
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Weichao Cao, Yongjin Wang, Qayyum Shehzad, Zeyi Liu, Rongji Zeng2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 333-342
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialPeony seed oil is full of nutrition and exert positive effects on human’s health. The influences of seven solvents (isopropanol, acetone, Hx:Iso (n-hexane/isopropanol, 3:2 v/v), Chf:Me (chloroform/methanol, 1:1 v/v), ethyl acetate, n-hexane, and petroleum ether) on the oil yields, lipid composition, minor components and antioxidant capacity of peony seed oil were compared in this study. Results indicated that the highest oil yield (35.63%) was obtained using Hx:Iso, while Chf:Me showed the best extraction efficiency for linolenic acid (43.68%), trilinolenoyl-glycerol (15.00%), and dilinolenoyl-linoleoyl-glycerol (18.01%). For minor components, Chf:Me presented a significant advantage in the extraction of tocopherol (601.49 mg/kg), and the peony seed oil extracted with petroleum ether had the highest sterols (4089.82 mg/kg) and squalene contents (66.26 mg/kg). Although the use of isopropanol led to a lower sterol content, its extracts showed a significant higher polyphenol content (68.88 mg GAE/kg) than other solvents and exhibited the strongest antioxidant capacity. Additionally, correlation analysis revealed that polyphenols were the most important minor component for predicting the antioxidant capacity of peony seed oil. The above information is valuable for manufacturers to select suitable solvents to produce peony seed oil with the required levels of fatty acids and minor components for targeted end-use.
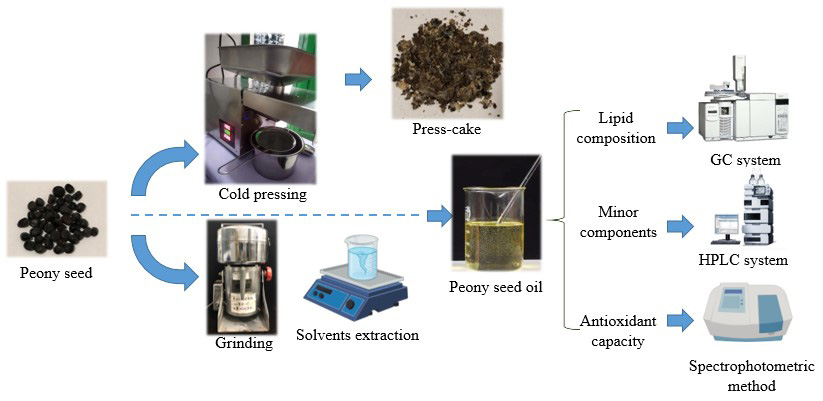 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (320K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (320K) -
Pimwalan Ornla-ied, Sirinapa Rungsang, Chin Ping Tan, Dongming Lan, Yo ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 343-351
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSAbstract: This research synthesized structure lipids (SL) from blends of fully hydrogenated palm kernel oil (FHPKO), coconut oil (CNO) and fully hydrogenated palm stearin (FHPS) by enzymatic interesterification (EIE)using rProROL, an sn-1,3-specific lipase from Rhizopus oryzae, as a catalyst. Five physical blends of FHPKO:CNO:FHPS were prepared with the following wt. ratios: 40:10:50, 50:10:40, 60:10:30, 70:10:20 and 80:10:10. The EIE reactions were carried out at 60℃ for 6 h in a batch-type reactor using rProROL 10% wt. of the substrate. It was found that EIE significantly modified the triacylglycerol compositions of the fat blends resulting in changes in the crystallization and melting behavior. In particular, SL obtained from EIE of blend 70:10:20 exhibited high potential to be used as a cocoa butter substitute (CBS) because it showed similar solid fat content curve to the commercial CBS and crystallized into fine spherulites and desirable β′ polymorph.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1752K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1752K)
-
Shogo Taguchi, Yuta Kimura, Yuka Akiyama, Yasuaki Tachibana, Takuji Ya ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 353-362
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBicelles are extensively used as the parent assemblies of functional membrane materials. This study characterizes membrane fluidity in fatty acid/detergent bicelles containing carboxyl boron-dipyrromethene (BODIPY C12) and pyrromethene as fluorescent probe molecules. The anisotropy value of BODIPY C12 and pyrromethene in the phospholipid vesicles depended on the phase state of the vesicles. The anisotropy of the fluorescent probe molecules in bicelles of oleic acid/3-[(3-cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio]-2-hydroxypropane sulfonate (OA/CHAPSO) was then evaluated. The OA/CHAPSO bicelles were prepared by mixing CHAPSO detergent solution with OA vesicles at different molar ratios, X OA (= [OA]/([OA]+[CHAPSO])). The anisotropies of the probes in the OA/CHAPSO bicelles increased with decreasing X OA. BODIPY C12 in the range 0.30 ≤ X OA ≤ 0.70 exhibited a distinctly larger anisotropy than pyrromethene. This result agreed with the increase in packing density associated with the adsorption of CHAPSO molecules on the OA bilayer membrane in the OA/CHAPSO bicelle, revealing that the anisotropy of BODIPY C12 molecule enables membrane-fluidity evaluation in OA/CHAPSO bicelles.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3422K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3422K)
-
