
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Shigeru Arai2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 397-403
Shigeru Arai2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 397-403
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCyano (CN) groups are equivalent to carbonyl as well as amino- and hydroxymethyl groups. Therefore, their catalytic introduction under metal catalysis is an important issue in synthetic organic chemistry. Ni-catalyzed hydrocyanation is one of the most well-investigated, powerful tools for installing a CN group. However, it is still difficult to control chemo- and regioselectivity. In this review, the author uses allenes to enable regio-, stereo-, and face-selective transformations to natural product synthesis and axial chirality transfer.
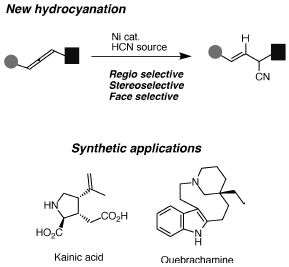 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickRegioselective cyanation of simple and non-activated carbon–carbon bonds catalyzed by nickel complexes is described. This protocol enables to use of the substituted allenes for regio- and stereocontrolled transformations and their applications for cyclization, 3-component coupling reaction, heterocycle formation as well as natural product synthesis are demonstrated. The author reveals the origin of the above selectivity by axial chirality transfer process using optically active allenes as substrates. Steric bulk of substituents is found to be a key factor for discrimination of allenyl carbon–carbon double bonds in hydrometallation step.
Download PDF (1852K) Full view HTML
-
Miyako Yoshida, Honami Kojima, Atsushi Uda, Tamami Haraguchi, Minoru O ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 404-409
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe purpose of the study was to evaluate the ability of different beverages to mask the bitterness of zopiclone and eszopiclone in tablet formulations using the artificial taste sensor and human gustatory sensation testing. The beverages tested for bitterness-masking effects were: Mugicha, Sports beverage, Lactic acid drink, Orange juice and a diluted simple syrup (an 8.5% sucrose solution). The bitterness intensities estimated by the taste sensor of zopiclone or eszopiclone one-tablet solutions mixed with the various beverages, corresponded well with the observed bitterness intensities measured by gustatory sensation testing. The Sports beverage, Lactic acid drink and Orange juice significantly suppressed the bitterness intensity of both zopiclone and eszopiclone 1-tablet solutions compared with water when tested in the artificial taste sensor. Sports beverage, Lactic acid drink and Orange juice all contain citric acid as acidifier, so it was postulated that citric acid was involved in the mechanism of bitterness intensity suppression of zopiclone and eszopiclone 1-tablet solutions by these three beverages. It was then shown that citric acid suppressed the bitterness intensity of a zopiclone one-tablet sample solution in a dose-dependent manner. 1H-NMR spectroscopic analysis of mixtures of citric acid with zopiclone suggested that the carboxyl groups of citric acid interact with the amine group on zopiclone. This study therefore showed that the bitterness intensities of zopiclone and eszopiclone can be suppressed by citric-acid-contained beverages and suggests that this bitterness suppression is due to a direct electrostatic interaction between citric acid and the two drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (669K) Full view HTML -
Jiayuan Jiao, Wanqiu Wang, Haihong Guang, He Lin, Yanxin Bu, Yunhua Wa ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 410-418
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML2,4,5-Trichloro-6-((2,4,6-trichlorophenyl)amino)isophthalonitrile (SYD007) is a small molecule compound that was synthesized according to the structure of diarylamine. In this study, we evaluated the anti-bladder activities of SYD007, and determined its cytotoxic mechanism. We found that SYD007 exerted cytotoxicity to bladder cancer cells. Furthermore, SYD007 induced bladder cancer cell early apoptosis and arrested cell cycle. Mechanistically, SYD007 suppressed phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3) (Tyr705) level in parallel with increases of p-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and p-AKT. SYD007 significantly inhibited insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)-induced STAT3 activation through down-regulation of total IGF-1R level. No dramatic changes in IGF-1R mRNA levels were observed in SYD007-treated cells, suggesting that SYD007 acted primarily at a posttranscriptional level. Using molecular docking analysis, SYD007 was identified as an IGF-1R inhibitor. In summary, we reported that SYD007 exerted anti-bladder activities, and these effects were partially due to inhibition of IGF-1R/STAT3 signaling.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3636K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3636K) Full view HTML -
Zhijian Huang, Qian Li, Weixiang Ye, Qiang Zhang, Xiuyan Li2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 419-425
