
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Masaki Honda, Kazuya Murakami, Soo Takasu, Motonobu Goto2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1097-1106
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialFucoxanthin, a characteristic carotenoid found in brown seaweeds, has been reported to exert beneficial biological activities, including antiobesity and anticancer activities Moreover, the Z-isomers of this compound potentially have greater bioavailability and biological activities than the naturally predominant all-E-isomer. Therefore, the consumption of Z-isomer-rich fucoxanthin through daily meals and dietary supplements may have beneficial effects. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of different extraction conditions on the Z-isomer ratio and recovery of fucoxanthin obtained from Undaria pinnatifida using supercritical CO2 (SC-CO2), particularly focusing on the high-temperature conditions that enhance thermal Z-isomerization. High-temperature SC-CO2 extraction at ≥ 120°C was found to enhance the thermal isomerization of fucoxanthin. For example, when the extraction was performed at 40, 80, 120, and 160°C and 30 MPa for 30 min with a co-solvent (ethanol), the total Z-isomer ratios were 11.7, 11.5, 18.7, and 26.5%, respectively. Furthermore, the high-temperature extraction significantly improved fucoxanthin recovery under high-pressure (≥ 30 MPa) conditions in the presence of the co-solvent. For example, when fucoxanthin was extracted at 40, 80, 120, and 160°C under the same conditions as above, the recoveries were 17.5, 20.6, 30.7, and 29.5%, respectively. Hence, the high-temperature SC-CO2 extraction of fucoxanthin from U. pinnatifida would not only enhance health benefits of fucoxanthin via the Z-isomerization but also improve the productivity. Moreover, the use of non-toxic CO2 and a low-toxicity organic solvent (ethanol) ensures that the final fucoxanthin product is safe for consumption. The Z-isomer-rich fucoxanthin obtained using this method is accordingly considered to have potential for use as a dietary supplement.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (650K) -
Wei Xiong, Qiang Liang, Xia Xu, Shi-qin Zeng, Ling Zhao, Pu Xuan, Ying ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1107-1116
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWater degumming, mainly removes hydrated phospholipids, is the most common method applying in traditional edible oil production. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) adsorption has been proved as a green and efficient method for removing phospholipids from rapeseed oil. But both methods exhibited poor effect on okra seed oil. Based on a hypothesis that SiO2 can adsorb non-hydrated phospholipids, removal effect of non-hydrated phospholipids in okra seed oil was studied. Single factor test and response surface design were used to optimize the SiO2 adsorbing process in water-degummed oil. Meanwhile, the qualities and flavor changes of okra seed oil before and after degumming were compared and analyzed. The results showed that the optimized degumming procedure was: 1.43% (w/w) of SiO2 added into the water-degummed oil, and the mixture was stirred at 33.52℃ for 30.47 min. The maximum non-hydrated phospholipids removal rate reached 43.3%. Comparing with crude okra seed oil, the optimal degumming method resulted in the increase of peroxide value and the decrease of induction period (IP) of the oil. However, it had the same safety as the water and the SiO2 degumming methods. It could retain 62% of total phenols, which was less than the water and the SiO2 degumming methods (both about 79%). The differences of E-nose sensors among oils were most likely caused by the pyrazines. It is necessary to study the composition and properties of phospholipids and develop new methods to further improve the phospholipids removal rate of okra seed oil.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3158K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3158K) -
Leila Rezig, Lucy Martine, Thomas Nury, Kamel Msaada, Nesrine Mahfoudh ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1117-1133
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe present study provides the fatty acid, tocopherol, phytosterol, and polyphenol profiles of some Mediterranean oils extracted from pumpkin, melon, and black cumin seed oils and those of dietary argan seed oil. Gas chromatography analysis revealed that oleic and linoleic acids were the most abundant fatty acids. Argan and melon seed oils exhibited the highest levels of oleic acid (47.32±0.02%) and linoleic acid (58.35±0.26%), respectively. In terms of tocopherols, melon seed oil showed the highest amount (652.1±3.26 mg/kg) with a predominance of γ-tocopherol (633.1±18.81 mg/kg). The phytosterol content varied between 2237.00±37.55 µg/g for argan oil to 6995.55±224.01 µg/g for melon seed oil. High Performance Liquid Chromatography analysis also revealed the presence of several polyphenols: vanillin (0.59 mg equivalents Quercetin/100 g) for melon seed oil, and p-hydroxycinnamic acid (0.04 mg equivalents Quercetin/100 g), coumarine (0.05 mg equivalents Quercetin/100 g), and thymoquinone (1.2 mg equivalents Quercetin/100 g) for black cumin seed oil. The “Kit Radicaux Libres” (KRL) assay used to evaluate the scavenging properties of the oils showed that black cumin seed oil was the most efficient. On the light of the richness of all Mediterranean oil samples in bioactive compounds, the seed oils studied can be considered as important sources of nutrients endowed with cytoprotective properties which benefits in preventing age-related diseases which are characterized by an enhanced oxidative stress.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (585K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (585K) -
