
- Issue 4 Pages 349-
- Issue 3 Pages 241-
- Issue 2 Pages 135-
- Issue 1 Pages 1-
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Richiro Ushimaru2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 241-247
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNatural products from plants and microorganisms provide a valuable reservoir of pharmaceutical compounds. C–C bond formation and cleavage are crucial events during natural product biosynthesis, playing pivotal roles in generating diverse and intricate chemical structures that are essential for biological functions. This review summarizes our recent findings regarding biosynthetic enzymes that catalyze unconventional C–C bond formation and cleavage reactions during natural product biosynthesis.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2464K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2464K) Full view HTML
-
Akira Kotani2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 248
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (181K) Full view HTML
-
Masaki Toda, Kyoko Sugiyama, Fumiya Sato, Yusuke Sasano, Tsutomu Fujim ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 249-252
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLElectrochemical enzyme sensors are suitable for simple monitoring methods, for example, as glucose sensors for diabetic patients; however, they have several disadvantages arising from the properties of the enzyme. Therefore, non-enzymatic electrochemical sensors using functional molecules are being developed. In this paper, we report the electrochemical characterization of a new hydroxylamine compound, 7-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-7-ol (ABHOL), and its application to glucose sensing. Although the cyclic voltammogram for the first cycle was unstable, it was reproducible after the second cycle, enabling electrochemical analysis of ethanol and glucose. In the first cycle, ABHOL caused complex reactions, including electrochemical oxidation and comproportionation with the generated oxoammonium ions. The electrochemical probe performance of ABHOL was more efficient than the typical nitroxyl radical compound, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO), and had similar efficiency to 9-azabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane N-oxyl (ABNO), which is activated by the bicyclic structure. The results demonstrated the advantages of ABHOL, which can be synthesized from inexpensive materials via simple methods.
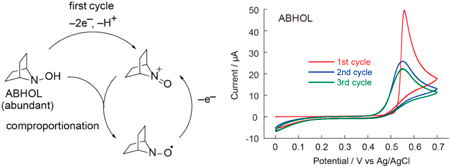 View full abstractDownload PDF (1058K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1058K) Full view HTML
-
Hikaru Ikeda, Akira Tokonami, Shigeki Nishii, Masashi Fujita, Yojiro Y ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 253-257
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study focused on the electrochemical properties of tetrazolium salts to develop a simple method for evaluating viable bacterial counts, which are indicators of drug susceptibility. Considering that the oxidized form of tetrazolium, which has excellent cell membrane permeability, changes to the insoluble reduced form formazan inside the cell, the number of viable cells was estimated based on the reduction current of the tetrazolium remaining in the bacterial suspension. Dissolved oxygen is an important component of bacterial activity. However, it interferes with the electrochemical response of tetrazolium. We estimated the number of viable bacteria in the suspension based on potential-selective current responses that were not affected by dissolved oxygen. Based on solubility, cell membrane permeability, and characteristic electrochemical properties of the tetrazolium salt 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium, we developed a method for rapidly measuring viable bacteria within one-fifth of the time required by conventional colorimetric methods for drug susceptibility testing.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1134K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1134K) Full view HTML -
Michiru Ito, Kazuharu Sugawara2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 258-265
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialGlycated albumin (GA) is one of the proteins that replaces several sugar moieties and can be used as an indicator of diabetes mellitus. We developed a sensing system that uses GA in the early detection of diabetes mellitus. In this study, H6Y4C acetylated (Ac-) at the N-terminals of the peptide was combined with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) to recognize glucose moieties. The Ac-H6Y4C-WGA was constructed as a GA-sensing probe. The tyrosine residues of Y4C exhibited an oxidation peak, and His-tag moieties were introduced to separate Ac-H6Y4C-WGA in the synthesis of the probe. The Ac-H6Y4C-WGA probe binds with the 1–2 molecules of Ac-H6Y4C per WGA using matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight (MALDI-TOF)-MS. Next, the functions of Ac-H6Y4C-WGA were evaluated using voltammetry. The number of electron-transfers was calculated based on the relationship between the peak potential and logarithm of scan rate and was 3.03. In the electrochemical measurements with mannose and bovine serum albumin, the peak currents were similar to that of GA alone. By contrast, a decrease in the peak current was suppressed when glucose was added to the solution containing the probe. As a result, Ac-H6Y4C-WGA was selectively bound to the glucose moieties of GA. The calibration curve via differential pulse voltammetry was proportional to the concentrations of GA and ranged from 1.0 × 10−12 to 2.0 × 10−11 M with a detection limit of 3.3 × 10−13 M.