Lu Wang, Huiyang Tu, Lingzhi Zeng, Ruichen Gao, Sumei Luo, Chao Xiong2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 363-370
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSColorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most prevalent disease in the world, with an estimated 1.2 million new cases each year. Spontaneous CRCs account for around 70% of all CRCs, are caused by somatic mutations. Minor variations or single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in oncogene or tumor-suppressor genes cause familial CRC. MSH2 and MSH6 genes are located on chromosome 2. These genes products are involved in the repair of DNA replication defects. If these proteins are changed, the replication errors are not rectified, resulting in damaged DNA leading to colorectal cancer. We employed a variety of computational methodologies to find nsSNPs that are harmful to the structure and function of the MSH6 protein and could be causing CRC in our study. SIFT, PROVEAN, Poly- Phen-2, PhD-SNP, and SNPs&GO were among the in silico methods used to do the computational research. According to the findings, mutations of G932Q, E1234Q, and F1104Q are important alterations in native MSH6 protein rs35717727 that may contribute to its dysfunction and, ultimately, disease. The study also provided three-dimensional structures of the native MSH6 protein and mutations. These nsSNPs should be considered as key target mutations in many disorders involving MSH6 dysfunction in future studies. This is the first thorough study to use in silico technologies to assess MSH6 gene variants, and it will be extremely useful in planning largescale investigations and developing precision medicines to treat disorders caused by these polymorphisms. Additionally, animal models of various autoimmune disorders with these mutations could aid in determining their precise involvement.
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1685K) -
Jianzhong Zhou, Xiaogang Zheng, Qigui Cai, Chunlin Song2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 371-378
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study we report the green synthesis of nontoxic, stable, and small size silver nanoparticle by Cinnamomum verum with reducing/capping ability without any toxic reducing agents. The in situ prepared AgNPs were characterized by advanced physicochemical techniques like FE-SEM, TEM, and UV-Vis study. It has been established that AgNPs have a spherical shape with a mean diameter from 10 to 45 nm. In the antioxidant test, the IC50 of AgNPs and BHT against DPPH free radicals were 191 and 242 µg/mL, respectively. In the cellular and molecular part of the recent study, the treated cells with AgNPs were assessed by MTT assay for 48 h about the cytotoxicity and anti-human lung adenocarcinoma properties on normal (HUVEC) and lung adenocarcinoma cell lines i.e. PC-14, LC-2/ad, and HLC-1. The IC50 of AgNPs were 259, 291, and 395 µg/mL against PC-14, LC-2/ad, and HLC-1 cell lines, respectively. The viability of malignant lung cell line reduced dose-dependently in the presence of AgNPs.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2839K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2839K) -
Jun Cai, Zhiwei Tao, Xin Chen, ende Yi2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 379-386
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSOsteosarcoma is a relatively uncommon tumor that is defined histologically by malignant cells developing osteoid. Osteosarcomas are mesenchymal cell tumors that cause abnormal bone growth. A combination of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors leads mesenchymal stem cells to develop into bone precursor cells, resulting in osteosarcoma. Only tumor suppressor genes, such as p53, Rb, RECQL4, BLM, and WRN, have been detected in inherited family illnesses with an OS susceptibility. These genes, in particular, play an essential role in the development of OS in individuals. In this research, core genes responsible for OS were determined using a microarray and systems biology. 234 genes encoding overexpression and down-regulation were identified, among which 60 were considered as key genes, many of which had known roles in bone growth. Transcriptional regulatory networks were developed with this data and subsequently partitioned to define cis-regulatory modules. Results indicate that several OS-specific genes have strongly conserved the clustering of bone-related cis-regulatory modules, thus promoting the hypothesis that a bone-related gene network is essential for understanding OS biology and may play a role in bone contractility and anomalies.
