
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yuying Zhang, Chunmao Lyu, Xianjun Meng, Wenxuan Dong, Hai Guo, Chunmi ...2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 939-950
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIn order to study the oxidative stability of hazelnut oil stored at room temperature, hazelnut oil accelerated oxidized at 62°C was used to determine peroxide value (POV), p-anisidine value (p-AV), total oxidation value (TOTOX), the content of fatty acids and volatile oxidative products. The correlation between the content of fatty acids or volatile oxidative products and three peroxidation indexes was analyzed. The results showed that the relative content of linoleic acid in hazelnut oil decreased significantly at the duration of accelerated oxidation (p < 0.05), which was in line with the zero-order oxidation kinetics model. The absolute content of four fatty acids all accorded with the zero-order oxidation kinetics model. Both relative and absolute content of linoleic acid can set up a slightly negative linear correlation with POV, p-AV and TOTOX, respectively (p < 0.05). The oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids in hazelnut oil produced a variety of volatile oxidation products, among which hexanal, 2-octenal, 2-decenal and 3-octene-2-one could establish a significantly positive correlation with POV, p-AV and TOTOX at a certain period of time, which could be used as a new index to evaluate the oxidative decomposition of unsaturated fatty acids in hazelnut oil during storage.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1084K) -
Wei Liu, Xianli Fu, Zhenzhen Li2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 951-958
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNatural tocopherols have strong antioxidant and physiological functions, which are mainly produced from vegetable oil deodorized distillates. In this work, a simple and green solvent extraction method based on deep eutectic solvent has been developed to simultaneously extract three isomers of tocopherols (α, γ and δ-tocopherols) from soybean oil deodorizer distillate (SODD). The key factor to affect the solvent extraction efficiency was proposed that phenolic deep eutectic solvents interacted with targeted tocopherols mainly through π-π bonds interaction. This sustainable extraction process included two steps. Firstly, total tocopherols were extracted from SODD at room temperature by phenolic deep eutectic solvent composed of ChCl and p-cresol. Subsequently, tocopherols were successfully separated from deep eutectic solvent phase by re-extraction with n-hexane, and tocopherols products could be simply recovered. Under the optimum extraction conditions, the extraction efficiency of total tocopherols (α, γ and δ-tocopherols) from SODD was 77.6% after extraction with phenolic deep eutectic solvent.
View full abstractDownload PDF (748K)
-
Yuying Wang, Jie Yu, Ning Xu, Guorong Wang, Xibo Wang2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 959-965
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSProtein hydrolysis on the freeze-thaw stability of emulsions prepared with soy protein - dextran conjugates were investigated. Soy protein isolate-dextran (SPI-D) and soy protein hydrolysates-dextran (SPH-D) conjugates with different degree of hydrolysis (DH) were formed by Maillard reaction. The formation of protein-polysaccharide conjugates between SPI/SPH and dextran molecules was confirmed by SDS-PAGE; this finding was consistent with the degree of glycation and the browning index. The freeze-thaw emulsion stability was investigated. The results confirmed that the SPH3-D (DH at 3%) emulsion with 3% DH of SPI exhibited the lowest creaming index after experiencing 1, 2, and 3 freeze-thaw cycles , with results of 7.69%, 20.74% and 31.30%, respectively. The SPH3-D emulsion had a significantly lower average particle size, which was reduced by 48.28% compared to the SPI-D emulsion. Meanwhile, the SPH3-D solution had low interfacial tension. The confocal laser scanning microscopy analysis indicated that the SPH3-D emulsions were strongly stable against the freeze-thaw treatment and could be used as effective emulsifiers in frozen foods.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1538K) -
Minh Quang Tran, Kazuya Nakata, Nick Serpone, Satoshi Horikoshi2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 967-975
