
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Toshihiro Itoh2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1261-1262
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (186K)
-
Karima Gharsallah, Leila Rezig, Fatma B’chir, Soumaya Bourgou, Nahed B ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1263-1273
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe present study aims to investigate the volatile compound and the triacylglycerol profiles of Tunisian cold pressed Moringa oleifera seed oil (MoSO) and to assess its thermal properties and its biological activities. GC-MS analysis identified thirty six phyto-compounds amounting to 98.99% of the total oil. These compounds were classified into eleven groups among which the fatty acid one exhibited the highest intensity (91.63%). Cis, 6-octadecenoic acid was the most abundant compound (70.68%). The triacylglycerol composition of MoSO was characterized by the predominance of the glycerol trioleate (OOO) (32.42±0.12%). Thermogravimetric analysis of MoSO showed that the oil possess an interesting thermal stability with a highly Onset temperatures (Tonset) of 390.72°C and 357.47°C, respectively in nitrogen and air atmospheres. By using the ABTS assay, MoSO exhibited an interesting antioxidant capacity of 365 μM TEAC. The oil was also endowed with a relatively strong anti-inflammatory activity since its treatment at the different concentrations tested (75, 150 and 300 μg/mL). However, no antimicrobial activity was observed. On the basis of the obtained results, MoSO could be used in diverse industrial applications such as pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food fields thanks to its thermal stability and interesting biological activities.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2650K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2650K) -
Junhua He, Xuehui Wu, Jun Liu, Yongfang Huang, Jianfeng Zhang2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1275-1287
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe ripening degree of camellia fruit is one of the key factors affecting the quality of camellia seed oil. In this study, taking Camellia semiserrata as the research object, the oil content, physicochemical indexes, nutritional indexes, fatty acid composition, and volatile compounds of camellia seed oils from various harvest dates (from September to October) were determined. The results showed that with the increase of the ripening degree of camellia fruit, the oil content of camellia seed increased at first and then decreased and reached the highest (58.74%) on September 30, while the acid value, peroxide value, β-sitosterol, α-tocopherol, and polyphenols of camellia seed oil showed a downward trend. Among them, the highest contents of β-sitosterol, α-tocopherol, and polyphenols were observed on September 2, which were 6881.60, 311.34, and 78.08 mg/kg, respectively. In terms of the fatty acid composition of camellia seed oils, the content of oleic acid increased at first and then decreased, the content of linoleic acid and palmitic acid decreased gradually, while the content of stearic acid increased gradually. A total of 37 volatile compounds were identified in different samples, including 12 aldehydes, 5 ketones, 12 alcohols, 2 acids, 5 esters, and 1 other. With the increase of the ripening degree, the concentration of aldehydes and alcohols increased at first and then decreased, the concentration of ketones and esters decreased gradually, but the concentration of acid compounds had no obvious rule. In addition, the camellia seed oils from various harvest dates were classified and comprehensively evaluated by principal component analysis and grey relation analysis. The results showed that different camellia seed oils could be divided into three groups, and the comprehensive score of camellia seed oils on September 30 was the highest. In general, this work can provide theoretical guidance for the harvest date of Camellia semiserrata.