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3263K) -
JiaKun Shen, Huijuan Dong, Chunyan Li, Jingxiu Yan2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 387-394
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, iron nanoparticles were prepared and synthesized in aqueous medium using Cinnamomum verum as stabilizing and reducing agents. We determined the anti-acute leukemia potentials of FeNPs against acute T cell leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. FeNPs inhibited half of the DPPH molecules in the concentration of 139 µg/mL. MTT assay was used on J.RT3-T3.5 (Acute T cell leukemia cell line), Jurkat, Clone E6-1 (Acute T cell leukemia cell line), MOLT-3 (Acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line), TALL-104 (Acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line), and HUVEC (Normal cell line) for analyzing of cytotoxicity and anti-acute leukemia effects of FeNPs. These nanoparticles had high cell death and anti-acute leukemia effects against J.RT3-T3.5, Jurkat, Clone E6-1, MOLT-3, and TALL-104 cell lines. Among the above cell lines, the best result of anti-acute leukemia properties of composite was gained in the cell line of Jurkat, Clone E6-1. All result showed the iron nanoparticles may be used as a chemotherapeutic treatment drug of leukemia in humans.
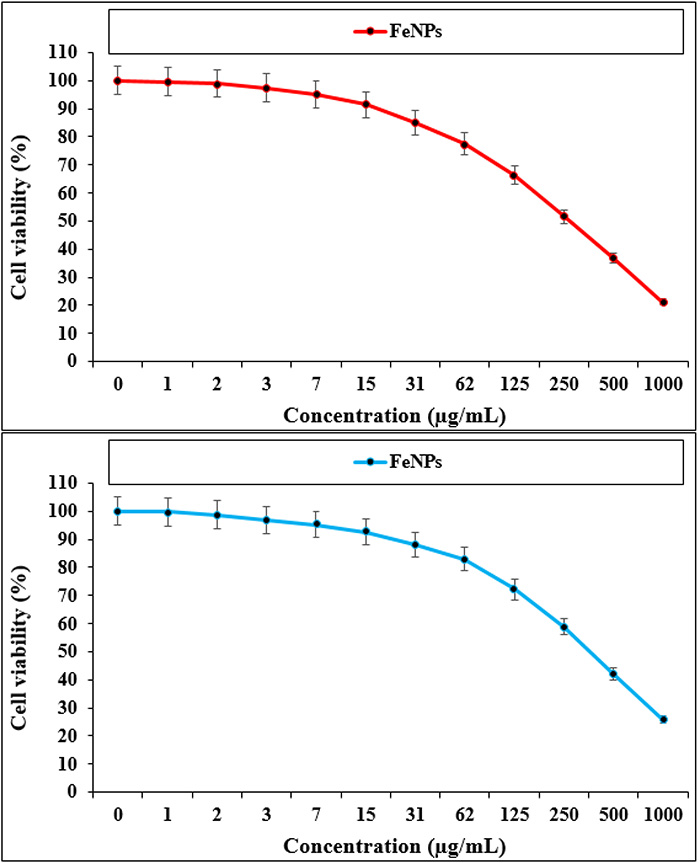 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1615K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1615K) -
Proteomic Analysis of Swertiamarin-treated BV-2 Cells and Possible Implications in NeuroinflammationGaowa Wang, Jin Quan, Nari Su, Ping Li, Qing Yu2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 395-400
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 11, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe purpose of this study was to explore the neuroprotective role of swertiamarin on neuro-inflammation, and analyzed its potential mechanism by proteomics. We used LPS to induce a inflammatory model on BV-2 cells, then 10, 25, 50 μg/mL swertiamarin was used to treat the LPS pretreated BV-2 cells. We used ELISA to detect the effect of swertiamarin on the expression of inflammation related indicators such as IL-1β, il-6, IL-18 and TNF-α. The proteomics based on TMT-LC-MS/MS analysis was performed to explore the anti-inflammatory effects of swertiamarin by bioinformatics analysis. We found swertiamain was able to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion in a does dependent manner, including IL-1β, IL‐6, IL-18 and TNF-α. These results were further verified by western blot. The proteomics analysis results suggested that the potential bioprocessings which regulated by swertiamarin mainly involved in cellular response to carbon monoxide, strand displacement, palmitoleoyltransferase activity, D2 dopamine receptor binding, RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity. The present study may provide a promising approach to treat and prevent neuro-inflammation diseases. It is preliminarily indicated that swertiamarin will play an important role in clinical anti-neuroinflammation process in the future.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (953K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (953K)
-
Nattha Srihera, Yue Li, Tian-Tian Zhang, Yu-Ming Wang, Teruyoshi Yanag ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 401-410