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPatients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and hyperlipidemia are with high risk of myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary death events. The combined use of ezetimibe and atorvastatin could improve treatment efficacy and safety. To explore the efficacy and safety of ezetimibe in combination with atorvastatin for the treatment of patients with T2DM and acute coronary syndrome (ACS). This was a non-randomized cohort study of 95 consecutive, treatment-naïve patients with T2DM and ACS treated at the Quanzhou First Hospital of Fujian Province between February 2014 and March 2016. According to the treatment strategy they selected, the patients were categorized into the atorvastatin (n = 46) and atorvastatin + ezetimibe (n = 49) groups. The patients were followed up at 2 weeks and 12 months. The primary endpoints included the incidence of adverse cardiovascular events and changed in blood lipids and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). At 12 months, serum total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were significantly lower, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly higher in the atorvastatin + ezetimibe (EZ) group than in the atorvastatin group (all p < 0.05). The LDL-C control rate at 12 months was significantly higher in the atorvastatin + EZ group compared with the atorvastatin group (p = 0.006). Seven patients in the atorvastatin group were re-hospitalized for angina pectoris, while only one patient in the atorvastatin + EZ group was re-hospitalized for angina pectoris (p = 0.02). The efficacy of atorvastatin + EZ in treating T2DM patients accompanied with ACS was significantly higher than using atorvastatin alone. This combined strategy has good safety profile, and could be recommended for clinical application.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (481K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (481K) Full view HTML -
Hirotomo Moriwaki, Yu-Shi Tian, Norihito Kawashita, Tatsuya Takagi2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 426-432
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLQuantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) techniques, especially those that possess three-dimensional attributes, such as the comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA), are frequently used in modern-day drug design and other related research domains. However, the requirement for accurate alignment of compounds in CoMFA increases the difficulties encountered in its use. This has led to the development of several techniques—such as VolSurf, Grid-independent descriptors (GRIND), and Anchor-GRIND—which do not require such an alignment. We propose a technique to construct the prediction model that uses molecular interaction field grid potentials as inputs to convolutional neural network. The proposed model has been found to demonstrate higher accuracy compared to the conventional descriptor-based QSAR models as well as Anchor-GRIND techniques. In addition, the method is target independent, and is capable of providing useful information regarding the importance of individual atoms constituting the compounds contained in the chemical dataset used in the proposed analysis. In view of these advantages, the proposed technique is expected to find wide applications in future drug-design operations.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2079K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2079K) Full view HTML -
Majid A. Ganaie, Basit L. Jan, Tajdar H. Khan, Khalid M. Alharthy, Ish ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 433-438
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
Advance online publication: February 20, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOxaliplatin is a third generation platinum based anti-cancer drug used against various human malignancies but displays genotoxic properties against normal cells. Naringenin is a naturally occurring bioflavonoid that possesses anti-oxidant properties and has protective effects against DNA damage. The aim of this study is to examine the protective effects of naringenin on oxaliplatin-induced DNA damage in mice. A total of 50, male BALB/c mice were randomly divided equally into five groups. Oxaliplatin toxicity was induced by a single dose (7 mg/kg body weight (b.w.)) injection (intraperitoneally (i.p.)) of oxaliplatin. Naringenin was given orally for ten consecutive days at two doses, 20 mg/kg b.w. (dose I) and 40 mg/kg b.w. (dose II), to group I and group II, respectively. On the tenth day of the experiment, animals in groups III, IV, and V were given a single i.p. injection of oxaliplatin (7 mg/kg b.w.). All the animals were sacrificed 24 h after oxaliplatin treatment. The extent of genotoxicity was assessed by multiple genotoxicity assays (8-hydroxydeoxy-guanosine marker, comet, micronucleus and chromosomal aberration assays, oxidative stress-marker Glutathione evaluation) in order to determine diverse kinds of DNA damage. The results indicated that naringenin administration significantly reduced the DNA damage induced by oxaliplatin possibly due to its strong anti-oxidant properties. The results suggest that naringenin is a potential candidate for future development as a chemoprotective agent against chemotherapy associated complications.