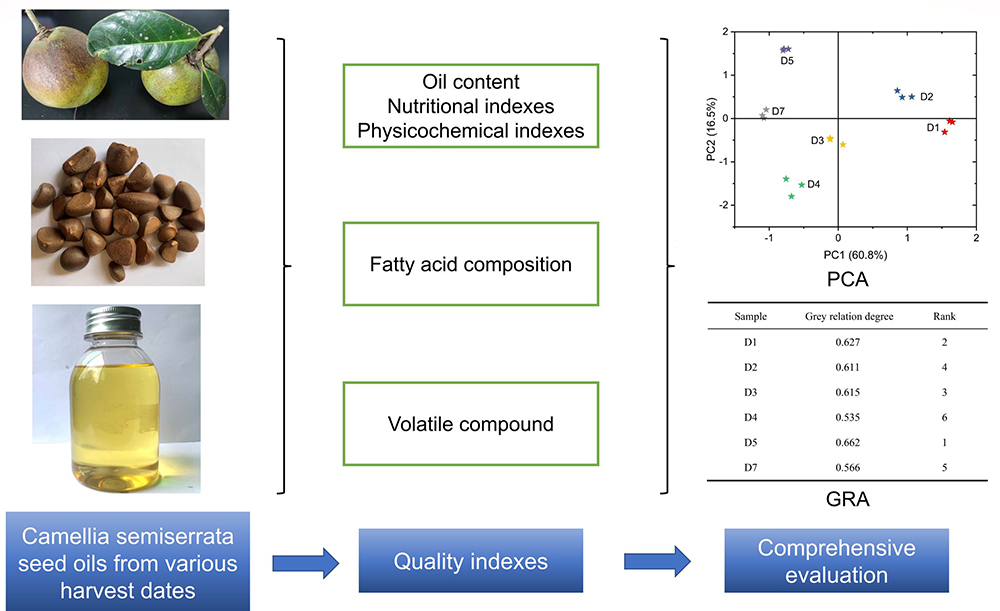 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1475K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1475K) -
Kazuya Murakami, Motonobu Goto, Masaki Honda2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1289-1297
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis study aimed to investigate the effect of extraction conditions (temperature, pressure, and entrainer content) on the total Z-isomer ratio and recovery of lycopene in the extracts obtained after supercritical CO2 (SC-CO2) extraction of lycopene from tomato powder, with a particular focus on high-temperature conditions (≥ 80°C). The results showed that high-temperature SC-CO2 extraction promoted the thermal isomerization of lycopene in a temperature-dependent manner up to 120℃. For example, when lycopene extraction was carried out at 80, 100, 120, and 140°C and a pressure of 30 MPa with an entrainer, ethanol, for 180 min, the total Z-isomer ratios obtained were 25.0, 57.2, 67.2, and 67.0%, respectively. The entrainer content also affected the Z-isomer ratio of lycopene, but the pressure had little effect. Interestingly, when SC-CO2 extraction was performed under high-temperature conditions (≥ 100°C), the extraction efficiency of lycopene was dramatically improved, e.g., when lycopene was extracted at 80, 100, 120, and 140°C under the same other conditions as above, the recovery rates of lycopene were 4.6, 28.5, 79.9, 84.8%, respectively. In general, SC-CO2 extraction of fat-soluble components is performed at temperatures in the range of 40-80°C because the SC-CO2 density decreases with increasing temperature, and thus, their solubility (extraction efficiency) decreases. However, our results showed that the lycopene recovery increased in a temperature-dependent manner, which might be due to the solubility enhancement associated with thermal Z-isomerization of lycopene (i.e., lycopene Z-isomers have greater solubility than the naturally occurring all-E-isomer). The high-temperature SC-CO2 extraction of lycopene from tomato materials not only enhances the Z-isomer ratio of lycopene in the resulting extracts but also improves lycopene recovery. This new finding will greatly contribute to the value addition and cost reduction of natural lycopene sources obtained by SC-CO2 extraction.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (612K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (612K) -
Abebe Teshome, Belay Dereje, Chibuzo S. Nwankwo, Charles Odilichukwu R ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1299-1308
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSPhysiochemical properties, lipid breakdown, β-carotenoids, tocopherols, and vitamins as well as amino and fatty acid profiles of Soxhlet-extracted oil from five different garden cress (Lepidium sativum L.) seed genotypes (namely: CG8, CG7, CG17, CG4, and 207910) across Ethiopia regions were investigated. Results showed that despite the seeds’ proximate peak and least values, the extraction yield, viscosity, specific gravity, refractive index, lipid breakdown, and boiling point of garden cress seed oil across the genotypes noticeably varied with promising amino and fatty acid profiles. Further, the genotype CG17 obtained greater quantities of β-carotenoids, tocopherols and vitamin values compared to the other genotypes.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (727K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (727K)
-
Noriko Takada, Masaru Oya2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1309-1318
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe conditions that significantly affect the biodegradability of linear alkylbenzene sulfonate (LAS) based on previous studies were categorized. Among these previous studies, we focused on those that used activated sludge and river water as inocula in biodegradation studies. Analyzing the results of these studies revealed two types of methylene blue active substances (MBAS) removal curves in primary biodegradation, and the study conditions that differentiated the two types were analyzed, along with verification studies. The effects of the LAS concentration and interfacial activity during biodegradation were analyzed to set the concentration of LAS in this study. Surface tension was measured as an indicator of interfacial activity and biodegradation was measured by oxygen demand. Two widely used surfactants, alcohol ethoxylate and sodium dodecyl sulfate, were evaluated to clarify the significance of the effective concentration range of LAS. The concentration of LAS was set at 10 or 20 mg/L in the verification study. Acclimatization and the concentration balance of LAS and river water were the strongest factors in studies using activated sludge and river water, respectively. Our classification chart may be helpful in analyzing and comparing the conditions of previous and current studies. Such understanding of the study conditions and practical evaluation may aid in avoiding misleading environmental impact assessments of LAS.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1493K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1493K) -
