
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Hiroki Shigehisa2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 339-346
Hiroki Shigehisa2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 339-346
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this review, I tell the story of the cobalt chemistry that has been developed in my group since 2011. First, we achieved the total synthesis of polyketide natural product trichodermatide A, which involved a late-stage Isayama-Mukaiyama hydration of an enol ether using cobalt(II) acetylacetonate (Co(acac)2) that gave the desired product chemo-, regio-, and diastereoselectively. After our report of this total synthesis in 2013, we were required to revise the originally reported structure of trichodermatide A following the accurate and important report from the Trauner group. Second, we found unique cobalt-catalyzed hydroelementation reactions of olefins involving a cobalt-salen complex, N-fluoro-2,4,6-trimethylpyridinium salt, and a silane reagent. Under these reaction conditions, a carbocationic or carbon radical species is generated from an olefin, and then C–X (X=O, N, C, F) bond formation occurs with good functional group tolerance for a broad substrate scope. This review also covers recent examples of switching chemistry and natural product synthesis involving my cobalt chemistry reported by several groups.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes the total synthesis of polyketide natural product trichodermatide A. The late-stage Isayama-Mukaiyama hydration of an enol ether using Co(acac)2 gives the desired product chemo-, regio-, and diastereoselectively. In addition, the unique cobalt-catalyzed hydroelementation reactions (C–X (X = O, N, C, F) bond formation) of olefins involving a cobalt-salen complex, N-fluoro-2,4,6-trimethylpyridinium salt, and a silane reagent occurs with good functional group tolerance via a carbocationic or carbon radical species.
Download PDF (1233K) Full view HTML
-
 Davor Jovan Korčok, Nada Aleksandar Tršić-Milanović, Nevena Djuro Ivan ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 347-352
Davor Jovan Korčok, Nada Aleksandar Tršić-Milanović, Nevena Djuro Ivan ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 347-352
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
Advance online publication: January 19, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLProbiotics are increasingly more present both as functional foods, and in pharmaceutical preparations with multiple levels of action that contribute to human health. Probiotics realize their positive effects with a proper dose, and by maintaining a declared number of probiotics cells by the expiration date. Important precondition for developing a probiotic product is the right choice of clinically proven probiotic strain, the choice of other active components, as well as, the optimization of the quantity of active component of probiotic per product dose. This scientific paper describes the optimization of the number of probiotics cells in the formulation of dietary supplement that contains probiotic culture Lactobacillus plantarum 299v, iron and vitamin C. Variations of the quantity of active component were analyzed in development batches of the encapsulated probiotic product categorized as dietary supplement with the following ingredients: probiotic culture, sucrosomal form of iron and vitamin C. Optimal quantity of active component L. plantarum of 50 mg, was selected. The purpose of this scientific paper is to select the optimal formulation of probiotic culture in a dietary supplement that contains iron and vitamin C, and to also determine its expiration date by the analysis of the number of viable probiotic cells.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe number of probiotic cells in the formulation of the dietary supplement that contains probiotic culture Lactobacillus plantarum 299v, sucrosomal iron, and vitamin C was optimized. Optimal quantity of active component Lactobacillus plantarum 299v of 50 mg was selected (50 mg) and expiration date was also determined by the analysis of the number of viable probiotic cells. The effects of the selected formulation were confirmed by the clinical study that presented better iron absorption in the subjects who used capsules with Lactobacillus plantarum 299v together with iron and vitamin C.
