
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Xiaolin Yin, Wei Liu, Pengcheng Meng, Guolong Yang, Jingnan Chen2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1427-1438
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBlend oils composed by leaf lard (LL) and cottonseed oil stearin (COS) were prepared and the thermal property, microstructure and crystallization of these blends were investigated in the present study. Solid fat content (SFC), thermal behaviors, triacylglycerols composition, crystal structure and morphology of the LL and COS blends were determined by pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance (pNMR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and polarized light microscope (PLM), respectively. SFC profiles and iso-solid diagrams indicated that SFCs of all blends were almost close to the weighted averages of the fat components at temperatures beyond 20°C; however, below 20°C, SFCs of blends exhibited higher than those of the weighted averages of the fat components. With the content of COS increasing, palmitic acid and linoleic acid in the blends increased, while stearic acid and oleic acid decreased; monounsaturated-disaturated (USS) and triunsaturated (UUU) glycerides in the blends enhanced, while monosaturated-diunsaturated (UUS) glycerides declined. The melting temperature of the blends decreased with the increase of COS content. The crystal forms in LL were β′ and β, and the packing pattern was double and triple chain length (2L and 3L). With COS in blends increasing, β′ form crystals and 3L pattern reduced. Polarized light micrographs showed that the number of crystal particles in the blends raised with the increase of COS content, meanwhile, the grainsize of the sample gradually decreased. Visual appearances of the blends indicated that blending LL with COS could efficiently reduce the graininess of LL. The addition of COS had a significant effect on the crystallization behavior of LL. LL presented one-step crystallization at 10°C and 20°C, while COS showed two-step crystallization at 10°C and one-step crystallization at 20°C. However, the blends exhibited obvious two-step crystallization at 10°C, one-step or slight two-step crystallization at 20°C.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2357K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2357K) -
Ariane Kluczkovski, Leticia Bezerra, Beatriz Januário, Emerson Lima, P ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1439-1444
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCarcinogenic metabolites of fungi such as aflatoxins play a toxic role in some tree nuts and need to be monitored in their by-products, such as oil. In this context, Brazil nut (Bertholletia excelsa) oil, which is a commodity of great economic importance to Brazil, requires attention to monitor the presence of these toxic agents. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the presence of aflatoxins in Brazil nut oil and relate it to the presence of fatty acids in the oil as a surveillance tool for food safety. Brazil nut oil samples (n= 25) were acquired in northern Brazil as (a) non-branded products (n= 07) produced by local farmers using artisanal methods from nuts to be discarded by the industry and (b) industrialized products (n= 18). The samples were analyzed for total aflatoxin content by high-performance liquid chromatography and fatty acid content by nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Seven (28%) samples were positive for the aflatoxin fractions (B1 + B2 + G1 + G2), ranging from undetected (<2.32) to 50.87 μg/kg. Of the aflatoxin positive samples evaluated by NMR analysis, it was not possible to state that the presence of a particular fatty acid can interfere or influence aflatoxin contamination. This was the first study with data on aflatoxin occurrence in Brazil nut oil. Nevertheless, further research is required to relate saturated or unsaturated fatty acid content with aflatoxin levels. We also suggest the implementation of systems to prevent contamination of the raw materials (seed) and detoxification of the oil to guarantee the product’s safety and quality.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
-
Shogo Taguchi, Yuta Kimura, Yuka Akiyama, Yasuaki Tachibana, Takuji Ya ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1445-1452