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 11, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSLiposomes are widely used as carrier system for bioactive ingredients and usually need to be stabilized by cholesterol. However, the relationship between cholesterol intake and human health has been controversial. The objective of this study was to develop novel multifunctional nanoliposomes stabilized by sea cucumber sulfated sterols via the thin-film hydration method. The liposomes obtained from this study were obviously stable for more than 27 days at 4°C. Astaxanthin was successfully encapsulated by a novel uniform liposome prepared with a mass ratio of egg yolk lecithin to sea cucumber sulfated sterols at 3:1. The mean particle size was 109.53±0.30 nm with 0.241±0.005 polydispersity index and zeta potential value of -21.13±1.01 mV. Astaxanthin-loaded liposome stabilized by sea cucumber sulfated sterols exhibited significantly higher antioxidant activities in terms of DPPH radical-scavenging activity and reducing power than the mixture of astaxanthin and blank sea cucumber sulfated sterols liposome during storage of 6 and 12 days, respectively. The in vivo digestion and absorption results showed that the bioavailability of dietary astaxanthin encapsulated in liposomes could significantly be improved. Being an efficient carrier with multifunctions, the novel liposome stabilized by sea cucumber sulfated sterols had great potential in functional food development and biomedical applications.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1944K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1944K) -
Ayaka Nakamura, Asuka Kawahara, Hajime Takahashi, Takashi Kuda, Bon Ki ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 411-417
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, the antibacterial properties of the volatile components of four essential oils (cinnamon, clove, origanum, and peppermint oil) and five of their components (allyl isothiocyanate (AITC), carvacrol, citral, eugenol, and (+)-limonene) against five food-related bacteria (Escherichia coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Typhimurium, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Enterococcus faecalis) were evaluated. The results of disc volatilization method revealed that AITC exhibited antibacterial activity against the five tested strains at the lowest concentration, as did cinnamon oil and carvacrol. Moreover, the total aerobic bacterial count in coleslaw salad was suppressed in all test groups treated with AITC compared to that in control.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (489K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (489K) -
Shinji Yamashita, Tomoya Tsuruma, Mikio Kinoshita, Teruo Miyazawa2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 419-423
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 11, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe have previously reported that dietary glucosylceramide (GlcCer) and rice extracts containing GlcCer reduce the formation of aberrant crypt foci (ACF) in the colons of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH)-treated mice, as a precursor model of colon cancer. This study investigated the impact of alkali-stable neutral lipids (NLs) containing free ceramides (Cer) and sterols on the formation of ACF in mice for the purpose of searching for functional components, irrespective of GlcCer, in rice extracts. The fraction was prepared from sake lees as a rice fermentation byproduct. Dietary NLs suppressed the marked increase in colon ACF treated with DMH.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (383K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (383K)
-
Iram Liaqat, Babar Gulab, Uzma Hanif, Aisha Sultan, Ayesha Sadiqa, Uro ...2021 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 425-434
