
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Tetsuro Ito, Wei Li2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 136-137
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (242K) Full view HTML
-
Yohei Saito, Tomoya Nishida, Kyoko Nakagawa-Goto2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 138-155
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLMeroterpenoids are a distinctive class of natural products found in various organisms, including animals, plants, bacteria, algae, and particularly fungi. Among them, spiromeroterpenoids, which have a spiro-ring connecting a terpenoid and a non-terpenoid moiety, are markedly unique. Currently, only a limited number of plants from the families Myrtaceae, Hypericaceae, Annonaceae, Asteraceae, and Lauraceae are known to biosynthesize spiromeroterpenoids. The non-terpene moiety of plant-derived spiromeroterpenoids is generally a polyketide, mainly a functionalized phloroglucinol derivative such as syncarpic acid and tasmanone. However, a flavanone, as found in the syzygioblanes isolated from Syzygium oblanceolatum (Myrtaceae), is another rare non-terpene component. The terpene moieties are restricted to monoterpenes or sesquiterpenes. The spiro-ring is generally formed by [m + n] cyclization or, in some cases, by radical or ionic cyclization.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2323K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2323K) Full view HTML
-
Masashi Fukaya, Kaori Ryu, Tetsuro Ito2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 156-161
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSulfur-containing compounds are found in various medicinal products, where they play crucial roles in biological activities such as antimicrobial, anticancer, and other therapeutic effects. These compounds are commonly found in species of Allium, especially onions and garlic; however, there is little evidence of their presence in other plants. In particular, sulfur-containing iridoid glycosides with anticancer properties, which are very promising compounds as pharmaceutical seeds, have been isolated from Paederia scandens (Rubiaceae), also known as the skunk vine because of its strong smell caused by methyl mercaptan. Herein, we describe the isolation and structural elucidation of 3 new iridoid glycosides from the aerial parts of P. scandens. Their biosynthetic pathways are also discussed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (738K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (738K) Full view HTML -
Kanami Watanabe, Yohei Saito, Shuichi Fukuyoshi, Katsunori Miyake, Dav ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 162-167
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe phytochemical investigation of the rainforest plant Croton argyratus (Euphorbiaceae) led to the isolation of two halimane-type diterpenes, crotargyolides A (1) and B (2), with an uncommon γ-lactone ring at C-5 and C-9, together with a crotofolane-type diterpene, 3-hydroxylated crotofolin C (3, crokocrotogenoid A), and the known clerodane diterpenes, junceic acid (4) and epoxyjunceic acid (5). The structures of the newly isolated compounds were elucidated by various NMR techniques, high resolution (HR)MS analysis, and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectroscopy. The proposed biosynthetic pathway of 1 from 4 was discussed. Crotargyolide A (1) and known compounds 4 and 5 were evaluated for antiproliferative activity and displayed no growth inhibitory effect toward all tested tumor cell lines.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (703K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (703K) Full view HTML -
Yuka Yoshizawa, Nana Fujita, Akihito Yokosuka, Yoshihiro Mimaki2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 168-172
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialTwo new isoflavone glucosides, irisolone 4′-O-[O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside] (1) and iriskashmirianin 4′-O-[O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside] (2) were isolated from the underground parts of Iris florentina (Iridaceae). The structures of 1 and 2 were determined based on extensive spectroscopic data analyses and hydrolytic cleavage results. The isoflavone derivatives previously isolated from this plant were evaluated for their ability to inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end products.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (459K) Full view HTML -
Ryura Tateiwa, Yudai Nakama, Ayaka Murase, Tomoki Mizoguchi, Makoto In ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 173-178
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialRetinoid X receptors (RXRs) are nuclear receptors involved in various crucial biological processes, such as gene regulation, metabolism, and cell differentiation. They predominantly function as heterodimers with other nuclear receptors and modulate gene expression in response to ligand binding. Additionally, they act as therapeutic targets for different conditions, such as cancer and metabolic disorders. Although synthetic RXR agonists, such as bexarotene, are used in clinical settings, they exert adverse side effects. In this study, to explore insights into potential natural RXR agonists as alternatives to existing drugs, we isolated 14 coumarins, including 1 new compound from Boenninghausenia albiflora var. japonica (Rutaceae). Among them, daphnoretin methyl ether (14), a known biscoumarin, was found to exhibit subtype-nonspecific RXR agonist activity.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (917K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (917K) Full view HTML -
