
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Shinobu Takizawa2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 299-315
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOrganocatalytic enantioselective domino reactions are an extremely attractive methodology, as their use enables the construction of complex chiral skeletons from readily available starting materials in two or more steps by a single operation under mild reaction conditions. Thus, these reactions can save both the quantity of chemicals and length of time typically required for the isolation and/or purification of synthetic intermediates. Additionally, no metal contamination of the products occurs, given that organocatalysts include no expensive or toxic metals. The aza-Morita–Baylis–Hillman (aza-MBH) reaction is an atom-economical carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction between α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds and imines mediated by Lewis base (LB) catalysts, such as nucleophilic phosphines and amines. aza-MBH products are functionalized chiral β-amino acid derivatives that are highly valuable as pharmaceutical raw materials. Although various enantioselective aza-MBH processes have been investigated, very few studies of aza-MBH-type domino reactions have been reported due to the complexity of the aza-MBH process, which involves a Michael/Mannich/H-transfer/β-elimination sequence. Accordingly, in this review article, our recent efforts in the development of enantioselective domino reactions initiated by MBH processes are described. In the domino reactions, chiral organocatalysts bearing Brønsted acid (BA) and/or LB units impart synergistic activation to substrates, leading to the easy synthesis of highly functionalized heterocycles (some of which have tetrasubstituted and/or quaternary carbon stereocenters) in high yield and enantioselectivity.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3009K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3009K) Full view HTML -
 Toshihiko Tashima2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 316-325
Toshihiko Tashima2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 316-325
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDiscriminatory drug delivery into target cells is essential to effectively elicit the drug activity and to avoid off-target side effects; however, transporting drugs across the cell membrane is difficult due to factors such as molecular size, hydrophilicity, intercellular adhesiveness, and efflux transporters, particularly, in the brain capillary endothelial cells. Drug delivery into the brain is blocked by the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Thus, developing drugs for the central nervous system (CNS) diseases remains a challenge. The approach based on receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) can overcome this impassable problem at the BBB. Well-designed molecules for RMT form conjugates with the ligand and drugs via linkers or nanoparticles. Cell penetrating peptides (CPPs), receptor-targeting peptides, and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are often used as ligands. The binding of ligand to the receptor on the endothelial cell surface induces endocytosis. Existing exosomes comprising the conjugates move in the cytoplasm and fuse with the opposite plasma membrane to release them. Subsequently, the transcytosed conjugate-loaded drugs or released drugs from the conjugates elicit activity in the brain. As receptors, transferrin receptor (TfR), low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), and insulin receptor (InsR) have been used to intendedly induce transcytosis. Presently, several clinical trials on CNS drugs for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson disease are hindered due to poor drug distribution into the brain. Therefore, this strategy based on RMT is a promising method for CNS drugs to be transported into the brain. In this review, I introduce the practicality and possibility of drug delivery into brain across the BBB using RMT.
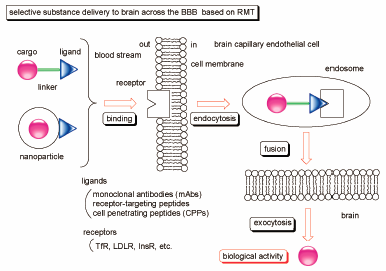 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickIn drug development, drug delivery into brain across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a serious problem. Particularly, the BBB is impermeable to large and medium-sized molecules. Accordingly, drugs for diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) are unable to elicit their activity in brain. However, receptor-mediated transcytosis can solve such impermeability. Actually, using receptors such as transferrin receptor (TfR), low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), and insulin receptor (InsR), that express on the surface of brain capillary endothelial cells, delivered well-designed drugs into brain through endocytosis and exocytosis. This methodology will be a promising approach to cure patients suffering from CNS diseases.