Akriti Dhyani, Priyanka Kumari Singh, Rajni Chopra, Meenakshi Garg2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1135-1144
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSPerilla seed oil is mainly composed of omega-3 fatty acid (α-linolenic acid, ALA). Despite being nutritionally favorable and rich in unsaturated fatty acids, its low oxidative stability limits its application in food. Thus, the present study aimed to formulate a stable oil blend using perilla seed oil with selected vegetable oil of higher stability characteristics and balance the ratio of the fatty acids. Hence, improving the nutritional and functional value of the blended oil. Perilla seed oil was blended with different edible oil (palm olein, coconut oil, and groundnut oil) in ratios of 20:80 and 30:70. All the blended oils were studied for their fatty acid composition, physicochemical properties, oxidative stability, and nutritional quality index. It was found that perilla seed oil blended with saturated oil like palm olein had improved physicochemical properties and oxidative stability (0.5 h to 6.5 h). The fatty acids ratio of perilla and palm olein blends was close to the recommended value given by the World health organization (WHO). The nutritional quality indices (atherogenic index, the thrombogenic index, and hypocholesterolemic: hypercholesterolemic ratio) of blended oil were also improved compared to the individual oils.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (968K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (968K) -
Haoduo Yang, Ying Dong, Dongying Wang, Xuede Wang2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1145-1158
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe frying process, a popular cooking technique, is widely used in the food industry around the world for the production of fried foods. Nevertheless, it is always accompanied by potential challenges including lipid peroxidation of vegetable oils. In this study, the influence of the coriander leaves essential oil (CLEO) on the oxidative stability of sunflower oil under frying conditions and the sensory attributes of fried food (Chinese Mahua) during the sensory evaluation were investigated. The results indicated that compared with the control, CLEO at 0.12 g/kg could obviously suppress the increases for the total polar compounds (TPC), thiobarbituric acid (TBA), color, conjugated dienes (CD), conjugated trienes (CT) and viscosity of sunflower oil, and prominently restrain the oxidization procedure of unsaturated fatty acid (UFA). Meanwhile, the decline in the sensory attributes for the Chinese Mahua was significantly inhibited. Furthermore, the study revealed the antioxidant effect of CLEO was mainly attributed to two compounds, carvacrol and limonene, which were separated by the bioassay-guided fractionation. Consequently, CLEO and the two compounds may be employed as potential natural antioxidants to improve the oxidation stability of sunflower oil under frying conditions.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2570K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2570K)
-
Yoshimune Nonomura, Urara Tsuchiya, Mayu Taguchi, Reiichiro Tsuchiya, ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1159-1168
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFrictional properties are one of the most important physical factors in the design of cosmetic dispersions in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid. The effects of ingredients and formulations on frictional properties have been previously reported. In this study, the frictional properties of 33 cosmetic dispersions were evaluated using a sinusoidal motion friction evaluation system when applied on an artificial skin. A detailed analysis of the velocity dependence of the friction coefficient demonstrated that all cosmetic dispersions exhibited stable pattern and the friction behavior did not change during the round trip. We analyzed friction-based parameters by principal component analysis and demonstrated that the principal components Z 1 and Z 2 include the static friction coefficient μ s, kinetic friction coefficient μ k, delay time δ, and viscosity coefficient C, and that these factors are involved in characterizing friction dynamics. The cluster analysis on Z 1 and Z 2 suggested that these dispersions can be classified in three groups with respect to friction dynamics. These results can help understand the characteristics of cosmetics and control their function and utility.
