
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Takayoshi Suzuki2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 135
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (182K) Full view HTML
-
Ryo Nakajima2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 136-142
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the aging global population, prostate cancer is a worldwide health problem because the incidence rate of this disease increases at advanced ages. Although early-stage prostate cancer can be treated by total prostatectomy, the surgery causes side effects, such as incontinence and dysuria, that lower QOL. Once the disease progresses to metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), there are no effective chemotherapeutic agents without systematic side effects. Therefore, targeted therapies for mCPRC are urgently needed. Traditional antibody–drug conjugate treatments for prostate cancer have been tested in clinical trials and several side effects have been observed. Meanwhile, small-molecule drug conjugates (SMDCs) have certain advantages over antibody drug conjugates in terms of non-immunogenicity, reproducibility, and permeability. In this review, prostate-specific membrane antigen-targeted SMDCs for treating prostate cancer are summarized.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (921K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (921K) Full view HTML
-
Takashi Osawa, Satoshi Obika2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 143-148
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialDNA-encoded libraries (DELs) are attracting attention as a screening tool in the early stages of drug discovery. In the development of DELs, drug candidate compounds are chemically synthesized on barcode DNA. Therefore, it is important to perform the synthesis under mild conditions so as to not damage the DNA. On the other hand, coumarins are gaining increasing research focus not only because they possess excellent fluorescence properties, but also because many medicines contain a coumarin skeleton. Among the various reactions developed for the synthesis of coumarins thus far, Knoevenagel condensation followed by intramolecular cyclization under mild conditions can yield coumarins. In this study, we developed a new synthetic method for preparing a coumarin-conjugated oligonucleotide library via Knoevenagel condensation. The results showed that coumarins substituted at the 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-positions could be constructed on DNA to afford a total of 26 coumarin-conjugated DNAs. Moreover, this method was compatible with enzymatic ligation, demonstrating its utility in DEL synthesis. The developed strategy for the construction of coumarin scaffolds based on Knoevenagel condensation may contribute to the use of DELs in drug discovery and medicinal chemistry.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (825K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (825K) Full view HTML -
Motoharu Hirano, Hidetomo Yokoo, Nobumichi Ohoka, Takahito Ito, Takash ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 149-154
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAntimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are promising therapeutic agents against bacteria. We have previously reported an amphipathic AMP Stripe composed of cationic L-Lys and hydrophobic L-Leu/L-Ala residues, and Stripe exhibited potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Gramicidin A (GA), composed of repeating sequences of L- and D-amino acids, has a unique β6.3-helix structure and exhibits broad antimicrobial activity. Inspired by the structural properties and antimicrobial activities of LD-alternating peptides such as GA, in this study, we designed Stripe derivatives with LD-alternating sequences. We found that simply alternating L- and D-amino acids in the Stripe sequence to give StripeLD caused a reduction in antimicrobial activity. In contrast, AltStripeLD, with cationic and hydrophobic amino acids rearranged to yield an amphipathic distribution when the peptide adopts a β6.3-helix, displayed higher antimicrobial activity than AltStripe. These results suggest that alternating L-/D-cationic and L-/D-hydrophobic amino acids in accordance with the helical structure of an AMP may be a useful way to improve antimicrobial activity and develop new AMP drugs.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1301K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1301K) Full view HTML -
Yuri Takada, Kyohei Adachi, Yuka Fujinaga, Yasunobu Yamashita, Yukihir ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 155-160
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPeptides have recently garnered attention as middle-molecular-weight drugs with the characteristics of small molecules and macromolecules. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) is a potential therapeutic target for lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and leukemia, and some peptide-based LSD1 inhibitors designed based on the N-terminus of SNAIL1, a member of the SNAIL/SCRATCH family of transcription factors, have been reported. The N-terminus of SNAIL1 peptide acts as a cap of the catalytic site of LSD1, inhibiting interactions with LSD1. However, the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of these inhibitors is not yet fully understood. Therefore, in the present study, we aimed to uncover the SAR and to identify novel SNAIL1 peptide-based LSD1 inhibitors. We synthesized peptide inhibitor candidates based on truncating the N-terminus of SNAIL1 or substituting its amino acid residues. In the truncation study, we found that SNAIL1 1–16 (2), which was composed of 16 residues, strongly inhibited LSD1. Furthermore, we investigated the SAR at residues-3 and -5 from the N-terminus and found that peptides 2j and 2k, in which leucine 5 of the parent peptide is substituted with unnatural amino acids, cyclohexylalanine and norleucine, respectively, strongly inhibited LSD1. This result suggests that the hydrophobic interaction between the inhibitor peptides and LSD1 affects the LSD1-inhibitory activity. We believe that this SAR information provides a basis for the development of more potent LSD1 inhibitors.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1452K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1452K) Full view HTML -