Download PDF (693K) Full view HTML
-
Kota Tanaka, Hiroshi Takiyama2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 326-331
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLOiling-out is a unique phenomenon that the liquid phase is separated into two parts during crystallization. The emergence of new liquid phase changes the environment where crystals nucleate and grow, we call “mother phase,” because target material and impurities become distributed to each phase according to their own particular distribution ratios. In our previous study on crystallization of an intermediate compound with impurities (denoted Imp-A, -B, and -C), we found that when oiling-out was formed, incorporation of Imp-C was inhibited, because Imp-C was distributed to the mother phase less than Imp-A and -B. In this study, we explored the effect of EtOH solution composition on impurity profile of the crystallized product in oiling-out crystallization, and found that the low content of Imp-B in the EtOH solution, the higher content of Imp-C in the crystallized product. Our finding revealed that not only oiling-out but also Imp-B played a key role in inhibiting the incorporation of Imp-C into the crystals.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3408K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3408K) Full view HTML -
 Kenzo Yahata, Yuki Kaneko, Shuji Akai2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 332-335
Kenzo Yahata, Yuki Kaneko, Shuji Akai2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 332-335
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
Advance online publication: February 04, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHerein, we describe a novel synthetic method for 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from 5-substituted tetrazoles using cobalt-catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination reaction of nonactivated olefins. Owing to its mild conditions, the method enabled the use of substrates having acid-labile functional groups, such as silyloxy and methoxymethyloxy groups. By using optically active cobalt complexes, asymmetric intermolecular hydroamination of nonactivated olefins, a longstanding challenge in synthetic organic chemistry, was developed to produce optically active disubstituted tetrazoles.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickAn efficient synthetic method for 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from 5-substituted tetrazoles is developed. In this paper, the authors established a cobalt-catalyzed site-selective alkylation of tetrazoles via atom-economic hydroamination reaction between tetrazoles and non-activated olefins. The authors also applied the developed reaction to an asymmetric intermolecular hydroamination of non-activated olefins, which is one of the longstanding problems in synthetic organic chemistry.
Download PDF (476K) Full view HTML -
Kenzo Yahata, Shin Yoshioka, Shuhei Hori, Shu Sakurai, Yuki Kaneko, Ka ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 336-338
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
Advance online publication: February 19, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialKetones are a fundamental functionality found throughout a range of natural and synthetic compounds, making their synthesis essential throughout the chemical disciplines. Herein, we describe a one-pot synthesis of ketones via decatungstate-mediated formal dehydrogenative coupling between aldehydes and non-activated hydrocarbons. A variety of substituted benzaldehydes and cycloalkanes could be used in the optimized reaction to produce the desired ketones in moderate yields. The decatungstate photocatalyst functions in two reactions in this synthesis, catalyzing both the coupling and oxidation steps of the process. Notably, the reaction displays both high atom economy and sustainability, as it uses light and oxygen as key energy sources.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (494K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (494K) Full view HTML
-
Takehiro Nakamura, Riku Nagafuji, Fumihiko Ogata, Naohito Kawasaki2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 339-344
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, we prepared novel Mg/Fe/Al hydroxides (MFA series: denoted by MFA1, MFA2, MF, and MA) and investigated their properties using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, the specific surface area, and amount of hydroxyl groups. Additionally, the phosphate adsorption capabilities of the MFA series or Fe–Mg type hydrotalcites (FHT3.0 and FHT5.0) were evaluated by examining the effects of the solution pH and contact time, and analyzing the adsorption isotherm and desorption characteristics. In MFA1, a strong correlation exists between the amount of adsorbed phosphate ions and surface hydroxyl groups, with a correlation coefficient of 0.95. The adsorption kinetics data fitted using the pseudo-second-order model performs better than the pseudo-first-order model. The adsorption isotherm data were also fitted using both the Freundlich and Langmuir models. Finally, the phosphate ions adsorbed on the MFA1 surfaces were desorbed using sodium hydroxide solution. These results indicate that MFA1 offers great potential for phosphate ion adsorption from aqueous solutions and functions as a renewable adsorbent.
