
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Jun Shimokawa2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 105-115
Jun Shimokawa2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 105-115
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe divergent total syntheses of three types of heteropolycyclic natural products, namely gelsedine-type alkaloids, amathaspiramide alkaloids, and erythrina alkaloids, are outlined. A strategy involving a late-stage pluripotent common synthetic intermediate prepared via original and innovative transformations was employed. A brief description of the philosophy and criteria for choosing the synthetic targets and common synthetic precursors, as well as details regarding the development of the overall synthetic schemes from a common intermediate are discussed.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThree divergent total syntheses of heteropolycyclic natural product groups, namely gelsedine-type alkaloids, amathaspiramide alkaloids, and erythrina alkaloids, are outlined. These syntheses employed the strategy for designing a late-stage pluripotent common synthetic intermediate that is prepared via the formulation of original and innovative transformations. Brief description of the philosophy and criteria for choosing synthetic targets and common synthetic precursors, as well as the details of development of the overall synthetic schemes mapped around the designed common intermediate are discussed.
Download PDF (1906K) Full view HTML
-
 Satoshi Shuto2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 116
Satoshi Shuto2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 116
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLEditor's pickNucleosides and nucleotides have fascinated chemists and biologists, because nucleosides and nucleotides are of vital importance not only as components of ribo- and deoxyribonucleic acids in central dogma, but also as a wide variety of biofunctional molecules. This current topic summarized the recent progress on chemical ligation of oligonucleotides, nucleoside antibiotics, unnatural base pairs, antiviral/antitumor nucleoside analogues, protecting groups for oligonucleotide prodrugs, and nucleotide second messengers.
Download PDF (153K) Full view HTML
-
Hiroshi Abe, Yasuaki Kimura2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 117-122
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLChemical ligation of oligonucleotides (ONs) is the key reaction for various ON-based technologies. We have tried to solve the problems of RNA interference (RNAi) technology by applying ON chemical ligation to RNAi. We designed a new RNAi system, called intracellular buildup RNAi (IBR-RNAi), where the RNA fragments are built up into active small-interference RNA (siRNA) in cells through a chemical ligation reaction. Using the phosphorothioate and iodoacetyl groups as reactive functional groups for the ligation, we achieved RNAi effects without inducing immune responses. Additionally, we developed a new chemical ligation for IBR-RNAi, which affords a more native-like structure in the ligated product. The new ligation method should be useful not only for IBR-RNAi but also for the chemical synthesis of biofunctional ONs.
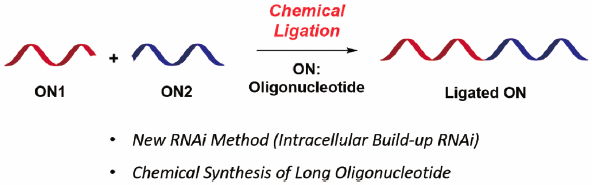 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2392K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2392K) Full view HTML -
Akira Katsuyama, Satoshi Ichikawa2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 123-131
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMuraymycins, isolated from a culture broth of Streptomyces sp., are members of a class of naturally occurring nucleoside antibiotics. They are strong inhibitors of the phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase (MraY), which is responsible for the peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Since MraY is an essential enzyme among bacteria, muraymycins are expected to be a novel antibacterial agent. In this review, our efforts to synthesize muraymycin D2, simplify the chemical structure, improve antibacterial spectrum, and solve the X-ray crystal structure of the muraymycin D2/MraY complex are described.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2757K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2757K) Full view HTML -
Noriko Saito-Tarashima, Noriaki Minakawa2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 132-138
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this review, we have summarized the research effort into the development of unnatural base pairs beyond standard Watson–Crick (WC) base pairs for synthetic biology. Prior to introducing our research results, we present investigations by four outstanding groups in the field. Their research results demonstrate the importance of shape complementarity and stacking ability as well as hydrogen-bonding (H-bonding) patterns for unnatural base pairs. On the basis of this research background, we developed unnatural base pairs consisting of imidazo[5′,4′:4.5]pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines and 1,8-naphthyridines, i.e., Im : Na pairs. Since Im bases are recognized as ring-expanded purines and Na bases are recognized as ring-expanded pyrimidines, Im : Na pairs are expected to satisfy the criteria of shape complementarity and enhanced stacking ability. In addition, these pairs have four non-canonical H-bonds. Because of these preferable properties, ImNN : NaOO, one of the Im : Na pairs, is recognized as a complementary base pair in not only single nucleotide insertion, but also the PCR.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1476K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1476K) Full view HTML -