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSTitanium dioxide (TiO2) has been proven to be an excellent system for wettability patterning purposes because of its super hydrophilic ability and its oxidative/reductive degradation of substances when exposed to UV radiation. TiO2 substrates upon which was deposited a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of n-octadecyltrimethoxysilane (ODS) shifts the surface to become super hydrophobic, which when subjected to UV irradiation causes the ODS compound to be degraded with the substrate turning back to be super hydrophilic. Such events allow wettability patterns to be easily created. The objective of this study was to reduce the time required to construct a wettability pattern. For this purpose, highly photoactive TiO2 nanoparticles were coated onto a titanium plate whose surface had been previously oxidized at high temperatures in an electric furnace. The subsequent TiO2/Ti system was microwaved and simultaneously irradiated with ultraviolet light (UV) to further accelerate its photocatalytic activity. Using a set of photomasks and both UV and microwave irradiation, the generation of a pattern was achieved 15 times faster (2 min versus 30 min) compared to an earlier result that used only UV radiation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1878K)
-
Guolong Yang, Tong Tong, Yingying Yang, Wei Liu, Xuede Wang2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 977-988
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFree fatty acids (FFAs) are the important material used in food, personal care, emulsifiers, adhesives and surfactants. In order to enhance the preparation of FFAs, the effects of reaction variables, optimization, thermodynamic property for the Amano lipase PS catalyzed hydrolysis of pine nut oil (PNO) using deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as co-solvents were studied. The results showed that FFAs could be successfully prepared from pine nut oil through Amano lipase PS catalyzed hydrolysis using Choline chloride:Urea (ChCl:U, 1:2, mol/mol) as co-solvent. Under the optimal conditions (reaction temperature 46°C, water amount 38%, DES addition 43%, lipase dosage 7.6%, reaction time 13 h), the maximum content of FFAs in the products and degree of hydrolysis (DH) of oil were up to 89.1 ± 1.9% and 92.7 ± 2.2%, respectively. The effects of reaction variables on the hydrolysis increased in the order of DES addition < reaction temperature < reaction time < lipase dosage < water amount. The thermodynamics (Arrhenius equation) for the triglycerides hydrolysis was V = 4289.39·exp(-22942.09/RT) with the activation energy (Ea) of 22.94 kJ/mol. The Gibbs free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH) and entropy (ΔS) were 81.50 ± 2.64 kJ/mol, 20.18 ± 0.12 kJ/mol and -184.59 ± 0.36 J/mol/K, respectively. The lipase in the aqueous DES could be directly re-used for 3 times.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1850K) -
Manpreet Kaur, Akshita Mehta, Reena Gupta2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 989-993
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLipase is a potential biocatalyst and can be exploited for various applications such as food, pharmaceutical, oleochemistry, organic chemistry, biofuels and in detergent industries. In the present study, lipase from Aspergillus fumigatus was purified to homogeneity by SDS and Native PAGE and evaluated as biocatalyst for the synthesis of methyl butyrate which is a flavor ester. A purification fold of 6.96 was achieved by using Octyl Sepharose column chromatography. Methyl butyrate was synthesized by trans-esterification of vinyl butyrate with methanol, in a medium containing n-hexane as a solvent. The molar ratio of 2:2 (vinyl butyrate:methanol) was found to be optimum for the synthesis of methyl butyrate. The yield of methyl butyrate was maximum when reactants were incubated for 16 h at an incubation temperature of 40°C. The maximum yield (86%) of ester was obtained with 30 µg/ml of purified lipase.
View full abstractDownload PDF (355K)
-
Keizo Umegaki, Kaori Yokotani, Shinsuke Marumoto, Mitsuo Miyazawa2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 995-1002
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSColeus forskohlii extract (CFE), a popular weight-loss herbal product, induces hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) and fatty liver in mice; however, its main bioactive ingredient, forskolin, does not show such effects. To ensure the safety of CFE as a dietary supplement, identification of the compounds implicated in the induction of hepatic CYP and fatty liver is required. In this study, we separated a crude CFE extract into 5 fractions (Fr.) by column chromatography and administered the fractions to mice for one week to assess their ability to induce CYP and fatty liver. CYP induction was detected for all fractions, indicating that many compounds may be involved in CYP induction, while fatty liver was only detected for Fr. 2. Further isolation and purification of Fr. 2 by column chromatography identified 14-deoxycoleon U as a major compound and crocetin dialdehyde as a pigment compound. An in vivo mouse study revealed that crocetin dialdehyde had no effect on the liver and, as 14-deoxycoleon U was the major compound in Fr. 2, it is likely that the active compound inducing fatty liver in CFE is 14-deoxycoleon U. These findings will facilitate the preparation of standardized safe CFE ingredients for dietary supplements.
