
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Barry Union R. Kayanan, Rosario S. Sagum2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 875-884
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
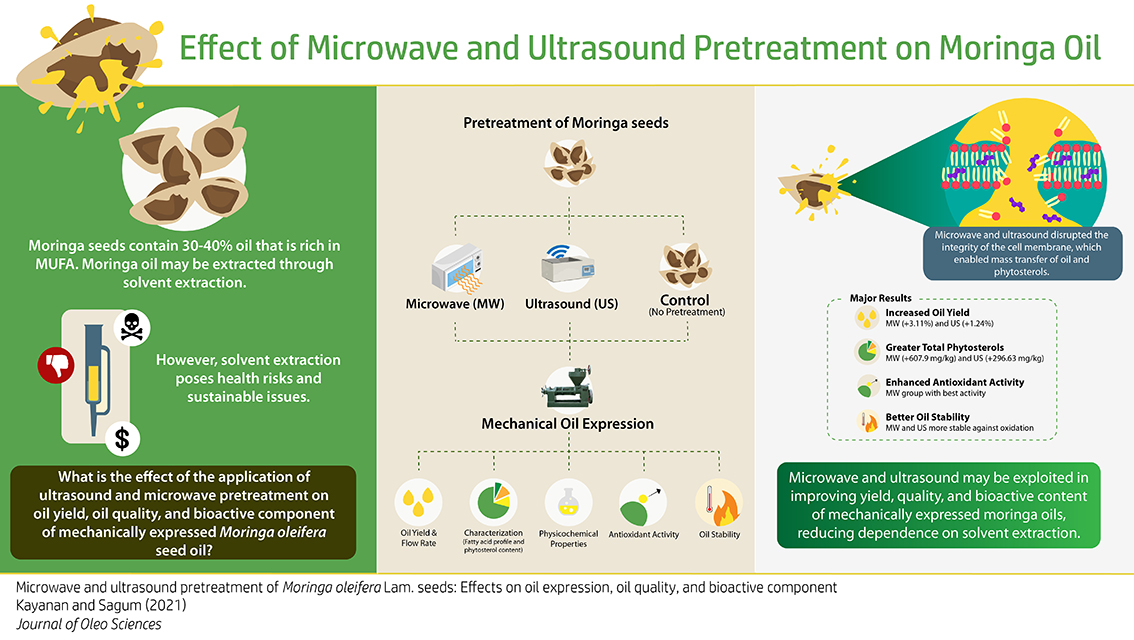
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis study investigates the application of green technologies (microwave and ultrasound pretreatment) in the extraction of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed oil and its effects on oil expression, oil quality, and bioactive component. Moringa seeds were pretreated with microwave (90 W, 60 s) or ultrasound (50 W, 1 h) before mechanical expression. A separate group received no pretreatment before oil extraction. Oils from these groups were then compared. Results show that oil yield increased with ultrasound pretreatment (1.24%) and significantly increased with microwave pretreatment (3.11%). For oil flow rate, the microwave and ultrasound pretreatment resulted in faster extraction (7.67 and 6.93 kg/h respectively) as compared with the control (6.51 kg/h). For physicochemical parameters, the microwave and ultrasound group had significantly less free fatty acids and significantly greater unsaponifiable matter as compared with the control. For fatty acid composition, results show that moringa seeds procured from Davao Oriental had greater oleic acid content (~77%) as compared with those reported by other literature. For phytosterol content, the predominant phytosterols found were β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, and campesterol. Microwave and ultrasound pretreatment significantly increased total phytosterol (680.58 and 369.32 mg/kg respectively) as compared with the control (72.69 mg/kg) due to the mass transfer of the phytosterols. Microwave and ultrasound pretreatment also led to stigmastanol formation. For antioxidant activity, a comparison of both DPPH and FRAP assays depicts that the microwave group exhibited the best overall antioxidant activity. Lastly, for oil stability, a lower peroxide value was found in the microwave and ultrasound groups across time intervals, which may be attributed to their antioxidant activity. In summary, ultrasound and microwave pretreatment can improve oil expression, oil quality, and bioactive content of the mechanically expressed moringa oils.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (378K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (378K) -
Lirong Xu, Xin Ji, Gangcheng Wu, Emad Karrar, Ling Yao, Xingguo Wang2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 885-899
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn order to study the flavor of French fries (FFs) prepared in different frying oils, we identified and compared the volatiles of FFs fried in high-oleic sunflower oil (HSO), sunflower oil (SO), linseed oil (LO), and palm oil (PO) during prolonged 24 h frying time. 47 different kinds of volatiles were presented, and aldehydes were the most abundant compounds. The FFs prepared in SO were rich in alkadienals, especially the (E, E)-2,4-decadienal, thus inducing the highest deep-fried odor. The content of alkenals was higher in FFs prepared in HSO, among which (E)-2-nonenal and 2-undecenal provided the undesirable oily flavor. Whereas, FFs prepared in PO were rich in alkanals, and showed an undesirable green aroma because of hexanal. Besides, the aldehydes in FFs fried in LO were the least with more undesirable flavor substances (e.g. (E, E)-2,4-heptadienal). In addition, except for the FFs fried in LO, the aldehydes in other FFs showed an increasing trend. While, the volatiles from the Maillard reaction (e.g. pyrazines) showed no clear pattern. Meanwhile, frying process had optimum frying window (approximately 12 h with total polar compounds content of 14.5%-22.2% in different oils), and the French fries prepared in this period obtained higher flavor score. Therefore, the comparison related to volatiles of FFs provided a basis for the flavor control to a certain extent.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1724K) -
Isam A. Mohamed Ahmed, Fahad AL-Juhaimi, Nurhan Uslu, Mehmet Musa Özca ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 901-909
