
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Hiromichi Fujioka, Takashi Ohshima2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 1
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (174K) Full view HTML
-
Yasunari Monguchi, Tomohiro Ichikawa, Hironao Sajiki2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 2-9
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis paper describes practical and selective hydrogenation methodologies using heterogeneous palladium catalysts. Chemoselectivity develops dependent on the catalyst activity based on the characteristic of the supports, derived from structural components, functional groups, and/or morphologies. We especially focus on our recent development of heterogeneous palladium catalysts supported on chelate resin, ceramic, and spherically shaped activated carbon. In addition, the application of flow technology for chemoselective hydrogenation using the palladium catalysts immobilized on molecular sieves 3A and boron nitride is outlined.
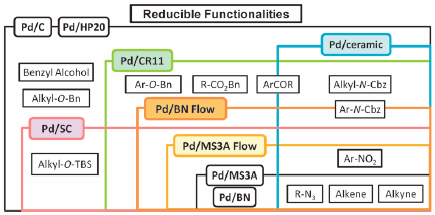 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5456K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5456K) Full view HTML -
Reiya Ohta, Hiromichi Fujioka2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 10-18
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLRecent progress in the chemoselective reduction and alkylation of carbonyl functions using our in situ protection method is described. Methods that enable reversal or control of the reactivity of a carbonyl functional group are potentially useful. They open up new areas of synthetic organic chemistry and change the concept of retrosynthesis because they remove the need for complicated protection/deprotection sequences. In this account, we discuss the strategy and applications of our in situ protection method using phosphonium salts.
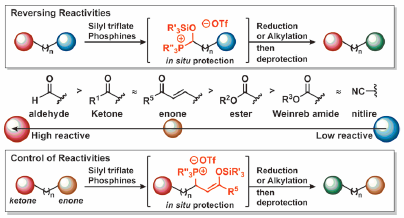 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1637K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1637K) Full view HTML
-
Zhao Li, Masamichi Tamura, Ryo Yazaki, Takashi Ohshima2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 19-21
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA highly chemoselective conjugate addition of amino alcohols to α,β-unsaturated ester using a soft Lewis acid/hard Brønsted base cooperative catalyst was developed. This catalysis achieved chemoselective addition of a hydroxy group over an amino group. Moreover, soft metal alkoxide generation enabled chemoselective soft conjugate addition over hard transesterification. Various amino alcohols, including unprecedented cyclic β-amino alcohol, were applicable to the present catalysis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (512K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (512K) Full view HTML -
Shun-ichiro Uesugi, Yusuke Sasano, Shogo Matsui, Naoki Kanoh, Yoshihar ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 22-24
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA concise, protecting-group-free synthesis of the antipsychotic agent (+)-nemonapride has been achieved featuring a europium(III) trifluoromethanesulfonate (Eu(OTf)3)-catalyzed C4 selective aminolysis of a 3,4-epoxy alcohol by benzylamine and an expedient use of the resulting 4-benzylamino-1,3-diol product for constructing the pyrrolidine skeleton.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (503K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (503K) Full view HTML
-
Hironori Takeuchi, Yoshihiro Ueda, Takumi Furuta, Takeo Kawabata2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 25-32
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA short-step total synthesis of the natural glycosides pterocarinin C and tellimagrandin II (eugeniin) has been performed by sequential and site-selective functionalization of free hydroxy groups of unprotected D-glucose. The key reactions are β-selective glycosidation of a gallic acid derivative using unprotected D-glucose as a glycosyl donor and catalyst-controlled site-selective introduction of a galloyl group into the inherently less reactive hydroxy group of the glucoside.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1743K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1743K) Full view HTML
-
 Eito Yoshioka, Shigeru Kohtani, Takurou Hashimoto, Tomoko Takebe, Hide ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 33-35
Eito Yoshioka, Shigeru Kohtani, Takurou Hashimoto, Tomoko Takebe, Hide ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 33-35
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: December 26, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the presence of charge–transfer complexes between iodine and tertiary amines, the aqueous-medium atom-transfer radical reactions proceeded under visible light irradiation without the typical photocatalysts.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn this paper, the authors used the charge-transfer complexes between iodine and tertiary amines for the initiation of atom-transfer radical reactions. The visible light irradiation of charge-transfer complex in the ground state gives the excited state complex, in which the single electron transfer from the donor amine to the acceptor iodine proceeds effectively to give an iodine radical.