Download PDF (473K) Full view HTML -
 Kayoko Shimada-Takaura, Yuto Nakamura, Masaya Kawase, Katsuko Komatsu, ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 353-357
Kayoko Shimada-Takaura, Yuto Nakamura, Masaya Kawase, Katsuko Komatsu, ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 353-357
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPaeoniae Radix is one of the crude drugs frequently used in traditional Japanese medicine (Kampo medicine). It takes abundant labor and time to cultivate Paeonia lactiflora for medicinal use; high production cost is one of the main reasons why the domestic production of Paeoniae Radix is decreasing in Japan. To promote the production of Paeoniae Radix, we focused on Paeonia cultivars that produce commercially valuable flowers and investigated their possibility for medicinal use. We prepared 28 batches of peony roots derived from P. lactiflora, which were cultivated in Japan; 4 batches were crude drug samples, and 24 batches were cultivar roots. The elements contained in these samples were measured using inductively coupled plasma (ICP)-MS. The obtained data were then analyzed by principal component analysis (PCA) and back propagation artificial neural network (BPANN) analysis. No significant differences were found between the profiles of elements contained in crude drugs and cultivar roots. However, PCA results indicated a high similarity of the multielement fingerprints of crude drugs. Using the PCA results, we also assessed visible cluster trends and found that 5 batches of cultivars also showed fingerprints related to those of crude drugs. We certified this classification by BPANN. From the perspective of metallomics, our findings suggest that these 5 batches of Paeonia cultivars could be alternatives to crude drugs.
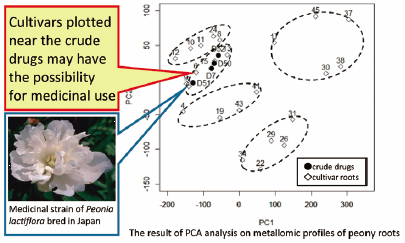 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickPaeoniae Radix, the dried root of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas, is frequently used in traditional Japanese medicine. This paper studied the metallomic profiles between Paeoniae Radix (crude drugs) and the dried roots of various cultivar strains of Paeonia lactiflora produced in Japan in order to seek the strain which derives both commercially variable flowers and medicinally available roots to promote the domestic production. The results suggest that those cultivars can be alternatives to crude drugs from the point of view of metallomics.
Download PDF (920K) Full view HTML -
Xian-Hai Lv, Zi-Li Ren, Hao Liu, Hai-dong Li, Qing-Shan Li, Li Wang, L ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 358-362
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAcetohydroxy acid synthase (AHAS; EC 2.2.1.6, also referred to as acetolactate synthase, ALS) has been considered as an attractive target for the design of herbicides. In this work, an optimized pyrazole sulfonamide base scaffold was designed and introduced to derive novel potential AHAS inhibitors by introducing a pyrazole ring in flucarbazone. The results of in vivo herbicidal activity evaluation indicates compound 3b has the most potent activity with rape root length inhibition values of 81% at 100 mg/L, and exhibited the best inhibitory ability against Arabidopsis thaliana AHAS. With molecular docking, compound 3b insert into Arabidopsis thaliana AHAS stably by an H-bond with Arg377 and cation–π interactions with Arg377, Trp574, Tyr579. This study suggests that compound 3b may serve as a potential AHAS inhibitor which can be used as a novel herbicides and provides valuable clues for the further design and optimization of AHAS inhibitors.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (725K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (725K) Full view HTML -
Daisuke Imahori, Takahiro Matsumoto, Naoto Kojima, Tomohiro Hasei, Meg ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 363-367
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo novel and two known compounds, 4-quinolylaldoxime and indole-3-aldehyde, were isolated from a reaction mixture consisting of D-glucose and L-tryptophan at physiological temperature and pH. The chemical structures of the two novel compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis such as X-ray crystallography. One of the novel compound and the indole-3-aldehyde showed mutagenicity toward Salmonella typhimurium YG1024 with S9 mix. Furthermore, 4-quinolylaldoxime was detected from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat plasma by LC-MS/MS analysis; however, the isolated compounds were not detected in rat diet extracts. To our knowledge, this is the first report in which 4-quinolylaldoxime was detected in rat plasma. These results suggest that amino-carbonyl reaction products may be formed in diabetic condition and induce genetic damage.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (565K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (565K) Full view HTML -
Chihiro Takei, Yui Ohno, Tomohiro Seki, Ryotaro Miki, Toshinobu Seki, ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 368-374
