
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yosuke Masuda, Noriyuki Yamaotsu, Shuichi Hirono2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 889-892
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to predict the potencies of mechanism-based reversible covalent inhibitors, the relationships between calculated Gibbs free energy of hydrolytic water molecule in acyl-trypsin intermediates and experimentally measured catalytic rate constants (kcat) were investigated. After obtaining representative solution structures by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, hydration thermodynamics analyses using WaterMap™ were conducted. Consequently, we found for the first time that when Gibbs free energy of the hydrolytic water molecule was lower, logarithms of kcat were also lower. The hydrolytic water molecule with favorable Gibbs free energy may hydrolyze acylated serine slowly. Gibbs free energy of hydrolytic water molecule might be a useful descriptor for computer-aided discovery of mechanism-based reversible covalent inhibitors of hydrolytic enzymes.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML
-
Tarek Fathy El-Moselhy, Peter Ayoub Sidhom, Eman Ahmed Esmat, Nageh Ah ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 893-903
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialResurgence to target L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels has been applied by the synthesis of two series of nifedipine analogues where the ortho- or a meta-nitrophenyl ring is retained. A pre-synthetic molecular docking study with a receptor model followed by molecular alignment has been performed on 47 compounds to predict the most active member. The IC50 values revealed that some of the compounds are similar to or more active than nifedipine. Substitution of groups at the 3- and 5-positions of the dihydropyridine (DHP) ring gave 3k, which is more active than nifedipine. Our valid three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) model prefigures the influence of lipophilicity, bulkiness and chelating effects of the C3 and C5 substituents. Bulky groups interfere with ring-to-ring hydrophobic interaction with tyrosine (Tyr)4311 and limit the efficiency of increasing the length of the hydrocarbon chain of esters at the 3- and 5-positions of the DHP ring as an approach to increasing the activity. The presence of a chelating substituent on the phenyl ring at the 4-position of the DHP ring ensures strong binding to the receptor and hence stabilization of the closed-channel conformation. The validation of 3D-QSAR model indicated its proficiency in predicting activity of newly compounds belonging to the same chemical class.
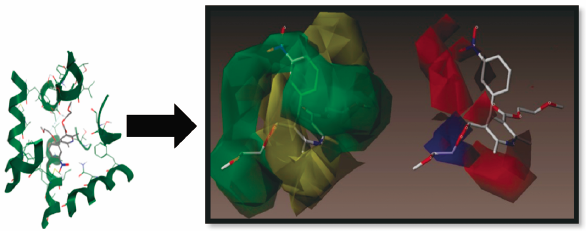 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2376K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2376K) Full view HTML -
Yifan Zhong, Xiaoyan Han, Shengbin Li, Hui Qi, Yali Song, Xiaoqiang Qi ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 904-910
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialN-Myristoyltransferase (NMT) has been validated pre-clinically as a target for treatment of fungal infections. Various substituted thiochroman-4-one derivatives have been synthesized by an efficient method. The synthesized compounds 7a–y and 8a–t were evaluated for their in vitro antifungal activity against the Canidia albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Epidermophyton floccosum, Mucor racemosus, Microsporum gypseum and Aspergillus nigerstrain. A series of compounds exhibited significant activity (minimal inhibitory concentrotion (MIC)=0.5–16 µg/mL) against Canidia albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans. The antifungal activity of compound 7b was reached to that of fluconazole, which can serve as a good starting point for further studies of structural diversity of the NMT inhibitors. The molecular docking studies revealed an interesting binding profile with very high receptor affinity for NMT of Canidia albicans.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3443K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3443K) Full view HTML -
Gil Mendes Viana, Deivid Costa Soares, Marcos Vinicius Santana, Lilian ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 911-919
