
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
 Atsushi Nakayama2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 422-431
Atsushi Nakayama2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 422-431
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLNatural products are important for the development of pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals; thus, their synthesis and medicinal chemistry research is critical. Developing a total synthesis pathway for natural products confirms their structure and provides the opportunity to modify the structure in a targeted manner. A simple modification of a single oxidation step can increase the biological activity, or the complexity of the molecule can alter the property. Herein, we discuss the asymmetric total synthesis of dihydroisocoumarin-type natural products, the creation of novel antibacterial compounds through partial structural modification, and the development of antioxidants with high activity and low toxicity through dimerization strategies.
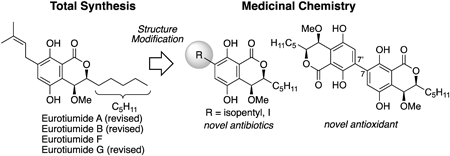 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickNatural products have played an important role in drug discovery. Recently, pseudo-natural products, whose structures have been modified based on natural products, have received much attention due to their unique biological properties that differ from the parent compounds. This review describes a series of total syntheses and structural elucidations of eurotiumides and developments of pseudo-natural products carried out by the author concerning the dihydroisocoumarin-type natural products eurotiumides with potent biological activities. One-point chemical structural modification and the dimerization strategy have led to the promising compounds, which are more active than the parent natural product.
Download PDF (2337K) Full view HTML -
 Okiko Miyata2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 432-453
Okiko Miyata2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 432-453
Published: May 01, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe have developed efficient synthetic reactions using enamines and enamides carrying oxygen atom substituent on nitrogen, such as N-alkoxyenamines, N,α-dialkoxyenamines, N-alkoxyanamides, and N-(benzoyloxy)enamides. The umpolung reaction by polarity inversion at the β-position of N-alkoxyenamines afforded α-alkyl-, α-aryl-, α-alkenyl-, and α-heteroarylketones by using aluminum reagent as nucleophiles. Furthermore, one-pot umpolung α-phenylation of ketones has been also developed. We applied this method to umpolung reaction of N,α-dialkoxyenamine, generated from N-alkoxyamide to afford α-arylamides. The vicinal functionalization of N-alkoxyenamines has been achieved with the formation of two new carbon–carbon bonds by using an organo-aluminum reagent and subsequent allyl magnesium bromide or tributyltin cyanide. A sequential retro-ene arylation has been developed for the conversion of N-alkoxyenamides to the corresponding tert-alkylamines. The [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of N-(benzoyloxy)enamides followed by arylation afforded cyclic β-aryl-β-amino alcohols bearing a tetrasubstituted carbon center. The resulting products were converted into the corresponding sterically congested cyclic β-amino alcohols, as well as the dissociative anesthetic agent Tiletamine.
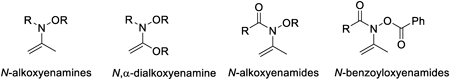 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThis review describes the development of new synthetic methodologies for polyfunctional compounds using enamines and enamides carrying an oxygen atom substituent on nitrogen atom, such as N-alkoxyenamines, N,2-dialkoxyenamines, N-alkoxyenamides, and N-(benzoyloxy) enamides that have not received much attention. The efficient synthetic reactions using N-alkoxy-enamines and enamides as substrates proceed in the presence of triarylaluminum reagent via cleavage of a relatively lower energy N–O bond, and formation of new stronger bonds to afford 2-arylketones, 2-arylcarboxylic acids, tert-alkylamies carrying aryl group, 1,2-disubstituted phenethylamines, and 2-amino-2-arylethanols that are useful as partial structures in biologically active compounds.