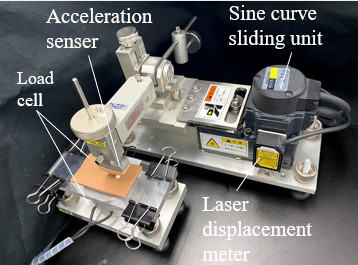 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2910K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2910K) -
Naoaki Ikeda, Kenji Aramaki2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1169-1180
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSHydrogels formed by low-molecular-weight gelators have reversible sol-gel transition and responsiveness to various stimuli, and are used in cosmetics and drug applications. It is challenging to obtain hydrogels using novel gelators because subtle differences in their molecular architecture affect gelation. Organogelators (which form organogels) are insoluble in water, and their use as hydrogelators has not previously been considered. However, a surfactant-mediated gelation method was reported in which organogelators were solubilized in water by surfactants to form hydrogels using 12-hydroxyoctadecanoic acid. To investigate whether this method can be applied with other organogelators, the formation of hydrogel using a glutamic-acid-based organogelator was studied here. Hydrogels were formed by solubilizing 1:1 mixtures of glutamate-based organogelators, N-lauroyl-L-glutamic acid dibuthylamide, and N-2-ethylhexanoyl-L-glutamic acid dibutylamide in aqueous micellar solutions of anionic surfactant (sodium lauroyl glutamate) and cationic surfactant (cetyltrimethylammonium chloride). The minimum gelation concentration of the hydrogel was ~0.2-0.6 wt%. By changing the molar fraction of cetyltrimethylammonium chloride in the mixed surfactant, either spherical or wormlike micelles were formed. The hydrogel with wormlike micelles had a higher sol-gel transition temperature than that with spherical micelles and formed fine self-assembled fibrillar networks. Additionally, the hydrogel with the spherical micelles was elastic, whereas that with wormlike micelles was viscoelastic, suggesting that networks of the organogelators and wormlike micelles coexisted in the hydrogel from the wormlike micellar solution. Moreover, the hydrogel suppressed the reduction in the storage modulus at higher temperatures compared with the micellar aqueous solution, indicating that the elastic properties of the organogelator networks were maintained at high temperatures. The gel fibers of the hydrogel partially formed a loosely aggregated structure as the temperature increased, the fibers bundled via hydrophobic interactions, and new cross-linking points formed spontaneously. This phenomenon corresponded with an inflection point in the temperature-dependent storage modulus of the hydrogel.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4281K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4281K)
-
Iram Liaqat, Zubreen Shaanzeh, Asia Bibi, Urooj Zafar, Sajida Naseem, ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1181-1188
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBacterial resistance to already present antibiotics demands for new approaches in field of medicine. Scientists prefer nanoparticles (NPs) due to their promising potential in many applications. Two bacterial strains, Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis were used for biogenic synthesis of NPs. Characterization of prepared NPs was accomplished using UV-vis spectroscopy and fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The prepared NPs were confirmed by the color change from pale yellow to having white deposition for Zn NPs while from dark green to light green for Ni NPs. UV-vis spectroscopy of E. coli and B. subtilis based ZnNPs showed highest peak at 354nm and 362nm, respectively. Likewise, E. coli and B. subtilis NiNPs showed peaks at 246 nm and 238 nm, respectively. Antibacterial activity of B. subtilis based ZnNPs showed significant (p ≤ 0.05) zone of inhibition (ZOI; 27.3±0.6) against B. subtilis and 26.66±0.67 against E. coli at 100 mg/mL. Antibacterial activity of E. coli based ZnNPs showed 8.3±0.3 ZOI against B. subtilis and 6.6±0.3 ZOI against E. coli while NiNPs showed (25.0±0.0 mm) (ZOI) against B. subtilis and (25.0 ± 0.3 mm) against E. coli. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of E. coli ZnNPs showed values of 6.7±0.3 μg/mL for E. coli and 4.7±0.3 μg/mL for B. subtilis. MIC of B. subtilis ZnNPs showed 5.3±0.3 μg/mL for E. coli and 6.6±0.3 μg/mL for B. subtilis while NiNPs showed 33.0±1.0 μg/mL against E. coli and 24.0±1.0 μg/mL against B. subtilis as effective inhibitory concentrations. Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of E. coli ZnNPs showed 7.3±0.3 μg/mL for E. coli and 8.3±0.3 μg/mL for B. subtilis. MBC of B. subtilis ZnNPs showed 7.6±0.3 μg/mL for E. coli and 8.6±0.3 μg/mL for B. subtilis while NiNPs showed 45.7±1.3 μg/mL against E. coli and 33.0±1.0 μg/mL against B. subtilis as effective inhibitory concentrations. It was concluded from the current study that biogenically synthesized ZnNPs and NiNPs are effective as promising antibacterial agents and have potential applications in biomedical fields.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1090K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1090K)