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 11, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis study is first to test Pakistani honey bees, Apis dorsata and A. cerana honey samples as anti biofilm, anti quorum sensing (QS) and biofilm dispersal agents honey against multispecies biofilm of bacteria (obtained from obese patients). Briefly, five previously identified isolates Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Morganella morganii and Klebsiella pneumoniae (MT448672-MT448676) were selected. Antibiogram study of all five isolates was tested against three antibiotics viz., erythromycin (20 µg/mL), lincomycin (100 µg/mL) and rifampicin (100 µg/mL). In order to form multispecies biofilm, identified bacteria were grown in batch culture by mixing equal volumes (OD590nm = 0.1) of 2, 3 and 5 bacterial isolates. In total 11 groups (g1-g11) were made. Crystal violet (CV) staining method was used to evaluate the antibiofilm potential and biofilm dispersal potential of both honey samples. QS inhibition in P. aeruginosa was measured following culture supernatant method. Antibiogram study showed significant (p < 0.05) resistance by P. aeruginosa against tested antibiotics. E. coli, M. morganii and K. pneumoniae were significantly susceptible to erythromycin and S. aureus to lincomycin. Both honey samples at 2% and 5% concentrations showed significant (p < 0.05) inhibition potential of multispecies biofilm by all test groups (g1-g11). Though A. dorsata honey significantly inhibited biofilm formation at 2 and 5% against all groups but 2% concentration was highly significant against g2-g4 groups. Regarding A. cerana honey, 2% concentration was significantly effective against g1, g4-g7 and g9-g11 groups. Both honey samples significantly inhibited QS at 2 and 5%. The 5% concentration of A. dorsata honey significantly dispersed biofilm by all groups compared to 2% which showed dispersal potential only by g2 and g3 groups. Accordingly, honey samples showed significant antibiofilm, anti-QS and biofilm dispersal potentials thus can be considered as good alternative to antibiotics.
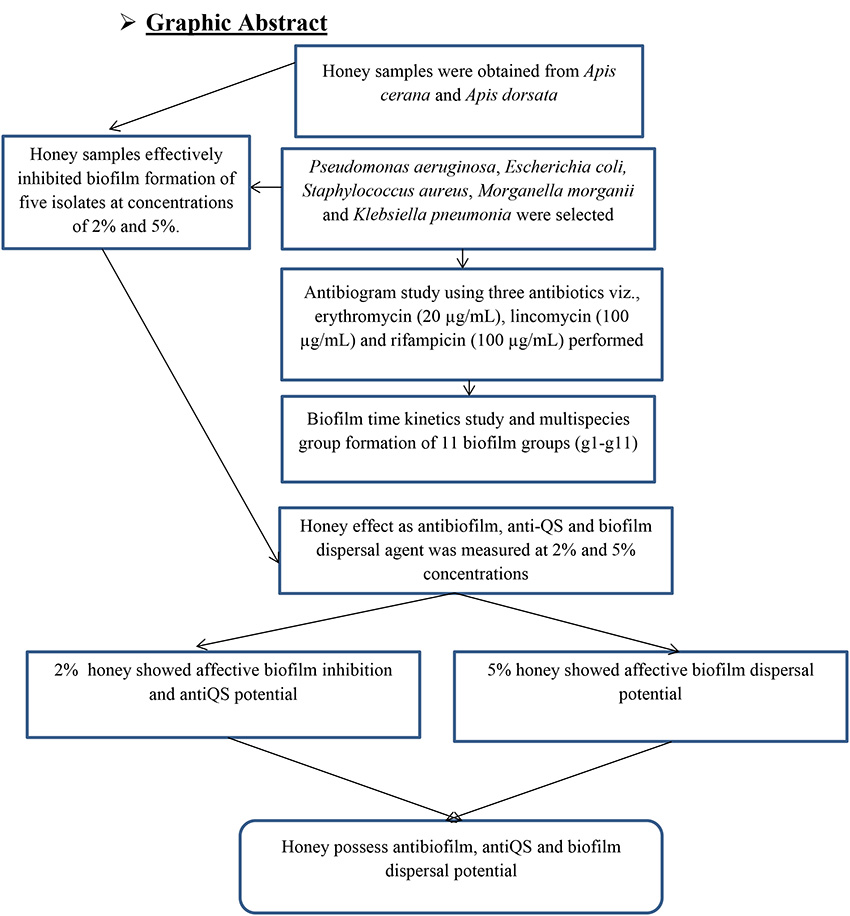 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (676K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (676K) -
Yi-Xi Feng, Xin-Xin Lu, Yue-Shen Du, Yu Zheng, Ding Zeng, Shu-Shan Du2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 435-443
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSStored products have been damaged by insects. Multiple approaches for pest management are employed. Among these approaches, botanical insecticide is an emerging one. This work investigated the pest management potential of Magnolia coriacea and Magnolia macclurei essential oils (EOs) to three major stored-product insects, namely the red flour beetle, cigarette beetle and booklouse. Magnolia coriacea and M. macclurei EOs showed promising contact toxicity to the cigarette beetle, with LD50 values of 11.7 and 12.3 μg/adult. The contact toxicity of M. coriacea EOs to the booklouse (LC50 = 95.5 μg/cm2) was much stronger than that of M. macclurei EOs (LC50 = 245.4 μg/cm2). To explore the contribution of individual compounds to insecticidal activity of EOs, chemical analysis was performed by GC-MS. Results showed that nerolidol (27.84%), agarospirol (18.34%), elixene (15.84%) and helminthogermacrene (12.69%) were major compounds of M. coriacea EOs, β-guaiene (60.31%) and elixene (20.42%) dominated in M. macclurei EOs. Nerolidol and β-guaiene showed contact activity to three insect species. Nerolidol showed stronger contact toxicity to the red flour beetle and cigarette beetle than M. coriacea EOs did, both samples were similar to the booklouse. β-Guaiene was much stronger to the red flour beetle and booklouse, but weaker to the cigarette beetle than M. macclurei EOs did. The repellent effects of EOs and compounds were at various levels. Generally, results suggested that the contact toxic potential of samples could serve as management for the cigarette beetle and booklouse, while repellent effect would be used to control the red flour beetle.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3296K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3296K)