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSOleic acid/3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-2-hydroxypropane sulfonate (OA/CHAPSO) bicellar mixtures are potential functional membrane materials. The lipid transfer during the formation of these bicellar mixtures was evaluated. The OA/CHAPSO bicellar mixture was prepared by mixing a solution of OA vesicles as a source of bilayer membranes with a solution of CHAPSO as a detergent at different composition ratios, x OA (= [OA] / ([OA] + [CHAPSO])). The lipid transfer was evaluated based on the leakage of fluorescent probe molecules, i.e., carboxyl boron-dipyrromethene (BODIPY C12), from the OA bilayer membranes. Mixing the CHAPSO solution with the OA vesicle eliminated the self-quenching of BODIPY C12 because of the leakage of BODIPY C12 molecules. The apparent rate constant of the leakage increased with decrease in x OA to 0.60. However, at x OA ≤ 0.60, the apparent rate constants barely changed. The correlation between the leakage of the BODIPY C12 molecules and the transfer of OA molecules enables the evaluation of the lipid transfer during the OA/CHAPSO bicellar mixture formation through the observation of the self-quenching of BODIPY C12.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (794K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (794K) -
Kyoka Yoshitaka, Eiichi Toorisaka2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1453-1458
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe improvement in the stability of solid-in-oil-in-water (S/O/W) emulsions, which are used as carriers for protein delivery, was investigated. For this purpose, emulsions were prepared using trimyristin, a solid fat, as the oil phase, and using the membrane emulsification and solvent evaporation methods. The samples were made into stable fine emulsions using polyvinyl alcohol, a hydrophilic polymer, as an emulsifier, and by controlling the particle size uniformly. The S/O/W emulsions prepared by this method showed almost no leakage of encapsulated proteins and exhibited controlled release in an intestinal environment.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1616K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1616K) -
Yoshimune Nonomura, Urara Tsuchiya, Mayu Taguchi, Reiichiro Tsuchiya, ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1459-1467
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFrictional properties are one of the most important physical factors in the design of powder cosmetics. In this study, 21 powder cosmetics were applied to artificial skin, and their friction characteristics were evaluated using a sinusoidal motion friction evaluation system. Three friction profiles were observed that depended on the sliding velocity. Principal component analysis showed that the principal component (Z), which characterized the friction dynamics of powder cosmetics, included the static friction coefficient (μ s), the kinetic friction coefficient (μ k), the delay time (δ), and the viscosity coefficient (C). Furthermore, a cluster analysis on Z suggested that powder cosmetics can be classified into three groups according to their friction dynamics. These results may be helpful to understand the phenomena that occur during the application of powder cosmetics.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3091K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3091K)
-
Ling Li, Xiyue Song, Meng Ouyang, Attalla F. El-kott, Mutasem Z. Bani- ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1469-1480
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFlavonoid compounds are a group of polyphenolic molecules that are in vegetables, fruit, and grain. Laboratory studies and epidemiological investigations have indicated diverse beneficial biochemical properties of flavonoids, including anticancer, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, and anti-osteoporosis. We have recorded results for the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) Reductase and urease enzymes at the µM level. In this search, inhibition results of Panicolin on HMG-CoA reductase and tyrosinase enzymes recorded lower values of 113.98±14.38 and 2.57±0.20 µg /mL, respectively. Additionally, inhibition results of Panicolin on urease and α-amylase showed good values of 64.20±7.43 and 15.92±2.81 µg/mL, respectively. The chemical activities of panicolin against α-amylase, urease, tyrosinase, and HMG-CoA reductase, were determined by performing the molecular modeling study. The anti-cancer activities of panicolin were investigated against HL-60, THP-1, K562, and Molt-4 cell lines and IC50 values of Panicolin on these cell lines were obtained 12.94±1.04, 63.17±5.81, 15.05±1.02, and 10.84±0.65 µg/mL, respectively. The chemical activities of this compound against some of the expressed surface receptor proteins (Platelet-activating factor receptor, CD13, transferrin receptor, and CD44) in the cell lines were evaluated using molecular modeling calculations. The results revealed the possible interactions and their features at an atomic level. The docking scores suggested that panicolin has a significant binding affinity to the enzymes and proteins. Moreover, this compound constructed strong contacts with the enzymes and receptors. Therefore, panicolin could be a potential inhibitor for enzymes and cancer cells.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4985K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4985K) -