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialLeishmaniasis is a neglected tropical disease caused by protozoan parasites belonging to the genus Leishmania. Currently, the drugs available for treatment of this disease present high toxicity, along with development of parasite resistance. In order to overcome these problems, efforts have been made to search for new and more effective leishmanicidal drugs. The aim of this study was to synthesize and investigate the leishmanicidal effect of N,N′-disubstituted thioureas against Leishmania amazonensis, with evaluation of their in silico pharmacokinetics and toxicity profiles. Our results showed that different thioureas could be obtained in high to moderate yields using simple reaction conditions. Nine thiourea derivatives (3e, 3i, 3k, 3l, 3p, 3q, 3v, 3x and 3z) were active against parasite promastigotes (IC50 21.48–189.10 µM), with low cytotoxicity on mice peritoneal macrophages (CC50>200 µM), except for thiourea 3e (CC50=49.22 µM). After that, the most promising thioureas (3k, 3l, 3p, 3q and 3v) showed IC50 ranging from 70 to 150 µM against L. amazonensis amastigotes in infected macrophages. Except for thiourea 3p, the leishmanicidal activity of the derivatives were independent of nitric oxide (NO) production. Thioureas 3q and 3v affected promastigotes cell cycle without disturbing the mitochondrial membrane potential. Furthermore, our derivatives showed satisfactory theoretical absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, toxicity (ADMET) properties. These data indicate that thiourea derivatives are good candidates as leading compounds for the development of new leishmanicidal drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (521K) Full view HTML -
Kyoko Ishikawa, Fumika Karaki, Kaoru Tayama, Eika Higashi, Shigeto Hir ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 920-929
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBuprenorphine shows strong analgesic effects on moderate to severe pain. Although buprenorphine can be used more safely than other opioid analgesics, it has room for improvement in clinical utility. Investigation of compounds structurally related to buprenorphine should be an approach to obtain novel analgesics with safer and improved profiles compared to buprenorphine. In the course of our previous studies, we observed that derivatives obtained by cyclizing C-homomorphinans were structurally related to buprenorphine. Hence, we synthesized cyclized C-homomorphinan derivatives with various oxygen functionalities on the side chains and evaluated their in vitro pharmacological profiles for the opioid receptors. Among the tested compounds, methyl ketone 2a with an N-methyl group showed full agonistic activities for the μ and the δ receptors and partial agonistic activity for the κ receptor. These properties were similar to those of norbuprenorphine, a major metabolite of buprenorphine, which reportedly contributes to the antinociceptive effect of buprenorphine. From these results, we concluded that cyclized C-homomorphinan would be a possible lead compound to obtain novel analgesics with buprenorphine-like properties.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1174K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1174K) Full view HTML -
 Saori Terazawa, Yuka Uemura, Yuka Koyama, Susumu Kawakami, Sachiko Sug ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 930-939
Saori Terazawa, Yuka Uemura, Yuka Koyama, Susumu Kawakami, Sachiko Sug ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 930-939
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMicrotropins Q–W, (2S,3R)-2-ethyl-2,3-dihydroxybutyrate of various glucosides and glucose, as well as three ent-labdane diterpenoid glucosides, named microtropiosides G, H and I, an ursane-type triterpene diglucoside and a flavonoid glycoside were isolated from the MeOH extract of the leaves of Microtropis japonica. The structure of microtropioside A, also isolated from the branches of M. japonica, was elucidated spectroscopically in a previous experiment and was found to possess a rare seven-membered oxyrane ring. Its structure was confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis of its pentaacetate.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickSince an antileukemic ansa macrolide, maytansine was first isolated from Maytenus ovata, plants belong to Celastraceae draw the attention of natural product chemists. The authors focused on the plants collected in Okinawa Islands, and Celastraceae plant, Microtropis japonica was chosen for the target material. ent-Labdane glycoside and 6'-O-(2"S,3R")-2"-ethyl-2",3"-dihydroxybutyrates of aliphatic alcohol β-D-glucosides branches have been isolated from leaves and branches respectively. Current investigation of leaves afforded further ent-labdane glucosides, 6'-O-2"-ethyl-2",3"-dihydroxybutyrates of aliphatic alcohol β-D-glucosides, ursane-type triterpene diglucoside, and flavonol glycoside.