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPrevious studies have shown that reversible chemical bond formation between phenylboronic acid (PBA) and 1,3-diol can be utilized as the driving force for the preparation of layer-by-layer (LbL) films. The LbL films composed of a PBA-appended polymer and poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) disintegrated in the presence of sugar. This type of LbL films has been recognized as a promising approach for sugar-responsive drug release systems, but an issue preventing the practical application of LbL films is combining them with insulin. In this report, we have proposed a solution for this issue by using PBA-appended insulin as a component of the LbL film. We prepared two kinds of PBA-appended insulin derivatives and confirmed that they retained their hypoglycemic activity. The LbL films composed of PBA-appended insulin and PVA were successfully prepared through reversible chemical bond formation between the boronic acid moiety and the 1,3-diol of PVA. The LbL film disintegrated upon treatment with sugars. Based on the results presented herein, we discuss the suitability of the PBA moiety with respect to hypoglycemic activity, binding ability, and selectivity for D-glucose.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2560K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2560K) Full view HTML -
Kohta Mohri, Kohei Miyata, Tomomi Egawa, Sohei Tanishita, Rikito Endo, ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 375-381
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe have been investigating the potential of oligoarginine-linked polymers as an adjuvant for mucosal vaccination that induces immunoglobulin G (IgG) in systemic circulation and immunoglobulin A (IgA) secreted on the mucosa. Our latest infection experiments demonstrated that mice immunized nasally with a mixture of inactivated influenza viruses and poly(N-vinylacetamide-co-acrylic acid) (PNVA-co-AA) modified with D-octaarginine were perfectly protected from homologous virus infection. On the contrary, virus infection was observed in mice immunized with the antigen alone. This difference was presumably due to insignificant induction of secreted IgA on the nasal mucosa in the latter mice. Since it was unclear whether the current induction level was sufficient for heterologous virus infection, we evaluated the effects of the chemical structures of oligoarginines conjugated to PNVA-co-AA on induction of intranasal IgA. The number and optical activity of the arginine residues and the degree of modification with oligoarginines in the polymer backbone were listed as a factor that would influence IgA induction. Mouse experiments revealed that maximization of the modification resulted in an increase in adjuvant activities of oligoarginine-linked polymers most effectively. Glycine segments inserted between oligoarginines and the polymer backbone were a prerequisite for the maximization. The highest IgA level was observed when antigens were coadministered with diglycine-D-octaarginine-linked PNVA-co-AA.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (596K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (596K) Full view HTML -
 Kotaro Kimura, Keishi Yamasaki, Hideaki Nakamura, Mamoru Haratake, Kaz ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 382-390
Kotaro Kimura, Keishi Yamasaki, Hideaki Nakamura, Mamoru Haratake, Kaz ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 382-390
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNanoparticles prepared using human serum albumin (HSA) have emerged as versatile carriers for improving the pharmacokinetic profile of drugs. The desolvation of HSA using ethanol followed by stabilization through crosslinking with glutaraldehyde is a common technique for preparing HSA nanoparticles, but our knowledge concerning the characteristics (or functions) of HSA nanoparticles and their efficiency when loaded with drugs is limited. To address this issue in more detail, we prepared anthracycline-loaded HSA nanoparticles. Doxorubicin-loaded HSA nanoparticles with a size similar to doxorubicin-unloaded particles could be prepared by desolvating at a higher pH (8–9), and the size (100–150 nm) was optimum for delivery to tumor tissues. Using this procedure, HSA nanoparticles were loaded with other anthracycline derivatives, and all showed cytotoxicity in cancer cells. However, the efficiency of drug loading and dissolution rate were different among them possibly due to the differences in the type of association of the drugs on nanoparticles (doxorubicin and daunorubicin; covalently bound to nanoparticles, pirarubicin; both covalently bound to and adsorbed on nanoparticles, aclarubicin; adsorbed on nanoparticles). Since the formulation of such drug-loaded HSA nanoparticles should be modified for efficient delivery to tumors, the findings reported herein provide the useful information for optimizing the formulation and the production process for the HSA nanoparticles using a desolvation technique.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThe desolvation of human serum albumin (HSA) using ethanol followed by stabilization through crosslinking with glutaraldehyde is a common technique for preparing HSA nanoparticles. Doxorubicin-loaded HSA nanoparticles with a size optimum for delivery to tumor tissues could be prepared by desolvating at a higher pH and intracellular uptake of the nanoparticles in cancer cells could be observed. HSA nanoparticles were also prepared with other anthracycline derivatives, and all showed cytotoxicity in cancer cells. However, the efficiency of drug loading and dissolution rate were different among them possibly due to the differences in the type of association of the drugs on nanoparticles.
