
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Tetsuhiro Nemoto2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 624-632
Tetsuhiro Nemoto2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 624-632
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
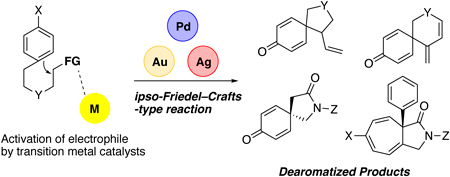
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo develop dearomatization reactions based on a nucleophilic activation of phenols, naphthols, and indoles, ipso-Friedel–Crafts-type C-alkylation must be selectively promoted over competitive O- or N-alkylation reactions. Resolving this chemoselectivity issue is essential for developing this class dearomatization reaction. We found that various dearomatization reactions could be developed using appropriately designed aromatic substrates with an electrophilic moiety for intramolecular reactions. This review describes the transition-metal-catalyzed dearomatization reactions developed by our group. π-Allylpalladium species, η3-propargylpalladium species, alkynes activated by Au(I) species, and silver carbene species could be applied as electrophiles in our reaction system, which provided access to a wide variety of dearomatized products from planar aromatic compounds in a highly chemoselective manner.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickTo develop dearomatization reactions based on a nucleophilic activation of phenols, naphthols, and indoles, ipso-Friedel–Crafts-type C-alkylation must be selectively promoted over competitive O- or N-alkylation reactions. Resolving this chemoselectivity issue is essential for developing this class dearomatization reaction. Author’s research group found that various dearomatization reactions could be developed using appropriately designed aromatic substrates with an electrophilic moiety for intramolecular reactions. This review describes dearomatization reactions using Pd catalysis, Au catalysis, and Ag catalysis, which provided access to a wide variety of dearomatized products from planar aromatic compounds in a highly chemoselective manner.
Download PDF (3170K) Full view HTML
-
Shota Tokunaga, Chie Uchikoshi, Kyu Hayashi, Hironori Suzuki, Masataka ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 633-640
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialNobiletin (NOB) is a flavonoid with attractive pharmaceutical characteristics, including anti-Alzheimer’s, anti-inflammation, and anti-cancer properties, but it has low solubility in water, resulting in reduced bioavailability. Its solubility must be improved to develop NOB as a drug. Cocrystal engineering can change the physicochemical properties of an active pharmaceutical ingredient and generate remarkable drug candidates that are superior in drug formulation. In this report, extensive co-crystal screening of NOBs with 31 cocrystal formers (coformers) with various functional groups was carried out by the liquid-assisted grinding method. As a result, four cocrystals (NOB with urea (URE), oxalic acid, gallic acid and salicylic acid) and one solvate crystal (NOB with formic acid (FOR)) were found. Powder X-ray diffraction and thermal analysis revealed the unique crystal morphology of all the obtained samples. In addition, the crystal structures of two of them (NOB-URE and NOB-FOR) were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The results revealed that NOB-URE and NOB-FOR are new cocrystals or solvate crystals consisting of molar ratios of 1 : 2 and 1 : 0.73, respectively. In NOB-URE, we could observe a transient increase in solubility due to supersaturation, suggesting that URE is one of the better coformers of NOB.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2354K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2354K) Full view HTML -
Akira Takagi, Kazuki Usuguchi, Ippei Takashima, Kensuke Okuda2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 641-649
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialOne aspect of cancer-specific environments, nutrient starvation, is a factor in cancer cell resistance to treatment with chemotherapeutic agents and development of malignancy. Our newly synthesized novel glucose derivative β-1,3,6-O-tribenzoyl-D-glucose (3) showed preferential cytotoxicity against PANC-1 human pancreatic cancer cells as well as HT-29 human colon cancer cells depending on low nutritional environment. The amount of ester functionalization in 3 is important. None of the mono- and tetrabenzoylated D-glucose analog showed cytotoxicity, and dibenzoylated D-glucoses showed only limited cytotoxicity. Fluorescence imaging with double staining of Hoechst 33342 and propidium iodide clearly showed that 3 actually causes cell death in a nutrient deprived medium. We thus demonstrate that an inexpensive natural product, D-glucose, is a unique template for attachment of acyl moieties to target tolerance to nutrient starvation. We expect these compounds will lead to additional compounds to treat refractory cancers by diversification of chemically modified glucose.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1407K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1407K) Full view HTML -