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, the combined effect of different packaging materials (transparent PET, transparent glass, glass-PET bottle and tin), some aromatic herbs (thyme, rosemary, sage and olive leaf) and also their essential oils (thyme, rosemary and sage) on fatty acid composition of virgin olive oil was investigated during storage period. The initial amounts of the main fatty acids as oleic, palmitic and linoleic acids were determined as 72.89%, 11.89% and 8.96%, respectively. The addition of aromatic plants and essential oils did not effect the fatty acid profile. Also, packaging materials had a minor influence on fatty acids. In the 6th month of storage, the oleic acid contents of olive oils showed the increase in all of samples. The highest increase was observed in olive oil stored in glass-PET (74.30-75.01%), followed by stored in glass bottle (73.41-74.82%). Generally, during the storage, the differences of fatty acid contents were in minor level. The fatty acid composition of olive oils stored under different essential oil and extract concentrations showed partial differences depending on the extract type and concentration.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (245K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (245K)
-
Keisuke Matsuoka, Mamoru Arima, Yusuke Goto, Shiho Yada, Tomokazu Yosh ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 911-918
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSMonoammonium glycyrrhizinate is produced by the neutralization of glycyrrhizic acid from plant licorice with ammonia. In this study, the physicochemical properties of aqueous monoammonium glycyrrhizinate were investigated from the viewpoint of surface chemistry. The structure of the amphiphilic molecule is bola type, comprising two glucuronic acid moieties having two carboxylic acids groups and an aglycone part having a carboxylic acid at the opposite end of the molecule from the glucuronic acids. We found that the physicochemical properties of aqueous monoammonium glycyrrhizinate are dependent on the ionization of the carboxylic acid groups. The solubility of monoammonium glycyrrhizinate gradually increased above pH 4 in the buffer solution. The critical micelle concentration (CMC) and surface tension at the CMC (γCMC) of monoammonium glycyrrhizinate were determined by the surface tension method to be 1.5 mmol L-1 and 50 mN m-1 in pH 5 buffer and 3.7 mmol L-1 and 51 mN m-1 in pH 6 buffer, respectively. The surface tension gradually decreased with increasing concentration of monoammonium glycyrrhizinate in the pH 7 buffer, but the CMC was not defined by the curve. Light scattering measurements also did not reveal a clear CMC in the pH 7 buffer. The ionization of the carboxylic acid groups in the bola-type amphiphilic molecule with increasing pH is disadvantageous for micelle formation. Cryo-transmission electron microscopy showed that monoammonium glycyrrhizinate forms rod-like micelles in pH 5 buffer, and small angle X-ray scattering experiments confirmed that the average micellar structure was rod-like in pH 5 buffer. Thus, it was found that monoammonium glycyrrhizinate can form micelles only in weakly acidic aqueous solutions.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1240K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1240K) -
Hirobumi Shibata, Yoshinobu Iizuka, Masato Amano, Erika Takayanagi, Ta ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 919-925
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialZinc oxide (ZnO) particles were synthesized in the presence of anionic surfactants (ASs). The effect of ASs on the morphology of the ZnO particles was investigated by using ASs with various alkyl chain lengths and changing the molar ratio of AS/ZnSO4. Hexagonal plate-like ZnO particles were formed in the presence of ASs. Adsorption of the AS on the c face of the ZnO crystals inhibited (promoted) crystal growth along the c-axis (ab-axis) direction. Increasing the molar ratio of AS/ZnSO4 decreased the particle thickness, owing to the resulting increase in the coverage of the c face with AS. The particle diameter of the hexagonal plate-like ZnO particles (the diagonal length of the hexagonal plate) increased with increasing alkyl chain length of AS as a result of the van der Waals interactions between the alkyl chains. The data indicate that the particle diameter and thickness can be controlled by fine-tuning the van der Waals interactions between the alkyl chains and the coverage of the c face of the ZnO particles with AS.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1162K)
-
Shaojie Yuan, Tong Zhang2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 927-936