Download PDF (3100K) Full view HTML
-
Sudipta Mukherjee, Jasmina Khanam2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 454-470
Published: May 09, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 09, 2024
Advance online publication: April 19, 2024JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study investigates the efficacy of modified Albizia procera gum as a release-retardant polymer in Diltiazem hydrochloride (DIL) matrix tablets. Carboxymethylated Albizia procera gum (CAP) and ionically crosslinked carboxymethylated Albizia procera gum (Ca-CAP) were utilized, with Ca-CAP synthesized via crosslinking CAP with calcium ions (Ca2+) using calcium chloride (CaCl2). Fourier Transform (FT) IR analysis affirmed polymer compatibility, while differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) assessed thermal behavior and crystallinity, respectively. Zeta potential analysis explored surface charge and electrostatic interactions, while rheology examined flow and viscoelastic properties. Swelling and erosion kinetics provided insights into water penetration and stability. CAP’s carboxymethyl groups (–CH2–COO−) heightened divalent cation reactivity, and crosslinking with CaCl2 produced Ca-CAP through –CH2–COO− and Ca2+ interactions. Structural similarities between the polymers were revealed by FTIR, with slight differences. DSC indicated modified thermal behavior in Ca-CAP, while Zeta potential analysis showcased negative charges, with Ca-CAP exhibiting lower negativity. XRD highlighted increased crystallinity in Ca-CAP due to calcium crosslinking. Minimal impact on RBC properties was observed with both polymers compared to the positive control as water for injection (WFI). Ca-CAP exhibited improved viscosity, strength, controlled swelling, and erosion, allowing prolonged drug release compared to CAP. Stability studies confirmed consistent six-month drug release, emphasizing Ca-CAP’s potential as a stable, sustained drug delivery system over CAP. Robustness and accelerated stability tests supported these findings, underscoring the promise of Ca-CAP in controlled drug release applications.
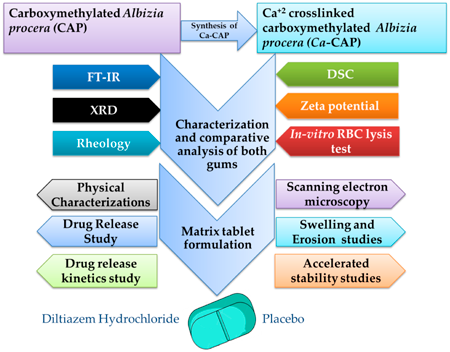 View full abstractDownload PDF (7327K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (7327K) Full view HTML -
 Hidetomo Yokoo, Yoshitaka Aoyama, Takashi Matsumoto, Eiichi Yamamoto, ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 471-474
Hidetomo Yokoo, Yoshitaka Aoyama, Takashi Matsumoto, Eiichi Yamamoto, ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 471-474
Published: May 15, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 15, 2024
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialThe solid-state properties of drug candidates play a crucial role in their selection. Quality control of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) based on their structural information involves ensuring a consistent crystal form and controlling water and residual solvent contents. However, traditional crystallographic techniques have limitations and require high-quality single crystals for structural analysis. Microcrystal electron diffraction (microED) overcomes these challenges by analyzing difficult-to-crystallize or small-quantity samples, making it valuable for efficient drug development. In this study, microED analysis was able to rapidly determine the configuration of two crystal forms (Forms 1, 2) of the API ranitidine hydrochloride. The structures obtained with microED are consistent with previous structures determined by X-ray diffraction, indicating microED is a useful tool for rapidly analyzing molecular structures in drug development and materials science research.
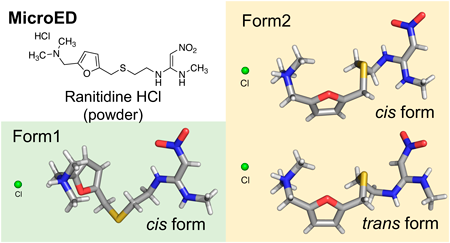 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickThe solid-state properties of drug candidates are crucial for their selection process. Traditional crystallographic techniques for structural analysis have limitations and require high-quality single crystals. Microcrystal electron diffraction (microED) can overcome these challenges by analyzing difficult-to-crystallize or small-quantity samples. In this study, microED rapidly determined the configuration of two crystal forms of the active pharmaceutical ingredient ranitidine hydrochloride. The structures obtained through microED were consistent with those determined by X-ray crystallography, demonstrating that microED is a valuable tool for efficiently elucidating molecular structures in drug development and materials science
Download PDF (1633K) Full view HTML -
 Takehiro Nishimura, Kei Kudo, Miho Izumikawa, Ikuko Kozone, Junko Hash ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 475-479
Takehiro Nishimura, Kei Kudo, Miho Izumikawa, Ikuko Kozone, Junko Hash ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 475-479
Published: May 16, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 16, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHeterologous expression of natural compound biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) is a robust approach for not only revealing the biosynthetic mechanisms leading to the compounds, but also for discovering new products from uncharacterized BGCs. We established a heterologous expression technique applicable to huge biosynthetic gene clusters for generating large molecular secondary metabolites such as type-I polyketides. As an example, we targeted concanamycin BGC from Streptomyces neyagawaensis IFO13477 (the cluster size of 99 kbp), and obtained a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone with an insert size of 211 kbp that contains the entire concanamycin BGC. Interestingly, heterologous expression for this BAC clone resulted in two additional aromatic polyketides, ent-gephyromycin, and a new compound designated as JBIR-157, together with the expected concanamycin. Bioinformatic and biochemical analyses revealed that a cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster in this BAC clone was responsible for the production of these type-II polyketide synthases (PKS) compounds. Here, we describe the production, isolation, and structure elucidation of JBIR-157, determined primarily by a series of NMR spectral analyses.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pickAuthors have developed heterologous expression technique applicable to huge biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) which produce large molecular secondary metabolites. Authors targeted concanamycin BGC (~100 kb) in Streptomyces neyagawaensis IFO13477. Interestingly, heterologous expression of a BAC clone of which insert size was 211 kb involving the entire concanamycin resulted in the production of a new compound JBIR-157 in addition to concanamycin. INADEQUATE analysis revealed that JBIR-157 consists of an unusual new skeleton produced by the cryptic type-II polyketide synthases (PKS) BGC. In this study, authors reported the production, isolation, structure elucidation, and proposed biosynthetic mechanism of JBIR-157.