 Kou Nakamura, Masako Yamasaki, Hirofumi Ohashi, Shiki Saito, Koudai As ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 650-654
Kou Nakamura, Masako Yamasaki, Hirofumi Ohashi, Shiki Saito, Koudai As ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 650-654
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
Advance online publication: May 26, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAlthough aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhRs) are related to the metabolic pathway of xenobiotics, recent studies have revealed that this receptor is also associated with the life cycle of viruses and inflammatory reactions. For example, flutamide, used to treat prostate cancer, inhibits hepatitis C virus proliferation by acting as an AhR antagonist, and methylated-pelargonidin, an AhR agonist, suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokine production. To discover a novel class of AhR ligands, we screened 1000 compounds derived from fungal metabolites using a reporter assay and identified methylsulochrin as a partial agonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Methylsulochrin was found to inhibit the production of hepatitis C virus (HCV) in Huh-7.5.1 cells. Methylsulochrin also suppressed the production of interleukin-6 in RAW264.7 cells. Furthermore, a preliminary structure–activity relationship study using sulochrin derivatives was performed. Our findings suggest the use of methylsulochrin derivatives as anti-HCV compounds with anti-inflammatory activity.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickAryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is known to be related to the metabolic pathway of xenobiotics but recent studies revealed that AhR is also associated with the life cycle of the virus and inflammatory reactions. In this article, the authors screened a natural product library and identified methylsulochrin as a partial agonist of AhR. Methylsulochrin exhibited antiviral activity against the hepatitis C virus and suppressed the production of an inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-6, in macrophages. These results suggested the possibility of methylsulochrin derivatives as anti-hepatitis C virus compounds with anti-inflammatory activity.
Download PDF (543K) Full view HTML -
Kaito Yamashiro, Renya Ikemoto, Fumihiko Ogata, Shigeharu Tanei, Naohi ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 655-660
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEutrophication is caused by the inflow of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, into closed waterbodies from wastewater. Calcination of oyster shells greatly increases their capacity for phosphate removal; however, information available on this mechanism and the capacity for phosphate removal under different initial pH values and temperatures is less. Herein, we investigated the utilization of oyster shells for phosphate removal under different pH and temperature conditions. Oyster shell powder (OSP) was calcined in a muffle furnace at temperature ranges of 200–1000 °C. Each OSP sample was added to a phosphate solution and the suspension was shaken under different pH and temperature conditions. The main component of OSP changed from CaCO3 to CaO after calcination at approx. 800 °C. The amount of phosphate removal by the calcined OSPs at 800 and 1000 °C was higher than that removal by the other OSPs. Further, the amount of calcium elution from the OSPs calcined at 800 and 1000 °C was higher than that elution from the other OSPs. This was because the solubility of CaO was higher than that of CaCO3. The amount of phosphate removal by the OSP and calcined OSPs at 200–600 °C was the highest at pH 5–7, and increased with increasing reaction temperature. These findings suggested that the mechanism of phosphate removal may involve adsorption in the OSP and OSPs calcined at 200–600 °C, whereas it is associated with coagulation settling and adsorption in the OSPs calcined at 800 and 1000 °C.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2743K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2743K) Full view HTML
-
Fumihiko Ogata, Ayako Tabuchi, Noriaki Nagai, Megumu Toda, Masashi Ota ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 661-664