Takashi Kikuchi, Danyang Liu, Kouharu Otsuki, Kazuo Koike, Wei Li2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 179-188
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe Silene genus plants in the Caryophyllaceae family are a large genus with over 850 species. It has been known that Silene genus plants contain triterpenoid saponins. These saponins have glucuronic acid in the sugar chain and are difficult to separate in chromatography. In this study, a strategy was developed to clarify the distribution of triterpenoid saponins in whole plants of Silene vulgaris by isolation of neutralized saponins using methylation reactions, which were used as standard substances for LC-MS analysis, and elucidating their characteristic MS and MS/MS fragment patterns. The n-butanol fraction of the methanol extract from the whole plant of S. vulgaris was separated to obtain fractions including saponins by octadecyl silica column chromatography. Then, each fraction was treated with trimethylsilyl diazomethane for methylation of the carboxyl groups of glucuronic acid in the molecules, and five triterpenoid methylated saponins (7a, 13a, 14a, 16a, and 17a) were isolated using HPLC. The chemical structures of the isolated compounds were determined by spectroscopic analyses including NMR and MS, and their characteristic fragmentations were also clarified in LC-MS and MS/MS. It was performed on the n-butanol fraction from the whole plant of S. vulgaris, and the chemical structures of 22 triterpenoid saponins were estimated based on the MS and MS/MS fragmentation patterns of the isolated triterpenoid saponins.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1457K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1457K) Full view HTML -
Bo-Yuan Zhao, Ben-Song Xin, Shuang Qiu, Guo‐Dong Yao, Xiao‐Xiao Huang, ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 189-194
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialSix flavonoids (1–6), including 3 previously undescribed compounds (1–3), were isolated from the dried roots and stem skins of Daphne giraldii Nitsche. The strategy of LC-tandem mass spectrometry-based Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) molecular network technology and NMR-based Small Molecule Accurate Recognition Technology (SMART) technology facilitated the precise separation of isopentenyl flavonoids in D. giraldii. The structures were determined through comprehensive spectroscopic analysis. Furthermore, all compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activity against Hep3B cells. Specifically, compounds 1 and 3 exhibited significant cytotoxicity with IC50 values of 5.52 ± 0.57 and 2.53 ± 0.49 μM, respectively, compared to the positive control sorafenib (IC50 = 7.08 ± 0.23 μM).
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2477K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2477K) Full view HTML -
Tomohisa Kanai, Tatsuya Shirahata, Shunsuke Nakamori, Rin Sato, Akito ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 195-204
Published: March 07, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 07, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThis study established a 1H-NMR-based biochemometric approach for the isolation of biologically active compounds from complex extracts. In both pharmacognosy and natural product chemistry, reliably isolating bioactive compounds typically necessitates repeating time-consuming and laborious isolation and purification steps, presenting a bottleneck in many studies. We applied biochemometric methods to accurately estimate active compounds, thus minimizing the number of assays and isolation steps. The rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum Hance (Zingiberaceae) have been continuously prescribed in traditional Japanese medicine as stomachics and analgesics, despite a limited understanding of the mechanisms underlying these effects. Additionally, transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 (TRPV1) plays a role in modulating nociception, respiratory defense responses, and gastrointestinal protection. Accordingly, 1H-NMR-based biochemometry was employed to search for TRPV1-active components in A. officinarum rhizome extracts by combining TRPV1 activity intensity with 1H-NMR data. However, initially, the active component could not be identified because the principal component analysis loading plot primarily displayed only buckets of primary metabolites. Consequently, we applied orthogonal partial least squares to the 1H-NMR spectra, which allowed us to identify specific spectral bins at 1.66 ppm (aliphatic) and 7.02, 6.98, 6.82, and 6.74–6.58 ppm (aromatic), correlating with TRPV1-stimulating activity. Based on this prediction, diarylheptanoids were swiftly identified, and their potential to activate TRPV1 was confirmed by administering the identified compounds to TRPV1-expressing cells. These findings highlight the potential of chemometric analysis using 1H-NMR spectroscopy for identifying the chemical classes responsible for the bioactive properties of complex crude drug extracts.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3929K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3929K) Full view HTML