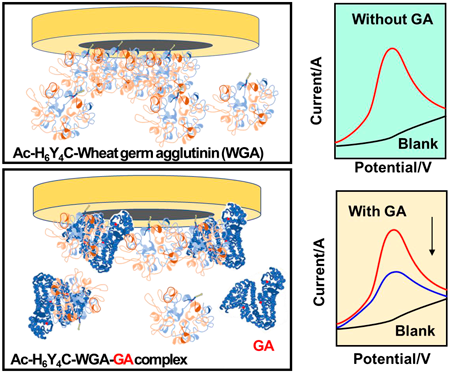 View full abstractDownload PDF (1800K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1800K) Full view HTML -
Akira Kotani, Miyu Sakazume, Koichi Machida, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Hideki ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 266-270
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn this study, an electrochemical analysis, coupled with the concept of back neutralization titration and the voltammetric determination of surplus acid, is proposed for determining the total alkalinity of water samples. When linear sweep voltammetry of 3,5-di-tert-butyl-1,2-benzoquinone (DBBQ) with H2SO4 in a water and ethanol (44 : 56, v/v) mixture was carried out using a bare glassy carbon working electrode, a cathodic prepeak of DBBQ caused by H2SO4 was observed on the voltammogram at a more positive potential than when compared with the original cathodic peak of DBBQ. When similar voltammetry was carried out in the presence of Na2CO3 and H2SO4, the cathodic prepeak height of DBBQ was decreased with an increase in the Na2CO3 concentration. The decrease of the cathodic prepeak height of DBBQ was found to be linearly related to the Na2CO3 concentration ranging from 0.025 to 2.5 mM (r2 = 0.998). The total equivalent concentrations of inorganic bases in samples of mineral water and tap water were determined, and then the results were converted to the total alkalinities of the water samples (mg/L CaCO3). The total alkalinities of the water samples determined by the present electrochemical analysis were essentially the same compared with those by the neutralization titration method. From these results, we were able to demonstrate that the present electrochemical analysis with accuracy and precision could be applied to determine the total alkalinity, which is one of the indicators to examine water quality. The present electrochemical analysis would contribute to achieving the sustainable development goals (SDGs) of #6 and #14.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (649K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (649K) Full view HTML -
 Fumiki Takahashi, Yuki Shimosaka, Shuki Mori, Mayu Kaneko, Yuta Haraya ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 271-279
Fumiki Takahashi, Yuki Shimosaka, Shuki Mori, Mayu Kaneko, Yuta Haraya ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 271-279
Published: March 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCodeine is a common analgesic drug that is a pro-drug of morphine. It also has a high risk of abuse as a recreational drug because of its extensive distribution as an OTC drug. Therefore, sensitive and selective screening methods for codeine are crucial in forensic analytical chemistry. To date, a commercial analytical kit has not been developed for dedicated codeine determination, and there is a need for an analytical method to quantify codeine in the field. In the present work, potential modulation was combined with electrochemiluminescence (ECL) for sensitive determination of codeine. The potential modulated technique involved applying a signal to electrodes by superimposing an AC potential on the DC potential. When tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II) ([Ru(bpy)3]2+) was used as an ECL emitter, ECL activity was confirmed for codeine. A detailed investigation of the electrochemical reaction mechanism suggested a characteristic ECL reaction mechanism involving electrochemical oxidation of the opioid framework. Besides the usual ECL reaction derived from the amine framework, selective detection of codeine was possible under the measurement conditions, with clear luminescence observed in an acidic solution. The sensitivity of codeine detection by potential modulated-ECL was one order of magnitude higher than that obtained with the conventional potential sweep method. The proposed method was applied to codeine determination in actual prescription medications and OTC drug samples. Codeine was selectively determined from other compounds in medications and showed good linearity with a low detection limit (150 ng mL−1).