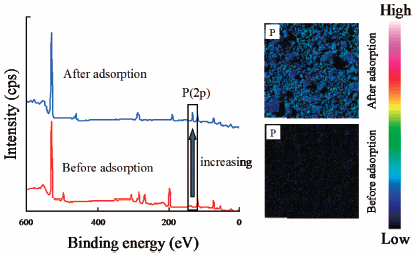 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1474K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1474K) Full view HTML -
 Toru Yamaguchi-Sasaki, Yunoshin Tamura, Yuya Ogata, Takanori Kawaguchi ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 345-362
Toru Yamaguchi-Sasaki, Yunoshin Tamura, Yuya Ogata, Takanori Kawaguchi ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 345-362
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRespiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one of the most common causes of lower respiratory tract infections and a significant pathogen for both adults and children. Although two drugs have been approved for the treatment of RSV infections, the low therapeutic index of these drugs have led pharmaceutical companies to develop safe and effective small-molecule anti-RSV drugs. The pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine series of compounds containing a piperidine ring at the 2-position of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold are known as candidate RSV fusion (F) protein inhibitor drugs, such as presatovir and P3. The piperidine ring has been revealed to facilitate the formation of an appropriate dihedral angle between the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold and the plane of the amide bond for exertion of anti-RSV activity. A molecular-dynamic study on newly designed compounds with an acyclic chain instead of the piperidine ring proposed and demonstrated a new series of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives, such as 9c with a 1-methyaminopropyl moiety, showing similar dihedral angle distributions to those in presatovir. Compound 9c exhibited potent anti-RSV activity with an EC50 value of below 1 nM, which was similar to that of presatovir. A subsequent optimization study on the benzene ring of 9c led to the potent RSV F protein inhibitor 14f with an EC50 value of 0.15 nM. The possibility of improving the biological properties of anti-RSV agents by modification at the 7-position of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine is also discussed.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickThis report describes the design, synthesis, and evaluation of a new series of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives for treatment against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). The pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine series of compounds containing a piperidine ring at the 2-position of the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold are known as candidate RSV fusion (F) protein inhibitor drugs. The piperidine ring has been revealed to facilitate the formation of an appropriate dihedral angle between the pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine scaffold and the plane of the amide bond for exertion of anti-RSV activity. A molecular-dynamic study on pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives focusing on the dihedral angles proposed and demonstrated potent anti-RSV inhibitors with an acyclic chain instead of a piperidine ring. A subsequent optimization study on pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives containing 1-methylaminopropyl group led to a highly potent anti-RSV agent with an EC50 value of less than 1 nM.
Download PDF (1872K) Full view HTML -
Ayaka Harada, Hiroyasu Tsutsuki, Tianli Zhang, Ruda Lee, Kinnosuke Yah ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 363-368
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPoly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) is a synthetic copolymer that has been used to design micro/nanoparticles as a carrier for macromolecules, such as protein and nucleic acids, that can be internalized by the endocytosis pathway. However, it is difficult to control the intracellular delivery to target organelles. Here we report an intracellular delivery system of nanoparticles modified with bacterial cytotoxins to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and anti-inflammatory activity of the nanoparticles. Subtilase cytotoxin (SubAB) is a bacterial toxin in certain enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) strains that cleaves the host ER chaperone BiP and suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) activation and nitric oxide (NO) generation in macrophages at sub-lethal concentration. PLGA-nanoparticles were modified with oligo histidine-tagged (6 × His-tagged) recombinant SubAB (SubAB-PLGA) through a pH-sensitive linkage, and their translocation to the ER in macrophage cell line J774.1 cells, effects on inducible NO synthase (iNOS), and levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α cytokine induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were examined. Compared with free SubAB, SubAB-PLGA was significantly effective in BiP cleavage and the induction of the ER stress marker C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) in J774.1 cells. Furthermore, SubAB-PLGA attenuated LPS-stimulated induction of iNOS and TNF-α. Our findings provide useful information for protein delivery to macrophages and may encourage therapeutic applications of nanoparticles to the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1261K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1261K) Full view HTML -
Senchuan Song, Yuliang Mai, Huahong Shi, Bing Liao, Fei Wang2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 369-379
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTyrosinase plays important roles in many different disease related processes, and the development of its inhibitors is particularly important in biotechnology. In this study, thirty-nine 3-/4-alkoxyphenylethylidenethiosemicarbazides were synthesized as novel tyrosinase inhibitors based on structure-based molecular design. Our experimental results demonstrated that thirty-one of them possess remarkable tyrosinase inhibitory activities with IC50 value below 1 µM, and 5a, 6e, 6g and 6t did not display any toxicity to 293T cell line at the concentration of 1000 µmol/L. According to the inhibitory activities, several compounds were selected for detail investigation on the structure–activity relationships (SARs), mechanisms of enzyme inhibition, inhibitory kinetics and cytotoxicity. In particular, the interaction between the selected inhibitors and the active center of tyrosinase was considered and discussed in detail based on their structural characteristics. Taken together, the results presented here demonstrated that the newly designed compounds are promising candidates for the treatment of tyrosinase-related disorders and further development of them may have significant contribution in biomedical science.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1425K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1425K) Full view HTML -
 Makoto Inai, Yuki Oguri, Mitsuyo Horikawa, Hiroto Kaku, Shinya Suzuki, ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 380-383
Makoto Inai, Yuki Oguri, Mitsuyo Horikawa, Hiroto Kaku, Shinya Suzuki, ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 380-383
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe cryptolactones A1, A2, B1, and B2 isolated from a Cryptomyzus sp. aphid were synthesized via the Mukaiyama aldol reaction and olefin metathesis. Their antipodes and derivatives were also synthesized by the same strategy to investigate structure–activity relationships. These compounds exhibited cytotoxic activity against human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells with IC50 values of 2.1–42 µM.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickAphids have unique polyketide pigments, which possess interesting biological activities such as cytotoxicity. In this article, the authors have focused on cryptolactone A1, A2, B1, and B2, colorless polyketide lactones, isolated from a colorless aphid, Cryptomyzus sp., and accomplished the asymmetric total syntheses of these compounds, their analogs bearing shorter carbon chains, and their antipodes. The investigation of structure-activity relationships among these compounds was carried out and revealed that both enantiomers exhibited similar cytotoxic properties towards HL-60 cell lines. However, compounds with shorter carbon chains were less cytotoxic than the others.