-
Fumihiko Ogata, Kazuya Ujita, Yugo Uematsu, Noriaki Nagai, Chalermpong ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 205-212
Published: March 12, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 12, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the present study, magnetic-calcined bamboo composite adsorbents (MCBC200, MCBC400, MCBC600, MCBC800, and MCBC1000) were prepared, and their physicochemical characteristics (scanning electron microscope images, differential thermogravimetric analysis, Fourier transform-IR, specific surface area, surface functional groups, and point of zero charge [pHpzc]) were evaluated. Furthermore, the adsorption capacity of methylene blue (MB, cationic dye) using the prepared adsorbents was assessed. The value of pHpzc and the specific surface area of MCBC400 were 7.8 and 50.6 m2/g, respectively. The amounts of acidic or basic functional groups of MCBC400 were relatively greater than those of the other adsorbents. The amount of MB adsorbed onto MCBC400 (31.9 mg/g) was higher than that onto other adsorbents. The adsorption of MB using MCBC400 was evaluated in relation to various parameters, including coexistence, solution pH, adsorption temperature, and contact time. The results followed the Langmuir isotherm model and a pseudo-second-order model with correlation coefficients of 0.980–1.000 and 0.996, respectively. MB was selectively adsorbed by MCBC400 in a binary solution system containing anionic dyes. Finally, one of the adsorption mechanisms was determined by analyzing the elemental distribution and the binding energy before and after the adsorption of MB. The current findings provide important information for removing MB with MCBC400 from the aqueous phase.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2868K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2868K) Full view HTML -
 Daisuke Mizunaga, Satoru Watano2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 213-226
Daisuke Mizunaga, Satoru Watano2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 213-226
Published: March 22, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 22, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTableting is a critical process in the manufacture of pharmaceutical tablets that directly influences product quality. Ensuring consistent quality between the research and development phase and commercial-scale production is essential during scale-up. In this study, we investigated methods for evaluating time-dependent deformation behavior using four excipients that exhibit different compression deformation behaviors. Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCPD) shows no viscoelasticity, whereas lactose monohydrate (LAC), cornstarch (CS), and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) exhibit viscoelasticity and viscoplasticity, although the degree of viscosity varies between them. In addition to investigating the known strain rate sensitivity (SRS), we performed mechanical energy evaluation based on the area under the force–displacement curve and stress relaxation tests. A trapezoid waveform was applied during the test, with loading punch speeds of 0.5 and 100 mm/s, and a dwell time of 4.5 s. The SRS value for DCPD approached approximately one, indicating no speed dependence, and the SRS increased in the order of LAC < MCC < CS, consistent with previous studies that used a saw-tooth waveform. Among the mechanical energies, the ratio of plastic flow energy to plastic energy, which depends on dwell time, followed a similar trend to SRS for the three materials other than DCPD. We conclude that axial stress relaxation is affected by machine deformation, whereas radial stress relaxation provides insight into the viscous behavior of the material. Under the test conditions, the effects of the punch-displacement profile and compression pressure on the mechanical energy and stress relaxation were more pronounced than those of SRS.
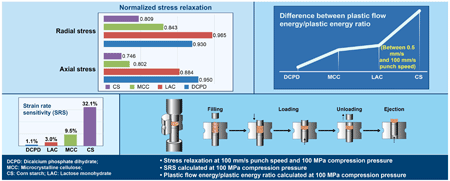 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickIn this manuscript, the authors investigate the time-dependent deformation behavior of powdered or granular materials during tableting using a compaction simulator. Four pharmaceutical excipients with different compression characteristics were analyzed using a trapezoidal punch displacement profile, where only the punch speed during loading was varied. By evaluating strain rate sensitivity, mechanical energy, and stress relaxation, differences in deformation behavior between the materials were identified. The results suggest that an accurate understanding of the time-dependent deformation characteristics of raw materials is important to support appropriate scale-up of the tableting process.