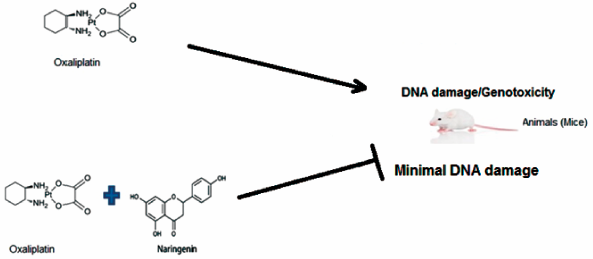 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (282K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (282K) Full view HTML -
 Norihiro Sakurai, Yasutaka Nakamura, Hiroshi Kawaguchi, Junko Abe, Koi ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 439-444
Norihiro Sakurai, Yasutaka Nakamura, Hiroshi Kawaguchi, Junko Abe, Koi ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 439-444
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method was developed and validated for the quantification of linezolid, PNU-142300, and PNU-142586 in human plasma. After protein precipitation using acetonitrile, the protein-free supernatant was separated using reverse-phase chromatography using an ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column and monitored at 254 nm. p-Toluic acid was used as the internal standard. No interference peak was observed at the retention times of linezolid, PNU-142300, PNU-142586, and p-toluic acid from blank plasma. The calibration curve of linezolid was linear from 0.2 to 50.0 µg/mL (coefficient of determination (r2) > 0.9999) and those of PNU-142300 and PNU-142586 were linear from 0.2 to 20.0 µg/mL (r2 > 0.9996 and > 0.9998, respectively). The intra- and inter-assay accuracy (%) and precision (relative standard deviation (RSD) %) of the three components were confirmed to meet the criteria of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration guidelines. Tests confirmed the stability of linezolid, PNU-142300, and PNU-142586 in plasma during three freeze-thaw cycles and long-term storage of frozen plasma for up to 30 d; in extracts they were stable in the UPLC autosampler for over 48 h at 4°C. Furthermore, plasma concentrations of linezolid, PNU-142300 and PNU-142586 in patients treated with linezolid could be measured using the UPLC method developed in this study. This assay would be a powerful tool for therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) analyses in the optimization of linezolid treatment.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes the development and validation of a method for measuring linezolid and its metabolites PNU-142300 and PNU-142586 in human plasma, using ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method. This method enables the simultaneous measurement of these three components within 3 min. Further, plasma concentrations of linezolid, PNU-142300 and PNU-142586 in patients treated with linezolid could be measured. The developed method is a useful tool for therapeutic drug monitoring and clinical pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) profiling of linezolid, as well as for dose optimization during treatment.
