
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Masaki Honda, Hakuto Kageyama, Takashi Hibino, Kohei Ichihashi, Wataru ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1529-1540
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecent investigations have demonstrated that some food ingredients and vegetable oils, such as onion, garlic, and sesame oil, enhanced thermal Z-isomerization of (all-E)-lycopene in tomatoes. However, the synergistic effects of these ingredients and oils have not yet been investigated. This study aims at clarifying how the combined use of lycopene Z-isomerization-promoting food ingredients and vegetable oils impacts thermal Z-isomerization of (all-E)-lycopene in tomato puree. Apart from a few exceptions, when olive oil was used as a reaction medium, the combined use of garlic, cabbage, broccoli, shiitake mushroom, and makonbu improved the total Z-isomer ratio of lycopene after heating compared to the separate use of the tested ingredients. However, when onion was used together with the other ingredients, the Z-isomer ratio significantly decreased compared to its individual use. Moreover, when garlic, cabbage, broccoli, shiitake mushroom, and makonbu were used with sesame and mustard oils, that exhibit higher Z-isomerizationpromoting effect than that of olive oil, the lycopene Z-isomerization reaction was further enhanced. However, when onion was combined with these oils, the Z-isomer ratio decreased compared to that measured upon the combined use of onion with olive oil. Our results on these synergistic effects are not only important for the food and drink manufacturing industries but also for daily home cooking.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (621K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (621K) -
Pan Gao, Chuanrong Hu, Dongping He2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1541-1549
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe aim of the study was to investigate the chemical properties of the most popular commercial extra virgin olive oils (EVOOs) in China. A total of 14 EVOO samples were collected and evaluated, and significant differences were observed with respect to physicochemical properties, fatty acid composition, minor components, and the oxidation stability index (OSI). The results showed that the chemical properties of EVOOs were significantly affected by different producing areas. The oleic acid (C18:1) content (average value: 77.80%), squalene content (average value: 6052.28 mg/kg), and OSI (average value: 9.90 h) of the Spanish olive oil were higher than those of the other oils investigated, while the total phenolic content (average value: 308.34 mg/kg) was the lowest. Greek EVOOs had the lowest total sterol content (average value: 1023.48 mg/kg) and OSI (average value: 4.22 h). The C18:1 content (66.42%) and squalene content (3173.42 mg/kg) of the EVOO from China were lower than those of the other oils, while the palmitic acid (C16:0, 16.82%), linoleic acid (C18:2, 12.18%), total phenolic (553.17 mg/kg), and total sterol content (1904.77 mg/kg) were higher than those of the other olive oils. The EVOOs of the various countries could be distinguished by hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). In addition, multiple linear regression (MLR) analyses between the OSI and chemical properties revealed that squalene (R = 0.729) and the unsaturation determined by the specific UV adsorption at 232 nm (K232, R = -0.300) were the main factors to affecting the EVOO oxidation stability.
View full abstractDownload PDF (310K)
-
Kana Miyasaka, Yoko Imai, Kazuo Tajima2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1551-1560
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe present study investigates the principle difference between three-phase emulsification and conventional emulsification methods (surfactant emulsification and the Pickering method). Conventional emulsification methods depend on intensive factors such as interfacial tension and wetting. In the proposed three-phase emulsification, soft hydrophilic nanoparticles adhere to the oil-water interface due to the van der Waals attraction and stabilize the emulsion. Therefore, it can be said that three-phase emulsification is “extensive emulsification” based on the mass of the hydrophilic nanoparticles and oil droplets. Extensive emulsification is irreversible because the van der Waals attraction acts between the particles unless the mass of the soft hydrophilic nanoparticles and oil droplets changes. The differences between three-phase emulsification and conventional emulsification methods were experimentally verified by comparing the difference in the stability of the emulsions resulting from the change in intensive factors, where the internal phase oil transitioned from solid to liquid. The emulsions prepared using the surfactant and Pickering methods were separated into oil and water by the solid-liquid phase transition of hexadecane in the internal oil phase. However, the emulsion prepared using three-phase emulsification maintained its emulsified state without any oil-water separation even when the internal oil phase underwent solid-liquid phase transition. From the results obtained, it can be concluded that three-phase emulsification is an irreversible method because its mechanism is based on extensive factors. Furthermore, this irreversible method allows the emulsification of various oils that cannot be emulsified by conventional methods, and it is also possible to directly mix emulsions prepared with different oils. The authors also call attention to the possibility of improving emulsion characters and new developments in emulsion science.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1173K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1173K) -
Takanori Saito, Rina Ishii, Masaaki Akamatsu, Takaya Sakai, Kenichi Sa ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1561-1567