Fan Yang, Xiaoqiang Shi, Weidong Yang, Chao Gao, Zhenyu Cui, Wentao Wa ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1481-1492
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSRenal tissue plays a crucial function in maintaining homeostasis, making it vulnerable to xenobiotic toxicity. Pueraria montana has more beneficial potential against the various diseases and has long history used as a traditional Chinese medicine. But its effect against the renal cancer not scrutinize. The goal of this study is to see if Pueraria montana can protect rats from developing kidney tumors caused by diethylnitrosamine (DEN) and ferric nitrite (Fe-NTA). Wistar rats was selected for the current study and DEN (use as an inducer) and Fe-NTA (promoter) for induction the renal cancer. For 22 weeks, the rats were given orally Pueraria montana (12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg) treatment. At regular intervals, the body weight and food intake were calculated. The rats were macroscopically evaluated for identification of cancer in the renal tissue. The renal tumor makers, renal parameters, antioxidant enzymes, phase I and II enzymes, inflammatory cytokines and mediators were estimated at end of the experimental study. Pueraria montana treated rats displayed the suppression of renal tumors, incidence of the tumors along with suppression of tumor percentage. Pueraria montana treated rats significantly (p < 0.001) increased body weight and suppressed the renal weight and food intake. It also reduced the level of renal tumor marker ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and [3H] thymidine incorporation along with suppression of renal parameter such as uric acid, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urea and creatinine. Pueraria montana treatment significantly (p < 0.001) altered the level of phase enzymes and antioxidant. Pueraria montana treatment significantly (p < 0.001) repressed the level of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and improved the level of interleukin-10 (IL-10). Pueraria montana treatment suppressed the level of prostaglandin (PGE2), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), nuclear kappa B factor (NF-κB) and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1). Pueraria montana suppressed the inflammatory necrosis, size the bowman capsules in the renal histopathology. Pueraria montana exhibited the chemoprotective effect via dual mechanism such as suppression of inflammatory reaction and oxidative stress.
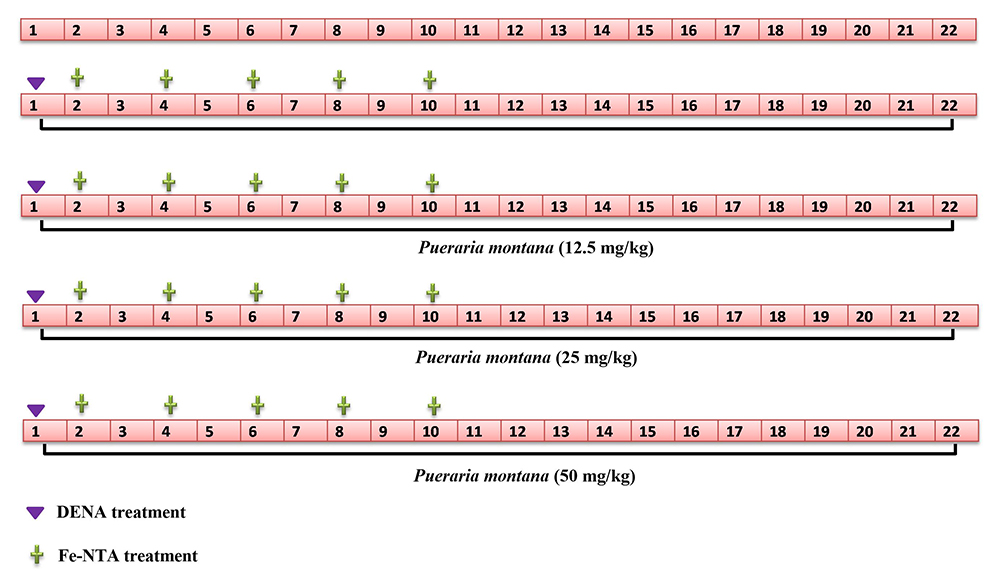 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2830K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2830K) -
Kenshi Watanabe, Miho Nishijima, Shinzo Mayuzumi, Tsunehiro Aki2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1493-1500
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThraustochytrid, Aurantiochytrium sp., produces various lipids such as polyunsaturated and saturated fatty acids, carotenoids, and other hydrocarbons, which are useful in the fields of health foods, cosmetics, fine chemicals, and biofuels. Lignocellulosic biomass, which is abundant and cheap, is a promising feedstock for producing cheaper bulk and high-value-added products using Aurantiochytrium sp. However, the steam explosion of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient enzymatic saccharification generates substances that inhibit the growth of microorganisms. In this study, the inhibitory activities of these by-products on the growth and lipid production of Aurantiochytrium sp. were investigated. Aurantiochytrium sp. was found to be highly sensitive to furfural and vanillin and moderately sensitive to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and syringaldehyde. Washing steam-exploded bagasse with water, followed by activated charcoal treatment, significantly reduced furfural, which was a major inhibitory component in the saccharified solution.
