
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Febri Odel Nitbani, Putra Jiwamurwa Pama Tjitda, Hermania Em Wogo, Ann ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 781-793
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
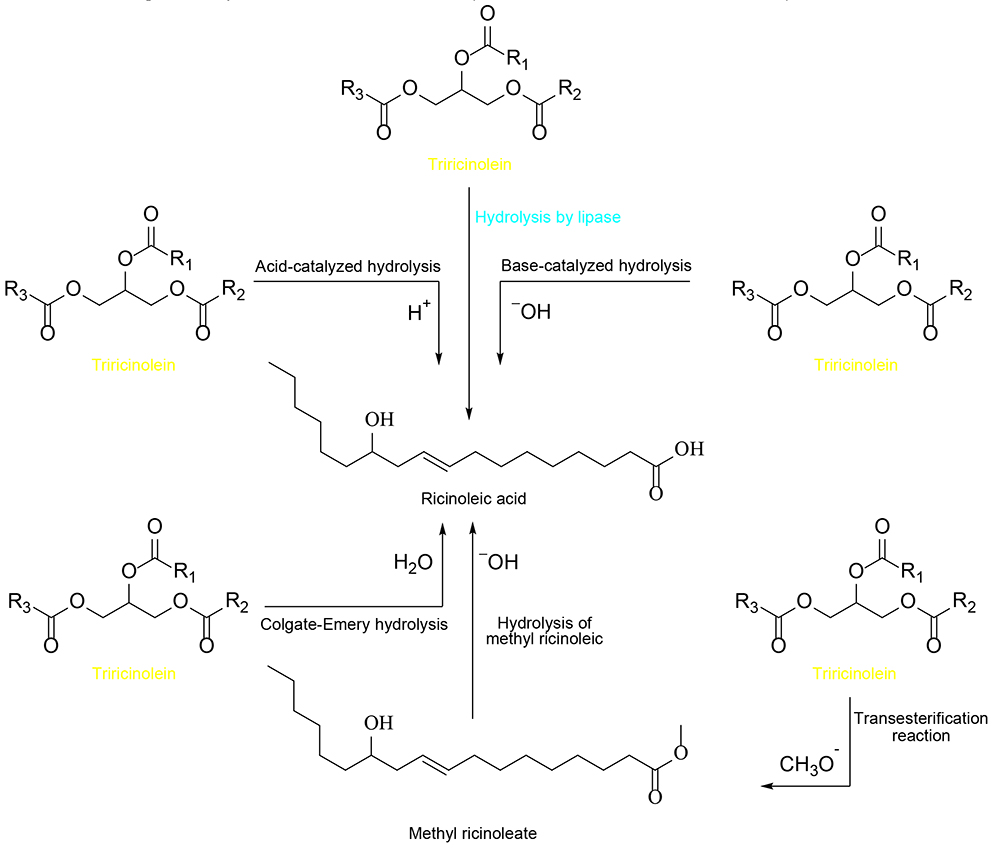
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCastor oil is a vegetable product extracted from Ricinus communis L (castor seed), which is primarily considered an important commercial value for the manufacturing of soaps, lubricants, coatings, etc. It is rich in hydroxylated fatty acids (ricinoleic acid, 89-92%) and is widely used in the cosmetic, pharmaceutical, oleochemical, and agricultural industries. This oil has also been confirmed as a bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, and antiherpetic agents, due to the ricinoleic acid having functional groups, such as -COOH, -OH, and -C=C-. Furthermore, it is converted into various acid derivative compounds with several applications. Therefore, this article reviewed some reaction stages to the preparation of ricinoleic acid from castor oil. Several methods or reaction pathways were employed in the preparation procedure, such as the Twitchell and Colgate-Emery processes, as well as the alkaline catalyzed, transesterification with methyl ricinoleic, and lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis, respectively. Although each of these preparation methods has advantages and disadvantages, the most effective technique was the hydrolysis through the use of the enzyme lipozyme TL IM. Besides being a green method, the conversion rate in the hydrolysis process was 96.2 ± 1.5%
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (676K) Full view HTML
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (676K) Full view HTML
-
Daniel Dodoo, Francis Adjei, Samuel Kofi Tulashie, Stephen Awuku, Jack ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 795-811
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis study conducts postmarketing surveillance for the photosensitised oxidation of vegetable oils (VOs) stored in different conditions in the marketplace during commercialisation. Coconut oil, palm kernel oil, soybean oil and sunflower oil were exposed to direct sunlight and kept in the dark for six weeks. The results showed a significant (p < 0.05) increase in PV and a severe decrease in the iodine value, chlorophyll, β-carotene, colour content, and the fatty acid compositions (oleic and linoleic acids mainly) in the light-exposed VOs. The FTIR analysis also identified the formation of the hydroperoxides (3444 cm-1), secondary oxidation products (1743 - 1723 cm-1) and the loss of the cis-disubstituted olefins (723 cm-1) bands in the light-exposed VOs. This indicated that oils exposed to light for an extended period of time could undergo photosensitised oxidation due to photosensitisers like chlorophyll. In contrast, the unexposed VOs showed no significant change (p > 0.05) in their chemical compositions. The photosensitised oxidation increased in the order: coconut oil < palm kernel oil < soybean oil < sunflower oil.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5862K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (5862K) -
Chunling Huang, Dong Cao2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 813-822
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
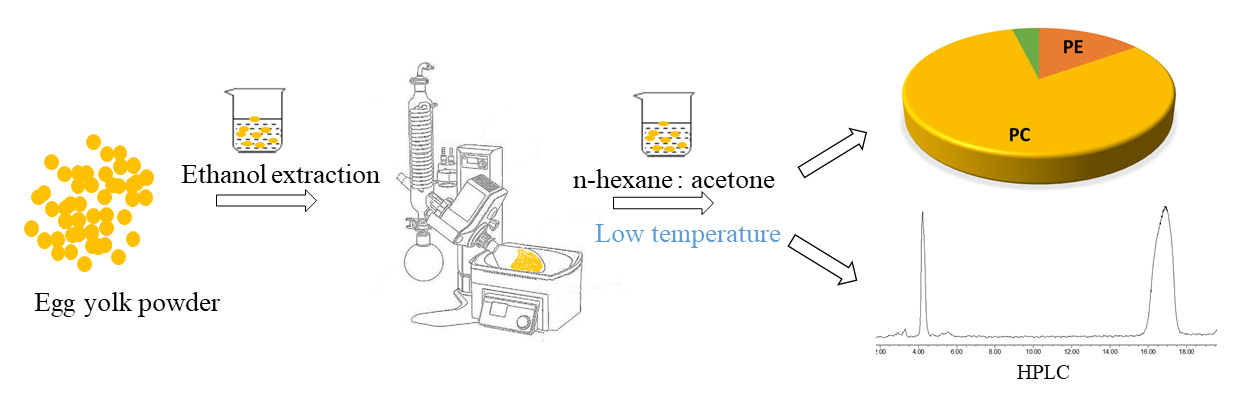
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSEggs are nutritious and cheap and easily available. Egg yolk is one of the sources of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). PC and PE have good emulsifying properties, and they are widely used and in high demand for pharmaceutical, feed and cosmetic applications. Red cordyceps egg yolk powder (RCEYP) was selected as the raw material to obtain high content of PC and PE by ethanol extraction and low temperature cryoprecipitation in n-hexane-acetone system (HAS), in which the process conditions of PC and PE extraction by HAS process were optimized. The phospholipids were quantified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with evaporative light scattering detector (ELSD). The effects of freezing time, material-liquid ratio, acetone washing times, solvent ratio of n-hexane to acetone and freezing temperature on the PC and PE contents and the phospholipid yield were investigated. The optimal conditions for the extraction of PC and PE from RCEYP by HAS were determined by Box-Behnken design (BBD) as follows: the solvent ratio of n-hexane to acetone was 1:6, the freezing time was 11.31 h, and the freezing temperature was -19°C. The total content of (PC+PE) in the phospholipids precipitated under these conditions amounted to 96.16%, of which 81.12% was PC and 15.04% was PE.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2006K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2006K) -
