
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Jiayin Hu, Tingting Hu, Zhe Guo, Yonggui Song, Lina Shan, Xianbao Shi2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 669-678
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThis study aimed to evaluate the interspecies difference in metabolism of mulberrin and examine the interaction between mulberrin and CYP enzymes or recombinant human uridine 5′-diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes. Liver microsomes from human (HLMs), Beagle dog (DLMs), minipig (PLMs), monkey (MLMs), rabbit (RLMs), rat (RAMs), and mouse (MIMs) were used to investigate metabolic diversity among different species. Additionally, recombinant human supersomes were used to confirm that metabolic enzymes are involved in the biotransformation of mulberrin. We also evaluated the influence of mulberrin on protein expression by Western blot analysis. Mulberrin metabolism showed significant interspecies differences. We found four and two metabolites in phase I and II reaction systems, respectively. In phase I metabolism profiles of mulberrin for HLMs, PLMs and MLMs conformed to the classic Michaelis–Menten kinetics, RAMs and MIMs followed biphasic kinetics; phase II reaction of mulberrin in HLMs, DLMs, PLMs, MLMs, RLMs, RAMs and MIMs followed biphasic kinetics. UGT1A1 were the major CYP isoforms responsible for the metabolism of mulberrin. Mulberrin showed potent inhibitory effects against CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2E1, UGT1A1, UGT1A3 and UGT2B7 with IC50 values of 54.21, 9.93, 39.12, 3.84, 2.01, 16.36 µM, respectively. According to Western blot analysis, mulberrin can upregulate the protein expression of CYP2C19, and downregulate the expression levels of CYP3A5 and CYP2C9 in HepG2 cells as concentration increased. The interspecies comparisons can help find other species with metabolic pathways similar to those in humans for future in vivo studies.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2039K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2039K) Full view HTML -
Shiki Saito, Hirofumi Ohashi, Kou Nakamura, Junichiro Otagaki, Kazane ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 679-683
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe liver X receptor is a nuclear hormone receptor that regulates lipid metabolism. Previously, we had demonstrated the antiviral properties of a liver X receptor antagonist associated with the hepatitis C virus and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. In this study, we screened a chemical library and identified two potential liver X receptor antagonists. Spectroscopic analysis revealed that the structures of both antagonists (compounds 1 and 2) were cyclic dimer and trimer of esters, respectively, that consisted of phthalate and 1,6-hexane diol. This study is the first to report the structure of the cyclic trimer of phthalate ester. Further experiments revealed that the compounds were impurities of solvents used for purification, although their source could not be traced. Both phthalate esters exhibited anti-hepatitis C virus activity, whereas the cyclic dimer showed anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 activity. Cyclic phthalate derivatives may constitute a novel class of liver X receptor antagonists and broad-spectrum antivirals.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (973K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (973K) Full view HTML -
Zhan Gao, Runze Xia, Peijian Zhang2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 684-693
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 02, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn order to predict the anti-gastric cancer effect of [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives (1,2,3-TPD), quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies were performed. Based on five descriptors selected from descriptors pool, four QSAR models were established by heuristic method (HM), random forest (RF), support vector machine with radial basis kernel function (RBF-SVM), and mix-kernel function support vector machine (MIX-SVM) including radial basis kernel and polynomial kernel function. Furthermore, the model built by RF explained the importance of the descriptors selected by HM. Compared with RBF-SVM, the MIX-SVM enhanced the generalization and learning ability of the constructed model simultaneously and the multi parameters optimization problem in this method was also solved by particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm with very low complexity and fast convergence. Besides, leave-one-out cross validation (LOO-CV) was adopted to test the robustness of the models and Q2 was used to describe the results. And the MIX-SVM model showed the best prediction ability and strongest model robustness: R2 = 0.927, Q2 = 0.916, mean square error (MSE) = 0.027 for the training set and R2 = 0.946, Q2 = 0.913, MSE = 0.023 for the test set. This study reveals five key descriptors of 1,2,3-TPD and will provide help to screen out efficient and novel drugs in the future.