Yuichi Yoshimura, Yukako Saito, Yoshihiro Natori, Hideaki Wakamatsu2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 139-146
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMany attempts have been made to synthesize structurally novel nucleoside derivatives in order to identify effective compounds for the treatment of tumors and virus-caused disease. At our laboratories, as part of our efforts to synthesize 4′-thionucleosides, we have identified and characterized biologically active nucleosides. During the course of our synthetic study, we developed the Pummerer-type thioglycosylation reaction. As a result, we synthesized a potent antineoplastic nucleoside, 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-4-thio-arabino-furanosyl)cytosine (4′-thioFAC), and several novel 4′-thionucleosides that possess antiherpes virus activities.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (762K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (762K) Full view HTML -
Hisao Saneyoshi, Akira Ono2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 147-154
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn recent years, nucleic acid-based drug therapeutics have gained considerable attention for their potential in the treatment of various diseases. However, their therapeutic value is greatly hindered by the challenge of delivering them into cells. One possible strategy to improve cellular uptake is the use of “prodrug-type oligonucleotide medicine” in which negatively charged phosphodiester moieties are masked by bio-labile protecting groups. In this review, we describe our recent studies related to bio-labile protecting groups for phosphodiester moieties in the development of prodrug-type oligonucleotide medicines.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1188K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1188K) Full view HTML -
Satoshi Shuto2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 155-161
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR), a general mediator involved in Ca2+ signaling, has the characteristic 18-membered ring consisting of an adenine, two riboses and a pyrophosphate, in which the two primary hydroxy groups of the riboses are linked by a pyrophosphate unit. This review focuses on chemical synthetic studies of cADPR analogues of biological importance. Although cADPR analogues can be synthesized by enzymatic and chemo-enzymatic methods using ADP-ribosyl cyclase, the analogues obtained by these methods are limited due to the substrate-specificity of the enzymes. Consequently, chemical synthetic methods providing a greater variety of cADPR analogues are required. Although early chemical synthetic studies demonstrated that construction of the large 18-membered ring structure is difficult, the construction was achieved using the phenylthiophosphate-type substrates by treating with AgNO3 or I2. This is now a general method for synthesizing these types of biologically important cyclic nucleotides. Using this method as the key step, the chemically and biologically stable cADPR mimic, cADP-carbocyclic-ribose (cADPcR) and -4-thioribose (cADPtR), were synthesized.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2226K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2226K) Full view HTML
-
May Thuu Mon, Supachai Yodkeeree, Wanisa Punfa, Wilart Pompimon, Pornn ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 162-169
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCrebanine (CN), tetrahydropalmatine (THP), O-methylbulbocapnine (OMBC) and N-methyl tetrahydropalmatine (NMTHP) are isoquinoline derived natural alkaloids isolated from tubers of Stephania venosa. We investigated chemo-sensitizing effects of these alkaloids in ovarian cancer cells and evaluated underlying molecular mechanisms involved in chemo-sensitivity. Detection of cell apoptosis was evaluated by using flow cytometry. Cell viability was analyzed using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Chou-Talalay median effect principle was used to evaluate potential drug interactions. Protein analyses were performed on ovarian carcinoma cells using Western blotting upon treatment with anticancer drug and alkaloids. Aporphine alkaloids, such as CN and OMBC, enhanced cisplatin sensitivity in intrinsic cisplatin resistant SKOV3 cells, but not in cisplatin sensitive A2780 cells. Protoberberine alkaloids, such as THP and NMTHP, had no synergistic effect on cisplatin sensitivity in either cell line. Chemo-sensitizing effects of CN and OMBC in SKOV3 cells were mediated via activating apoptosis-induced cell death through caspase-3, -8 and cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and via inhibiting anti-apopotic and survival protein expression, such as Bcl-xL, Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 