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialWe determine the effects of the α-gel (α-form hydrated crystal) domain size on the viscosity of water-diluted α-gels consisting of the N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]docosanamide (APA-22) L-lactic acid salt, 1-octadecanol (C18OH), and water. A decrease in the C18OH mole content results in increased domain size and viscosity of the water-diluted α-gel system. Additionally, when a sample is prepared by slow cooling and/or at low stirring speed, the domain size and viscosity of the water-diluted α-gel system increase. A similar increase in the domain size and viscosity of the α-gel system is observed for annealed samples. The observed change in the α-gel domain size is explained by the crystal growth theory.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (953K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (953K)
-
Yasuhiro Hara, Bo Zhang, Akira Suzuki, Satoshi Yamaguchi, Jun Adachi, ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1569-1577
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: November 25, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialTriglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy (TGCV), a rare cardiovascular disorder caused by genetic or acquired dysfunction of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), is marked by defective intracellular lipolysis that results in excessive accumulation of triglycerides (TGs) in the myocardium and coronary arteries, leading to intractable heart failure (HF). We have developed a specific treatment for TGCV using tricaprin, a medium chain TG, as part of a governmental rare disease project in Japan. We recently reported that tricaprin diet improved cardiac TG metabolism and left ventricular function in an ATGL-knockout (KO) mouse, a mouse model for TGCV. Here, we report the effect of tricaprin on the myocardial proteome of KO mice to elucidate the mechanisms of action of tricaprin at protein expression levels. We compared proteomic changes in the hearts of KO mice fed control or tricaprin diet. Tandem mass tag-based shotgun proteomics identified 1832 proteins common to all sample groups. Whole proteomic distribution in the heart was largely up-regulated in KO mice fed control diet. When using cut-off values (>1.5 or <0.67, FDR-adjusted p value<0.01), in fact, 65 proteins were up-regulated whereas only 2 proteins were down-regulated in the hearts of KO mice fed control diet. The former included proteins assigned to “Cardiac Arrhythmia”, and “Cardiac Damage” reflecting HF by a toxicity function analysis. One of the latter was Ces1d, which is known to regulate intracellular TG metabolism. These proteomic changes observed in KO mice were dramatically rescued by the tricaprin diet. These results indicated that tricaprin diet ameliorated HF in a TGCV mouse model at protein expression levels and also provided important clues to understand mechanisms for the beneficial effect of tricaprin.
View full abstractDownload PDF (865K) -
Samet Kocabay, Serap Çetinkaya2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1579-1584
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSLactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been demonstrated to have roles in many applications, ranging from lowering of cholesterol to immunological development. In this study, Lactobacillus fermentum was isolated from a new-born’s faeces and its genotypic and probiotic characterizations were performed. Our results showed that the survival rate of isolated Lactobacillus fermentum was 39.39% at pH 2 and 81.34% in the stimulated gastric juice at pH 3. It also digested bile salts. Its surface hydrophobicity was found to be 57.59% in n-hexane. These findings indicated that the isolate can be a good probiotic candidate.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1220K) -
Sumeyra Savas, Serap Çetinkaya2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1585-1589
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSalmonella enterica subspecies enterica causes salmonellosis in humans and animals and is an important cause of food infections worldwide. In recent years, the multiple-locus variable-number of tandem repeat (VNTR) analysis (MLVA), a fast molecular typing method with strong epidemiological discrimination, has facilitated the effective control of diverse infections. This study aimed at the typing of 28 human origined Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella infantis, and Salmonella typhimurium strains by using a single MLVA protocol. Previously these strains have been identified by pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) method and it has been shown that each strain produced a distinct PFGE banding profile. One MLVA protocol was tested on 3 serotypes simultaneously and it produced three banding patterns specific to each of the three common Salmonella serotypes. MLVA also constitute a relatively more cost-effective and faster method than PFGE.
View full abstractDownload PDF (466K) -
Angga Sanjaya, Avidlyandi Avidlyandi, Morina Adfa, Masayuki Ninomiya, ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1591-1595
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialLichens produce a variety of secondary metabolites that could be potential sources of pharmaceutically useful chemicals. However, only a limited number of lichen metabolites have been investigated for their biological significance. The objective of this study was to identify the potential compounds responsible for the antileukemic activity of lichen Teloschistes flavicans. Among three fractions (n-hexane, EtOAc, and MeOH-H2O), the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fraction of T. flavicans methanolic extract showed the strongest inhibition in the HL-60 cell line. Additionally, the EtOAc fraction was further purified to obtain a new depsidone, 2,7-dichloro-3,8-dimethoxy-1,6,9-trimethyl-11H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4]dioxepin-11-one, named as flavicansone, along with rhizonic acid, parietin, and vicanicin. Flavicansone demonstrated the most significant inhibitory action against cell proliferation among the four isolated compounds.