Download PDF (480K) Full view HTML
-
Mio Tange, Akino Matsumoto, Miyako Yoshida, Honami Kojima, Tamami Hara ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 36-41
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe purpose of the study was to evaluate the adsorption of filgrastim on infusion sets (comprising infusion bag, line and filter) and to compare the adsorption of the original filgrastim preparation with biosimilar preparations using HPLC. The inhibitory effect of polysorbate 80 on this adsorption was also evaluated. Filgrastim was mixed with isotonic sodium chloride solution or 5% (w/v) glucose solution in the infusion fluid. Filgrastim adsorption on infusion sets was observed with all preparations and with both types of infusion solution. The adsorption ratio was about 30% in all circumstances. Filgrastim adsorption on all parts of the infusion set (bag, line and filter) was dramatically decreased by the addition of polysorbate 80 solution at concentrations at or over its critical micelle concentration (CMC). The filgrastim adsorption ratio was highest at a solution pH of 5.65, which is the isoelectric point (pI) of filgrastim. This study showed that the degree of filgrastim adsorption on infusion sets is similar for original and biosimilar preparations, but that the addition of polysorbate 80 to the infusion solution at concentrations at or above its CMC is effective in preventing filgrastim adsorption. The addition of a total-vitamin preparation with a polysorbate 80 concentration over its CMC may be an effective way of preventing filgrastim adsorption on infusion sets.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (678K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (678K) Full view HTML -
Md. Ashraf Ali, Noriko Kataoka, Abdul-Hackam Ranneh, Yasunori Iwao, Sh ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 42-48
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMonoolein cubosomes containing either spironolactone (SPI) or nifedipine (NI) were prepared using a high-pressure homogenization technique and characterized in terms of their solubility and oral bioavailability. The mean particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, solubility and encapsulation efficiency (EE) values of the SPI- and NI-loaded cubosomes were determined to be 90.4 nm, 0.187, −13.4 mV, 163 µg/mL and 90.2%, and 91.3 nm, 0.168, −12.8 mV, 189 µg/mL and 93.0%, respectively, which were almost identical to those of the blank cubosome. Small-angle X-ray scattering analyses confirmed that the SPI-loaded, NI-loaded and blank cubosomes existed in the cubic space group Im3̄m. The lattice parameters of the SPI- and NI-loaded cubosomes were 147.6 and 151.6 Å, respectively, making them almost identical to that of blank cubosome (151.0 Å). The in vitro release profiles of the SPI- and NI-loaded cubosomes showed that they released less than 5% of the drugs into various media over 12–48 h, indicating that most of the drug remained encapsulated within the cubic phase of their lipid bilayer. Furthermore, the in vivo pharmacokinetic results suggested that these cubosomes led to a considerable increase in the systemic oral bioavailability of the drugs compared with pure dispersions of the same materials. Notably, the stability results indicated that the mean particle size and PDI values of these cubosomes were stable for at least 4 weeks. Taken together, these results demonstrate that monoolein cubosomes represent promising drug carriers for enhancing the solubility and oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K) Full view HTML -
Takatoshi Terada, Toshiro Ohtsubo, Yasunori Iwao, Shuji Noguchi, Shige ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 49-55
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe purpose of this study was to develop a deeper understanding of the key physicochemical parameters involved in the release profiles of microsphere-encapsulated agrochemicals at different temperatures. Microspheres consisting of different polyurethanes (PUs) were prepared using our previously reported solventless microencapsulation technique. Notably, these microspheres exhibited considerable differences in their thermodynamic characteristics, including their glass transition temperature (Tg), extrapolated onset temperature (To) and extrapolated end temperature (Te). At test temperatures below the To of the PU, only 5–10% of the agrochemical was rapidly released from the microspheres within 1 d, and none was released thereafter. However, at test temperatures above the To of the PU, the rate of agrochemical release gradually increased with increasing temperatures, and the rate of release from the microspheres was dependent on the composition of the PU. Taken together, these results show that the release profiles of the microspheres were dependent on their thermodynamic characteristics and changes in their PU composition.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1717K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1717K) Full view HTML -