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickCodeine, is used worldwide and abused as a recreational drug. The authors developed a system to selectively and sensitively detect codeine from over-the-counter medications containing interfering drug components by electrochemiluminescence (ECL) combined with potential modulated technique (PM). The sensitivity for detection of codeine by PM-ECL was more than one order of magnitude larger than that obtained in conventional potential sweep mode. The established technique was applied to codeine determination in over-the-counter drugs and medicines and was not affected by the presence of structurally similar chemicals. The proposed method expected to apply as a sensitive on-site analytical method for a wide range of detection, especially clinical and forensic analysis.
Download PDF (1892K) Full view HTML
-
Xiangming Wang, Menghui Zhao, Chengguo Ju, Hui Gao, Wei Wang2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 280-285
Published: March 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2024
Advance online publication: February 07, 2024JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study investigated the hepatoprotective effects of Juncus effusus (J. effusus) and Carbonized J. effusus against liver injury caused by D-galactosamine (D-GalN) in mice. J. effusus and Carbonized J. effusus were administered by gavage once daily starting seven days before the D-GalN treatment. The results of the study indicated that J. effusus and Carbonized J. effusus suppressed the D-GalN-induced generation of serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), hepatic malondialdehyde (MDA) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) was observed. The values of superoxide dismutase (SOD) exhibited an increase. In addition, J. effusus and Carbonized J. effusus promoted the protein expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), NADPH quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO-1), heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) as well as the mRNA expression of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO-1 and Glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC). The compressed Carbonized J. effusus demonstrated the optimum impact. These results suggest that J. effusus and Carbonized J. effusus protect against D-GalN-induced acute liver injury through the activation of the Nrf2 pathway.
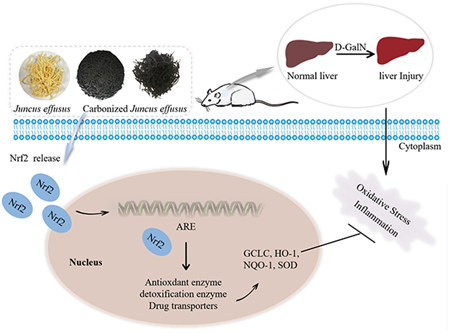 View full abstractDownload PDF (4065K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4065K) Full view HTML -
Effect of Concomitant Drugs on Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate Hydrate in Artificial Intestinal JuiceYuri Mizuno, Fumihiko Ogata, Yugo Uematsu, Naohito Kawasaki2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 286-293
Published: March 06, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo explore drug interactions involving sodium zirconium cyclosilicate hydrate (SZC) and concomitant drugs like calcium antagonists (amlodipine and nifedipine) and β-blockers (carvedilol and bisoprolol), we investigate how these concomitant drugs influenced the administration of SZC in an artificial intestinal juice. Initially, we assessed the potassium ion adsorption capacity, ranking it as follows: calcium polystyrene sulfonate (CPS, 54.9 mg/g) < sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS, 62.1 mg/g) < SZC (90.8 mg/g). However, the adsorption equilibrium was achieved in the order of CPS ≒ SPS (within 1 min) < SZC (within 1 h). Subsequently, we determined the residual percentages of amlodipine, nifedipine, carvedilol, and bisoprolol, finding them to be 79.0–91.9% for SZC, 0.38–38.4% for SPS, and 0.57–29.0% for CPS. These results suggest the efficacy of SZC in managing hyperkalemia alongside concomitant drugs in an artificial intestinal juice, with particular emphasis on amlodipine (calcium antagonist) and carvedilol (β-blocker). Additionally, we identified the presence of carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen components from both drugs on the SZC surface following interaction. We also evaluated how amlodipine, nifedipine, carvedilol, and bisoprolol affected the administration of SZC in the presence of potassium ions. Our results indicate that potassium ions and concomitant drugs did not interfere with each other in the artificial intestinal juice. These results offer valuable insights into the administration of SZC in conjunction with concomitant drugs. Lastly, the presented data shows qualitative results in this study.