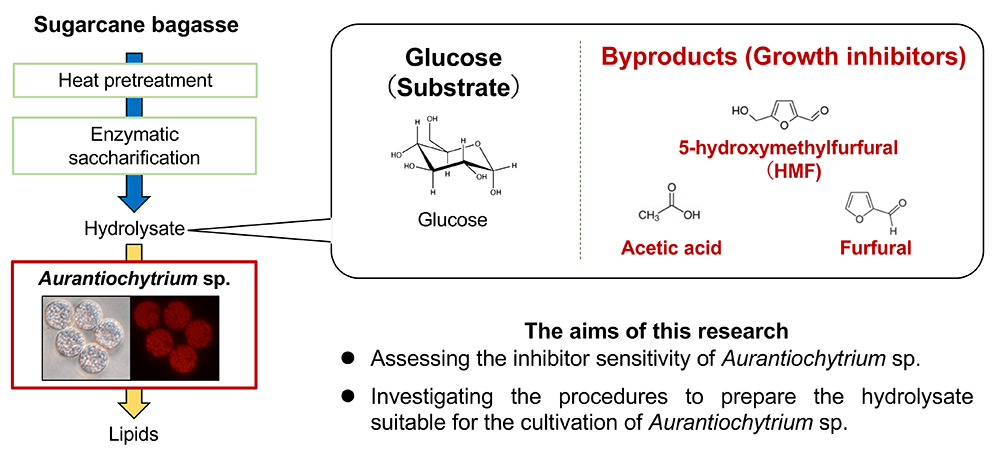 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (500K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (500K)
-
Lei Zhang, Songtao Sui, Si Wang, Jinbo Sun2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1501-1510
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSeveral therapeutic approaches were also urgently needed as ischaemic stroke was one of the most common brain disorders. Many phytochemicals have recently been discovered for the advancement of lead-like libraries that are concentrated on the peripheral and central nervous systems. Science does not yet understand how these drugs work, nor do they comprehend their in vivo characteristics. We investigated the potential benefits of corosolic acid (CA) in the treatment of brain injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Injury occurs after a 2-hour transient occlusion of the posterior cerebral artery and subsequent reperfusion (after 20 hours). Furthermore, the experiment assessed the size of the infarct, the amount of brain water present, as well as the neurofunctional conditions in rats. In the study, several markers of inflammation and cytokines associated with brain injury were measured. The Elisa kit was used in this study to measure the mRNA expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin 1β, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and nitrous oxide (NO). The CA treatment significantly reduced brain water content, brain infarction volume, neurological scores, and Evans blue leakage (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001). Experimental rats were treated with CA after a significantly reduced level of anti-inflammatory, pro-inflammatory, and oxidative stress mediators was noted in their body tissues and serum (p < 0.001). By suppressing inflammatory responses in rats, CA demonstrated anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3579K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3579K)
-
Hiroyuki Takeuchi, Hiroko Jimbo, Ai Sumiyoshi, Akira Omori, Kazue Naka ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1511-1519
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSA high-fat diet is believed to be a risk factor for hypertension through inducing obesity. It has been reported that variants of the fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) and beta-3 adrenergic receptor (B3AR) genes are associated with obesity and blood pressure. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of dietary fat on blood pressure with or without the variant of the FTO and B3AR genes. A total of 227 healthy Japanese women aged 18 to 64 years were recruited for measurement of nutrient intake and blood pressure. The single nucleotide polymorphism rs9939609 of the FTO gene and rs4994 of the B3AR gene were genotyped. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was applied to investigate the relationship between fat intake and blood pressure. A hierarchical multiple regression analysis was performed to determine whether the genotype interacts with fat intake to affect blood pressure. No significant correlations were found between fat intake and either systolic or diastolic blood pressure. A significant negative correlation was found between fat intake and both blood pressures in the FTO-gene-variant group, but not in the normal-FTO-gene group. In hierarchical multiple regression analysis, the interaction of fat intake and the gene variant showed significance, and the change in coefficient of determination (R 2) was significantly increased with increases of the interaction variable. These results indicate that the effect of fat intake on blood pressure may be modified by the variant of the FTO gene such that a high-fat diet intake may be associated with a decrease of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in healthy Japanese women with the FTO variant. Our results did not support the hypothesis that a high-fat diet increases blood pressure.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (267K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (267K)
-
Worrapan Poomanee, Warat Leelapornpisid, Khajornsak Trakoolpua, Ivan S ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1521-1530