Download PDF (724K) Full view HTML -
 Yumiko Yamano, Haruna Sasaki, Akimori Wada2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 940-944
Yumiko Yamano, Haruna Sasaki, Akimori Wada2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 940-944
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA mild deacylation method for 3,5-dinitrobenzoates using methanolic solutions of amines, such as dialkylamines, was developed. The method’s versatility was confirmed by applying it to synthesizing a key intermediate for Colorado potato beetle pheromone.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn the article, a mild deacylation method for 3,5-dinitrobenzoates, which are often used to improve their diastereomeric or enantiomeric purities by recrystallization and also widely used as a pro-nucleophile in the Mitsunobu reaction, has been developed by using methanolic solutions of amines, such as dialkylamines. Removal of dinitrobenzoyl groups undergoes without affecting existing acetyl groups and also without affecting stereochemistry in α-hydroxy ketone. Encouraged by the promising versatility, the authors successfully applied this method to the efficient asymmetric synthesis of Colorado potato beetle pheromone.
Download PDF (583K) Full view HTML -
 Arato Kimoto, Ayako Watanabe, Eiichi Yamamoto, Tatsuya Higashi, Masaru ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 945-949
Arato Kimoto, Ayako Watanabe, Eiichi Yamamoto, Tatsuya Higashi, Masaru ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 945-949
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn recent years, nanomedicines have received growing attention in a range of medical applications, including selective drug delivery technology. In this context, the analysis of liposome stability and drug release from liposomes is of particular importance, as the efficacy of a nanomedicine is determined by the release of the encapsulated drug. We investigated the influence of the surrounding environment on the stability and release of the encapsulated drug (i.e., doxorubicin) from DOXIL. Thus, for the purpose of this study, we selected the liposomal anticancer drug, DOXIL, as a typical nanomedicine, and investigated the influence of the surrounding environment on release of doxorubicin from DOXIL. We found that two pathways existed for doxorubicin release, namely the collapse of DOXIL, and an increase in the permeability of the lipid bilayer. DOXIL collapse occurred upon the addition of high concentrations (>60%) of a methanol solution, while an increase in permeability occurred at temperatures above the phase transition temperature of the DOXIL lipid bilayer, under basic conditions, and in the presence of membrane-permeable bases (e.g., Tris). As DOXIL is particularly stable and limited collapse of DOXIL occurred under physiological conditions, it is expected that doxorubicin release within the body took place through permeability changes in the lipid bilayer of the DOXIL structure.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe authors described that membrane-permeable bases accelerated the release of encapsulated drug, doxorubicin, from DOXIL by using a HPLC column for nanomedicine analysis.
Download PDF (641K) Full view HTML -
 Shuai Zhang, Xiao-jia Liu, Rui Tang, Hai-xin Wang, Hai-ying Liu, Yu-mi ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 950-958
Shuai Zhang, Xiao-jia Liu, Rui Tang, Hai-xin Wang, Hai-ying Liu, Yu-mi ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 950-958
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA series of novel disulfides containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety were designed, synthesized, and the structures of all products were identified by spectral data (IR, NMR, and high resolution (HR)-MS). Their in vitro antiproliferative activities were evaluated using 2-(2-methoxy-4-nitro-phenyl)-3-(4-nitro-phenyl)-5-(2,4-disulfopheyl)-2H-tetrazolium monosodium salt (CCK-8) assay against human cancer cell lines, A549 (human lung cancer cell), HeLa (human cervical cancer cell), SMMC-7721 (human liver cancer cell) and normal cell lines L929. The bioassay results indicated that most of the tested compounds 6a–k, 7a–k and 8a–k exhibited antiproliferation with different degrees, and some compounds showed better effects than positive control 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) against various cancer cell lines. Among these compounds, compound 6e exhibited the most potent inhibitory activity against A549 cells with IC50 value of 3.62 µM. Compounds 6i, 7a, 7g, 8a and 8b showed significantly antiproliferative activities against HeLa cells with IC50 values of 3.88, 3.76, 3.59, 3.38 and 3.12 µM, respectively. Compounds 6a, 7a and 8a owned high antiproliferative activities against SMMC-7721 cells with IC50 values of 2.54, 2.69 and 2.31 µM, respectively. Furthermore, all of the tested compounds showed weak cytotoxic effect against the normal cell lines L929. Based on the preliminary results, the substituent groups are vital for improving the potency and selectivity of this class of compounds.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn the article, a series of novel disulfides containing 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety were synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro antiproliferative activities using CCK-8 assay against human cancer cell lines A549, HeLa, SMMC-7721 and normal cell lines L929. The bioassay results indicated that most of the tested compounds exhibited antiproliferation with different degrees, and some compounds inhibited the proliferation better than positive control 5-fluorouracil against various cancer cell lines. Furthermore, all compounds showed weak cytotoxic effect against L929 cells. Therefore, the results suggest that the substituent groups are vital for improving the potency and selectivity of this class of compounds.