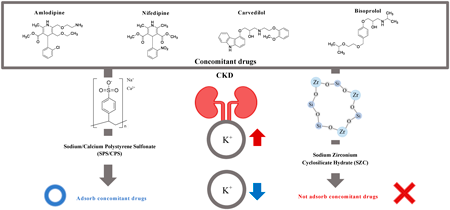 View full abstractDownload PDF (4450K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (4450K) Full view HTML
-
Akihiro Yokoyama, Ayaka Chino, Kenta Rakumitsu2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 294-297
Published: March 08, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 08, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAiming to synthesize a cyclic hexaamide, 4-bromo-3-(isobutylamino)benzoic acid was subjected to self-condensation reactions in the presence of either dichlorotriphenylphosphorane in 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane or tetrachlorosilane in pyridine. However, instead of the targeted cyclic hexaamide, the cyclic triamide and the cyclic tetraamide were obtained. The cyclic hexaamide was successfully synthesized via the self-condensation of the dimer, which was synthesized in five steps from 4-bromo-3-(isobutylamino)benzoic acid. A thorough screening of the self-condensation conditions was performed to improve the yield of the target macrocycle. In addition, the linear hexamer was synthesized by stepwise deprotection and condensation, and its cyclization afforded the cyclic hexaamide in good yield.
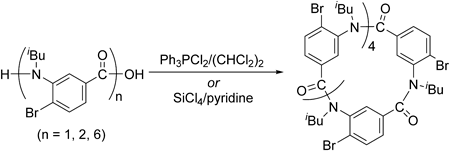 View full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (561K) Full view HTML
-
Masaki Higashino, Kiyohiko Sugano2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 298-302
Published: March 13, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 13, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe current study aimed to explore the impact of buffer species on the dissolution behavior of orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) containing a basic polymer and its influence on bioequivalence (BE) prediction. Fexofenadine hydrochloride ODT formulations were used as the model formulations, Allegra® as the reference formulation, and generic formulations A and B as the test formulations. Allegra®, generic A, and generic B are ODT formulations that contain aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymers E (Eudragit® E, EUD-E), a basic polymer commonly used to mask the bitter taste of drugs. Both generic A and generic B have been known to be bioequivalent to Allegra®. The dissolution tests were conducted using a compendial paddle, with either bicarbonate (10 mM, pH 6.8) or phosphate buffer (25 mM, pH 6.8) as the dissolution media. A floating lid was employed to cover the surface of the bicarbonate buffer to prevent volatilization. Results indicated that in phosphate buffer, the dissolution profiles of Allegra and generic B significantly varied from that of generic A, whereas in the bicarbonate buffer, the dissolution profiles of Allegra, generic A, and generic B were comparable. These findings suggest that the use of bicarbonate buffer may offer a more precise prediction of human bioequivalence compared to phosphate buffer.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1484K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1484K) Full view HTML -
Keisuke Yoshida, Wataru Hirano, Ryuuki Ota, Shinji Kitagaki2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 303-308
Published: March 12, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 12, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAmine-free phosphorylation of various alcohols was developed with 4-methylpyridine N-oxide in the presence of 4 Å molecular sieves at room temperature. This mild method gave various phosphorylated products in high yield and could be applied to acid- or base-sensitive substrates. Furthermore, this method was also effective for the chemoselective phosphorylation of diols or polyols.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (739K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (739K) Full view HTML
-
Chiyuki Awahara, Daiki Oku, Kazuya Kobayashi, Yasunao Hattori2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 309-310