-
Yutaka Hattori, Sayo Tsutsui, Chihiro Yamada, Yota Kobayashi, Tomoyuki ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1189-1193
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWe investigated the effects of dietary supplementation with sodium butyrate (NaB) on the lipid levels, gene expression, and proteins related to lipid metabolism in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) rat models fed a high-sucrose diet for 3 weeks. Supplementation with 1% and 3% NaB reduced high-sucrose-induced hepatic triacylglycerol levels and expression of genes and proteins related to fatty acid synthesis, such as fatty acid synthase and malic enzyme, in a dose-dependent manner. NaB supplementation did not affect hepatic cholesterol levels or expression of genes related to β-oxidation. NaB may prevent high-sucrose-induced NAFLD by repressing the fatty acid synthesis pathway.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (386K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (386K) -
Shunsuke Higaki, Reiko Inai, Susumu Mochizuki, Akihide Yoshihara, Tats ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1195-1198
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSweetspire (Itea) is the only plant that accumulates rare sugars d-allulose and allitol. However, no reports have indicated that sweetspire has a beneficial physiological activity in mammalians. We have examined the effect of dietary dried sweetspire powder (SP) on body fat accumulation in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Twenty-four male Wistar rats were randomized into three groups, the control (C), SP, and rare sugar (RS) groups. The SP diet contained 5% SP (contained 0.4% d-allulose and 0.6% allitol in the diet), and the RS diet contained the same amount of rare sugars as the SP diet. All rats were given free access to the experimental diets for 8 weeks. The percentages of intra-abdominal adipose tissue and total body fat were significantly lower in the SP group than in the C group, suggesting that SP has an anti-obesity effect. Furthermore, this anti-obesity effect may be attributed to the rare sugars in SP.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (274K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (274K)
-
Hidayat Ur Rahman, Muhammad Hamdi Mahmood, Najm Us Sama, Muhammad Afza ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1199-1206
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSPain is a sensation a humans sense as a protective mechanism against physical injury. This sensation is closely related to inflammation. It ranges from mild to highly obnoxious. It is well-known that the levels of the inflammatory biomarker, C-reactive protein (CRP), increase manifold in acute inflammation and pain. Olive oil, known to have many phytochemicals, has been traditionally used to alleviate pain. Amongst major phenolic compounds in olive oil are oleuropein (OLE), hydroxytyrosol (HT), tyrosol, and oleocanthal. Whether the analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties in olive oil are due to any specific interections is not known. Therefore, this study aimed to elucidate the possible anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive properties in those major phenolic compounds by using molecular docking software MOE 2015, comparing the energy value and binding site of phenolic compounds to that of well-known synthetic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and phosphocholine. The docking experiment showed that all compounds could directly interact with CRP. Oleuropein had the most potent interaction with CRP (-7.7580), followed by indomethacin (-6.0775), oleocanthal (-5.5734), ibuprofen (-5.3857), phosphocholine (-4.3876), HT (-4.2782), and tyrosol (-4.2329). Interestingly, the present study found other phytochemicals in olive oil that can be exploited as potential, safe, and cost-effective lead compound(s) for analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity, as supported by its molecular docking data.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2278K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2278K) -
Chunlian Li, Qiuyang Cai, Xianyi Wu, Zekai Tan, Lewen Yao, Shiyuan Hua ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1207-1219