Haiyun Chen, Guolian Tan, Jie Cao, Gaoxiao Zhang, Peng Yi, Pei Yu, Yew ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 56-65
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
Advance online publication: October 14, 2016JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialOxidative stress plays a crucial role in neurological diseases, resulting in excessive production of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. In this work, we designed and synthesized a series of tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) derivatives and investigated their abilities for scavenging free radicals and preventing against oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage in vitro. Among them, compound 22a, consisted of TMP, caffeic acid and a nitrone group, showed potent radical-scavenging activity. Compound 22a had broad neuroprotective effects, including rescuing iodoacetic acid-induced neuronal loss, preventing from tert-butylhydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced neuronal injury. Compound 22a exerted its neuroprotective effect against t-BHP injury via activation of the phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. Furthermore, in a rat model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion, compound 22a significantly improved neurological deficits, and alleviated the infarct area and brain edema. In conclusion, our results suggest that compound 22a could be a potential neuroprotective agent for the treatment of neurological disease, particularly ischemic stroke.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1831K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1831K) Full view HTML -
Meropi Sklepari, Nikolaos Lougiakis, Athanasios Papastathopoulos, Nico ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 66-81
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of new pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridines bearing various 1, 3, 5 or 1, 3, 7 pattern substitutions, were designed and synthesized. Some of them showed interesting inhibitory activity mainly against glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)α/β as well as against cdc2-like kinases 1 (CLK1) and dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A), with good selectivity and remarkable structure–activity relationships (SARs), without being cytotoxic. Molecular simulations in correlation with biological data revealed the importance of the existence of N1-H as well as the absence of a bulky 7-substituent.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1490K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1490K) Full view HTML -
Guoqing Sui, Wen Zhang, Kun Zhou, Yulin Li, Bingyu Zhang, Dan Xu, Yong ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 82-89
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAs a part of our continuing research on amine derivative antifungal agents, 19 novel target compounds containing 1,2,4-triazole and tertiary amine moieties were designed and synthesized, and their in vitro antifungal activities against six phytopathogenic fungi (Magnaporthe grisea, Alternaria solani, Fusarium solani, Curvularia lunata, A. alternata, F. graminearum) were assayed. All target compounds were elucidated by means of 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, high resolution (HR)-MS, and IR analysis. The results showed that most of the derivatives exhibited obvious activity against each of the fungi at 50 µg/mL. Among them, compounds 7f, l, and o displayed excellent activity against A. solani with median effective concentration values (EC50) of 2.88, 8.20, and 1.92 µg/mL. 7o in particular was superior to tebuconazole (EC50=2.03 µg/mL), a commercial fungicide. Furthermore, compounds 7j, k, and m also showed good activity against F. graminearum with EC50 values of 11.60, 5.14, and 16.24 µg/mL, and the value of 7k was extremely close to that of tebuconazole (EC50=3.13 µg/mL). The preliminary analysis of the structure–activity relationship (SAR) demonstrated that combination of the active structure of 1,2,4-triazole with the tertiary amine group containing benzene rings effectively increased the antifungal activities. Generally, introducing halogen atoms obviously improved activities against most of the test fungi to varying degrees, while the presence of OMe decreased the activities. Thus, the results strongly indicate that the newly synthesized derivatives should be lead compounds for the development of novel antifungal agents for the effective control of phytopathogenic fungi.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (762K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (762K) Full view HTML -
Maher Abd El-Aziz El-Hashash, Sobhi Mohamed Gomha, Elham Ezz El-Arab2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 90-96