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIt is well known that inflammatory reactions and oxidative stress play a key role in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemia and secondary injury. Boeravinone B (BB) proofed their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, but their neuroprotective effects still unknown. In this experimental study, we explore the neuro-protective effect of Boeravinone B on the ischemia/reperfusion and explore the possible mechanism. Male Wistar rats were used for the current experimental study. First induces natural I/R injury in rats and treated with BB and nifedipine, respectively. Rats were subjected to ischemia after 6 consecutive days by occlusion of the bilateral common carotid arteries (BCCAO). Neurological score, biochemical, antioxidant, pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory parameters were estimated in the serum and brain tissue. BB treatment significantly (p < 0.001) suppressed neuronal injury, dose-dependently decreased the cerebral water content. BB treatment altered the pro-inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant and inflammatory mediators in the serum and brain tissue. BB regulated the expression of glycine (Gly), glutamic acid (Glu), taurine (Tau), aspartic acid (Asp) and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and enhanced the activity of Na+, K+ ATPase and Ca2+ ATPase. BB significantly (p < 0.001) reduced antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione reductase (GR); inflammatory cytokines include interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β); inflammatory mediators include prostaglandin (PGE2), nuclear kappa factor B (NF-κB) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), respectively. In this study, we have found that Boeravinone B exhibited protection against cerebral I/R by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1746K) -
Keisuke Kimura, Mizuki Morisasa, Takafumi Mizushige, Rikuo Karasawa, C ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 937-946
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSMuscle atrophy refers to skeletal muscle loss and dysfunction that affects glucose and lipid metabolism. Moreover, muscle atrophy is manifested in cancer, diabetes, and obesity. In this study, we focused on lipid metabolism during muscle atrophy. We observed that the gastrocnemius muscle was associated with significant atrophy with 8 days of immobilization of hind limb joints and that muscle atrophy occurred regardless of the muscle fiber type. Further, we performed lipid analyses using thin layer chromatography, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and mass spectrometry imaging. Total amounts of triacylglycerol, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin were found to be increased in the immobilized muscle. Additionally, we found that specific molecular species of phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylcholine, and sphingomyelin were increased by immobilization. Furthermore, the expression of adipose triglyceride lipase and the activity of cyclooxygenase-2 were significantly reduced by atrophy. From these results, it was revealed that lipid accumulation and metabolic changes in specific fatty acids occur during disuse muscle atrophy. The present study holds implications in validating preventive treatment strategies for muscle atrophy.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3100K)
-
Tamotsu Tsukahara, Hiroto Hara, Hisao Haniu, Yoshikazu Matsuda2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 947-954
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialLysophospholipids (LPLs) are small bioactive lipid molecules characterized by a single carbon chain and a polar head group. LPLs have recently shown to be involved in many physiological and pathological processes such as nervous system regulation. In our previous studies, a porcine liver decomposition product (PLDP) has been identified as a substance that improves cognitive function at old ages. This PLDP is a rich source of LPLs, including lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) and lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE). This study was designed to evaluate the anti-inflammatory effect of these LPLs on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated SIM-A9 microglial cells in terms of cytokine expression and oxidative stress and to investigate the potential mechanisms underlying these effects. SIM-A9 cells were pretreated with LPLs prior to LPS stimulation, and the anti-inflammatory potential of the LPLs in LPS-induced SIM-A9 cells was examined. Pretreatment with LPLs significantly inhibited the LPS-induced expression of IL-6 in SIM-A9 cells. Furthermore, oxidative-related protein, NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) levels were markedly increased in the LPS-treated cells, and pretreatment with LPC and LPE significantly reduced to basal levels. In addition, LPS-induced ROS production was eliminated in apocynin-treated cells, indicating that ROS production was dependent on Nox2. Our findings revealed that pretreatment with LPC and LPE decreased LPS-stimulated ROS production. These results indicated that LPC and LPE exerted significant protective effects against LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in SIM-A9 cell.