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCurrently, bioactive compounds derived from nature have been thought to be promising anti-acne substances owing to the variety of potential biological effects. This study aimed to evaluate the ameliorative effect of Bouea macrophylla Griffth seed extract against bacteria-induced acne inflammation for the first time in terms of antibacterial effects against acne-inducing bacteria, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Initially, extracting procedures were optimized and five different extracts were obtained. Considering their antibacterial activities against Cutibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis, ethanolic and ethyl acetate fractions exerted a notable effect which were highly superior above those of polyphenol standards. Additionally, these two extracts presented outstanding antioxidant capacities in terms of DPPH and ABTS radicals scavenging effects, reducing power, and inhibitory effect on lipid peroxidation which also play a role in the exacerbation of acne inflammation. Besides, inhibition on lipid peroxidation and reducing power of ethanolic fraction were significantly (p<0.05) better than those of ethyl acetate fraction which was corresponding to their phenolic and ellagic acid contents. However, flavonoids found in ethyl acetate fraction might play an important role in its potentials. After that, the anti-inflammatory effects of the extracts were elucidated by means of inhibition on nitric oxide production from LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cell lines at which the effects of both extracts were dosedependency. Taken together, our findings have apparently proven that B. macrophylla seed extracts exerted a variety of potential properties including antioxidation, anti-acne-inducing bacteria, and anti-inflammatory effects which could serve as a promising anti-acne agent for cosmeceutical applications.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (440K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (440K)
-
Shigesaburo Ogawa, Katsuya Iuchi, Taro Tsubomura, Kiichiro Totani, Set ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1531-1540
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
J-STAGE Data Supplementary materialIn molecular biology research, a vitamin E (VE) vehicle (VE dissolved in organic solvent) is often added to water media without a stabilizer. However, the detailed behavior of VE colloids in water media is unclear. In this study, we reveal that VE nanoemulsion readily forms in water-based media through the existing protocol. The colloid size was changed from 39 nm to the submicron scale by adjusting the initial concentration of the VE solution and adding a buffer. The radical scavenging effect of the dispersed nanosized VEs is comparable to that of the water-soluble antioxidant Trolox, providing excellent antioxidant performance in colloid form. The cytoprotection effect of the VE colloids under a lipid oxidation condition largely depends on the size of the nanodispersion. Smaller dispersed particles are more efficient radical scavengers than larger particles for a constant VE amount owing to sophisticated uptake behavior of cell. This unveiled fundamental knowledge pave the way for a preparative protocol of stabilizer-free VE vehicles, which are expected to become widely used in molecular biology research.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3063K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3063K) -
Masaki Honda, Daishi Takezaki, Masahiro Tanaka, Masashi Fukaya, Motono ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1541-1550
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