Download PDF (485K) Full view HTML -
Siti Khadijah Lukman, Rania Hussein Al-Ashwal, Naznin Sultana, Syafiqa ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 445-451
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLElectrodeposition is commonly used to deposit ceramic or metal coating on metallic implants. Its utilization in depositing polymer microcapsule coating is currently being explored. However, there is no encapsulation of drug within polymer microcapsules that will enhance its chemical and biological properties. Therefore, in this study, ginseng which is known for its multiple therapeutic effects was encapsulated inside biodegradable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microcapsules to be coated on pre-treated medical grade stainless steel 316L (SS316L) using an electrodeposition technique. Polyaniline (PANI) was incorporated within the microcapsules to drive the formation of microcapsule coating. The electrodeposition was performed at different current densities (1–3 mA) and different deposition times (20–60 s). The chemical composition, morphology and wettability of the microcapsule coatings were characterized through attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and contact angle analyses. The changes of electrolyte colors, before and after the electrodeposition were also observed. The addition of PANI has formed low wettability and uniform microcapsule coatings at 2 mA current density and 40 s deposition time. Reduction in the current density or deposition time caused less attachment of microcapsule coatings with high wettability records. While prolonging either one parameter has led to debris formation and melted microcapsules with non-uniform wettability measurements. The color of electrolytes was also changed from milky white to dark yellow when the current density and deposition time increased. The application of tolerable current density and deposition time is crucial to obtain a uniform microcapsule coating, projecting a controlled release of encapsulated drug.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2341K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2341K) Full view HTML -
Midori Sakamoto, Tetsuya Kaneko, Yuya Orito, Yasushi Shimoda, Makoto N ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 452-460
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe Michael reaction of malonates with maleates afforded the corresponding adducts in high yields with high enantioselectivities (up to 98% enantiomeric excess (ee)) by using dilithium 3,3′-dichlorobinaphtholate as a catalyst. The obtained Michael adducts could be converted to optically active tricarboxylic acid (TCA) derivatives via the Krapcho reaction.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (639K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (639K) Full view HTML -
 Eriko Sato, Shoji Kudo, Hiroshi Takiyama2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 461-466
Eriko Sato, Shoji Kudo, Hiroshi Takiyama2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 461-466
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCrystallization by pH adjustment, as a type of reaction crystallization, is a solid–liquid separation method widely used in the area of pharmaceutical and pharmaceutical intermediate manufacturing. On the other hand, 3-alkenyl cephem compound is a typical zwitterionic pharmaceutical intermediate that possesses both an amino group and a carboxylic acid group. Such structure affords three main pH regions in solution and results in difficulties using crystallization by pH adjustment for isolation. As a consequence, 3-alkenyl cephem compound is usually crystallized at the point away from the solubility curve, causing unrestricted nucleation and flocculation behavior for the deposited particles which is difficult to filtrate. In this study, the pKa of 3-alkenyl cephem compound was intensively investigated to inhibit the nucleation. An optimal pH level point was also sought to make monodisperse particles. In particular, during crystallization by pH-modulation operation, the key point was identified to be the number of primary particles aggregated in the secondary particles. It was revealed that the increment number of primary particles led to the generation of larger monodisperse particles. This investigation, combined with solid–liquid equilibrium, enabled the acquisition of target species with good operability for filtration process. This present investigation becomes the prosperity in the zwitterion compound production that it has hardships to crystallize and filtrate.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick3-Alkenyl cephem compound is a pharmaceutical intermediate. It is typically crystalized by pH adjustment method. However, since the filtration time in the solid-liquid separator is a bottleneck in the production, there is a need to control crystal morphology while changing the pH. This study could be shorten filtration time by pH-modulation operation that repeating the crystallization operation in the vicinity of solubility. The obtained monodisperse particles were like a pseudo-growth body in which a large number of primary particles were aggregated and increased, rather than being a crystallite growth.