Sunday Edet Etuk, Kokoete Raymond Okokon, Uduak A Essiet2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 823-827
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSTrichosanthes cucumerina seed and seed oil have been investigated for their chemical, physico-chemical properties, characterization and fatty acid profile. The properties were assessed by standard methods and the fatty acid profile was carried out using gas chromatography fatty acid methyl ester analysis. The seed was found to contain 71.1% crude oil, 1.6% Crude Protein, 2.9% carbohydrate, 2.8% crude Fiber, and 1.6% Ash. Iodine, Peroxide, and Acid the molecular weights of the seed oil are 0.84 gI2 of oil, 2.0 meq O2/kg oil and 4.0 mg/KOH/g, respectively, with 4.0 Free Fatty Acid and a Saponification Value of 379.12 mg/g. The oil is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids that are vital for growth, maintenance of the cell membrane, development, and boosting of the immune system in humans. It qualifies to be classified as an edible vegetable oil and can also be useful in the soap and cosmetic industry.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (241K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (241K)
-
Takumi Motoyama, Yuka Katsuumi, Hiromu Sasakura, Tetsuya Nakamura, His ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 829-837
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSOil-in-water (O/W) emulsions containing ethanol have been used in food, cosmetics, paints, and other applications. However, O/W emulsions with long-term stability are difficult to produce at high ethanol concentrations because the adsorption of the emulsifier at the O/W interface is restricted by ethanol. In this study, to resolve this issue, we prepared ethanol-containing O/W emulsions with high dispersion stability using a series of polyglycerol monofatty acid esters (PGFEs) with different fatty acid chain lengths, which are bio-safe nonionic surfactants, as emulsifiers. First, aqueous PGFE solutions containing 0-50 wt% ethanol were prepared and then O/W emulsions were formed using limonene as the oil phase. When decaglycerol stearic acid ester (DGMS, C18) was used as the emulsifier, an O/W emulsion with fine droplets (~30 nm in size) was successfully obtained at an ethanol concentration of 35 wt%. This emulsion remained stable for more than four weeks, during which no phase separation occurred, indicating its high dispersion stability. Furthermore, aqueous DGMS solutions containing 30-40 wt% ethanol were viscous, and a lamellar liquid crystal phase was observed to be dispersed in these solutions. The formation of this lamellar liquid crystal phase at the O/W interface led to an interfacial film with superior viscoelastic properties. The results suggested that the stability of the emulsions was determined by the balance between the decrease in interfacial tension caused by the addition of ethanol and the density (rigidity) of the DGMS film formed at the O/W interface. Finally, to further improve the dispersion stability of the ethanol-containing O/W-type emulsions, O/W emulsions were prepared using a mixture of two PGFEs with different degrees of glycerol polymerization, that is, systems having different hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2695K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2695K)
-
Mudassar Hussain, Iram Liaqat, Sikander Ali, Nauman Aftab, Mobina Ulfa ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 839-834