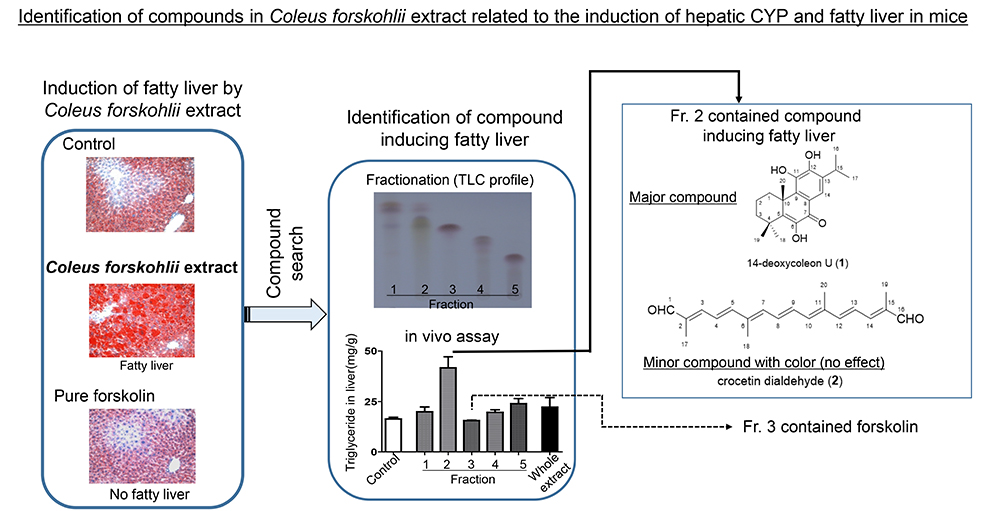 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (688K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (688K)
-
Shukan Okano, Yoshiko Honda, Tohru Kodama, Mayumi Kimura2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 1003-1009
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFrankincense essential oil, obtained from Boswellia carteri, is a popular essential oil, which is widely used in many parts of the world. While some of its properties are known, its effects on stress and sleep have not been studied. The effects of frankincense essential oil and its major components, limonene and α-pinene, on plasma corticosterone and glutathione (GSH) levels, as well as on sleep and wakefulness behaviour, were studied in sleep-deprived rats. The substances were applied topically after dilution in jojoba oil (vehicle). As compared to vehicle, frankincense essential oil at a dilution of 1/1000 (1:103) significantly reduced corticosterone levels (p < 0.05). In contrast, its major constituents (α-pinene and limonene), elevated levels of this stress hormone. Frankincense, limonene and α-pinene, all led to significant reductions in plasma GSH levels. Although frankincense dose-dependently reduced plasma concentrations of antioxidant ions albeit to levels insufficient to neutralize oxidative stress; levels of products of oxidative metabolism metabolites were decreased by the frankincense. In sleep-deprived rats, frankincense 1:103 respectively increased and decreased the amount of wakefulness and non-rapid eye movement sleep. Frankincense essential oil can counter the effects of stress by effectively relieving sleep debt and maintaining antioxidant capacity without increasing oxidative stress, and, therefore, may be beneficial in the management of stress.
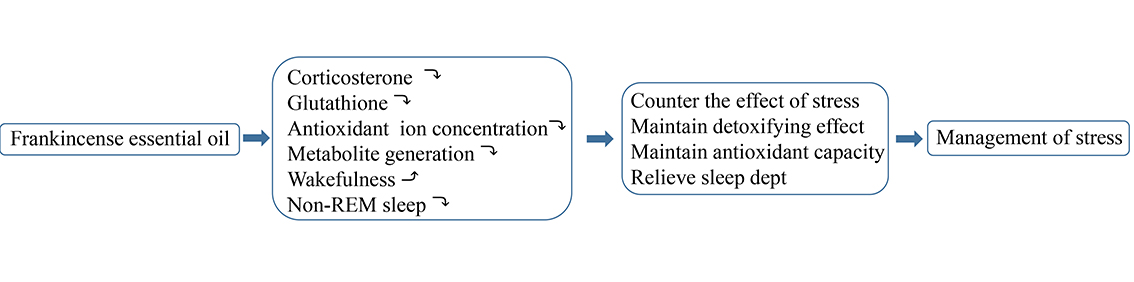 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1164K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1164K) -
Osman Üçüncü, Şeyda Merve Karataş, Cemalettin Baltacı, Mustafa Karakös ...2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 1011-1017
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: June 10, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis work reports the chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of essential oils from the aerial parts of Gentiana gelida BIEB. for the first time in literature. The oils from the aerial parts (flower, leaf and stem) were obtained by Clevenger-type apparatus and characterized by GC-FID and GC-MS. While tricosane (21.67%) was the main component of flower oil, hexadecanoic acid was the most abundant component of leaf and stem oils in ratios 26.46% and 31.89%, respectively. Additionally, all essential oils of G. gelida were investigated for their antimicrobial activity against eight Gram negative bacteria, four Gram positive bacteria and five fungi, using agar dilution method and antioxidant activities by using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging and Folin-Ciocalteu assays. The flower oil of G. gelida showed stronger antimicrobial and antioxidant activities than those of stem and leaf. The amount of total phenolic content and scavenging activity of the flower oil were found 525.35±8.24 mg GAE/L and 49.30±1.25%, respectively.
