rats treated with the FEN-patch was significantly increased by treatment with 5% SLS. These results suggest that the sebum affected the release, accumulation, and absorption of FEN from the FEN-patch, and the FEN concentration in the blood was reflected by the balance of the suppression of drug release and the enhancement of drug accumulation in the skin with SLS.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (840K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (840K) Full view HTML -
 Shinichi Sato, Hiroyuki Nakamura2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 885-890
Shinichi Sato, Hiroyuki Nakamura2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 885-890
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTyrosyl radical generation is one of the major factors for hemin/peroxide-induced oxidative stress. A method for trapping tyrosyl radical directly was developed using N-methyl luminol derivative, a tyrosine labeling reagent. N-Methyl luminol derivative selectively forms a covalent bond with a tyrosine residue under the single-electron oxidation condition. This reaction labels oxidative stress hotspots not only at the protein level but also at the level of tyrosine residues undergoing oxidation. Human serum albumin complexed with hemin was labeled at Tyr138, the tyrosine residue closest to the hemin binding site and most strongly subjected to oxidative stress caused by hemin/H2O2. Oxidatively damaged proteins were visualized in protein mixtures.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickTyrosyl radical generation plays a major role in hemin/peroxide-induced oxidative stress. The authors developed a method for trapping tyrosyl radicals using a derivative of N-methyl luminol, a tyrosine labeling reagent. The derivative selectively forms a covalent bond with tyrosine residue (tyrosine click reaction) under single-electron oxidation conditions. This reaction labels oxidative stress hotspots not only at the protein level but also at the level of tyrosine residues undergoing oxidation. The cover picture depicts an image of tyrosine click reaction to aid in the visualization of hemin/peroxide-induced oxidative stress generated in blood vessels.
Download PDF (2138K) Full view HTML
-
Ryota Jin, Akihiro Hisaka2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 891-894
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
Advance online publication: July 01, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis, conventional models are described by ordinary differential equations (ODE) that are generally solved in their Laplace transformed forms. The solution in the Laplace transformed forms is inverse Laplace transformed to derive an analytical solution. However, inverse Laplace transform is often mathematically difficult. Consequently, numerical inverse Laplace transform methods have been developed. In this study, we focus on extending the modeling functions of Nonlinear Mixed Effect Model (NONMEM), a standard software for PK and population pharmacokinetic (PPK) analyses, by adding the Fast Inversion of Laplace Transform (FILT) method, one of the representative numerical inverse Laplace transform methods. We implemented PREDFILT, a specialized PRED subroutine, which functions as an internal model unit in NONMEM to enable versatile FILT analysis with second-order precision. The calculation results of the compartment models and a dispersion model are in good agreement with the ordinary analytical solutions and theoretical values. Therefore, PREDFILT ensures enhanced flexibility in PK or PPK analyses under NONMEM environments.
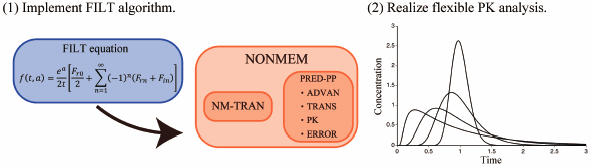 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (460K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (460K) Full view HTML -
Rikako Ohnishi, Masumi Sugawara, Tetsuya Ezawa, Yoshihiro Sohtome, Mik ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 895-898
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe have developed a catalytic aerobic oxidative dimerization reaction of benzofuranones using a Pd(II)-µ-hydroxo complex. Radical-radical cross-coupling of the resulting dimers with azo compounds enabled the one-pot synthesis of structurally congested benzofuranones having two distinct vicinal all-carbon quaternary centers.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (662K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (662K) Full view HTML -
Yuta Miura, Yohei Saito, Masuo Goto, Kyoko Nakagawa-Goto2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 899-902
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe first total synthesis of (±)-neocaryachine (1) was achieved using a radical cyclization to produce the dibenzo-9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane pavine skeleton, following a Bischler–Napieralski reaction to construct an intermediate benzylisoquinoline. The resulting racemic mixture was separated by chiral column chromatography to provide pure (+)- and (−)-1.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (477K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (477K) Full view HTML -
Magie Melanie Kapojos, Delfly Booby Abdjul, Hiroyuki Yamazaki, Akiho Y ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 9 Pages 903-906
Published: September 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBioassay screening using Indonesian plants, such as traditional foods (vegetables, spices, and tea) and folk medicinal herbs, identified eight protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) 1B inhibitory and two antibacterial plants. The leaves of Syzygium polyanthum (Wight) Walp. were examined in more detail to define PTP1B inhibitory components, resulting in the isolation of a new active acylbenzene (1) along with four related congeners of 1 (2–5) and four oleanane triterpenes (6–9). The structure of 1 was elucidated as 12-oxo-12-(2,3,5-trihydroxy-4-methylphenyl)dodecanoic acid based on its spectroscopic data. The acylbenzenes 1 and 3–5 inhibited PTP1B activity with IC50 values ranging between 9.5 and 14 µM, whereas the triterpenes 7–9 also suppressed this activity with IC50 values of 3.3–5.7 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (369K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (369K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|