View full abstractDownload PDF (346K)
-
Hirofumi Watanabe, Masaki Okawara, Yoshiharu Matahira, Takashi Mano, T ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1597-1607
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSObjectives: Plasmalogen, phospholipids with previously shown associations with dementia, has attracted attention as a substance found in some studies to improve cognitive function. The effects of ascidian-derived plasmalogens on cognitive performance improvement were assessed in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study including Japanese adult volunteers with mild forgetfulness.
Methods: Participants consumed either the active food containing ascidian-derived plasmalogen (1 mg as plasmalogen) or the placebo food for 12 weeks, and their cognitive performance was assessed by Cognitrax. Participants were randomly allocated into the intervention (ascidian-derived plasmalogen; 8 males, and 17 females; 45.6 ± 11.1 years) or the placebo (9 males, and 15 females; mean age, 46.4 ± 10.8 years) group. Results: Compared to the placebo group, the intervention group showed a significant increase score in composite memory (eight weeks: 3.0 ± 16.3 points, 12 weeks: 6.7 ± 17.5 points), which was defined as the sum of verbal and visual memory scores.
Conclusions: These results indicate the consumption of ascidian-derived plasmalogen maintains and enhances memory function. This study was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trial Registry (UMIN-CTR, registry no. UMIN000026297). This study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
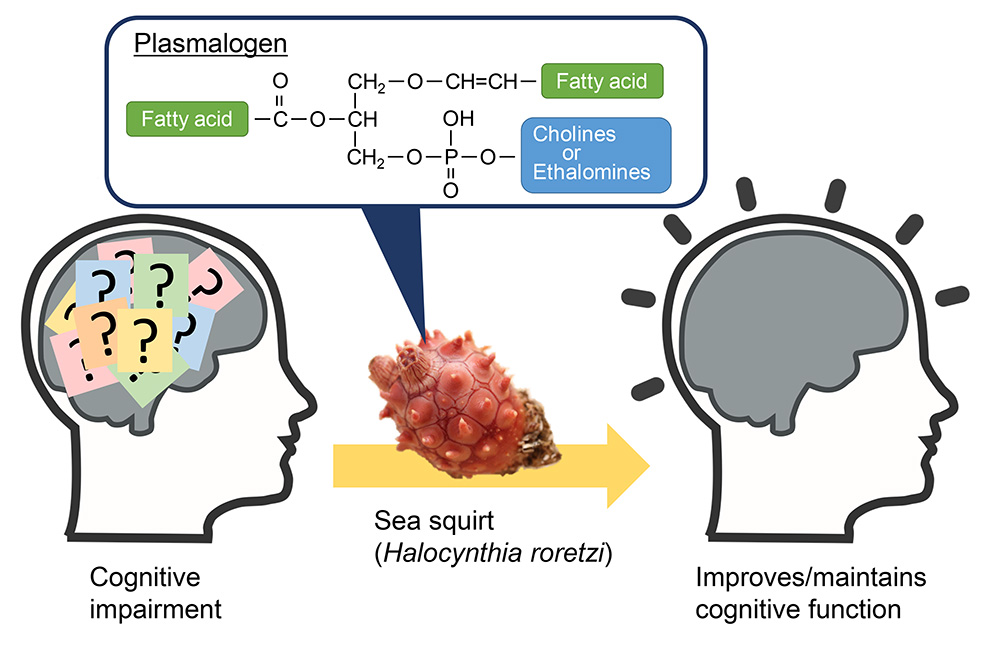 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (498K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (498K) -
Sheng-hua He, Chun-hong Liu, Rong-chun Wang, San-jiu Zhou, Wei-yun Guo ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1609-1618
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe surface compositions and structure of oil bodies (OBs) are dependent on the oil crop, and these factors affect in vitro gastrointestinal digestion behaviors. Herein, a comparative study was conducted to examine the in vitro gastrointestinal digestion characteristics of two natural emulsions prepared with soybean seeds and rapeseed OBs during gastrointestinal digestion process. The average particle size of soybean OBs and rapeseed OBs emulsions was 0.46 and 5.02 µm, respectively. The droplet size of soybean seed and rapeseed OBs emulsions was large with relatively low zeta-potentials at 30 min digestion time in simulated gastric fluid condition. The droplet size of two natural OBs emulsions decreased with increasing digestion time in simulated gastric fluid condition. The average droplet size of both emulsions gradually decreased with increasing digestion time in simulated intestinal fluid conditions. The zeta-potential of the two emulsions increased with increasing digestion time in simulated intestinal fluid conditions. The extent of free fatty acids of soybean OBs emulsions was significantly higher than rapeseed after 20 min digestion time in simulated intestinal fluid conditions. The obtained results suggested that plant OBs could be useful as natural emulsifiers in the development of functional food and achieve controlled release of bioactive compounds from emulsions during gastrointestinal digestion.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5910K)
-
Tarique Panhwar, Sarfaraz Ahmed Mahesar, Syed Tufail Hussain Sherazi, ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1619-1626
