
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Na-Na He, Jian-An Wang, Di Huang, Xiao-Long Sun, Feng Ding, Long Zhao, ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 798-803
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFour new magnolol derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their in vitro anti-cancer properties. Among these, compound 3 showed the most potent cytotoxic activity against the SMMC-7721, SUN-449, and HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, with IC50 values of 3.39, 4.11, and 6.88 µM, respectively. Compound 3 also induced apoptosis of SMMC-7721 cells by down-regulating Bcl-2 and Akt protein levels, up-regulating of Bax protein level, and cleaving caspase-9 and -3. In addition, transwell assays showed that compound 3 significantly suppressed the migration and invasion of SMMC-7721 cells, which was confirmed based on the down-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 (MMP-2, and MMP-9) protein levels.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5411K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (5411K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Ishizu, Yuka Fujitani, Runa Nishio, Haruka Kamei2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 804-811
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe stoichiometry and precipitate yield of a complex of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCg) and cyclo(Pro-Xxx) (Xxx = phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr)) were evaluated using integrated values of their proton signals by quantitative 1H-NMR (q NMR). It was determined to be a 1 : 1 complex of EGCg and cyclo(Pro-Xxx). The change in the chemical shift value of proton signals of cyclo(Pro-Xxx) in 1H-NMR spectra by adding standard amounts of EGCg was investigated. Differences in chemical shift values of H8α, H7αβ, H8β, H10, H9, and H3 proton signals between cyclo(L-Pro-L-Phe) and cyclo(D-Pro-D-Phe), and those of H8α, H7αβ, H8β, H10, H9, H3, and H13 proton signals between cyclo(L-Pro-L-Tyr) and cyclo(D-Pro-D-Tyr) were observed as a significant difference at 54 mmol/L of EGCg. It was found that their chirality was clearly recognized by EGCg. The significant difference in the change of the chemical shift value of H8α proton signals between cyclo(L-Pro-L-Xxx) and cyclo(D-Pro-D-Xxx) was the largest, and the difference was considered to have resulted from the difference in the ratio of extended conformer in equilibrium between folded and extended conformers. Such a significant difference in change values between cyclo(L-Pro-D-Xxx) and cyclo(D-Pro-L-Xxx) was not observed due to a rigid intramolecular CH–π interaction. EGCg did not clearly recognize the chirality of cyclo(L-Pro-D-Xxx) and cyclo(D-Pro-L-Xxx).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3047K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3047K) Full view HTML -
A Fluorescence Biosensor for Tyrosinase Activity Analysis Based on Silicon-Doped Carbon Quantum DotsQiang Chen, Lili Zheng, Xiaoqin Deng, Menghan Zhang, Wendi Han, Zhengj ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 812-818
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
Advance online publication: September 14, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTyrosinase (TYR) plays a pivotal role in the biosynthesis of melanin, and its activity level holds critical implications for vitiligo, melanoma cancer, and food nutritional value. The sensitive determination of TYR activity is of great significance for both fundamental research and clinical investigations. In this work, we successfully synthesized silicon-doped carbon quantum dots (Si-CQDs) through a one-pot hydrothermal method with trans-aconitic acid as carbon source and N-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]ethylenediamine as the dopant, exhibiting remarkable fluorescence quantum yield (QY) and photostability. Correspondingly, Si-CQDs were used as a probe to construct a sensitive, rapid, and user-friendly fluorescence method for TYR detection. The method relied on the oxidation of isoprenaline (ISO) by TYR, where Si-CQDs were employed as a highly efficient probe. The testing mechanism was the internal filtering effect (IFE) observed between Si-CQDs and the oxidative system of ISO and TYR. Under the optimized conditions, the fluorescence strategy exhibited a detection range of 0.05–2.0 U/mL for TYR with a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.041 U/mL. Furthermore, we successfully demonstrated the accurate determination of TYR levels in human serum, showcasing the promising potential of this method in various practical scenarios.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3371K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3371K) Full view HTML -
 Shota Oyama, Mao Tomita, Moeka Hata, Yu Mikame, Tsuyoshi Yamamoto, Eis ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 819-823
Shota Oyama, Mao Tomita, Moeka Hata, Yu Mikame, Tsuyoshi Yamamoto, Eis ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 819-823