Download PDF (427K) Full view HTML -
 Hirotaka Sasaki, Kotaro Kiyotaki, Ayumi Imayoshi, Kazunori Tsubaki2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 384-391
Hirotaka Sasaki, Kotaro Kiyotaki, Ayumi Imayoshi, Kazunori Tsubaki2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 384-391
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialVarious aromatic lactones have been synthesized and their regioselectivity (1,2-addition vs. 1,4- or 1,6-addition) investigated in reactions with organolithium species, particularly n-BuLi and sec-BuLi. The regioselectivity varied greatly depending on various factors, such as the bulkiness of both substrates and organolithium species, and types of solvent and cosolvent. In particular, 1,4-addition with dearomatization occurred preferentially using sec-BuLi as the nucleophile in tetrahydrofuran (THF) with hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA) or N,N′-dimethylpropyleneurea (DMPU) as cosolvent. For sec-BuLi, the reaction was estimated to proceed through a single-electron transfer mechanism.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pick
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractEditor's pickOrganic reactions using dearomatization have attracted much attention as a new approach to constructing complicated cyclic molecules. This paper describes the regioselectivity of nucleophilic addition of organolithium species (in particular, n-BuLi and sec-BuLi) to various aromatic lactones. The results of many experiments indicated that the regioselectivity varied greatly depending on various factors, such as the bulkiness of both substrates and organolithium species, and types of solvent and cosolvent. It is particularly interesting that the reactions mechanism of the addition of organolithium species differed between n-BuLi (via ionic process) and sec-BuLi (via one electron transfer process).
Download PDF (718K) Full view HTML -
Kousuke Tamura, Makoto Ono, Takefumi Kawabe, Motomu Ohara, Etsuo Yonem ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 392-397
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe degradation pathway of a taxane derivative and anticancer agent, DS80100717, was investigated. Several degradants were generated under acidic, basic, and oxidative stress conditions in solution. The chemical structures of eight degradants of DS80100717 were elucidated using MS and NMR. The major degradant of the DS80100717 drug substance derived by heating in solid-state was the N-oxide form via oxidation and C2′-epimer of the side chain via acid hydrolysis. We proposed previously unreported degradation pathways of DS80100717 with taxane derivatives such as paclitaxel, docetaxel, and cabazitaxel.
 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (683K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (683K) Full view HTML
-
Keisuke Tsuchiya, Tomohiro Umeno, Genichiro Tsuji, Hidetomo Yokoo, Mas ...2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 398-402
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLPhotopharmacology has attracted attention as an approach for the development of novel therapeutics because it allows regulation of the bioactivity of compounds based on their conformational change by photo-irradiation. Previously, we have reported several types of selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulators based on diphenylmethane skeleton. To develop novel photopharmacological reagents, we designed and synthesized a set of ER ligands based on azobenzene skeleton, which can switch its conformation following UV irradiation. Our results showed that after UV irradiation, the Z-form of the synthesized compound 9 interacted with ERα, with a KD value of 2.5 µM, whereas the E-form of compound 9 did not bind ability to ERα at 10 µM.
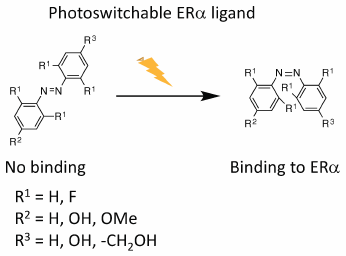 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (639K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (639K) Full view HTML
-
2020 Volume 68 Issue 4 Pages 403
Published: April 01, 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (750K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|