Download PDF (6261K) Full view HTML -
Takuya Sotome, Takeshi Oshizaka, Tomoaki Toyama, Keiko Shinozaki, Sato ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 227-233
Published: March 25, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 25, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe wearing of medical gowns during anticancer drug preparation is recommended for the prevention of drug exposure. Non-breathable and breathable gowns (gown− and gown+, respectively) are both available. However, anticancer drugs may permeate “gown+.” In the present study, water, hydrophilic and lipophilic dyes, and aqueous solutions of several model chemicals with different physical properties (pyridoxine, antipyrine, ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate, and butyl p-hydroxybenzoate) were applied to four types of gowns and their chemical permeabilities were measured. The permeability of gowns to vaporized ethanol was also investigated because several volatile anticancer drugs are currently used in the treatment of cancer. The results obtained showed that the hydrophilic chemical, pyridoxine, did not permeate any of the gowns tested. Furthermore, gowns became more permeable as the lipophilicity of chemicals increased. No significant changes were observed in the chemical permeability between “gown−” and “gown+,” suggesting that the protective efficacy of the gowns against permeation by anticancer drugs was similar regardless of breathability. On the contrary, “gown + ” was permeable to vaporized ethanol, whereas “gown−” was not. The present study demonstrates the need for safety measures in lipophilic or volatile anticancer drug handling and the importance of developing medical gowns that are highly resistant to chemical permeation.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1481K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1481K) Full view HTML -
 Takuya Oishi, Takuya Nagato, Chikara Tsujikawa, Takuya Minamiguchi, Sa ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 234-245
Takuya Oishi, Takuya Nagato, Chikara Tsujikawa, Takuya Minamiguchi, Sa ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 234-245
Published: March 28, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 28, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialMultivariate statistical process control (MSPC) has attracted considerable attention as a monitoring method for pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. However, there are few examples of its application in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and previous studies have shown high false-positive rates. One of the reasons is the use of inappropriate scaling factors. In pharmaceutical processes, the number of experiments for MSPC modeling tends to be small because the active pharmaceutical ingredients are expensive. Subsequently, the standard deviation, a common scaling factor for some variables, becomes too small, and the model may become sensitive to small variations. In this study, we have proposed methods for determining the appropriate scaling factors. These methods were applied to granulation and drying processes in pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. The MSPC model can detect changes in the process parameters and raw materials used during continuous wet granulation and fluidized bed drying using the proposed scaling method.
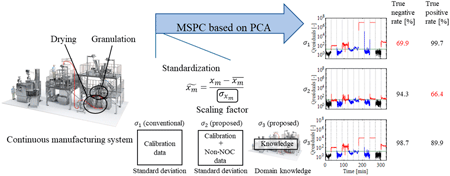 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickMultivariate statistical process control (MSPC) has attracted considerable attention as a monitoring method for pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. However, there are few examples of its application in pharmaceutical manufacturing, and previous studies have shown high false positive rates. In this study, the authors proposed a method to improve the accuracy of anomaly detection using MSPC by determining the appropriate scaling factor used for standardization and applied it to the granulation and drying processes in pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. The proposed method reduces the false positive rate compared to conventional methods and can detect changes in process parameters and raw materials.
Download PDF (3167K) Full view HTML -
 Keita Kajino, Tomoya Sugai, Ryoji Kise, Riko Suzuki, Akihisa Tokuda, Y ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 246-256
Keita Kajino, Tomoya Sugai, Ryoji Kise, Riko Suzuki, Akihisa Tokuda, Y ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 246-256
Published: March 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe δ-opioid receptor (DOR) is a promising target for developing novel analgesics due to its lower risk of causing side effects compared to the μ-opioid receptor (MOR), which is commonly associated with dependence, respiratory depression, and other adverse effects. KNT-127, a DOR-selective agonist with a morphinan skeleton, offers analgesic and antidepressant benefits without inducing convulsions at therapeutic doses, unlike the conventional DOR agonist SNC80. While previous studies have suggested that KNT-127 exhibits reduced β-arrestin recruitment, a signaling pathway implicated in adverse opioid effects, the ligand structural basis for this biased signaling remains unclear. In this study, we explored the structure–signal relationships of KNT-127, focusing on its quinoline moiety, which is known to serve as an address domain responsible for DOR selectivity. Modifying the quinoline moiety by removing the aromatic rings reduced DOR selectivity and potency in relation to G-protein activation while diminishing both the potency and efficacy of β-arrestin recruitment. These results suggest that the morphinan skeleton is critical for reduced β-arrestin recruitment, while the quinoline moiety differentially modulates G-protein activation and β-arrestin recruitment. Together, our study expands the message-address concept, previously limited to receptor selectivity, by providing structural insights into the G-protein-biased agonism of DOR agonists, thereby guiding the design of safer DOR-targeting therapeutics.