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
Advance online publication: September 21, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialExosomes are a type of extracellular vesicles that contain diverse molecules and are present in our body fluids. They play a crucial role in transporting materials and transmitting signals between cells. Currently, there have been numerous reports on the use of exosomes in drug delivery systems (DDS). However, most existing methods for utilizing exosomes in DDS require the isolation and purification of exosomes, which raises concerns about yield and potential damage to the exosomes. Recently, we have developed a novel DDS called “ExomiR-Tracker” that harnesses exosomes without the need for isolation and purification. This system aims to deliver nucleic acid drugs effectively. ExomiR-Tracker consists of an anti-exosome antibody equipped with nona-D-arginines (9 mer) and nucleic acid drugs which have complementary sequence of target microRNA (anti-miR). In this study, we modified ExomiR-Tracker by incorporating branched nona-D-arginines (9 + 9 mer) molecules (referred to as Branch ExomiR-Tracker) and evaluated its efficacy in lung adenocarcinoma cells (A549 cells). The improved complex formation ability and enhanced cellular uptake of anti-miR, demonstrated by our findings, highlight the advantages of incorporating branched oligoarginine peptides into the ExomiR-Tracker platform. These results represent significant progress in revealing the effectiveness of Branch ExomiR-Tracker against adhesive cancer cells, which has not been shown to be effective with the conventional Linear ExomiR-Tracker.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickExosomes, a kind of extracellular vesicles, have actively been researched as the drug delivery system (DDS) for nucleic acid drugs. The authors previously reported exosome-hijacking antibody-oligonucleotide conjugate “ExomiR-Tracker”, which is consisting of cationic oligoarginine linker-introduced anti-exosome antibody (anti-Exo) and nucleic acid drugs. In this article, it was revealed that the intracellular delivery capability of nucleic acid drugs and the functional inhibition of target gene in lung adenocarcinoma cells was significantly improved by branched oligoarginine adapted ExomiR-Tracker (Branch ExomiR-Tracker) as compared to conventional one. Their findings demonstrate the promising potential of ExomiR-Tracker as a tool for delivering nucleic acid drugs and provide novel insights into the exosome-hijacking DDS.
Download PDF (2864K) Full view HTML -
Makoto Ozaki, Motoshi Shimotsuma, Takefumi Kuranaga, Hideaki Kakeya, T ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 824-831
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
Advance online publication: August 24, 2023JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialD-Amino acids, which are present in small amounts in living organisms, are responsible for a variety of physiological functions. Some bioactive/biomolecular peptides also contain D-amino acids in their sequences; such peptides express different functions than peptides composed only of L-form amino acids. Among the 20 amino acids that make up proteins, threonine (Thr) and isoleucine (Ile) have two chiral carbons and thus have two enantiomers and diastereomers. These stereoisomers have been previously analyzed through HPLC using chiral columns or chiral resolution labeling reagents. However, the separation and identification of these stereoisomers are highly laborious and complicated. Herein, we propose an analytical method for the separation and identification of Ile stereoisomers through LC–MS using our original chiral resolution labeling reagent, 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-L-valine-N,N-dimethylethylenediamine-amide (L-FDVDA) and a PBr column packed with pentabromobenzyl-modified silica gel. Twenty DL-amino acids including Thr stereoisomers (41 amino acids including glycine) were separated and identified using C18 column. Ile stereoisomers could be separated using not a C18 column but a PBr column. Additionally, we showed that peptides containing Thr and Ile stereoisomers can be accurately detected through labeling with L-FDVDA.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2440K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2440K) Full view HTML -
Junko Tsukioka, Tomoka Takami, Yuki Ario, Seikou Nakamura2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 832-837
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
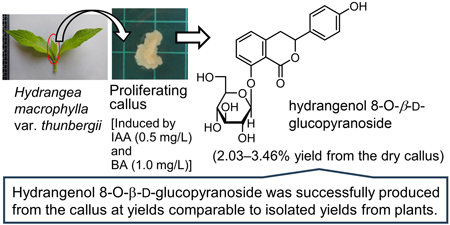