-
Edhuan Ismail, Saidatul Sophia Sha’arani, Shota Azuma, Tetsuo Uchikosh ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 445-457
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 11, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialElectrokinetic properties such as the mobility, surface charge, and zeta potential of sub-millimeter particles are vital parameters in various industrial applications. Their measurement and control in aqueous media have been extensively studied. However, despite their growing importance, the electrokinetic properties of organic solvents have not been studied as thoroughly as those of aqueous media. An electrophoresis cell with a microscope monitor was designed for the electrokinetic studies of sub-millimeter particles in cyclohexane, which is a solvent with very low permittivity. The movement of large particles in the range of 4 ~ 478 µm was successfully traced under a strong electric voltage up to 1100 V, even without the addition of surfactants. The particle sizes were at least 300 times larger than those reported previously. By applying electric fields up to 55 kV/m, the electrophoretic mobilities were measured to be of the order of 10-9 to 10-7 m2/V∙s through image processing of the recorded particle movement. Five organic sub-millimeter particles had charge densities in the range of -3.5 ~ 4.4 e/µm2, and polyethersulfone particles showed extremely high mobilities. The surface charge of organic and inorganic particles is mainly generated by the dissociation of hydroxide groups or by the protonation to surface Lewis base oxygen atoms.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2346K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2346K) -
Saeed A. S. Al-Zuhairy, Wesam R. Kadhum, Muqdad Alhijjaj, Mustafa M. K ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 3 Pages 459-468
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: March 02, 2022
Advance online publication: February 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSTransdermal administration represents a major advancement over traditional pharmaceutical dosing methods. However, a frequent issue is inadequate penetration of the active medicinal component through the skin. As a result, in the current research, we assessed the utility of newly developed petrolatum-liquid crystal (LC) ointment formulations and characterized their biocompatibility and function in the transdermal drug delivery system. To begin, we made petrolatum-LC formulations using p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) as a hydrophilic model molecule. The viscosity, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), particle diameters, and z-potential were measured to assess the physicochemical properties of the formulations. A dialysis release technique was used to evaluate medication release from petrolatum-LC formulations. In vitro testing was performed to determine the potential to enhance skin penetration. The biocompatibility of the produced formulations was further tested using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and single-cell gel electrophoresis. According to the results, the novel petrolatum-LC formulations are biocompatible and effective in forming hexosomes. PABA skin penetration was significantly enhanced by the new petrolatum-LC formulations. According to this study, petroleum-LC formulations are more efficient than commercial petrolatum in terms of skin permeability improvement and PABA skin concentration.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1412K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1412K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|