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of pyrazolyl-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines, pyrazolyl-tetrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines, pyrazolyl-benzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines and bis-azolopyrimidines were prepared by reaction of pyrazolyl-chalcones or its bis-pyrazolyl-chalcones with the appropriate heterocyclic amines as aminotriazole, aminotetrazole, 2-aminobenzimidazole and 4,6-dimethyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-3-amine by grinding method. The newly synthesized compounds have been characterized on the basis of elemental analysis and spectral data (IR, 1H- and 13C-NMR, Mass). Moreover, the newly synthesized products were screened for their in vitro antibacterial activities and the results showed that compounds 5f and 11d exhibited excellent activities compared with penicillin G and streptomycin as reference drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (780K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (780K) Full view HTML
-
Haruka Katsui, Sachiko Sugimoto, Katsuyoshi Matsunami, Hideaki Otsuka, ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 97-101
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFrom the leaves of Cananga odorata var. odorata, three relatively large molecules, namely two aryl naphthalene lignan diesters of canangafruticoside A and one cyclobutane lignan diester of canangafruticoside A, were isolated along with four known compounds. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated based on spectroscopic evidence.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (419K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (419K) Full view HTML -
Masateru Ono, Yukio Fujiwara, Tsuyoshi Ikeda, Cheng Pan, Mona El-Aasr, ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 102-106
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNewly characterized, atypical sulfides, garlicnins G (1), I (2), and J (3), were isolated from the acetone extracts of garlic bulbs, Allium sativum. Their production pathways are regarded as different from those of cyclic sulfoxides, 3,4-dimethyltetrahydrothiophene-S-oxide derivatives such as onionins A1–A3, garlicnins B1–B4 and C1–C3.
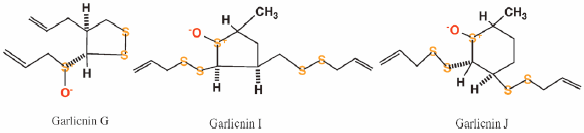 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (624K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (624K) Full view HTML -
Masateru Ono, Satoko Oda, Shin Yasuda, Tomoko Mineno, Masafumi Okawa, ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 107-111
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFour hexaglycosides of methyl 3S,12S-dihydroxyhexadecanoate (1–4) were provided after treatment of the crude convolvulin fraction from Rhizoma Jalapae Braziliensis (the root of Ipomoea operculata (GOMES) MART., Convolvulaceae) with indium(III) chloride in methanol. The structures of 1–4 were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic and chemical methods. Their sugar moieties were partially acylated with organic acids including (3S,9R)-3,6:6,9-diepoxydecanoic (exogonic) acid, (E)-2-methylbut-2-enoic (tiglic) acid, and isovaleric acid.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (528K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (528K) Full view HTML -
Kohei Yamada, Naoko Hayakawa, Hikaru Fujita, Masanori Kitamura, Muneta ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 112-115
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAcid-catalyzed allylating reagent 2,4,6-tris(allyloxy)-1,3,5-triazine (TriAT-allyl) and its substituted derivatives have been developed. The reaction of acid-, and alkali-labile alcohols with these reagents in the presence of a catalytic amount of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (TfOH) afforded the corresponding allyl ethers in good yields. Reactions using these reagents with an unsymmetrically-substituted regioisometric allyl group suggested that a single isometric allylic cation species would be involved.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML -
Faradiba Abdul Rasyid, Shuichi Fukuyoshi, Hirokazu Ando, Katsunori Miy ...2017Volume 65Issue 1 Pages 116-120
Published: January 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialNew clerodane diterpene, 16-hydroxy-pentandralactone (1) and known diterpene acuminolide (2) were isolated from the methanol extract of Vitex cofassus leaves. The chemical structure and the absolute configuration of 1 were determined by MS, NMR and electron circular dichroism (ECD) experiments. The isolated compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative activities against a panel of human tumor cell lines, including a multidrug-resistant (MDR) cell line. Both compounds showed potent antiproliferative activities against all the tested cell lines with IC50 values of 5.4–11.4 µM. Their effects on cell viability were also tested using vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Compound 1 inhibited VEGF-stimulated HUVEC proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Based on these results, compound 1 could be a candidate for antitumor agent and inhibitor of angiogenesis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (651K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (651K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|