Yugo Mishima, Shusuke Tomoshige, Shinichi Sato, Minoru Ishikawa2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 161-165
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLYM-1, an allosteric modulator of heat-shock 70 kDa protein (Hsp70), inhibits cancer cell growth, but the mechanism is not yet fully understood. Here, we show that YM-1 induces the degradation of bromodomain containing 4 (BRD4), which mediates oncogene expression. Overall, our results indicate that YM-1 promotes the binding of HSP70 to BRD4, and this in turn promotes the ubiquitination of BRD4 by C-terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP), an E3 ubiquitin ligase working in concert with Hsp70, leading to proteasomal degradation of BRD4. This YM-1-induced decrease of BRD4 would contribute at least in part to the inhibition of cancer cell growth.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1210K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1210K) Full view HTML -
Genichiro Tsuji, Takashi Kurohara, Takuji Shoda, Hidetomo Yokoo, Takah ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 166-172
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe recent discovery of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a mutagenic N-nitrosamine, in pharmaceuticals has adversely impacted the global supply of relevant pharmaceutical products. Contamination by N-nitrosamines diverts resources and time from research and development or pharmaceutical production, representing a bottleneck in drug development. Therefore, predicting the risk of N-nitrosamine contamination is an important step in preventing pharmaceutical contamination by DNA-reactive impurities for the production of high-quality pharmaceuticals. In this study, we first predicted the degradation pathways and impurities of model pharmaceuticals, namely gliclazide and indapamide, in silico using an expert-knowledge software. Second, we verified the prediction results with a demonstration test, which confirmed that N-nitrosamines formed from the degradation of gliclazide and indapamide in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, especially under alkaline conditions. Furthermore, the pathways by which degradation products formed were determined using ranitidine, a compound previously demonstrated to generate NDMA. The prediction indicated that a ranitidine-related compound served as a potential source of nitroso groups for NDMA formation. In silico software is expected to be useful for developing methods to assess the risk of N-nitrosamine formation from pharmaceuticals.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1802K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1802K) Full view HTML -
Atika Nurani, Yasunobu Yamashita, Yuuki Taki, Yuri Takada, Yukihiro It ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 173-178
Published: February 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHistone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) is a zinc-dependent HDAC that catalyzes the deacetylation of nonhistone proteins. It is involved in cancer development and HDAC8 inhibitors are promising candidates as anticancer agents. However, most reported HDAC8 inhibitors contain a hydroxamic acid moiety, which often causes mutagenicity. Therefore, we used machine learning for drug screening and attempted to identify non-hydroxamic acids as HDAC8 inhibitors. In this study, we established a prediction model based on the random forest (RF) algorithm for screening HDAC8 inhibitors because it exhibited the best predictive accuracy in the training dataset, including data generated by the synthetic minority over-sampling technique (SMOTE). Using the trained RF-SMOTE model, we screened the Osaka University library for compounds and selected 50 virtual hits. However, the 50 hits in the first screening did not show HDAC8-inhibitory activity. In the second screening, using the RF-SMOTE model, which was established by retraining the dataset including 50 inactive compounds, we identified non-hydroxamic acid 12 as an HDAC8 inhibitor with an IC50 of 842 nM. Interestingly, its IC50 values for HDAC1 and HDAC3-inhibitory activity were 38 and 12 µM, respectively, showing that compound 12 has high HDAC8 selectivity. Using machine learning, we expanded the chemical space for HDAC8 inhibitors and identified non-hydroxamic acid 12 as a novel HDAC8 selective inhibitor.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (932K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (932K) Full view HTML
-
Shinnosuke Okazaki, Kaho Senda, Ayaka Tokuta, Misa Inagaki, Kazuo Kama ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 179-185