Advance online publication: September 09, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialCoffee is a beverage that is consumed worldwide, and the demand for decaffeinated coffee has increased in recent years. This study aimed to investigate the effect of roasting conditions on the concentration of physiologically active compounds in coffee beans with and without supercritical CO2 decaffeination treatment. Decaffeination treatment markedly reduced caffeine concentration and slightly reduced trigonelline concentration in the coffee beans, whereas the concentrations of chlorogenic acids (chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogenic acid, and neochlorogenic acid) were largely unchanged. Roasting was performed using a hot-air coffee roaster machine and the coffee beans were treated at different peak temperatures (125-250℃), different hold times at the peak temperature (120-240 s), and different temperature increase times to reach the peak temperature (60-180 s). Roasting conditions such as long hold and long temperature rise times at high temperatures (≥ 225℃) significantly degraded coffee compounds except for caffeine, with similar degradation rates between non-decaffeinated and decaffeinated coffee beans. In contrast, the L* value of decaffeinated coffee decreased with less thermal history compared to that of non-decaffeinated coffee. This allowed for the complete roasting of decaffeinated coffee with a lower thermal history compared to those of non-decaffeinated counterparts, suppressing the degradation of several coffee compounds. For example, comparing the similar L* values between coffee beans with and without decaffeination treatment, it was found that the former tended to contain more chlorogenic acid. Generally, decaffeination results in the loss of physiologically active compounds along with caffeine, which is a major concern. However, this study showed that appropriate control of decaffeination and roasting conditions can limit the degradation of several valuable coffee compounds, such as trigonelline and chlorogenic acid.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1024K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1024K) -
Saif Kareem Abdul Hussein, Ahmed Mahdi Rheima, Fatin Fadhel Al-Kazaz, ...2022Volume 71Issue 10 Pages 1551-1561
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 30, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSorbitol accumulation in the tissue is known to cause diabetic complications. Nanotechnology-enabled biosensor methods have high sensitivity, selectivity, and more rapid detection of an analytic for sorbitol which is used as a biomarker of diabetic complications. The biosensor used aldose reductase from serum blood to oxidize the NADPH by the enzymatic reaction and reduce glucose to sorbitol. Biosensors can be developed for diagnostic testing. Developing a simple, sensitive, and rapid method for sorbitol detection is significant for efficient monitoring of diabetic complications like neuropathy at the initial stages. This project synthesized quantum dots of copper sulfide (CuS QDs) to fabricate an Electrochemical sensor for the detection of sorbitol by the UV-irradiation technique. The crystal structure of CuS QDs was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), which confirmed the synthesized sample’s hexagonal shape. The structure of the manufactured product was examined using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and the result revealed just copper (Cu) and sulfide (S) elements, indicating that the synthetic material was pure. The morphology, optical properties, and particle size were investigated by scanning electron microscope (SEM), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), and transmission electron spectroscopy (TEM), respectively. The particle sizes of the CuS QDs were found to range between 5.4 to 9.1 nm. The CuS QDs will be dedicated to the conventional methods to synthesize the modified electrode functionalized with NADPH and covered with CuS QD (Ti-TiO2/CuS/NADPH) demonstrated switchable interfacial properties. The electrochemical process was characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV). The developed sensor was successfully tested to detect sorbitol in human serum samples. The high catalytic activity and the redox behavior of CuS QD make it an efficient matrix for the realization of sorbitol. These results indicate that CuS QD is a suitable candidate material for developing enzyme-based sorbitol biosensors.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3865K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3865K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|