Supplementary materialDihydroisocoumarins, hydrangenol 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), phyllodulcin 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), hydrangenol (3), and phyllodulcin (4), are well-known as the major secondary metabolites in the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla var. thunbergii. Dihydroisocoumarins are pharmaceutical compounds with diverse bioactivity. Although dihydroisocoumarins are commonly isolated from Hydrangea plants or via organic chemical synthesis, their production via callus induction is considered a promising alternative. In the present study, callus induction and proliferation of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii, and constituents 1–4 were quantified in calluses cultured in 17 different media. We found that the combination of the phytohormones 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and 6-benzylaminopurine (BA) was useful for callus proliferation in H. macrophylla var. thunbergii. The balance and concentrations of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and BA greatly affected the contents of 1–4. Particularly, 1 (2.03–3.46% yield from the dry callus) was successfully produced from the callus induced by IAA (0.5 mg/L) and BA (1.0 mg/L) at yields comparable to isolated yields from plants. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to show that the calluses of H. macrophylla var. thunbergii contained 1. These findings may be useful for producing bioactive dihydroisocoumarins.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3961K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3961K) Full view HTML
-
 Ryosuke Kobayashi, Takashi Ono, Shungo Kumada, Kotaro Okada, Yoshinori ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 838-842
Ryosuke Kobayashi, Takashi Ono, Shungo Kumada, Kotaro Okada, Yoshinori ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 838-842
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study determined the content of solid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) powders dispersed in suspension-type pharmaceutical oral jellies using a low-field time-domain NMR (TD-NMR). The suspended jellies containing a designated API content were prepared and tested. Acetaminophen (APAP), indomethacin (IMC) and L-valine were used as test APIs. First, this study measured the T2 relaxation rate (the reciprocal of T2 relaxation time) by the Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) pulse sequence, and then evaluated whether the API content could be determined by the acquired T2 relaxation rate. The T2 relaxation rate negatively correlated with API content to a certain extent, but their correlation was not sufficient for achieving a precise determination. Subsequently, the solid–echo pulse sequence measurement was adopted for this study. We found that NMR signals corresponding to solid components strongly correlated with API content. Thus, this method achieved a precise determination of API contents in suspended jellies. In addition, this study confirmed the effect of API particle size on the T2 relaxation rate by using an L-valine-containing jelly: the T2 relaxation rate became faster when a smaller API size was incorporated into the suspended jelly, while there was no difference in terms of the NMR signals measured by solid–echo pulse sequence. From these findings, TD-NMR could be a powerful tool for evaluating the API dispersion state in suspended oral jellies.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThis study utilized low-field time-domain NMR (TD-NMR) to ascertain the solid active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) content in suspension-type pharmaceutical oral jellies. The authors prepared and tested jellies containing various APIs, such as acetaminophen (APAP), indomethacin (IMC), and L-valine. The authors determined that precise API content measurement in jellies was achieved by utilizing NMR signal intensity measured through the solid-echo pulse sequence. Additionally, the authors observed that smaller API particle sizes resulted in faster T2 relaxation rates. In summary, TD-NMR proves to be a robust tool for evaluating the dispersion state of API powders in pharmaceutical oral jellies.
Download PDF (634K) Full view HTML -
Hirofumi Ohashi, Kazane Nishioka, Tomoki Kurihara, Kou Nakamura, Masak ...2023Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 843-845
Published: November 01, 2023
Released on J-STAGE: November 01, 2023
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialJuglorubin is a natural dye isolated from the culture of Streptomyces sp. 3094, 815, and GW4184. It has been previously synthesized via the biomimetic dimerization of juglomycin C, a plausible genetic precursor. In this study, the derivatives of juglorubin, 1-O-acetyljuglorubin dimethyl ester and juglorubin dimethyl ester, were found to exhibit antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus (HCV) without exerting any remarkable cytotoxicity against host Huh-7 cells. They also inhibited liver X receptor α activation and lipid droplet accumulation in Huh-7 cells. These findings suggest that 1-O-acetyljuglorubin dimethyl ester and juglorubin dimethyl ester targeted the host factors required for HCV production.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (487K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (487K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|