Published: March 14, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 14, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe inhibition mode of a retro-inverso (RI) inhibitor containing a hydroxyethylamine dipeptide isostere against the human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 (HTLV-1) protease was examined. Enzymatic evaluation of the RI-modified inhibitor containing a D-allo-Ile residue revealed that HTLV-1 was competitively inhibited. IC50 values of the RI-modified inhibitor and pepstatin A, a standard inhibitor of aspartic proteases, were nearly equivalent.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (373K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (373K) Full view HTML -
 Takuya Kobayakawa, Hikaru Takano, Takahiro Ishii, Peter Bolah, Kohei T ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 311-312
Takuya Kobayakawa, Hikaru Takano, Takahiro Ishii, Peter Bolah, Kohei T ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 311-312
Published: March 16, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 16, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAn improvement of the two-photon excitation was achieved using 8-azacoumarin-type caged compounds, which showed large values of the two-photon uncaging action cross-section (δu >0.1 Goeppert–Mayer (GM)). In particular, the 7-hydroxy-6-iodo-8-azacoumarin (8-aza-Ihc)-caged compound showed an excellent uncaging action cross-section value (δu = 1.28 GM). Therefore, 8-azacoumarin-type photolabile protecting groups (PPGs) can be used as two-photon excitation sources.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickPhotolabile protecting groups (PPGs) have been utilized in many research fields such as organic synthesis and chemical biology because their fast and selective photocleavage proceeds under mild conditions. The authors previously reported the design and synthesis of 8-azacoumarin-type PPGs based on the alkene-to-amide replacement of the 6-bromo-7-hydroxy-coumarin-4-ylmethyl (Bhc) group. The characteristic feature of these PPGs is their aqueous solubility, which is remarkably higher than that of Bhc. The authors found that 8-azacoumarin-type PPGs can also be used as two-photon excitation sources because the photolytic efficiency for two-photon excitation showed preferable physicochemical values for applications in cells and tissues.
Download PDF (369K) Full view HTML
-
 Haruki Kanda, Ayaka Okabe, Shingo Harada, Tetsuhiro Nemoto2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 313-318
Haruki Kanda, Ayaka Okabe, Shingo Harada, Tetsuhiro Nemoto2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 313-318
Published: March 16, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 16, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialGenerating reliable data on functional group compatibility and chemoselectivity is essential for evaluating the practicality of chemical reactions and predicting retrosynthetic routes. In this context, we performed systematic studies using a functional group evaluation kit including 26 kinds of additives to assess the functional group tolerance of carbene-mediated reactions. Our findings revealed that some intermolecular heteroatom–hydrogen insertion reactions proceed faster than intramolecular cyclopropanation reactions. Lewis basic functionalities inhibited rhodium-catalyzed C–H functionalization of indoles. While performing these studies, we observed an unexpected C–H functionalization of a 1-naphthol variant used as an additive.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickReliable data on the compatibility and chemoselectivity of functional groups are essential for assessing the usefulness of chemical reactions. Authors systematically evaluated the functional group tolerance of carbene-mediated reactions as a core project of the Grant-in-Aid for Transformative Research Area A “Digitalization-driven Transformative Organic Synthesis”. In the course of this study, unexpected C-H functionalization of a naphthol derivative used as an additive was observed. Authors believe that collecting dependable information, including negative experimental results, plays a crucial role in developing organic synthesis.