View full abstractDownload PDF (477K) -
Zuhong Wang, Sha Xiao, Jun Huang, Sutao Liu, Mei Xue, Fang Lu2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 955-964
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSInflammatory reactions and oxidative stress play a major role in cancer expansion. Boeravinone B (BB) had already proofed their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects against various animal models of disease. In this experimental research, the chemoprotective effect of BB against skin cancer caused by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)/croton oil was investigated and the possible mechanism was explored. Swiss albino mice were used in the current protocol. 100 µg/100 mL acetone, DMBA was used for induction the skin cancer and, after the 2-week repeated dose of croton oil (1% in acetone) give to the mice till end of the protocol. The mice were received the oral dose of BB (1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg, body weight). The body weight and tumor incidence were estimated at regular time interval. At the end of the protocol, the antioxidant, phase I, phase II, pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators were scrutinized. The mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators were estimated. BB treatment significantly (p < 0.001) reduced tumor incidence, tumor yield, average latency period and tumor burden in a dose-dependent manner. BB treatment considerably (p < 0.001) reduced the levels of lipid peroxidation (LPO) and increased the level of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT) in DMBA/croton-induced skin cancer. BB treatment significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the level of phase I and phase II enzymes. BB treatment considerably reduced the cytokines include tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-18 (IL-18), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and inflammatory parameters such as transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), nuclear kappa B factor (NF-κB) and cycloxgenase-2 (COX-2) in DMBA/croton-induced skin cancer mice. BB considerably (p < 0.001) reduced the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators. The results of the current investigation suggest that oral administration of boeravinone B significantly reduced skin cancer in mice via reduction of inflammatory reaction.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1678K)
-
Koki Sugimoto, Ryota Hosomi, Takaki Shimono, Seiji Kanda, Toshimasa Ni ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 965-977
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialDue to the growing demand of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) as supplements and pharmaceutical products worldwide, there are concerns about the exhaustion of n-3 PUFA supply sources. We have successfully prepared high-quality scallop oil (SCO), containing high eicosapentaenoic acid and phospholipids contents, from the internal organs of the Japanese giant scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis), which is the largest unutilized marine resource in Japan. This study compared the cholesterol-lowering effect of SCO with fish oil (menhaden oil, MO) and krill oil (KO) in obese type II diabetic KK-A y mice. Four-week-old male KK-A y mice were divided into four groups; the control group was fed the AIN93G-modified high-fat (3 wt% soybean oil + 17 wt% lard) diet, and the other three groups (SCO, MO, and KO groups) were fed a high-fat diet, in which 7 wt% of the lard in the control diet was replaced with SCO, MO, or KO, respectively. After the mice were fed the experimental diet for 42 days, their serum, liver, and fecal lipid contents as well as their liver mRNA expression levels were evaluated. The SCO group had significantly decreased cholesterol levels in the serum and liver; this decrease was not observed in the MO and KO groups. The cholesterol-lowering effect of SCO was partly mediated by the enhancement of fecal total sterol excretion and expression of liver cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase, a rate-limiting enzyme for bile acid synthesis. These results indicate that dietary SCO exhibits serum and liver cholesterol-lowering effects that are not found in dietary MO and KO and can help prevent lifestyle-related diseases.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1021K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1021K) -
Hirofumi Enomoto, Shiro Takeda, Hajime Hatta2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 979-987
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSMatrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) is a powerful technique for visualizing lipids in biological tissues. Phosphatidylinositol (PI), a phospholipid in pork, is a major source of inositol in animal-derived foods believed to be protective against diseases related to pregnancy and cancer. However, the distribution of PI molecular species in pork is not well understood. Here, we performed MALDI-MSI analysis to investigate the distribution and composition of PI molecular species in pork chop comprising Longissimus thoracis et lumborum muscle (loin), intermuscular fat tissue, transparent tissue, and spinalis muscle. Twelve diacyl-PI molecular species were identified using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and MALDI-MS/MS analysis and visualized using MALDI-MSI. Spinalis muscle had the highest amount of identified PI molecular species, followed by loin, transparent tissue, and intermuscular fat tissue. The diacyl-PI molecular species containing hexadecadienoic, oleic, linoleic and eicosadienoic acids at the sn-2 position were mainly abundant in the loin and spinalis muscle, whereas those containing mead, arachidonic, docosatetraenoic, and docosapentaenoic acids at the sn-2 position were mainly abundant in both muscles as well as transparent tissues. Notably, the balance of PI molecular species differed among the tissues depending on fatty acid compositions at the sn-2 position. These results suggested that MALDI-MSI is a promising tool for assessing the association between individual pork tissues and the protective effects of PI molecular species against diseases related to pregnancy and cancer. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report showing tissue-specific distributions of PI molecular species in pork chop using MALDI-MSI.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3349K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3349K) -
Ayumi Fukazawa, Takuya Karasawa, Yuma Yokota, Saki Kondo, Toshiaki Aoy ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 989-993
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWe previously reported that consuming a ketogenic diet containing medium-chain triacylglycerols (MCTs) might be a valuable dietary strategy for endurance athletes. However, the long-term safety of the diet has not been established, and there is a concern that a higher intake of MCTs increases the liver triacylglycerol content. In this study, we found that consuming an MCT-containing ketogenic diet for 24 weeks decreased, rather than increased, the liver triacylglycerol concentration and did not aggravate safety-related blood biomarkers in male Wistar rats. Our results may therefore suggest that the long-term intake of a ketogenic diet containing MCTs may have no deleterious effects on physiological functions.