Mari Kaburagi, Tomoya Kojima, Kouichi Asakura, Taisuke Banno2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1319-1326
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
J-STAGE DataSelf-propelled droplets are of considerable interest as an appropriate model for understanding the self-propulsion of objects in the fields of nonequilibrium physics and nonlinear science. Several research groups have reported the monodirectional motion of droplets, that is, chemotaxis, using stimuli-responsive materials. However, the precise control of chemotaxis remains challenging from the perspective of synthetic chemistry because chemotactic motion is primarily induced by the consumption of reactive oil or surfactants. Herein, we report a chemical system containing pH-responsive fumaric acid derivatives, in which the oil droplet exhibited positive chemotaxis over a wide pH range-from basic to acidic conditions. From the measurements of the interfacial tension between the oil and aqueous phases, it was deduced that the positive chemotaxis was due to heterogeneity in the interfacial tension of the droplet surface, which was accompanied by the production of surface-active compounds in the pH gradient in a linear-type channel.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1243K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1243K)
-
Haiyang Shen, Qian Li, Youtao Yu2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1327-1335
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSHepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the 5th most common type of cancer in all types of cancers, globally. It is well known that the frequency of inflammatory reaction and oxidative stress increases during the HCC. The goal of this study was to see if decalactone could prevent rats against HCC caused by diethylnitrosamine (DEN). Single intraperitoneal administration of DEN (200 mg/kg) used as inducer and weekly intraperitoneal injection of phenobarbital (8 mg/kg) was used as promotor for induction the HCC in rats. Serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP) was used for the confirmation of HCC. Different doses of decalactone (5, 10 and 15 mg/kg) were orally administered to the rats. The body weight was determined at regular time. The hepatic, non-hepatic, antioxidant markers and inflammatory mediators were scrutinized. All groups of animals were scarified and macroscopically examination of the liver tissue was performed and the weight of organ (hepatic tissue) were estimated. Decalactone increased body weight while also suppressing hepatic nodules and tissue weight. Decalactone treatment reduced AFP, total bilirubin, and direct bilirubin levels while increasing albumin and total protein levels in a dose-dependent manner. Decalactone reduced lipid peroxidation (LPO) and increased catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels significantly (p < 0.001) (SOD). Decalactone lowered the levels of significantly (p < 0.001) inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory markers in the liver. Based on the findings, we may conclude that decalactone inhibited HCC in DEN-induced HCC animals via reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1190K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1190K) -
Lihong He, Jiawei Zheng, Siting Feng, Li Xu, Nanjing Zhong2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1337-1348
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, lipase A from Candida antarctica (CALA) was immobilized onto the macroporous resin NKA-9. Immobilization conditions (pH, time and CALA concentration) were studied, enzymatic activity and immobilization efficiency (IE) up to 968.89 U/g and 53.19% were respectively obtained under optimal conditions (immobilization pH 5.0, time 5 h and CALA concentration at 30 mg/mL). Then, the NKA-9 supported CALA (CALA@NKA-9) samples were used to catalyze glycerolysis in solvent-free system. With 0.25 g of the present CALA@NKA-9 (soybean oil 3.52 g and glycerol 0.184 g) and after 12 h reaction at 50 °C, diacylglycerols (DAG) content up to 64.37% and triacylglycerols (TAG) conversion at 83.33% were obtained. The relationship between temperature and TAG conversion was LnV 0 = 13.9310-6.4212/T for CALA@NKA-9. Meanwhile, the activation energy (Ea) of CALA@NKA-9 was calculated to be 53.39 kJ/mol. In addition, reusability in the glycerolysis reaction was also evaluated, and 57.82% of the initial glycerolysis activity was retained after 9 consecutive applications. Furthermore, the CALA@NKA-9 was also used to catalyze the esterification (esterification of fatty acids with glycerol), however, the present CALA@NKA-9 cannot initiate the esterification. Therefore, the present CALA@NKA-9 is shown to be potential for DAG production through glycerolysis reaction.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (993K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (993K) -