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSUmbelliferae plants, which are widely used as traditional Chinese medicine because of their characteristics of relieving rheumatism, alleviating fever, circulating blood and easing pain. This experimental study was based on ear edema model caused by 12-O-tetracycline-propylphenol-13-acetic acid (TPA) in mice and compared with the Ibuprofen (Ib) group. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used to analyse the composition of the essential oils from the four studied Umbelliferae plants (Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, A. dahurica (Hoffm.) Benth. & Hook.f. ex Franch. & Sav., A. pubescens Maxim and Foeniculum vulgare Mill.). Biologically active components in volatile oils from the four studied Umbelliferae plants were evaluated. The expression levels of inflammatory cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and RelA (p65) in mouse skin were determined by immunohistochemical method. The refractive index of the four essential oils was calculated. A total of 239 compounds were identified by GC-MS from the four studied plants, and the main constituents were osthole (44.61%, APEOs), obepin (0.59%, APEOs & 86.58%, FVEOs), undecanol (8.58%, ADEOs), α-muurolene (7.95%, ADEOs) and cis-anethol (9.11%, ADEOs). E-ligustilide (0.14%, APEOs & 81.14%, ASEOs), (-)-spathulenol (0.08%, FVEOs & 1.21%, ASEOs), (-)-terpinen-4-ol (4.91%, FVEOs), 2-butylthiolane (5.76%, APEOs) and α-bisabolol (3.80%, APEOs). This study showed that all the essential oils from the four studied Umbelliferae plants contained various lactones, including ligustrongolactone, trans-anisol and imperatorin. According to the results of the TPA induction test in the mouse ear edema model, the essential oils of four Umbelliferae plants reduced the levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, COX-2, IL-6 and p65. All of them showed extraordinary biological activity in anti-inflammatory, so they have potential application value for biomedical products, pharmaceutical preparations, natural functional nutrients and cosmetic additives.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1221K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1221K) -
Hong Li, Yiwen Kong, Wei Hu, Sheng Zhang, Wei Wang, Min Yang, Yicheng ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1221-1228
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe antifungal mechanism of plant essential oil has always been a concern in the agriculture and forestry science field. In this investigation, besides the evaluation of inhibitory activities of twenty-three essential oils against Candida albicans in vitro, identification and quantification of the chemical composition of Litsea cubeba essential oil by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry were investigated. Further development, we assessed the mechanism of L. cubeba essential oil against C. albicans by molecular docking. Litsea cubeba essential oil displayed the strongest inhibitory activity among these oils and the diameter of the circle against C. albicans was more than 50 mm. Maximum three components were identified with trans-citral (33.6%), cis-citral (30.3%), d-limonene (8.2%). Secretory aspartate protease (SAP5) and β-1,3-glucan synthase (β-1,3-GS) are two key enzyme proteins that inhibit the growth of C. albicans. Molecular docking studies reveal chemical binding forces of cis-citral, trans-citral and d-limonene to SAP5 are -21.76 kJ/mol, -22.18 kJ/mol and -24.27 kJ/mol, to β-1,3-GS are -23.01 kJ/mol, -25.52 kJ/mol and -23.85 kJ/mol, respectively. The most preferable binding mechanism was observed against SAP5 and β-1,3-GS due to hydrophobic interaction, as well as hydrogen bonding between citral molecules. The research results suggest the mechanism of chemical components in L. cubeba essential oil inhibits the growth of C. albicans, which provides a reference to the development and utilization of essential oil.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1517K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1517K)
-
Sureeporn Saknaphawuth, Boontida Pongthawornsakun, Piyamit Toumsri, La ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1229-1239