Download PDF (1460K) Full view HTML -
Masanori Kaihara, Kazuhiro Hojo, Tomokazu Tajiri, Atsushi Kambayashi, ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 467-475
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe aim of this study was to establish a novel approach to in vitro dissolution evaluation using a combination of the paddle method and a dialysis membrane, both to predict the overall in vivo performance of tacrolimus microspheres and also to identify a suitable dissolution test method to describe the in vivo initial burst phenomenon. This new dissolution method for evaluating the release of tacrolimus from microspheres consisted of rotating a customized paddle inside a dialysis membrane using a conventional paddle apparatus. Findings were compared with a method in which the paddle was rotated outside the dialysis membrane, the conventional paddle method, and the flow-through cell method. We concluded that the paddle method with a dialysis membrane and internal agitation, which was designed to mimic in vivo conditions, predicted the overall pharmacokinetic (PK) profile of tacrolimus microspheres whereas the conventional paddle method described the initial burst. These findings suggest that it may not be possible to predict both the PK profile and initial burst using a single analysis method. We therefore recommend that evaluation of the initial burst be performed separately. In conclusion, we propose that combination of the paddle method with a dialysis membrane and internal agitation to evaluate the overall PK profile, together with the paddle method to describe the in vivo initial burst, represents a novel approach to in vitro dissolution evaluation for microsphere formulations.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (870K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (870K) Full view HTML -
 Kenichi Matsuda, Takefumi Kuranaga, Ayae Sano, Akihiro Ninomiya, Kenta ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 476-480
Kenichi Matsuda, Takefumi Kuranaga, Ayae Sano, Akihiro Ninomiya, Kenta ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 476-480
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSurugamides are a group of non-ribosomal peptides isolated from marine-derived Streptomyces. Surugamide A (1) and its closely related derivatives, surugamides B–E (2–5), are D-amino acid containing cyclic octapeptides with cathepsin B inhibitory activity. The D-isoleucine (Ile), the nonproteinogenic amino acid residue embedded in 1, is less common in natural peptides because a rare Cβ-epimerization is required for its biosynthesis. Taking advantage of the synthetic route of 2 previously established by our group, we synthesized the cyclic octapeptide 1 containing D-Ile by solid phase peptide synthesis. The structure of 1 actually contains D-allo-Ile in place of D-Ile, which was corroborated by chemical syntheses and chromatographic comparisons.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickSurugamide A, a non-ribosomal peptide with cathepsin B inhibitory activity, and its closely related derivatives, surugamides B-E are cyclic octapeptides produced by several Streptomyces species. All these peptides except for surugamide B contain a D-Ile residue that involve Cβ-epimerization step during its biosynthesis. However, the genes responsible for this conversion is absent in the biosynthetic gene cluster of surugamides. To clarify this issue, surugamide A containing D-Ile as well as its epimer having D-allo-Ile were synthesized. HPLC and Marfey’s analyses showed that surugamide A actually possesses D-allo-Ile instead of D-Ile, requiring structural collection of this group of peptides.
Download PDF (806K) Full view HTML -
Xiao-guang Huang, Kun-nan Chen2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 481-486
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialQuinolone 006 is under development as an anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus quinolone antibiotic. A linear synthetic route was utilized to prepare the compound on a multi-kilogram scale with an overall yield of 71%. The process was optimized by controlling the temperature and the vacuum pressure. Examples of parameters examined in an effort to control the polymorphism of the 006 active pharmaceutical ingredient are described.
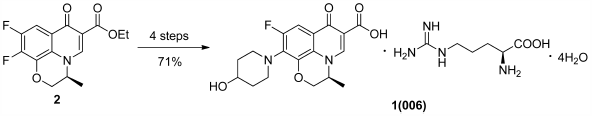 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (839K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (839K) Full view HTML -
Fumihiko Ogata, Noriaki Nagai, Megumu Toda, Masashi Otani, Takehiro Na ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 487-492