Muhammad Umar Khan, Saiqa Andleeb, Muhammad Fiaz Khan, Rozina Ghulam M ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1349-1361
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis study aims to analyze molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of earthworm species collected from different soil habitats of Poonch division Azad Kashmir Pakistan by using CO1 gene partial sequencing methodology. Samples gathered randomly from 18 study sites (127 localities) by digging and hand sorting methods were preserved in pure ethanol at -20°C. The modified CTAB (Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide) method extracted high quality DNA from region of representative earthworm’s caudal region. This extracted DNA was used to amplify the 700 bp partial region of the cytochrome oxidase I (COI) gene with LCO1490 and HCO2198 universal primers. All of the obtained amplified gene sequences were aligned, edited and analyzed using MEGA X software to characterize different species of earthworms. Thirty-eight (38) Barcoding sequences belonging to 11 different strains of earthworms were successfully generated. Their phylogenetic analysis revealed that 7 Barcoding sequences gave maximum similarity with the available online database, while the rest of the 4 sequences gave lower similarity than the maximum threshold level. The collected DNA barcode sequences were also clustered together by the maximum likelihood method and the resultant phylogenetic tree revealed they belong to different family lineages. Moreover the identified earthworm species have a close evolutionary link with the earthworm fauna of south and central Asia instead of Europe, which might be due to similar climate of both regions.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4920K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4920K) -
Sundas Nasreen, Saiqa Andleeb, Shaukat Ali, Kaleem Imdad, Uzma Azeem A ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1363-1374
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSProbiotics frontier in depressing the clinical bacterial pathogens to avoid multidrug resistance phenomenon. The present study aimed to determine the antibacterial efficiency of chitosan encapsulated probiotics isolated from buffalo milk samples against clinical bacterial pathogens. The Agar well method was used for antibacterial activity. Lactococcus lactis (A) and Lactobacillus curvattus (B) were isolated from fresh buffalo milk samples, identified via culturing media, Gram’s staining, biochemical tests, and antibiogram analysis. Encapsulation of probiotics was carried out using chitosan and was characterized via a scanning electron microscope. Antibiogram analysis elicit that L. lactis culture (A1) was highly sensitive to chloramphenicol (17.66±0.47 mm), tobramycin (15.33±0.47 mm), and ciprofloxacin (12.33±0.47 mm) and resistant against tetracycline, Penicillin G, Erythromycin, Amoxycillin, Ceftriaxone, Cephalothin, and Cephradine, while L. curvattus culture (B1) was affected by Ceftriaxone (18.67±0.47 mm), Amoxycillin (14.33±0.94 mm), Cephalothin (13.67±0.47 mm), Erythromycin (13.33±0.47 mm), Penicillin G (12.67±0.47 mm), Cephradine (10.33±0.47 mm), and Chloramphenicol (9.67±0.47 mm) and resistant against tetracycline, Tobramycin, and Ciprofloxacin. Antibacterial efficacy of non-encapsulated probiotic cultures was significant and maximum inhibition of bacterial were recorded compared to their cellular components. SEM of encapsulated probiotics revealed that they were successfully covered with a chitosan protective layer and could be effective as bio-preservatives due to being slowly released at the target site. The current study concluded that L. lactis, L. curvattus, and their cellular components have a significant bactericidal effect against infectious pathogens and could be used as a potential therapeutic drug against infectious diseases.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2568K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2568K)
-
Xiaojun Pang, Haojun Huang, Yuyu Wei, Jiyong Leng2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1375-1385