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSOrdered mesoporous carbon (OMC) has attracted a great deal of attention as catalyst support due to their tunable morphological and textural properties. In this study, the characteristics and catalytic properties of OMC-supported Pt catalysts prepared by one-step modified soft-template self-assembly method (Pt/OMC-one-pot) were compared to the Pt impregnated on OMC, activated carbon (AC), and nonuniform meso/macroporous carbon (MC) in the selective hydrogenation of furfural to furfuryl alcohol (FA) under mild conditions (50°C, 2 MPa H2). Larger Pt particle size (~4 nm) was obtained on the Pt/OMC-one-pot comparing to all the impregnated ones, in which the Pt particle sizes were in the range 0.5 - 2 nm. Reduction step was not necessary on the Pt/OMC-one-pot and among the catalysts studied, the Pt/OMC-one-pot exhibited the highest furfural conversion and FA selectivity under aqueous conditions. The use of methanol as the solvent resulted in the formation of solvent product (2-furaldehyde dimethyl acetal) instead. The amount of Pt being deposited, location of Pt particles, and metal-support interaction strongly affected recyclability of the catalysts because some larger size Pt particles with weak metal-support interaction could be leached out during the liquid-phase reaction, rendering similar catalytic performances of the various porous carbon supported catalysts after the 3rd cycle of run.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4241K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4241K)
-
Anum Naseer, Saiqa Andleeb, Abdul Basit, Wajid Arshad Abbasi, Samina E ...2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1241-1252
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
Advance online publication: July 06, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSHeavy metals contamination in the soil is a major threat to wildlife, the environment, and human health. Microbial remediation is an emerging and promising technology to reduce heavy metals toxicity. Therefore, the present research aimed to isolate and to identify the heavy metals tolerated bacteria from the Eisenia fetida for the first time, and to screen the bacto-remediation capabilities and plant growth promoting traits of vermi-bacterial isolates. Vermi-bacteria was isolated from the gut of E. fetida, identified through staining, culturing, biochemical tests, and ribotyping. Plant growth-promoting traits were also evaluated. Phylogenetic results revealed that isolated Vermi-bacterial strains showed resemblance with Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus aryabhattai, Staphylococcus hominis, Bacillus toyonensis, Bacillus cabrialesii, Bacillus tequilensis, Bacillus mojavensis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus toyonensis, Bacillus anthracis, and Bacillus paranthracis. All identified Vermi-bacterial species are Gram-positive (rod and cocci) in nature, not only indicated the efficient biosorption of lead, cadmium, and chromium but also produce all plant growth stimulating traits such as indole acetic acid (IAA), amylase, protease, lipase, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, and siderophore production, and also act as a phosphate solubilizers. Bacillus anthracis showed significant production of siderophore (33.0±0.0 mm), phosphate solubilizing (33.0±0.0 mm), proteolytic (15.0±0.0 mm), and lipolytic activities (20.0±0.0 mm) compared to other vermi-bacterial isolates. Bioaccumulation factor results revealed that Bacillus anthracis showed more accumulation of Cd (12.00±0.01 ppm), Cr (5.38±0.01 ppm), and Pb (4.38±0.01 ppm). Therefore, the current findings showed that all identified vermi-bacteria could be used as potential bactoremediation agents in heavy metals polluted environments and could be used as microbial biofertilizers to enhance crop production in a polluted area.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3532K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3532K) -
Toshifumi Tojo, Miki Tsuruoka, Takeshi Kondo, Makoto Yuasa2022Volume 71Issue 8 Pages 1253-1260
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: August 04, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialAccording to current research, cancer cell growth is suppressed by ω-3 fatty acids, which are essential fatty acids. On the other hand, ω-3 fatty acids are metabolized to bioactivities in vivo. A systematic evaluation of the ability of ω-3 fatty acids and their metabolites to suppress cancer cell growth has not been sufficiently conducted. Our work evaluated the effect of ω-3 fatty acids (docosahexaenoic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid), trans fatty acid, and the metabolites (Resolvin E1, Maresin 1) on cancer cell growth suppressibility. Our results suggest that there may be optimal fatty acids depending on the kind of cancer cells, the presence or absence of hydroxyl group, and the double bond structure involved.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (818K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (818K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|