Download PDF (4962K) Full view HTML -
Si-Li Zheng, Zhi-Yong Li, Zheng Zhang, Dong-Sheng Wang, Jian Xu, Chao- ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 391-398
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
Advance online publication: February 02, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMetrnl is a newly discovered secreted protein with neurotrophic activity and metabolic effect, while in earlier studies its circulating level in human was not explored. We evaluated two commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (DY7867-05, R&D Systems and SK00478-02, Aviscera Bioscience) for the detection of human circulating Metrnl. The DY7867-05 kit showed superiority over the SK00478-02 kit since it generated better curve fitting degree, smaller variation among tests, higher inter-assay reproducibility and better specificity, and could effectively detect human Metrnl in six types of blood samples. Subsequent analysis was performed using the DY7867-05 kit. Sample storage conditions were investigated. No gender difference in circulating Metrnl levels was found, while people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) had significantly lower Metrnl levels compared to the healthy controls.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1087K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1087K) Full view HTML -
Yosuke Masuda, Tomoki Yoshida, Noriyuki Yamaotsu, Shuichi Hirono2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 399-409
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe recently reported that the Gibbs free energy of hydrolytic water molecules (ΔGwat) in acyl-trypsin intermediates calculated by hydration thermodynamics analysis could be a useful metric for estimating the catalytic rate constants (kcat) of mechanism-based reversible covalent inhibitors. For thorough evaluation, the proposed method was tested with an increased number of covalent ligands that have no corresponding crystal structures. After modeling acyl-trypsin intermediate structures using flexible molecular superposition, ΔGwat values were calculated according to the proposed method. The orbital energies of antibonding π* molecular orbitals (MOs) of carbonyl C=O in covalently modified catalytic serine (Eorb) were also calculated by semi-empirical MO calculations. Then, linear discriminant analysis (LDA) was performed to build a model that can discriminate covalent inhibitor candidates from substrate-like ligands using ΔGwat and Eorb. The model was built using a training set (10 compounds) and then validated by a test set (4 compounds). As a result, the training set and test set ligands were perfectly discriminated by the model. Hydrolysis was slower when (1) the hydrolytic water molecule has lower ΔGwat; (2) the covalent ligand presents higher Eorb (higher reaction barrier). Results also showed that the entropic term of hydrolytic water molecule (−TΔSwat) could be used for estimating kcat and for covalent inhibitor optimization; when the rotational freedom of the hydrolytic water molecule is limited, the chance for favorable interaction with the electrophilic acyl group would also be limited. The method proposed in this study would be useful for screening and optimizing the mechanism-based reversible covalent inhibitors.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2054K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2054K) Full view HTML -
Wen-yi Mei, Ming-jun Yu, Sen Yao, Kui-ling Wang, Ri-sheng Yao2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 410-415
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
Advance online publication: February 08, 2018JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe anti-inflammatory effects of (R)-2-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl) ethyl-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-2-(2-p-tolylacetamido)propanamide (RH-1402), a previous designed small molecule Gastrin releasing peptide (GRP) antagonist were evaluated in adjuvant-induced arthritic model of rats, and the inhibitory effect on neutrophil migration induced by GRP was determined by a transwell system experiment in vitro. The arthritis was induced by injection of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) containing 10 mg/mL of heat killed mycobacterium into the left hind footpad. Experimental rats were randomly divided into 6 groups, including control, placebo, positive control group, RH-1402 of low/middle/high dose group. Disease incidence and severity was evaluated through scoring of the paw edema and histologic features of joint synovial. Blood of all experimental rats was collected for interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) cytokine levels. A transwell system was used to investigate whether RH-1402 would inhibit neutrophils migrating up a gradient of GRP in vitro. RH-1402 (5 and 10 mg/kg) significantly decreased adjuvant induced increased arthritis index during the administration period (days 14–20). Significant inhibition of joint synovial histological features can be found in the RH-1402 treated group, including alleviated Hyperplasia, Inflammatory of infiltration and activation of pannus formation. It also suppressed TNF-α and IL-1β level. Five and 10 mg/kg of RH-1402 significantly inhibited the effect of GRP on neutrophil migration with a dose dependent relationship. These findings indicate that RH-1402 have potential protective anti-inflammatory effects on experimental models of arthritis.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2390K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2390K) Full view HTML -