View full abstractDownload PDF (314K)
-
Claudete da Costa-Oliveira, Ygor Jessé Ramos, George Azevedo de Queiro ...2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 995-1005
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis work aimed to evaluate the impact of different storage conditions and light and temperature exposures on the visual aspect and chemical composition of the essential oil (EO) of Piper lhotzkyanum Kunth, obtained from leaves by hydrodistillation from a region of high altitude. For this purpose, aliquots of the EO were stored for up to 90 days (a) under a refrigerator condition of 5 ± 3°C, (b) under a long-term (LT) condition of 30 ± 2°C and 75 ± 5% relative humidity (RH) and an accelerated condition (AS) of 40 ± 2°C and 75 ± 5% RH, and (c) in a photostability test achieved in amber and colorless glass vials. The changes were monitored on days 0 (control), 60, and 90 for the refrigerator, LT, and AS conditions. All EO chemical analyses were assessed by GC-FID and GC-MS for quantification and identification, respectively. It is reported, for the first time, that the EO of P. lhotzkyanum is rich in the sesquiterpenes β-elemene and α-zingiberene. No significant changes in the EO was observed, revealing a minimal impact of temperature on the sample at the different storage conditions. However, there was a change in the content of α-zingiberene to bicyclogermacrene after exposure to light. The visual appearance of the samples was altered for all test conditions except the refrigerator condition. These results can potentially contribute to the product development of a bioactive EO from leaves of P. lhotzkyanum, a sesquiterpene rich natural material.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (510K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (510K)
-
Atsuhiro Iguchi, Shigesaburo Ogawa, Yukihiro Yamamoto, Setsuko Hara2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 1007-1012
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, cation-exchange resin was used to prepare an esterified antioxidant, sinapate ethyl ester (SE), using ethanolic extracts from rapeseed. A concentration of sinapic acid using the cation-exchange resin in 80% ethanol (aq) and subsequent interesterification of the extract in ethanol using the same resin afforded a product with a purity of 64 wt% and 100% of SE yield. Moreover, after purification using preparative thin-layer chromatography, almost 100 wt% purity was obtained. In an auto-oxidation test, purified SE conferred a much higher antioxidative effect on the bulk oil, emphasising the effectiveness of the protocol using cation-exchange resin for the purification.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (716K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (716K) -
Adeolu A. Awoyale, David Lokhat2021Volume 70Issue 7 Pages 1013-1026
Published: 2021
Released on J-STAGE: July 01, 2021
Advance online publication: June 11, 2021JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, hybridized feedstocks (mixtures of biomass) of cassava peels plus yam peels, as well as corn cobs plus rice husks biomass, were optimized using the response surface methodology centered on the statistical design of experiments (DOE) of the Box-Behnken design (BBD), to produce bioethanol. The feedstocks were locally sourced, hybridized (mixed), pretreated, and fermented before being distilled in a UOP3CC continuous distillation column. The BBD was applied using a 3-level, 3-factor process variables using pH, time, and particle size, and indicated as X1, X2, and X3, respectively. The bioethanol yield from the two hybridized biomass feedstocks was predicted by the developed quadratic polynomial models from BBD. For the hybridized biomass mixture of cassava peels plus yam peels, the optimal condition was statistically predicted as pH 5.00, fermentation time of 120.00 hours, and particle size of 362.5 microns, the predicted bioethanol yield under the optimal condition was 115.75 mL per 1500 g of hybridized biomass and the average volume of bioethanol obtained was 125.00 mL per 1500 g of biomass, which is within the projected range of the model equation, same applies to rice husks plus corn cobs hybridized biomass, but with a better prospect for bioethanol production.
View full abstractDownload PDF (7898K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|