Download PDF (469K) Full view HTML -
Li Zhang, Zhong-hong Liu, Xun-guan Cheng, Zhu Xia, Yu Liu, Yu Yu2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 959-966
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
Advance online publication: August 04, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe application of chemotherapeutics with chemical drugs is always challenged by their high toxicities throughout the body in clinical trials. Here, we reported a smart formulation of docetaxel developed by solid dispersion and effervescent techniques for efficient and safe delivery of chemical drug to lung tissue. To achieve a high delivery to lung with reduced systemic toxicity, docetaxel was loaded into a kind of lecithoid nanoparticles (DTX-LN) which were prepared by a solid dispersion and effervescent method. After intravenous administration of DTX-LN to rabbit, the docetaxel level in lung was approximately 37-fold higher than that of docetaxel injection (DTX-INJ, a commercial injection preparation of DTX/polysorbate 80 micelles) group at 0.5 h and showed the highest tissue distribution among all the organs. Besides, the targeting parameter Re value of total increased amount of DTX in lung (AUC0–t) ratio (DTX-LN to DTX-INJ) is about 16.69, indicating a significantly enhanced lung targeting ability of DTX-LN. In subacute toxicity study, DTX-LN displayed a reduced hematotoxicity, especially for the negative impacts on white blood cells, lymphocyte and granulocyte when compared with DTX-INJ during both weekly and 3-weekly schedules administration. In addition, histopathological analysis demonstrated that DTX-LN showed less tissue damages on rabbit heart and kidney compared to DTX-INJ. Hence, this work would provide an insight for improving lung delivery efficacy of drugs with reduced systemic toxicity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8914K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8914K) Full view HTML -
 Kozo Takayama, Shota Kawai, Yasuko Obata, Hiroaki Todo, Kenji Sugibaya ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 967-972
Kozo Takayama, Shota Kawai, Yasuko Obata, Hiroaki Todo, Kenji Sugibaya ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 967-972
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA large number of dissolution data were measured and integrated into a previously constructed tablet database composed of 14 kinds of compounds as model active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) with contents ranging from 10 to 80%. The database has contained physicochemical and powder properties of APIs, together with basic physical attributes of tablets such as the tensile strength and the disintegration time. In order to enhance the value of this database, drug dissolution data are essential to improving key information for designing tablet formulations. A four-layered artificial neural network (4LNN), newly implemented in commercially available software, was employed to predict dissolution data from physicochemical and powder properties of APIs. Our results showed that an excellent model for the prediction of dissolution data was achieved with 4LNN method. The function of 4LNN was appreciably better than that of conventional three-layered model, despite both models adopting the same number of nodes and algorithms for activation functions. Furthermore, linear regression models resulted in poor prediction of dissolution data.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickA four-layered artificial neural network (4LNN) was employed to predict dissolution data from physicochemical and powder properties of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) formulated in various kinds of tablets. Causal factors of APIs in the input layer were simplified into the nodes in the 1st hidden layer, properly integrated information would then be transferred to the nodes in the 2nd hidden layer, and finally the secured outcome was delivered in the output layer. An excellent model for the prediction of dissolution data was achieved with 4LNN method. The function of 4LNN was appreciably better than that of conventional three-layered model.