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2942K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2942K) Full view HTML -
Shunsuke Fujii, Yukihiro Shoyama, Shuichi Nomura, Takuhiro Uto2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 694-698
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLLicorice, the root of Glycyrrhiza spp., is used in a large number of herbal medicines, such as traditional Chinese medicines, Japanese Kampo medicines, and therapeutic drugs. Since glycyrrhizin (GL) is among the main components in licorice and exhibits numerous beneficial pharmacological activities, the content of GL directly affects biological activity. The quality control based on GL content is an important factor in ensuring biological activity; however, the content of GL in licorice varies depending on plant cultivation environment, genetic factors, and species type. Previously, we prepared an anti-GL monoclonal antibody (anti-GL mAb) and employed it in various immunochemical assays for quality control of licorice and licorice-based products. In this study, we employed the anti-GL mAb in chemiluminescence enzyme immunostaining (CLEIS) to develop a very simple, rapid, specific, and sensitive quality control assay for licorice products, with a limit of detection of 3.9 ng. Furthermore, the CLEIS assay enabled semiquantitative analysis of GL in Kampo medicines. Our results showed that multiple samples can be simultaneously analyzed using CLEIS, and it is a useful tool for determining GL content, as well as ensuring chemical quality control of licorice-containing products and herbal medicines.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (829K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (829K) Full view HTML -
 Takashi Osawa, Natsumi Yano, Hiroshi Aoyama, Satoshi Obika2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 699-706
Takashi Osawa, Natsumi Yano, Hiroshi Aoyama, Satoshi Obika2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 699-706
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialChemically modified nucleic acids are essential for the therapeutic application of oligonucleotides. In this study, 6′-C-spiro-thymidine exhibiting a fixed torsion angle γ was designed, synthesized, and incorporated into oligonucleotides. The conformational analysis of the 6′-C-spiro-thymidine monomer revealed that its torsion angle γ was in the +synclinal range (approx. 60°), which is similar to that in a natural RNA duplex, as expected. On the other hand, the sugar conformation of the RNA duplex is known to be predominantly an N-type, whereas that of the synthesized monomer was an S-type. The results of the UV melting analysis demonstrated that the duplex-forming ability of 6′-C-spiro-thymidine was inferior to that of natural DNA. Contrarily, 6′-C-spiro-thymidine could enhance the stability of oligonucleotides toward nucleases. Particularly, the incorporation of 6′-C-spiro-thymidine on the 3′-ends of the oligonucleotides significantly increased the nuclease resistance of the oligonucleotides.
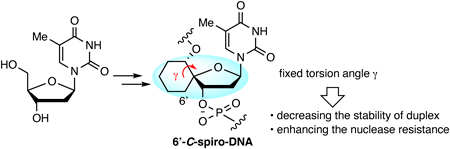 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickIn recent years, research on antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs) has progressed rapidly. These oligonucleotide therapeutics have great potentials for the treatment of diseases that are difficult to approach with conventional drugs. To apply oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents, they are generally modified with artificial nucleic acids because natural DNA and RNA do not have sufficient duplex-forming ability or stability against nucleases. In this report, the authors designed and synthesized 6ʹ-C-spiro-thymidine with a fixed torsion angle γ as a novel material for oligonucleotide therapeutics.