Published: February 03, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 03, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe total synthesis of the natural bicyclo[3.3.0]furanolactone polyketide, plakortone Q, was achieved in 24 steps from (R)-Roche ester. The main feature of this synthetic strategy is the stereoselective construction of a central tetrahydrofuran moiety with four consecutive stereoisomeric centers using the Upjohn dihydroxylation of oxiranyl-substituted alkenes and acid-mediated 5-endo-tet cyclization.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1017K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1017K) Full view HTML -
Guoqing Sui, Lili Shu, Ailing Zhang, Dan Li, Shuhua Cao2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 186-189
Published: February 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 09, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAs a part of our continuing exploration to discover new potential promising fungicide candidates, eighteen sulfonate derivatives (3a–3r) containing a kakuol moiety were designed and synthesized. Synthetic sulfonate derivatives were tested comprehensively for antifungal activities against four plant pathogenic fungi (Botrytis (B.) cinerea, Valsa (V.) mali, Fusarium (F.) graminearum, Sclerotinia (S.) sclerotiorum), and their structure activity relationships were summarized. Especially, derivatives 3i and 3j exhibited remarkable activity against V. mali, with the inhibition rates of 99.8 and 100%, which were slightly superior to that of carbendazim (98.9%), a reference fungicide. Moreover, derivatives 3a, 3k and 3q possess the broader antifungal spectrum against three tested plant pathogenic fungi with inhibition rates over 60%. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis indicated that the introduction of 2-F or 3-F into the benzene ring would give rise to a remarkable increase of the antifungal activity against V. mali.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2023K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2023K) Full view HTML
-
Shinji Oyama, Noriko Ogawa, Kaori Kawai, Kanako Iwai, Toshiya Yasunaga ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 190-199
Published: February 16, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 16, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialA co-amorphous model drug was prepared by the spray-drying (SD) of probucol (PC) and atorvastatin calcium trihydrate salt (ATO) as low water solubility and co-former components, respectively. The physicochemical properties of the prepared samples were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analysis, thermal analysis, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and dissolution tests. Stability tests were also conducted under a stress environment of 40 °C and 75% relative humidity. The results of PXRD measurements and thermal analysis suggested that PC and ATO form a co-amorphous system by SD. Thermal analysis also indicated an endothermic peak that followed an exotherm in amorphous PC and a physical mixture (PM) of amorphous PC and ATO; however, no endothermic peak was detected in the co-amorphous system. The dissolution profiles for PC in the co-amorphous sample composed of PC and ATO were improved compared to those for raw PC crystals or the PM. Stability tests indicated that the co-amorphous material formed by PC and ATO can be stored for 35 d without crystallization, whereas amorphous PC became crystallized within a day. Therefore, co-amorphization of PC and ATO prepared by SD is considered to be a useful method to improve the solubility of PC in water.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (933K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (933K) Full view HTML -
 Kousuke Araki, Minami Hara, Shohei Hamada, Takahiro Matsumoto, Seikou ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 200-208
Kousuke Araki, Minami Hara, Shohei Hamada, Takahiro Matsumoto, Seikou ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 200-208
Published: February 20, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 20, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialGlioblastoma (GBM) has a high mortality rate despite the availability of various cancer treatment options. Although cancer stem cells (CSCs) have been associated with poor prognosis and metastasis, and play an important role in the resistance to existing anticancer drugs and radiation; no CSC-targeting drugs are currently approved in clinical practice. Therefore, the development of antiproliferative agents against CSCs is urgently required. In this study, we evaluated the antiproliferative activities of 21 sesquiterpenoids against human GBM U-251 MG CSCs and U-251 MG non-CSCs. Particularly, the guaianolide sesquiterpene lactone cynaropicrin (1) showed strong antiproliferative activity against U-251 MG CSCs (IC50 = 20.4 µM) and U-251 MG non-CSCs (IC50 = 10.9 µM). Accordingly, we synthesized six derivatives of 1 and investigated their structure–activity relationships. Most of the guaianolide sesquiterpene lactones with the α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone moiety showed antiproliferative activities against U-251 MG cells. We conclude that the 5,7,5-ring and the α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone moiety are both important for antiproliferative activities against U-251 MG cells. The results of this study suggest that the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety, which has recently become a research hotspot in drug discovery, is the active center of 1. Therefore, we consider 1 as a potential lead for developing novel drugs targeting CSCs.