3 (cIAP-2), survivin and interleukin (IL) -6. Cisplatin stimulated protein kinase B (Akt) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathways, but not mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), activator protein 1 (AP-1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in SKOV3 cells. Akt/NF-κB signaling was blocked by CN and OMBC leading to increased sensitization to cisplatin. These findings demonstrate that CN and OMBC sensitizes SKOV3 cells to cisplatin via inhibition of Akt/NF-κB signaling and the down regulation of NF-κB mediated gene products. Our results suggest that alkaloids obtained from S. venosa could be used as chemo-sensitizers in ovarian cancer to sensitize and minimize the dose related toxicity of platinum-based chemotherapeutic drugs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2161K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2161K) Full view HTML -
 Majid Vahed, Saburo Neya, Katsumi Matsuzaki, Tyuji Hoshino2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 170-177
Majid Vahed, Saburo Neya, Katsumi Matsuzaki, Tyuji Hoshino2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 170-177
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAggregation and complex formation of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides on a neuronal cell membrane is a hallmark of neuro-disturbance diseases. In this work, we performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to investigate the initial stage of interactions of multiple Aβ42 peptides on a GM1 ganglioside-containing membrane that mimics a micro-domain on the neuronal cell surface. Conformational changes of Aβs due to adhesion on the membrane and subsequent molecular interactions among the Aβs were monitored. It was suggested from results of the two 1.0 µs simulation trials that stable complexes of Aβ peptides were not rapidly generated but that a steady binding of two Aβs was gradually formed. Observation of two Aβs that will be a complex with steady binding revealed that one Aβ was bound to the membrane surface, while the other was attached to the first one without strong contact with the membrane. The motion of the first one was restricted and its conformational change was limited, with the basic side-chains of Arg5 and Lys28 working as anchors to hold the Aβ helix region on the membrane. In contrast, the second one had high flexibility and showed diversity in its conformation. The second Aβ can search for an energetically favorable binding position on the first one. A parallel β-sheet structure was formed between the C-terminal sides of the two Aβs. Ala30 was critically important to lead the stable β-sheet conformation at the C-terminal hydrophobic domains of Aβs. In the N-terminal sides, helix structures were kept in both Aβs.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickAggregation of amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) is closely linked to several neurodegeneration diseases including Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular dynamics simulations were performed to clarify the initial stage of Aβs interaction on the lipid membrane that mimicked a micro-domain on the neuronal cell surface. Stable complexes of Aβ peptides were not rapidly generated in simulation, instead a binding of two Aβs was gradually developed. In a stable two Aβs complex, one is bound to the membrane surface, while the other is attached to the first one without strong contact with membrane. A parallel β-sheet structure is formed between the C-terminal sides of them.
Download PDF (2111K) Full view HTML -
Siyuan Wu, Shinji Harada, Takahiro Morikawa, Atsushi Nishida2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 178-183
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTotal syntheses of carbazomycins A and B were demonstrated using a ytterbium-catalyzed Diels–Alder reaction with (silyloxyvinyl)indole as a diene. The densely substituted benzene ring of the target compound was successfully constructed by functionalization of a hydrocarbazolone intermediate and subsequent aromatization using N-bromosuccinimide.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (698K) Full view HTML
-
Toshinori Suzuki, Akihiro Ogishi, Toru Shinohara, Shinya Suito2018 Volume 66 Issue 2 Pages 184-187
Published: February 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWhen 8-bromoadenosine was incubated with cysteine at pH 7.2 and 37°C, an exclusive product was generated. This product was identified as a cysteine substitution derivative of adenosine at the 8 position, 8-S-L-cysteinyladenosine. The reaction accelerated as pH increased from mildly acidic to basic conditions. The isolated cysteine adduct of adenosine decreased with a half-life of 15 h at pH 7.2 and 37°C. Similar results were obtained for the incubation of 8-bromo-2′-deoxyadenosine and 8-bromoadenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate with cysteine. These results suggest that 8-bromoadenine in nucleotides, RNA, and DNA can react with thiols, resulting in adducts under physiological conditions.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (414K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (414K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|