Download PDF (530K) Full view HTML -
Naoya Ito, Masataka Ito, Hironori Suzuki, Shuji Noguchi2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 480-486
Published: May 18, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 18, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialX-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy is a new method for the characterization of active pharmaceutical ingredients. XANES spectra show unique features depending on the electronic states of the X-ray absorbing elements and provide information about the chemical environment that affects the electronic states. In this study, six bisphosphonate hydrate crystals were used to investigate, for the first time, how the phosphorus K-edge XANES spectra are affected by the interatomic interactions and charged states of phosphonate moieties. Phosphorus K-edge XANES spectra showed several differences among the bisphosphonates. In particular, the chlorine atoms covalently bonded near the phosphonate and the number of electric charges of the phosphonate moieties seemed to have large effects on peak shape in XANES spectra. Unique shapes of the XANES spectra demonstrated that differences in interactions at the oxygen atoms of the phosphonate moieties could change the shapes of the XANES spectrum peaks to the extent that each material was distinguished based on the spectra. Since slight differences in interatomic interactions and charged states lead to variations in the spectra, XANES spectroscopy could be widely applied as the fingerprint method to evaluate active pharmaceutical ingredients.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2416K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2416K) Full view HTML -
Motoki Ito, Ryuhei Oda, Akari Shoji, Kazuhiro Higuchi, Shigeo Sugiyama2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 487-497
Published: May 21, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 21, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialHerein, we report the functionalization of polyhedral oligosilsesquioxanes (POSS) and related siloxanes with arynes. Using o-triazenylarylboronic acids as aryne precursors and silica gel as the activator, the transformation of siloxane bearing various arynophilic moieties on the side chains was achieved with high yields without touching the siloxane core. This method was applied to the conjugation of POSS and pharmaceutical cores using an aryne derived from the synthetic intermediate of cabozantinib. Furthermore, orthogonal dual functionalization of POSS was realized by combining the aryne reaction with Huisgen cyclization.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1014K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1014K) Full view HTML -
Junseong Ahn, Hyun-Ha Hwang, Soo Yeon Jung, Ja Yeon Lee, Choi Kim, Hye ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 498-506
Published: May 25, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 25, 2024
Advance online publication: May 11, 2024JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
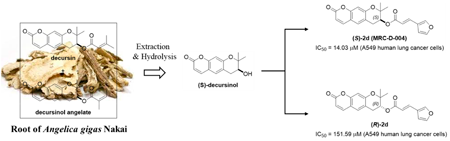
Supplementary materialUsing (S)-decursinol isolated from root of Angelica gigas Nakai (AGN), we semi-synthesized and evaluated a series of both enantiomerically pure decursin derivatives for their antiproliferative activities against A549 human lung cancer cells. All synthesized compounds showed a broad spectrum of inhibitory activities against the growth of A549 cells. Especially, compound (S)-2d with (E)-(furan-3-yl)acryloyl group showed the most potent activity (IC50: 14.03 µM) against A549 cancer cells as compared with the reference compound, decursin (IC50: 43.55 µM) and its enantiomer, (R)-2d (IC50: 151.59 µM). Western blotting assays indicated that (S)-2d more strongly inhibited Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription activation 3 (STAT3) phosphorylation than decursin in a dose-dependent manner, while having no effect on CXCR7 overexpression and total STAT3 level. In addition, (S)-2d induced cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and subsequent apoptotic cell death in A549 cancer cells. Our combined analysis of molecular docking studies and biological data suggests that the inhibition of JAK1 with (S)-2d resulted in loss of STAT3 phosphorylation and inhibition of cell growth in A549 cancer cells. These overall results strongly suggest that (S)-2d (MRC-D-004) as a novel JAK1 inhibitor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of A549 human lung cancers by targeting the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (2971K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (2971K) Full view HTML
-
Saw Yu Yu Hnin, Yu Nakashima, Hiroyuki Morita2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 507-511