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSGlioblastoma multiforme or GBM is a destructive malignancy of the central nervous system and is accountable for leading cause of cancer related mortality. Inadequate success rate of surgical interventions and development of resistance towards the current therapeutical regime provides impetus for exploring novel therapeutical interventions against the disease. Recently, several epidemiological studies have explored the plausible utility of natural, dietary compounds in influencing the development, progression, and cancer metastasis. Recently, different phytoconstituents of Cassia angustifolia were found to be associated with anti-microbial, anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the anti-proliferative efficacy of ethanolic leaf extract of C. angustifolia (LCaEt-OH) against rat derived glioblastoma C6 cells. Briefly, the anti-proliferative potential of LCaEt-OH was assessed using MTT assay, quantitative estimation of ROS, and evaluation of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). Moreover, the activity of caspases involved in intrinsic apoptotic pathways was also investigated using colorimetric kit followed by quantitative RT-PCR evaluation of modulation in gene expressions triggered due to LCaEt-OH treatment. Treatment of LCaEt-OH on C6 cells elucidated substantial dose-dependent decline in cellular viability. Furthermore, LCaEt-OH showed its efficacy in substantially enhancing intracellular ROS. LCaEt-OH also incited apoptosis in C6 cells by instigating nuclear condensation and dissipation of ΔΨm. In addition, LCaEt-OH mediated instigation of apoptosis was directly influenced by increased activity of caspases indispensable for intrinsic apoptotic pathway. These conclusive evidences indicate towards anticancer efficacy of LCaEt-OH against C6 cells.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3350K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3350K) -
Tatsuhiro Matsuo, Takako Yamada, Tetsuo Iida, Susumu Mochizuki, Akihid ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1387-1395
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSd-Allulose (d-psicose) is a rare sugar, that contains no calories and exhibits 70% relative sweetness when compared with sucrose. Recently, several studies have demonstrated the anti-obesity effect of d-allulose, mediated by suppressing lipogenesis and increasing energy expenditure. Medium-chain triacylglycerols (MCTs) are lipids formed by 3 medium-chain fatty acids (MCFAs) with 6-12 carbon atoms attached to glycerol. MCTs have been expensively studied to reduce body fat accumulation in rats and humans. The anti-obesity effect of MCTs was not confirmed depending on the nutritional conditions because MCT might promote lipogenesis. In the present study, we examined the effects of simultaneous intake of diets containing low (5%) or high (13%) MCTs, with or without 5% d-allulose, on body fat accumulation in rats (Experiment 1). Furthermore, we assessed the interaction between 5% MCT and 5% d-allulose in the diet (Experiment 2). In Experiment 1, intra-abdominal adipose tissue weight was significantly greater in the high MCT diet groups than in the commercial diet (control) group. d-Allulose significantly decreased weights of intra-abdominal adipose tissue, carcass fat, and total body fat, however, these weights increased as the amount of MCT added increased. In Experiment 2, d-allulose significantly decreased almost all body fat indicators, and these values were not influenced by the presence or absence of MCT addition. The anti-obesity effect of d-allulose was observed with or without dietary MCT, and no synergistic effect was detected between d-allulose and MCT. These results suggest that d-allulose is a beneficial food ingredient in diets aimed at reducing body fat accumulation. However, further research is required on the synergistic effects between d-allulose and MCTs.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (293K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (293K) -
Narito Asanuma2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1397-1402
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCeramide prepared from glucosylceramide (GlcCer) with Gluceribacter canis NATH-2371T was administrated to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) model mice. Dietary ceramide significantly suppressed the decrease in final body weight, and the increase in the disease activity index and myeloperoxidase activity more greatly than GlcCer in IBD mice. Intestinal microbiome profiles were found to be altered in IBD mice, but ceramide counteracted the changes. These results suggest that dietary plant-based ceramide may alleviate symptoms of IBD in mice.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (391K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (391K)
-
Takuhiro Uto, Tomoe Ohta, Eri Nakayama, Mina Nakagawa, Maki Hatada, Yu ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1403-1412