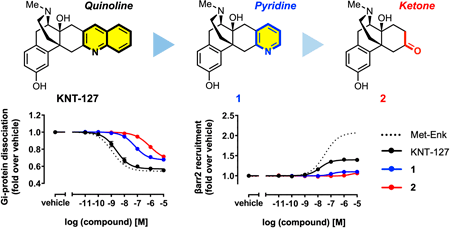 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
The δ-opioid receptor (DOR) is a promising therapeutic target with reduced side effects compared to μ-opioid receptor agonists. However, some DOR agonists, such as SNC80, have been reported to induce convulsions, potentially involving β-arrestin signaling. This study investigates the first structure–signal relationship of KNT-127, a morphinan-based DOR agonist, and demonstrates that the morphinan skeleton reduces β-arrestin recruitment, while the quinoline moiety modulates the bias between G protein and β-arrestin pathways. These findings expand the classical message–address concept and offer valuable insights into the rational design of functionally selective DOR agonists with improved safety profiles.Download PDF (2976K) Full view HTML -
Hiroaki Omori, Homare Kurashima, Nobuyuki Isshiki, Yasuharu Kashiwagur ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 257-263
Published: March 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSucroferric oxyhydroxide is a phosphate binder for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing dialysis. This study aimed to determine the effects of tablet size, shape, and tensile strength on disintegration time and friability of sucroferric oxyhydroxide-containing mini-tablets. A linear relationship between the disintegration time and tensile strength was observed across all mini-tablets, except for those with smaller tablets (diameters: <1.8 mm). However, the relationship between friability and tensile strength was not significantly correlated under linear or exponential approximations. Explaining friability solely based on tensile strength was challenging, indicating the role of tablet shape. To visualize the effects of mini-tablet shapes and tensile strength on their disintegration time and friability, response aspects were analyzed. The response surface analysis revealed that the disintegration time was not affected by the tablet shape. The friability of the mini-tablets with a cup depth/diameter of 0.209 was lower (<0.2) than that of tablets with other cup depth/diameter across all tested ranges of tensile strength (1–6). A cup depth/diameter of 0.2 was identified as optimal for minimizing the friability of mini-tablets and can be implemented in commercial production without issues. In conclusion, tablet shape should be carefully considered during the development of mini-tablets to ensure low friability.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1601K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1601K) Full view HTML
-
 Minoru Ozeki, Mizuki Tsuda, Serina Yamanouchi, Momoe Yamakawa, Kanako ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 264-267
Minoru Ozeki, Mizuki Tsuda, Serina Yamanouchi, Momoe Yamakawa, Kanako ...2025Volume 73Issue 3 Pages 264-267
Published: March 29, 2025
Released on J-STAGE: March 29, 2025
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialBuilding on our previously reported techniques, we developed a concise and highly stereoselective synthesis method for β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated esters. This synthesis comprises 3 reactions: the aldol reaction of acetic ester derivatives with ketones, the acetylation of tert-alcohols, and an elimination reaction utilizing 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU). During the acetylation process, acetic anhydride and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) facilitated the smooth acetylation of bulky tert-alcohols; however, employing DBU as a base reduced the yields. Additionally, the removal of excess DMAP effectively suppressed the formation of unwanted byproducts during the elimination step.
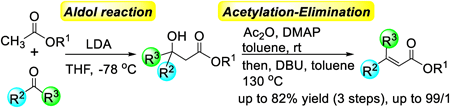 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickβ,β-Disubstituted α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, which are characterized by two distinct substituents at the β-position, are found in various bioactive molecules. In this paper, the authors report a concise and highly stereoselective synthesis method for β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated esters. This synthesis method comprises three well-known reactions: the aldol reaction of acetic ester derivatives with ketones, the acetylation of tert-alcohols, and an elimination reaction utilizing DBU. Two important findings, i.e., that the acetylation of bulky tert-alcohol proceeded efficiently using Ac2O and DMAP without DBU as a base, and that the formation of isomerized byproducts in the elimination reaction was suppressed by removing excess DMAP, enabled the synthesis of various β,β-disubstituted α,β-unsaturated esters.
Download PDF (537K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|