Download PDF (1906K) Full view HTML
-
Kathrine Anne Flores, Akie Okada, Florencio Arce Jr., Gerard Lee See, ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 319-323
Published: March 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 20, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAuraptene (Aur) is a naturally occurring monoterpene coumarin ether that exhibits numerous therapeutic properties. Its high lipophilicity and low skin penetration, however, limit its potential application for local and transdermal delivery. Biocompatible non-ionic sugar esters (SEs) possess beneficial properties for the development of transdermal formulations in delivering pharmaceutically challenging molecules such as graphene and Aur. In the present study, we conducted a series of experiments to demonstrate the effect of several previously unstudied SEs on the skin permeation and distribution of Aur by preparing gel- and dispersion-type formulations. Skin permeation and deposition experiments were conducted using a Franz diffusion cell with rat skin as the membrane. The dispersion-type formulations prepared using SEs had higher entrapment efficiency, as well as better skin permeation and retention profiles. The dispersion-type formulation containing sucrose palmitate (sSP) exhibited the highest skin permeation over 8 h. Notably, the enhancement effects on Aur concentration in full-thickness skin after the application of the dispersion-type formulation was higher than those of the control formulation. These results indicated that the prepared formulation has potential for use in the transdermal delivery of Aur in pharmaceutical and cosmetic products.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1129K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1129K) Full view HTML
-
 Riho Ogawa, Kouji Hara, Ayaka Kobayashi, Nobuyoshi Yoshimura, Yutaka T ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 324-329
Riho Ogawa, Kouji Hara, Ayaka Kobayashi, Nobuyoshi Yoshimura, Yutaka T ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 324-329
Published: March 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 21, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPolymeric nanofibers generated via electrospinning offer a promising platform for drug delivery systems. This study examines the application of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers for controlled lysozyme (LZM) delivery. By using various PVA grades, such as the degree of polymerization/hydrolysis, this study investigates their influence on nanofiber morphology and drug-release characteristics. LZM-loaded PVA monolithic nanofibers having 50% drug content exhibit efficient entrapment, wherein rapid dissolution is achieved within 30 min. The initial burst of LZM from the nanofiber was reduced as the LZM content was lowered. The initial dissolution is greatly influenced by the choice of PVA grade used; fully hydrolyzed PVA nanofibers demonstrate controlled release due to the reduced water solubility of PVA. Furthermore, coaxial electrospinning, which creates core–shell nanofibers with polycaprolactone as a controlled release layer, enables sustained LZM release over an extended period. This study confirms a correlation between PVA characteristics and controlled drug release and provides valuable insights into tailoring nanofiber properties for pharmaceutical applications.
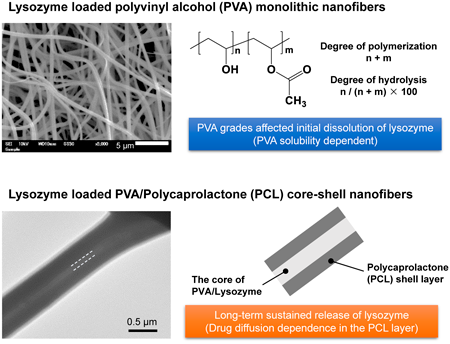 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The authors investigated the use of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers for the drug delivery of lysozyme (LZM), focusing on how different PVA grades affect drug release characteristics. PVA nanofibers with a 50% LZM content achieved efficient encapsulation and quick release within 30 minutes. Using fully hydrolyzed PVA led to more controlled release due to its reduced water solubility. Notably, the study highlighted coaxial electrospinning to create PVA/LZM nanofibers coated with polycaprolactone, facilitating extended drug release. This approach clarified the relationship between the characteristics of PVA in nanofibers and drug release properties, offering promising insights for pharmaceutical nanofibers.Download PDF (2575K) Full view HTML -
Reon Takeuchi, Junko Fujimoto, Yoshinori Taguchi, Ryuji Ide, Ryuji Kya ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 330-335
Published: March 25, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA 12-keto-type oleanolic acid derivative (4) has been identified as a potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) compound that demonstrates synergistic effects with several types of HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies. In the present study, we used a common key synthetic intermediate to carry out the late-stage derivatization of an anti-HIV compound based on the chemical structure of a 12-keto-type oleanolic acid derivative. To execute this strategy, we designed a diketo-type oleanolic acid derivative (5) for chemoselective transformation, targeting the carboxy group and the hydroxyl group on the statine unit, as well as the 3-carbonyl group on the oleanolic acid unit, as orthogonal synthetic handles. We carried out four types of chemoselective transformations, leading to identification of the indole-type derivative (16) as a novel potent anti-HIV compound. In addition, further optimization of the β-hydroxyl group on the statine unit provided the R-4-isobutyl γ-amino acid-type derivative (6), which exhibited potent anti-HIV activity comparable to that of 4 but with reduced cytotoxicity.