Download PDF (851K) Full view HTML -
 Shoko Tanaka, Tetsuo Narumi, Nobuyuki Mase, Kohei Sato2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 707-715
Shoko Tanaka, Tetsuo Narumi, Nobuyuki Mase, Kohei Sato2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 707-715
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialProteins modified in a controlled manner with artificial moieties such as fluorophores or affinity tags have been shown to be a powerful tool for functional or structural analysis of proteins. A reliable way to prepare proteins with a well-defined modification is protein synthesis. Although many successful syntheses have been reported, the poor aqueous solubility of synthetic intermediates causes difficulty in the chemical synthesis of proteins. Here we describe a solubilizing strategy for poorly soluble peptides which uses chemoselective incorporation of a hydrophilic tag onto a hydrazide in a peptide. We found that a hydrophilic tag possessing a dialkoxybenzaldehyde moiety can react with peptide hydrazides through reductive N-alkylation. No protecting groups are required for this reaction, and peptides modified in this way show enhanced solubility and consequently good peak separation during HPLC purification. The tag can be removed subsequently by treatment with trifluoroacetic acid to generate a free hydrazide, which can be converted in a one-pot reaction to a thioester for further modification. This method was validated by synthesis of a Lys63-linked ubiquitin dimer derivative. This late-stage solubilization can be applied in principal to any peptide and opens the possibility of the synthesis of proteins that have previously been considered inaccessible due to their poor solubility.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickChemically synthesized proteins are increasingly becoming a research tool for elucidating protein functions. Ligation technologies proceeding in aqueous conditions have accelerated chemical protein synthesis; however, poorly soluble characteristics of peptide intermediates often hamper the synthesis of proteins that researchers may need. Kohei Sato and co-workers report late-stage solubilization of peptide hydrazides using hydrophilic tags possessing a dialkoxybenzaldehyde moiety. The inherent advantage of this approach is the superior property for easy attachment and detachment of the solubilizing tags, which is ideal for a broad substrate scope. Using this methodology, the researchers synthesized a ubiquitin dimer derivative successfully.
Download PDF (1378K) Full view HTML
-
Takeshi Oshizaka, Rena Inaba, Mana Isono, Chihiro Takei, Issei Takeuch ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 716-719
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIonic liquids (ILs), defined as liquid salts composed of anions and cations, have the advantage of allowing constituent ions to be stably absorbed through biological membranes, such as skin. However, limited information is currently available on the effects of the physicochemical properties of constituent ions on the membrane permeation of ILs. Therefore, we herein investigated the effects of the polarity of constituent cations on the membrane permeation of each constituent ion from IL. Various ILs were prepared by selecting lidocaine (LID) as a cation and a series of p-alkylbenzoic acids with different n-octanol/water partition coefficients (Ko/w) as anions. These ILs were applied to a skin model, a silicone membrane, and membrane permeability was investigated. The membrane permeabilities of p-alkylbenzoic acids from their single aqueous suspensions were also measured for comparison. The membrane permeability of p-alkylbenzoic acid from the aqueous suspension increased at higher Ko/w. However, the membrane permeability of ILs was similar regardless of the Ko/w of the constituent p-alkylbenzoic acid. Furthermore, the membrane permeability of the counterion LID remained unchanged regardless of the constituent p-alkylbenzoic acid. These results suggest that even when the Ko/w of IL constituents markedly differs, the resulting IL does not affect membrane permeability.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (506K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (506K) Full view HTML -
Akihito Yokosuka, Chiaki Yamada, Makoto Saito, Shohei Yokogawa, Yoshih ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 720-725
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFive podophyllotoxin derivatives (1–5), two diterpenoids (6 and 7), three diterpenoid xylosides (8–10), a flavanonol glycoside (11), flavonol (12), and biflavonoid (13) were isolated from the leaves of Thujopsis dolabrata (Cupressaceae). Compounds 1, 6, and 8 were named (−)-β-isopeltatin, epi-nootkastatin 2, and acetoxyanticopalol 15-O-β-D-xylopyranoside, respectively. The structures of the isolated compounds were determined based on a detailed analysis of NMR spectroscopic data and through chromatographic and spectroscopic analyses following specific chemical transformations. The isolated compounds (1–5 and 7–11) were evaluated for their cytotoxicity toward HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells and Caki-1 human kidney carcinoma cells. The podophyllotoxin derivatives (1–5) exhibited cytotoxicity against both HL-60 and Caki-1 cells with IC50 values ranging from 0.00069 to 5.4 µM, and the diterpenoid derivatives (7–10) demonstrated cytotoxicity against HL-60 cells with IC50 values ranging from 4.5 to 11 µM. HL-60 cells treated with 8 exhibited apoptosis characteristics, such as accumulation of sub-G1 cells and nuclear chromatin condensation.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1373K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1373K) Full view HTML -