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA new mixed metal hydroxide adsorbent (NA11, molar ratioNi–Al = 1 : 1) was prepared and its physicochemical properties (specific surface area, amount of hydroxyl group, scanning electron microscopy images, X-ray diffraction analysis, elemental distribution, and binding energy) were studied. In addition, the amount of borate ion adsorbed using several adsorbents, including NA11, was evaluated in this study. The specific surface area of and amount of hydroxyl group in NA11 was greater than those of the other studied adsorbents. The amount of borate ion adsorbed showed similar trends to those of the specific surface area and number of hyrdroxyl groups, which indicated that the adsorption mechanism of borate ion was related to the specific surface area and the amount of hydroxyl group. After adsorption, the binding energy of boron B(1s) peaked, and the sulfur peak intensity S(2s) and S(2p) reduced. These results suggest that ion exchange between borate and sulfate ions was one of the adsorption mechanisms. Equilibrium adsorption was reached within 6 h in the case of NA11. These data were fitted into a pseudo-second-order model (r = 0.813–0.998). The solution pH affected the capacity of NA11 for adsorbing borate ion from aqueous solution. It was found that adsorbance was greatest at pH 10. Adsorption isotherm data were fitted to both the Freundlich (r = 0.986–0.994) and Langmuir (r = 0.997–0.999) isotherm equations. Collectively, it is suggested that NA11 is prospectively useful for the adsorption of borate ion from aqueous solutions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1374K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1374K) Full view HTML
-
Takako Ishiguro, Yukoh Sakata, Hidetoshi Arima, Daisuke Iohara, Makoto ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 493-497
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA system for releasing a fragrance, citral (CR) over an extended period of time using three types of enteric capsules is reported. The L- and M-type capsules released CR into media with a pH above 6, while the H-type capsule released CR at a pH above 7. The pH of the releasing medium was controlled by sodium borate (SB), i.e., by adding SB–methylcellulose (MC) prepared in different weight ratios (SB–MC 1 : 2, 1 : 1 and 2 : 1) to tablets and by compressing them at different pressures. The tablet containing a large amount of SB and that was pressed at higher pressures permitted the pH of the releasing medium to be changed from 5 to 9, at 4–5 h after the addition of SB to the tablets, while negligible changes were observed for tablets containing low amounts of SB and which were compressed at lower pressures. Reflecting these pH changes, CR was released after different periods of time when SB–MC tablets and capsules containing CR were simultaneously added to the releasing medium. When enteric capsules containing CR and the pH adjusting tablets were simultaneously added to a benzyl acetate (BA) solution, BA was released at a constant rate, while CR was released for different periods of time depending on the type of capsule used. The results suggest that fragrances could be released over different time frames by using enteric capsules and pH adjusting agents, for example, the release of fragrances with sedative effects at night time and with stimulating effects in the morning.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (602K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (602K) Full view HTML -
On the Electronic Nature of Bis((Z)-1-(benzo[d]oxazol-2-yl)-3.3.3-trifluoroprop-1-en-2-ate)palladiumKathleen L. May, Genki Watanabe, Ryosuke Saijo, Masami Kawase, Robert ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 498-500
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe electronic nature of the recently reported complex, bis((Z)-1-(benzo[d]oxazol-2-yl)-3.3.3-trifluoroprop-1-en-2-ate)palladium, is re-investigated by a combination of spectroscopy (NMR, IR, magnetic moment, etc.) and Density Functional Theory (DFT: B3LYP 6–31G*/LANL2DZ). In contrast to the recent report, the title complex displays all the properties of diamagnetism and hence retains the properties of a formally Pd(II) square planar complex with a bis-κ2-N,O-donor ligand set. A modified synthetic route is also presented which improves the yield of the compound.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (315K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (315K) Full view HTML -
Hiroyuki Tsutsumi, Ayano Sato, Satoru Fujino, Yusuke Fujioka, Takashi ...2019 Volume 67 Issue 5 Pages 501-504
Published: May 01, 2019
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAn aqueous solution of equimolecular amounts of 2-chloropyrimidine and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCg) afforded a colorless block crystal, which was determined to be a 2 : 2 complex of 2-chloropyrimidine and EGCg by X-ray crystallographic analysis. The 2 : 2 complex was formed by the cooperative effect of three intermolecular interactions, π–π and CH–π interactions, and intermolecular hydrogen bonds. Upon formation of the 2 : 2 complex, a 2-chloropyrimidine molecule was captured by a hydrophobic space formed by the three aromatic rings of A, B, and B′ rings of two EGCg molecules. The molecular capture abilities of various heterocyclic compounds using EGCg were evaluated by ratio of the heterocyclic compounds included in the precipitates of complex of EGCg to the heterocyclic compounds used. The amount of the heterocyclic compounds was measured by an integrated value of corresponding proton signals in the quantitative 1H-NMR spectrum.
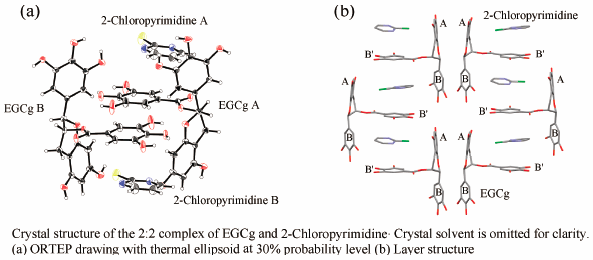 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (806K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (806K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|