View full abstractDownload PDF (340K)
-
Toshiharu Nagai, Tetsuaki Kinoshita, Erika Kasamatsu, Kazuaki Yoshinag ...2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 1019-1026
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe rapid and simultaneous separation of triacylglycerol (TAG) enantiomers and positional isomers was achieved using chiral high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). TAGs composed of two fatty acids, which were both saturated (P: palmitic acid or S: stearic acid) and unsaturated (O: oleic acid or L: linoleic acid; e.g., sn-PPO/sn-OPP/sn-POP: 1,2-dipalmitoyl-3-oleoyl-sn-glycerol/1-oleoyl-2,3-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycerol/1,3-dilpalmitoyl-2-oleoylglycerol), were resolved into three peaks using CHIRALPAK IF-3 without recycling on the HPLC system. For example, the mixture of sn-PPO/sn-OPP/sn-POP was resolved in 30 min, although it took 150 min to resolve sn-PPO/sn-OPP using CHIRALCEL OD-RH in a previous study using a recycling HPLC system. This novel chiral HPLC method was applicable for the separation of other TAG isomers, including sn-OOP/sn-POO/sn-OPO, sn-PPL/sn-LPP/sn-PLP, sn-LLP/sn-PLL/sn-LPL, sn-SSO/sn-OSS/sn-SOS, sn-OOS/sn-SOO/sn-OSO, sn-SSL/sn-LSS/sn-SLS, and sn-LLS/sn-SLL/sn-LSL. For TAGs composed of three fatty acids containing both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, the POL isomers were not sufficiently separated but the PSO and SOL isomers were partially separated into several peaks. Their elution order could be estimated by the fragment ions generated in the ion source of the mass spectrometer. However, TAGs consisting of only saturated or unsaturated fatty acids (e.g., sn-PSP/sn-PPS/sn-SPP and sn-OLO/sn-OOL/sn-LOO) were not separated. This novel chiral HPLC method is especially applicable for the analysis of TAG composition of semi-solid fats such as palm oil.
View full abstractDownload PDF (672K) -
Yayoi Miyagawa, Kyuya Nakagawa, Hiroyuki Fujita, Shuji Adachi2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 1027-1032
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMayonnaise is an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion containing oil at the weight fraction of about 70%, which is stable for over a year when stored at room temperature. The stability examination of more stable mayonnaise can be time-consuming. Mayonnaise rapidly separates into oil and aqueous phases when water in the mayonnaise evaporates, which increases the ionic strength of the aqueous phase and reduces electrostatic repulsion among oil droplets. Simulating this phenomenon under reduced pressure, the stability of mayonnaises with different sodium chloride concentrations [0, 1, 3, 5 or 8% (kg/kg-aqueous phase)] and acetic acid concentrations [0, 1, 5, 10, 15 or 20% (kg/kg-acetic acid solution)] was evaluated by comparing the duration of time before each mayonnaise sample separated into oil and aqueous phases. The durations (destabilization times) correlated with the sodium chloride concentrations for mayonnaises with 1% (kg/kg-acetic acid solution) acetic acid solution. Destabilization times were independent of the sodium chloride concentration, however, for mayonnaises with greater than 10% (kg/kg-acetic acid solution) acetic acid solution. The differences in destabilization times were ascribed to denaturation of egg yolk granules. The destabilization time of commercially available mayonnaise can be similarly explained. The results of this study, which showed that the increase in the ionic strength of the aqueous phase by evaporation assessed the stability of mayonnaise in expedition way, were consistent with previously reported findings.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (542K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (542K) -
Fahad Alderaywsh, Magdi A. Osman, Fahad Y. Al-Juhaimi, Mustafa A. Gass ...2019 Volume 68 Issue 10 Pages 1033-1040
Published: 2019
Released on J-STAGE: October 03, 2019
Advance online publication: September 11, 2019JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRoasting improved the determined protein and carbohydrate content of the flour compared to raw flour (p < 0.05). Baking enhanced the determined moisture and ash content of the flour compared to all treatments (p < 0.05). Similar amino acid content was found in both raw and treated flours with glutamic acid, glycine, arginine, and aspartic acid being predominant. Cooking reduced the total aromatic and non-essential amino acid content whereas roasting reduced the total essential amino acid content of samh flour. All treatments significantly (p < 0.05) decreased the antinutritional factors compared to untreated raw flour. Baking decreased the trypsin inhibitor activity by almost 98.7% whereas cooking reduced phytate and tannin content by 38.5% and 10.8, respectively. Roasting and baking significantly (p < 0.05) improved the in vitro protein digestibility of the flour. In vivo, the true faecal nitrogen digestibility of rats was significantly (p < 0.05) enhanced by all treatments. Baking and cooking increased (p < 0.05) the net protein utilization and biological value of the flour. Overall, the treatments improved the nutritional quality of samh flour.
View full abstractDownload PDF (397K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|