Takuji Magata, Yoshimi Hirokawa, Aya Furokawa, Kazuhisa Takeuchi, Yosh ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 416-422
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialPositional isomers of naturally occurring peptide subunits were synthesized via highly diastereoselective reduction of tert-butylsulfinyl ketimines as a key reaction. While NaBH4 reduction of ketimines derived from 2-thiazolyl ketones afforded the (RS,R)-isomer with moderate diastereoselectivity, L-Selectride® reduction afforded the (RS,S)-isomer as the sole product. In contrast, ketimines derived from tert-butyl 2-thiazolyl ketone afforded the (RS,R)-isomer with low diastereoselectivity by both NaBH4 and L-Selectride® reduction. Stereochemistry of the reaction was discussed based on calculation of the conformational energies for ketimines.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (901K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (901K) Full view HTML -
Ghassan Abu Sheikha, Majdi Mohammad Bkhaitan, Hanin Kalloush, Lama Ham ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 423-426
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHyperlipidemia is known as an elevation of plasma lipid components. It contributes significantly to atherosclerosis which is one of the most important causative factors in cardiovascular diseases. Agents that cause a dramatic decrease in serum lipid levels are of great value in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. For this purpose, a new series of benzimidazole propyl carboxamide benzophenone derivatives have been synthesized (7, 8, and 9). These compounds were tested in vivo to evaluate their potential hypolipidemic activity using Triton WR-1339 induced hyperlipidemic rats. All the synthesized compounds have proved to be highly biologically active, with compound 9 being the most active derivative.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (373K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (373K) Full view HTML -
Yaser Abdel-Moemen El-Badry, Mohammed Shafie Sallam, Mahr Abdel-Aziz E ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 427-433
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA set of novel series of 1,3,4-thiadiazolyl-sulfanyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-ones with anticipated antimicrobial activity has been synthesized. The synthetic protocol of the targeted compounds was accomplished by treating β-aroylacrylic acid 1 with 5-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol (2) to afford the thia-Michael adduct 3. Afterwards, the obtained thia-Michael adduct 3 was cyclized to 4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-ones 4a–d and the non-cyclized product hydrazone 5 by using different hydrazines. Moreover, adduct 3 was reacted with esters like diethyl malonate and ethyl acetoacetate affording 1,3,4-thiadiazolobutanamides 6a, b. Furthermore, the concurrent reaction of later butamides 6a, b with the hydrazine derivatives furnished thiadiazolopyridazin-3(2H)-ones 7a–d, 8, and butanoic acid 9.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (484K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (484K) Full view HTML -
Xi Liu, Xiao-Dong Kuang, Xiao-Ru He, Gang Ren, Yong Wang, Liu-Yun Xu, ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 434-438
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTwo new prenylated flavones, artocarnin A (2) and carpachromenol (12), together with 13 known prenylflavonoids (1, 3–11, 13–15) were isolated from the twigs of Artocarpus nigrifolius for the first time. Their structures were elucidated by high resolution-electrospray ionization (HR-ESI)-MS, NMR spectroscopic analysis, and in comparison with the reported data. Compounds 1–15 were evaluated for their antiproliferative effects against SiHa and SGC-7901 human cancer cell lines in vitro. The most active compound, eleocharin A (10), showed significant cytotoxicity on SiHa cells (IC50=0.7±0.1 µM) and inhibitory activity against SGC-7901 cells (IC50=8.3±0.2 µM) and could be considered as potential lead compound for further development of novel anti-tumor agents.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (418K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (418K) Full view HTML -
Zhaoxing Xu, Yongchao Yang, Xi Mai, Bin Liu, Yuanzhen Xiong, Lihuang F ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 439-451