Download PDF (776K) Full view HTML
-
Rosa María Chávez-Santos, Paul Eduardo Reyes-Gutiérrez, Rubén Omar Tor ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 973-981
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
Advance online publication: July 22, 2017JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn this study, the pyrrolo[2,1-a]isoquinolines 4a–n were synthesized in good yields in a three steps synthesis from the corresponding α,β-unsaturated esters starting materials. These compounds were tested on six human cancer cells lines to measure the cytotoxic activity as a function of the electronic properties and aromaticity of the substituent at the C-2 position of the pyrroloisoquinoline. Our results reveal that the cytotoxic activity could be explained in terms of the distribution of electronic density across the ring joined to C-2. Also, this study identified 3-hydroxy (4d) and 3-chloro (4j) derivatives with powerful cytotoxic activities. The IC50 values of these compounds were found to be comparable to those of the commercially available Topotecan, Irinotecan, Etoposide, Tamoxifen, and Cisplatin.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1551K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1551K) Full view HTML -
Yuta Ito, Misaki Matsuo, Takashi Osawa, Yoshiyuki Hari2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 982-988
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA facile synthesis of 2′-deoxy-5-trifluoromethyluridine and 2′-deoxy-5-trifluoromethylcytidine phosphoramidites from commercially available 2′-deoxyuridine and 2′-deoxycytidine was achieved, respectively. The obtained phosphoramidites were incorporated into oligonucleotides, and their binding affinity to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) was evaluated by UV-melting experiments. The triplex-forming abilities of oligonucleotides including 5-trifluoromethylpyrimidine nucleobases with dsDNA were decreased. Especially, the stability of the triplex containing a trifluoromethylcytosine (CF3C)-GC base triplet was low, likely due to the low pKa of protonated CF3C by the electron-withdrawing trifluoromethyl group. A slight decrease in stability of the duplex formed with ssRNA by oligonucleotides including 5-trifluoromethylpyrimidine nucleobases was only observed, suggesting that they might be applicable to various ssRNA-targeted technologies using features of fluorine atoms.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML -
Nathan Ray Alim, Shiki Miyazaki, Yasushi Shimoda, Masaharu Sugiura, Ma ...2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 989-993
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChiral phosphine oxide sequentially activates silicon tetrachloride and trichlorosilyl enol ethers to facilitate asymmetric aldol/vinylogous aldol reaction of 4-methoxy-3-penten-2-one and conjugated aldehydes in a highly enantioselective fashion, and the subsequent cyclization produced optically active 2,6-disubstituted 2,3-dihydro-4-pyranones bearing stereogenic centers at a remote position in a single operation.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML -
Kosuke Chiba, Yuichi Hashimoto, Takao Yamaguchi2017 Volume 65 Issue 10 Pages 994-996
Published: October 01, 2017
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2017
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe recently developed 4-azidophthalimide (AzPI) as a compact fluorogenic photoreactive tag that can be attached to ligands to achieve selective fluorescence labeling of target proteins even in the presence of a large excess of non-target proteins. To further establish the utility of the AzPI tag, we focused here on streptavidin labeling with biotin–AzPI conjugates, and evaluated the relation between the amount of covalently labeled streptavidin (labeling rate) and fluorescence intensity. The labeling rate was proportional to the fluorescence intensity under standardized photo-irradiation conditions. Prolongation of the photo-irradiation time led to a marked increase in the labeling rate, but this was accompanied by a gradual decrease in the fluorescence intensity, which appeared to be due at least in part to photo-induced degradation of the target streptavidin. These findings should be helpful for achieving sensitive fluorescence detection of target proteins by using the AzPI tag.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (850K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (850K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|