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSEnergy plays a key role in each sector of life ranging from basic needs to better standards of life. The world is concerned about 3 ps (population, poverty, and pollution). The increase of these three factors has led the search of the best alternative sources of energies to fulfill all needs of a modern way of life. Biodiesel is a sustainable energy source that has proved to be the best alternate of mineral diesel that possesses similar properties as found in mineral diesel. The recent trend in biodiesel research is towards the use of very cheap feedstock to make this substitute more economical. Following this similar trend, the attempt is made to produce biodiesel from less expensive feedstock namely; residual oil of spent bleaching clay (SBC). In the first step, the quantity of the residual oil that can be recovered followed by assessing its quality was investigated. Afterward, a two-step method of the transesterification process was employed to enhance the yield of methyl ester. The highest yield of 85% was obtained. Key fuel properties were measured and found in good agreement with ASTMD 6751 standards limits. The study also concerned with the practical availability of biodiesel in terms of its stability. For this purpose, produced biodiesel was evaluated for its oxidation stability during 90 days of storage by FT-IR and rancimat methods.
View full abstractDownload PDF (606K) -
Veerawat Teeranachaideekul, Boontida Morakul, Prapaporn Boonme, Warang ...2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1627-1639
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study aimed to evaluate the effect of solid lipid and oil structures on the physicochemical properties, kinetic release, photostability, and photoprotection of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) containing octyl methoxycinnamate (OMC). OMC was used as a model compound since it is an effective sunscreen agent and is widely used in sunscreen products; however, it is unstable after ultraviolet radiation (UVR) exposure. OMC-loaded NLC were prepared from different solid lipids (cetyl palmitate (CP) or tristearin) and oils (caprylic/capric triglyceride, isopropyl myristate or isononyl isononanoate) at a 4:1 ratio. After production, the particle size (z-ave) and polydispersity index (PDI) of OMC-loaded NLC ranged from 190 to 260 nm and were lower than 0.25, respectively, and the zeta potential (ZP) values were higher than |50 mV|. The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy results indicated no interaction among the components. Data obtained from differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction showed that the incorporation of oil into solid lipids disturbed the crystallinity of the lipid matrix, depending on the structure of the oil molecule. OMC loaded in tristearin-based NLC (OMC-tristearin-NLC) showed higher release of OMC than OMC loaded in CP-based NLC (OMC-CP-NLC). For photostability properties, OMC-CP-NLC prepared from isononyl isononanoate showed the highest stability owing to the less-ordered structure, providing space for accommodation of OMC, whereas the percentage of OMC remaining in tristearin-based NLC was comparable. Therefore, the degree of protection was dependent on the type of solid lipid and oil. As a result, branched-chain fatty acids provided a higher degree of disturbance than linear-chain fatty acid.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1707K) -
Qiaona Yuan, Mengjie Tu, Pan Gao, Chuanrong Hu, Dongping He2020Volume 69Issue 12 Pages 1641-1648
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: December 01, 2020
Advance online publication: November 12, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFlavoured rapeseed oils prepared using traditional technologies (oils A and B) and a fragrant rapeseed oil obtained using an enzymatic Maillard reaction (oil C) were analysed to show that oil C featured basic indicators and a fatty acid composition similar to those of traditional oils while exhibiting a higher comprehensive sensory evaluation score. Volatile component, odour activity value (OAV), and relative odour activity value (ROAV) analyses revealed that oil C had an elevated content of pyrazines (20.83%) and aldehydes (38.15%), which resulted in stronger charred and caramel flavours. The aroma of oil C was directly impacted by 3-methylbutyraldehyde (OAV > 1) and was modified by 3-methylthiopropionaldehyde and nonanal (RAOV > 1 in both cases). Thus, the developed technology was found to be well suited for the production of novel and safe fragrant rapeseed oil.
View full abstractDownload PDF (552K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|