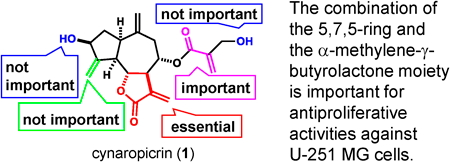 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe guaianolide sesquiterpene lactone cynaropicrin and its derivatives showed antiproliferative activity against human glioblastoma U-251 MG cells and their cancer stem cells. Accordingly, the authors synthesized several derivatives of cynaropicrin and investigated their structure-activity relationships. The authors conclude that the α-methylene-γ-butyrolactone moiety involved in the Michael addition reaction and the 5,7,5-ring are both important for antiproliferative activities. The results of this study suggest guaianolide sesquiterpene lactones are useful for developing anticancer drugs targeting glioblastoma.
Download PDF (731K) Full view HTML
-
Takeshi Oshizaka, Issei Takeuchi, Katsuya Mukae, Kenji Mori, Kenji Sug ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 209-212
Published: February 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 21, 2024
Advance online publication: January 26, 2024JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIonic liquid (IL) technology was used to enhance the stability of L-ascorbic acid (AA). Pyridoxine was selected as the counter cation for anionic AA in IL. After AA was dissolved in water at 40 °C, its ratio decreased to 3.2% after 7 d. In contrast, the IL formulation showed negligible degradation, with almost no loss of AA even after 28 d. These results suggest that the use of IL enhances the stability of AA.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (379K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (379K) Full view HTML
-
 Rei Ikeda, Tomoya Nishio, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 213-219
Rei Ikeda, Tomoya Nishio, Kyohei Kanomata, Shuji Akai2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 213-219
Published: February 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 21, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialNucleophilic deprotection of p-methoxybenzyl (PMB) [p-methoxyphenylmethyl (MPM)] ethers was developed using a heterogeneous oxovanadium catalyst V-MPS4 and a thiol nucleophile. The deprotection method had a wide reaction scope, including PMB ethers of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols bearing various functional groups. In addition, the PMB ether of an oxidation-labile natural product was successfully removed by V-MPS4 catalysis, while a common oxidative method of PMB deprotection afforded a complex mixture. The V-MPS4 catalyst was reusable up to six times without a significant loss in the product yield. The advantages of using the heterogeneous catalyst were further demonstrated by conducting the deprotection reaction in a continuous flow process, which resulted in a 2.7-fold higher catalyst turnover number and 60-fold higher turnover frequency compared to those of the corresponding batch reaction.
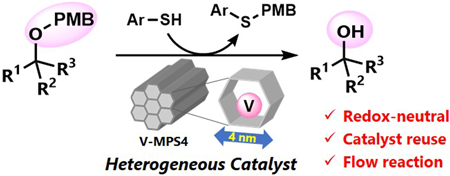 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickHeterogeneous catalysis has gained increasing interest in the growing demand of sustainable manufacturing of pharmaceutically relevant compounds. The authors report herein a mesoporous silica-supported oxovanadium (V-MPS4)-catalyzed nucleophilic removal of the p-methoxybenzyl (PMB) protective group on alcohols under mild and redox-neutral conditions. The method has a wide reaction scope, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols with various functional groups. The catalyst was reused six times without a significant loss in the conversion. The advantages of using the heterogeneous catalyst were further demonstrated by conducting the deprotection reaction in a flow process, which showed significantly higher turnover frequency compared to the batch reactions.