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe novel hydroxamates containing purine scaffold were designed, synthesized and screened for their biological activities as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Some of them exhibited excellent acti-HDACs activities and antiproliferative activities, the most promising compound was 7m′. Western blot analysis indicated the compounds 7f′, 7l′, 7m′, 7o′ could increase histone H3 acetylation levels in HCT116 and K562 cell lines, and 7m′ increased the level of acetyl histone H3 in a dose-dependent manner, which is similar to the behavior of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA). Molecular docking study revealed that the conformation of 7m′ in the active site of HDAC2 was similar to positive drug SAHA, which were oriented with the hydroxamic acid towards the catalytic center and formed metal binding with zinc ion.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1689K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1689K) Full view HTML -
Fumiaki Nakagaki, Shinya Uchida, Shimako Tanaka, Noriyuki Namiki2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 452-457
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study aimed to elucidate the appropriate physical characteristics that are clinically acceptable for gummi formulations. We prepared 11 placebo gummi formulations containing different amounts of gelatin and water and evaluated their penetration and restitution using a penetrometer and rheometer, respectively. Clinical sensory tests in 16 healthy volunteers (age, 23.4±0.9 years, mean±standard deviation) were conducted on the placebo gummi formulations using the visual analog scale (VAS) score to evaluate elasticity, hardness, and overall palatability, with a 5-point rating scale of preference. The penetration increased with decreasing amounts of gelatin or increasing amounts of water in the gummi formulations. Similarly, the VAS score of elasticity and hardness from the clinical sensory tests increased with increasing amounts of gelatin but decreased with increasing amounts of water. The relationship between the penetration and VAS scores of elasticity and hardness revealed good linear correlations. This suggests that the penetration was well reflected by the hardness results of the clinical VAS scores. The overall palatability evaluated using the VAS score increased until the penetration was 10 mm and then plateaued at >10 mm penetration. The 5-point rating score for preference revealed that >50% of volunteers “prefer” the gummi formulations with penetration values of 9.8 to 13.5 mm. These results suggest that gummi formulations likely have an appropriate window of hardness. Furthermore, appropriate gummi formulations with clinically preferred physical characteristics could be prepared by adjusting the amount of gelatin and water and measuring their penetration.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (510K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (510K) Full view HTML -
 Fumihiko Ogata, Noriaki Nagai, Yukine Kariya, Eri Nagahashi, Yuhei Kob ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 458-465
Fumihiko Ogata, Noriaki Nagai, Yukine Kariya, Eri Nagahashi, Yuhei Kob ...2018 Volume 66 Issue 4 Pages 458-465
Published: April 01, 2018
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2018
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we prepared Fe–Mg-type hydrotalcites (Fe-HT3.0 and Fe-HT5.0) with different molar ratios and evaluated their adsorption capability for nitrite and nitrate ions from aqueous solution. Fe-HT is a typical hydrotalcite-like layered double hydroxide. Adsorption isotherms, as well as the effects of contact time and pH were investigated, and it was found that Fe-HT can adsorb larger amounts of nitrite and nitrate ions than Al-HT (normal-type hydrotalcite). Adsorption isotherm data were fitted to both Freundlich (correlation coefficient: 0.970–1.000) and Langmuir (correlation coefficient: 0.974–0.999) equations. Elemental analysis and binding energy of Fe-HT surface before and after adsorption indicated that the adsorption mechanism was related to the interaction between the adsorbent surface and anions. In addition, the ion exchange process is related to the adsorption mechanism. The adsorption amount increased with increasing temperature (7–25°C). The experimental data fit the pseudo-second-order model better than the pseudo-first-order model. The effect of pH on adsorption was not significant, which suggested that Fe-HT could be used over a wide pH range (4–12). These results indicate that Fe-HT is a good adsorbent for the removal of nitrite and nitrate ions from aqueous solution.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis paper describes the development and characteristics of Fe–Mg type hydrotalcite (Fe-HT) with different molar ratios and the adsorption behavior of nitrite and nitrate ions onto that in aqueous solution. It is found that the adsorption capability onto Fe-HT of nitrite and nitrate ions is larger than that onto Al-Mg type hydrotalcite (Al-HT). Moreover, the adsorption mechanism of nitrite and nitrate ions involves the ion exchange process with chloride ions. We prepared and discovered Fe-HT, which is the novel adsorbent for the removal of inorganic nitrogen ions for water environment purification.
Download PDF (1465K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|