Yu Mikame, Yui Sakai, Ryo Tahara, Kinuka Doi, Tsuyoshi Yamamoto, Chika ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 726-730
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
Advance online publication: July 28, 2022JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSeveral psoralen-conjugated oligonucleotides (Ps-Oligos) have been developed as photo-crosslinkable oligonucleotides targeting DNA or RNA. To avoid potential off-target effects, it is important to investigate the selective photo-crosslinking reactivity of Ps-Oligos to DNA or RNA. However, the selectivity of these Ps-Oligos has not been reported in detail thus far. In this study, we evaluated the photo-crosslinking properties of two Ps-Oligos, 5′-Ps-Oligo and a novel Ps-Oligo containing 2′-O-{[(4,5′,8-trimethylpsoralen)-4′-ylmethoxy]ethylaminocarbonyl}adenosine (APs2-Oligo). Notably, 5′-Ps-Oligo preferentially crosslinked with DNA, whereas APs2-Oligo preferentially crosslinked with RNA. These results demonstrate the interesting crosslinking properties of Ps-Oligos, which will provide useful information for the molecular design of novel Ps-Oligos in future studies.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1332K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1332K) Full view HTML -
Hironori Suzuki, Daiki Matsubara, Yuuki Nakata, Masataka Ito, Shuji No ...2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 731-734
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSulfur K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy was evaluated for its ability to detect non-conventional C–H▪▪▪S hydrogen bonds in crystals of the sulfur-containing penam antibiotics ampicillin and amoxicillin. The XANES spectra of the nearly isomorphous crystals of ampicillin trihydrate and amoxicillin trihydrate were very similar, whereas that of ampicillin anhydrate displayed unique features. Single-crystal X-ray structure analyses revealed that the C–H▪▪▪S hydrogen bond geometries and the chemical types of the hydrogen donors differed between the isomorphous trihydrate crystals and ampicillin anhydrate crystal. These observations demonstrate that the shapes of the sulfur K-edge XANES spectra are dependent on the nature of the C–H▪▪▪S hydrogen bonds. Sulfur K-edge XANES spectroscopy shows promise for use in the detection and analysis of non-covalent interactions, including hydrogen bonds to sulfur atoms, within active pharmaceutical ingredients.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1376K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1376K) Full view HTML -
 Masaya Nakajima, Toshiyasu Yamauchi, Yusuke Adachi, Tetsuhiro Nemoto2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 735-739
Masaya Nakajima, Toshiyasu Yamauchi, Yusuke Adachi, Tetsuhiro Nemoto2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 735-739
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialComputational chemistry is useful in synthetic organic chemistry, as it can be used not only to analyze reaction mechanisms, but also to calculate biosynthetic pathways and to plan and evaluate strategies for total syntheses. Here we report the computation-guided total synthesis of vitisinol G, a resveratrol dimer.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe authors reported the computation-guided total synthesis of vitisinol G, a resveratrol dimer. Computational chemistry is useful in synthetic organic chemistry, as it can be used not only to analyze reaction mechanisms, but also to calculate biosynthetic pathways and to plan and evaluate strategies for total syntheses. They focused on the semi-pinacol rearrangement derived from calculations of the biosynthetic pathway of resveratrol dimers. DFT calculations were used to develop a synthetic strategy and the total synthesis of vitisinol G at 7.8% was achieved in 4 steps from resveratrol.
Download PDF (1132K) Full view HTML -
Yuta Miura, Yohei Saito, Kyoko Nakagawa-Goto2022 Volume 70 Issue 10 Pages 740-747
Published: October 01, 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2022
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCryptolaevilactones (CLs) A–L, found in the leaves and twigs of Cryptocarya laevigata, are unique natural meroterpenoids with a spiro[3.5]nonane skeleton. We report the total synthesis of a simplified model compound of CLs A–C. The synthetic route included introduction of a styryl group and coupling of a lactone moiety to a spiro ring system, which was constructed by a pinacol-like rearrangement.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2244K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2244K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|