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA colloidal silicate granulated nickel–aluminum–zirconium (CSG-NAZ) was prepared, and the chromium(VI) (Cr(VI)) ions recovery capacity was evaluated using a sodium sulfate solution in a column experiment. The amount adsorbed and breakthrough time were enhanced by decreasing the flow rate (flow rate is in the order of 3.0 > 2.0 > 0.5 mL). The breakthrough curves and model parameters were estimated using the Thomas and Yoon–Nelson models. The obtained data confirmed to fit both the Yoon–Nelson model (0.858–0.906) and the Thomas model (0.813–0.906). Additionally, Cr(VI) ions that adsorbed onto CSG-NAZ could be desorbed using a sodium sulfate solution in a column experiment. The total recovery percentage of Cr(VI) ions was 80.9% after six repetitions of adsorption/desorption. Finally, the obtained results revealed that CSG-NAZ was a candidate adsorbent for the recovery of Cr(VI) ions owing to its applicability toward a continuous system.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (590K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (590K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Ono, Kotaro Okada, Megumi Tsuchiya, Yoshihiro Hayashi, Shungo ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 665-669
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
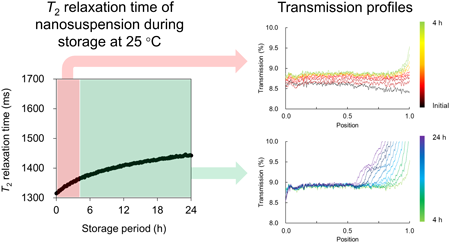
Supplementary materialThe time-domain NMR technique was utilized to monitor precisely the physicochemical stability of indomethacin (IMC) nanosuspensions using T2 relaxation time (T2). We investigated whether T2 values can distinguish between agglomeration and sedimentation. Nanosuspensions of IMC were prepared using aqueous wet bead milling with polyvinylpyrrolidone as a stabilizer. Prepared nanosuspensions were divided into two fractions: one was stored in the NMR equipment for continuous T2 measurements and the other was stored in the dispersion analyzer. Measurements of both nanosuspensions were carried out, without dilution, over a period of 24 h at 10-min intervals. Transmission profiles based on multilight scattering technology showed that agglomeration predominantly occurred at 25 and 35 °C immediately after wet bead milling up to 4 h, followed by sedimentation from 4 to 24 h. Upon measuring the T2 relaxation, T2 values at both 25 and 35 °C showed a two-step change—there was a significant prolongation in T2 values immediately after preparation of nanosuspensions up to approx. 4 h and a gradual prolongation in T2 values from approx. 4 to 24 h. Considering the results of transmission profiles, these two-step T2 changes correspond to agglomeration and sedimentation. In other words, this study established that monitoring the T2 values of nanosuspensions could be used to evaluate the agglomeration and sedimentation of contained drug particles. This technique does not directly observe the nanoparticles themselves, but the water molecules. Thus, measurement of T2 relaxation is considered to be a general-purpose technique, independent of the type of drug or polymer.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1461K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1461K) Full view HTML -
Mayu Fukada, Kazunori Kadota, Satoshi Nogami, Hiromasa Uchiyama, Yoshi ...2023Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 670-674
Published: August 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: August 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThis study developed easy-to-consume bitter taste-masking granules for the preparation of instant jelly formulations. Composite granules containing diphenhydramine hydrochloride (DPH) and polymers were prepared via spray drying. The taste-masking effect on DPH was evaluated with acceptable linearity between DPH concentration and intensity of bitterness using an electronic tongue sensor. The results indicated that ι-carrageenan could provide the greatest suppression effect on the DPH bitterness among the polymers selected for preparing spray-dried particles (SDPs). The thixotropic index (TI) of ι-carrageenan was higher than that of the other polymers. In addition, two sulfate groups per two galactose molecules in one unit of ι-carrageenan improved interaction with DPH. Compared to κ-carrageenan, the electrostatic interaction with DPH may be stronger. Easy-to-consume SDPs with ι-carrageenan were used to prepare instant jelly formulations. The instant jelly formulation containing DPH with ι-carrageenan (3.0%) met the criteria for texture properties (hardness, adhesiveness, and cohesiveness) for patients with difficulty swallowing, as specified by the Consumer Affairs Agency. Furthermore, instant jelly enhanced the bitter taste suppression of DPH. Overall, using spray-dried granules with ι-carrageenan, this technique for preparing instant jelly formulations is simple and inhibits the bitter taste of drugs, contributing to the development of oral dosage forms suitable for patients of all ages.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (922K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (922K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|