Published: May 28, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 28, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAmaryllidaceae alkaloids are structurally diverse natural products with a wide range biological properties, and based on the partial identification of the biosynthetic enzymes, norbelladine would be a common intermediate in the biosynthetic pathways. Previous studies suggested that norbelladine synthase (NBS) catalyzed the condensation reaction of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and tyramine to form norcraugsodine, and subsequently, noroxomaritidine/norcraugsodine reductase (NR) catalyzed the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent reduction of norcraugsodine to generate norbelladine. However, recent studies have highlighted possible alternative Amaryllidaceae alkaloid biosynthetic pathways via the formation of isovanillin and vanillin from the 4-O- and 3-O-methylation reactions of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde, respectively. Herein, we focused on NpsNBS and NpsNR, which were initially identified from Narcissus pseudonarcissus, and explored their substrate recognition tolerance by performing condensation reactions of tyramine with various benzaldehyde derivatives, to shed light on the Amaryllidaceae alkaloid biosynthetic pathway from the viewpoint of the enzymatic properties. The assays revealed that both NpsNBS and NpsNR lacked the abilities to produce 4′-O- and 3′-O-methylnorbelladine from isovanillin and vanillin with tyramine, respectively. These observations thus suggested that Amaryllidaceae alkaloids are biosynthesized from norbelladine, formed through the condensation/reduction reaction of 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde with tyramine.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1910K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1910K) Full view HTML
-
 Motoki Naka, Tomohiro Umeno, Mika Shibuya, Yuto Yamaberi, Atsushi Ueda ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 512-517
Motoki Naka, Tomohiro Umeno, Mika Shibuya, Yuto Yamaberi, Atsushi Ueda ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 512-517
Published: May 29, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 29, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) serve as potent vehicles for delivering membrane-impermeable compounds, including nucleic acids, into cells. In a previous study, we reported the successful intracellular delivery of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) with negligible cytotoxicity using a peptide containing an unnatural amino acid (dipropylglycine). In the present study, we employed the same seven peptides as the previous study to evaluate their efficacy in delivering plasmid DNA (pDNA) intracellularly. Although pDNA and siRNA are nucleic acids, they differ in size and biological function, which may influence the optimal peptide sequences for their delivery. Herein, three peptides demonstrated effective pDNA transfection abilities. Notably, only one of the three peptides previously exhibited efficient gene-silencing effect with siRNA. These findings validate our hypothesis and offer insights for the personalized design of CPPs for the delivery of pDNA and siRNA.
 View full abstractEditor's pick
View full abstractEditor's pick[Highlighted Paper selected by Editor-in-Chief]
Significant efforts have focused on developing cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) for delivering nucleic acids into cells. In this study, authors tested seven peptides for their effectiveness in delivering plasmid DNA (pDNA). These peptides had previously been used for small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery, with one peptide containing the dipropylglycine showing successful delivery with low cytotoxicity. Despite both being nucleic acids, pDNA and siRNA differ in size and function, potentially affecting optimal peptide sequences for delivery. The authors' results show that three peptides were effective in pDNA transfection, with only one also showing efficient siRNA delivery. These findings support our hypothesis and provide insights for designing CPPs for both pDNA and siRNA delivery.Download PDF (2615K) Full view HTML -
Masahiro Ikejiri, Aki Yoshimizu, Fumika Shiota, Ai Nagayama, Aki Fujis ...2024Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 518-523
Published: May 31, 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 31, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialWe have developed a series of 2-monoaryl-5-diarylmethylene analogs of the green fluorescent protein chromophore to study their viscosity-induced emission (VIE) properties. The analogs were synthesized by a condensation with methyl imidate and N-(diarylmethylene)glycinate. Among the analogs, the N-methylpyrrol-2-yl-substituted analog 1h induced the most remarkable VIE behavior in triglyceride and lipid bilayers probably due to the high π-electron-rich property of the pyrrole ring. The pyrrole substituent in imidazolone analogs can be expected to become a common template for introducing VIE behavior.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (1451K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (1451K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|