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialClove, a dried flower buds of Syzygium aromaticum, is used in traditional medicine, for culinary purposes, and in essential oil production. In our preliminary screening of crude drugs used in Japanese Kampo formulas, a methanol (MeOH) extract of clove buds was found to exhibit a melanin induction. To date, the effects of clove buds or their constituents on the activation of melanogenesis remain unclear. Thus, this study aimed to isolate active compounds from the MeOH extract of clove buds associated with melanin synthesis in melanoma cells and to investigate the molecular mechanism involved. The MeOH extract of clove buds increased melanin content in murine B16-F1 melanoma cells. To identify the active compounds responsible for melanin induction, the MeOH extract was suspended in water and successively partitioned using hexane, ethyl acetate (EtOAc), and n-butanol (n-BuOH). Comparative analysis revealed that the EtOAc fraction induced melanin synthesis. Bioassay-guided separation of the EtOAc fraction isolated three compounds including eugenol. The analysis of structure-activity relationships of eugenol and structurally related compounds indicated that eugenol was the most potent melanin inducer among the 11 compounds, and that a hydroxyl group at C-1 and a methoxy group at C-2 may contribute to melanin induction. Eugenol induced melanin synthesis in human HMV-II melanoma cells as well as in B16-F1 cells. Further analysis indicated that eugenol may invoke intracellular tyrosinase activity and expression of tyrosinase, tyrosinaserelated protein (TRP)-1, TRP-2, and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF). These results suggest that eugenol enhances melanin synthesis by upregulating the expression of MITF and subsequent expression of melanogenic enzymes, and that it may be a potent therapeutic agent for hypopigmentation.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1592K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1592K)
-
Nobuya Shirai2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1413-1419
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSGreen tea is a popular refreshing drink with several functional properties attributed to its bioactive compounds. The bioactive content and composition vary with several factors. Several advances in chromatographic studies have facilitated the study of chemical composition of green tea leaves; however, the content of organic acids, particularly quinic acid, has not been explored fully. Therefore, changes in the content of organic acids, including quinic acid, in green tea leaves, were investigated in this study. All the studied varieties contained large amounts of quinic and oxalic acids. Kukicha and Matcha contained the highest and lowest amounts of quinic acid, respectively. Furthermore, high-grade Matcha had a significantly lower quinic acid content than low-grade Matcha. The Asatsuyu sample had the lowest quinic acid content in 2018 and 2019 compared with the other green tea varieties. The content of quinic acid increased with maturity, but that of oxalic, malic, succinic, and citric acids decreased after a slight increase. Shading cultivation in Saeakari significantly lowered the quinic acid content and slightly increased the content of malic, citric, and oxalic acids. Malic acid and citric acid content in Yabukita changed with sunrise and sunset, but that of other organic acids did not show any considerable change. These results show that using an appropriate plucking time could lead to further improvement in the quality of green tea leaves. Overall, green tea is a good source of quinic acid, which will attract attention in future functional research on this drink.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (980K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (980K) -
Azusa Saika, Hideaki Koike, Shuhei Yamamoto, Tomohiro Sugahara, Akio K ...2022Volume 71Issue 9 Pages 1421-1426
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: September 01, 2022
Advance online publication: August 15, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe basidiomycetous yeast Pseudozyma tsukubaensis produces a mannosylerythritol lipid (MEL) homologue, a diastereomer type of MEL-B, from olive oil. In a previous study, MEL-B production was increased by the overexpression of lipase PaLIPAp in P. tsukubaensis 1E5, through the enhancement of oil consumption. In the present study, RNA sequence analysis was used to identify a promoter able to induce high-level PaLIPA expression. The recombinant strain, expressing PaLIPA via the translation elongation factor 1 alpha/Tu promoter, showed higher lipase activity, rates of oil degradation, and MEL-B production than the strain which generated in our previous study.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (662K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (662K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|