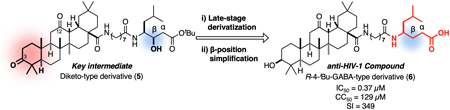 View full abstractDownload PDF (2648K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2648K) Full view HTML
-
 Synthesis of 2-Substituted Indoles via Migration Reaction of 3-Substituted Indoles with Triflic AcidKosuke Nakashima, Yuka Kudo, Yasuyuki Matsushima, Shin-ichi Hirashima, ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 336-339
Synthesis of 2-Substituted Indoles via Migration Reaction of 3-Substituted Indoles with Triflic AcidKosuke Nakashima, Yuka Kudo, Yasuyuki Matsushima, Shin-ichi Hirashima, ...2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 336-339
Published: March 25, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study showcases the 1,2-migration reactions of alkyl and aryl groups on the indole molecule. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid effectively facilitates the migration of the substituent from C3- to C2-position of the indole structure. The resulting C2-substituted indoles offer a valuable pathway for the synthesis of natural products and medicinal compounds.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickIndole is a crucial heterocycle found in various biologically active natural products and medicinal compounds. Therefore, developing convenient methodologies for modifying the indole structure is an interesting topic for the discovery of pharmaceuticals and functional materials. In this context, the authors report trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (2.1 equiv) efficiently facilitates the 1,2-migration reaction of the substituent from C3- to C2- position of the indole structure. Alkyl, aryl groups such as benzyl, isopropyl, phenyl were tolerated for this reaction (up to 98% yield).
Download PDF (506K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroaki Ichimaru, Masashi Kurimoto, Shigetoshi Kikuchi2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 340-344
Published: March 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 28, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialIn clinical diagnosis, magnetic polystyrene nanoparticles (MPS NPs) are commonly applied to, e.g., the chemiluminescent immunoassay (CLEIA). However, the conventional preparation method of MPS NPs requires a long duration of heating to form polymer particles, which is inefficient. In this study, we prepared MPS NPs by emulsion solvent-evaporation without heating. We evaluated the effect of the solvent in the water and organic phases on the magnetic particle content. MPS NPs prepared by 4% (v/v) MeOH aqueous solution and adding stearic acid (SA) (4MeSA–MPS NPs) exhibited the highest magnetic particle content. Furthermore, CLEIA analysis indicates that the C-reactive protein detection limit is 80 pg/mL. Thus, 4MeSA–MPS NPs are promising for clinical diagnoses.
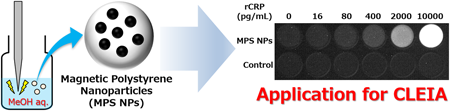 View full abstractDownload PDF (5633K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5633K) Full view HTML -
Makoto Okada, Takashi Nose2024 Volume 72 Issue 3 Pages 345-348
Published: March 30, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 30, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEperisone Hydrochloride was launched in Japan in 1983 and has been used to improve muscle tone and treat spastic paralysis (Originator: Eisai Co., Ltd.). However, its biochemical mechanism of action is unknown. SB Drug Discovery was used to evaluate purinergic P2X (P2X) receptor antagonism using fluorescence. In this study, we discovered that its target protein is the P2X7 receptor. Also, P2X receptor subtype selectivity was high. This finding demonstrates the (Eperisone-P2X7-pain linkage), the validity of P2X7 as a drug target, and the possibility of drug repositioning of Eperisone Hydrochloride.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (472K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (472K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|