Download PDF (738K) Full view HTML
-
Agnes Giovanni Marsius, Satria Hidayat, Damar Rastri Adhika, Akhmad Ze ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 220-225
Published: February 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 21, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCeO2 nanoparticles (nanoceria) were proposed as an alternative physical sunscreen agent with antioxidant properties and comparable UV absorption performance. Green synthesis of nanoceria with Ag and Ni dopants resulted in doped nanoceria with lower catalytic activity and biologically-safe characteristics. The doped nanoceria was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Rancimat Instrument, and UV-Vis Spectrophotometer for SPF (Sun Protection Factor) determination. XRD and TEM analysis showed that nanoceria had been successfully formed in nanoscale-sized with a change in crystallite size due to the crystal defect phenomenon caused by dopant addition. While the Rancimat test and band gap energy analysis were conducted to evaluate the oxidative stability and reactive oxygen species formation, it was confirmed that dopant addition could decrease catalytic activity of material, resulting in Ni-doped Ce with a longer incubation time (11.81 h) than Ag-doped Ce (10.58 h) and non-doped Ce (10.30 h). In-vitro SPF value was measured using the thin layer technique of sunscreen prototype with Virgin Coconut Oil (VCO)-based emulsion, which yielded 10.862 and 5.728 SPF values for 10% Ag-doped Ce and 10% Ni-doped Ce, respectively. The dopant addition of nanoceria could reduce catalytic activity and give a decent in vitro UV-shielding performance test; thus, Ag and Ni-doped nanoceria could be seen as promising candidates for alternative physical sunscreen agents.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3260K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3260K) Full view HTML
-
 Mayo Nakano, Kyohei Sakamoto, Naoto Yamasaki, Yui Asano, Masataka Oda, ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 226-233
Mayo Nakano, Kyohei Sakamoto, Naoto Yamasaki, Yui Asano, Masataka Oda, ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 226-233
Published: February 27, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 27, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialVizantin, 6,6′-bis-O-(3-nonyldodecanoyl)-α,α′-trehalose, has been developed as a safe immunostimulator on the basis of a structure–activity relationship study with trehalose 6,6′-dicorynomycolate. Our recent study indicated that vizantin acts as an effective Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) partial agonist to reduce the lethality of an immune shock caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). However, because vizantin has low solubility in water, the aqueous solution used in in vivo assay systems settles out in tens of minutes. Here, vizantin was chemically modified in an attempt to facilitate the preparation of an aqueous solution of the drug. This paper describes the concise synthesis of a water-soluble vizantin analogue in which all the hydroxyl groups of the sugar unit were replaced by sulfates. The vizantin derivative displayed micelle-forming ability in water and potent TLR-4 partial agonist activity.
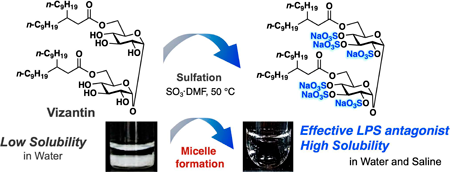 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickVizantin is a TLR-4 antagonist developed in the author's laboratory. In this article, to improve the water solubility of vizantin, the authors designed a new vizantin derivative in which all hydroxyl groups of the sugar unit were sulfated. It has been confirmed that the synthesized vizantin derivative spontaneously forms string-like micelles and dissolves in water. The authors also report that string-like micelles of more uniform size are formed in physiological saline than in distilled water, making it possible to prepare an ideal injection solution.
Download PDF (4975K) Full view HTML -
 Takayuki Yakura, Tomoya Fujiwara, Kanna Asakubo, Hema Naga Lakshmi Per ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 234-239
Takayuki Yakura, Tomoya Fujiwara, Kanna Asakubo, Hema Naga Lakshmi Per ...2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 234-239
Published: February 27, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: February 27, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe first lactam-type 2-iodobenzamide catalysts, 8-iodoisoquinolinones 8 (IB-lactam) and 9 (MeO-IB-lactam), were developed. These catalysts have a conformationally rigid 6/6 bicyclic lactam structure and are more reactive than the previously reported catalysts 2-iodobenzamides 4 (IBamide) and 5 (MeO-IBamide) for the oxidation of alcohols. The lactam structure could form an efficient intramolecular I---O interaction, depending on the size of the lactam ring.
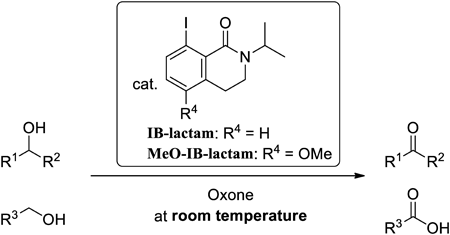 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Catalytic hypervalent iodine oxidation reactions have recently attracted attention to as an environmentally benign and safe method. The authors now report the first lactam-type 2-iodobenzamide catalysts, 8-iodoisoquinolinones (IB-lactams), that can act as a catalyst at room temperature for the oxidation of alcohols with Oxone (2KHSO5·KHSO4·K2SO4) and show the highest reactivity among their previously reported ones. They have a conformationally rigid 6/6 bicyclic lactam structure. The lactam structure could form an efficient intramolecular I---O interaction in its hypervalent species. The interaction could stabilize them to achieve rapid oxidation to pentavalent iodine species, which can oxidize alcohols to carbonyl compounds.Download PDF (770K) Full view HTML
-
2024Volume 72Issue 2 Pages 240
Published: March 02, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (101K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|