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSEarthworm, a ubiquitous (but neglected) macro-invertebrate, is found in terrestrial vicinity of Pakistan. Moreover, the occurrence of earthworms is often diverse with fluctuating quantity depending upon abiotic factors and land usage patterns. The aim of this study was to summarize all the reported information related to earthworm diversity in different areas of Pakistan. Almost all the data published from year 2001 to 2021 were collected. Following data organization, total 42 earthworm’s species including five families (Acanthodrilidae, Lumbricidae, Moniligastridae, Octochaetidae and Megascolecidae) were reported from various researchers. Among five families, family Acanthodrilidae was found to have only one specie (Ramiella bishambari), Lumbricidae consist of 10 species (Apporactodea rosea, Allolobophora trapezoids, Allolobophora chloroticaa, Aporrectodea longa, A. caliginosa, Bimastus parvus, Eisenia fetida, Helodrilus foetidus, Lumbricus terrestris and L. rubillus), Moniligastridae has two species (Drawida nepalensis and D. pellucida) while Octochaetidae possess only one specie (Eutyphoeus incommodus). The most abundant and diverse family Megascolecidae consist of 28 earthworm species in all habitats of different regions of Pakistan. Among geographical areas, Faisalabad was found as the richest territory with most reported earthworm species (i.e. 28). The current study suggests further in depth research to explore the unidentified and/ missing species of earthworms in Pakistan.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1383K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1383K) -
Nazish Mazhar Ali, Hafiz Muhammad Tahir, Muhammad Kamran Khan, Khajid ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 845-852
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDifferent plants are used medically and thofese therapeutic plants have great importance for healing contagious wounds. This herbal treatment is actually also a substitute of different antibiotics and having less side effects on intestinal systems of animals. The foremost concern of this study was to observe the antibacterial activity of Cinnamum zeylanicum and Acacia nilotica. Pathogenic bacteria obtained from wound samples and later identified by biochemical and molecular characterization. Methanol (an organic solvent) was used to extract Cinnamum zeylanicum and Acacia nilotica to check their antimicrobial exertion by using agar diffusion method. Different antibiotics such as, ampicillin, oflaxocin, ticarcillin and cefexime, showed their susceptibility toward antibiotics. The zone of inhibitions for antibiotic and plant extracts’ antibacterial activity were measured. Pathogenic bacteria were identified as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenesby molecular characterization. These bacteria showed susceptibility to antibiotics and also the plant extracts. Antibiotic oflaxocin showed maximum activity against these two pathogens (12.25 ± 0.44 and 12.375 ± 0.47) while antibiotic cefixime showed minimum effect (1.25 ± 0.28 and 0.625 ± 0.25). Plant extracts showed significant antibacterial activity with maximum activity (14 ± 0.9 by Acacia nilotica and 12 ± 0.5 by Cinnamum zeylanicum) in 100% solution. It can be concluded thatmethanolic extract of traditional therapeutic plants proved to be a promising source of antimicrobial agents against antibiotic resistant bacteria. Cinnamum zeylanicum and Acacia nilotica were observed to be competent as antibacterial tool against pathogenic bacterial strains.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2352K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2352K) -
Wei Sun, Yong Zhang, Xiaolu Ren, Lingzhi Cui, Jianguo Wang, Xiaohong ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 853-861
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialCoronavirus is one of the RNA viruses with the largest genome; It is a group of viruses known to infect humans very little until the end of the 20th century, generally causing infection in animals (bird, cat, pig, mouse, horse, bat). It is the causative agent of 15-30% of seasonal lower and upper respiratory tract infections, and may rarely cause gastrointestinal and nervous system infections. We have obtained results for the collagenase and elastase enzymes were at the micromolar level. We obtained IC50 results for the collagenase enzyme for 6-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin 257.22 ± 34.07 µM and for 2,5-dihydroxyacetophenone 74.46 ± 8.61 µM. 6-Hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin and 2,5-dihydroxyacetophenone were considered good inhibitors for elastase enzyme. Additionally, these compounds significantly decreased human pancreatic cancer cell viability from low doses. In addition, 100 µM dose of all compounds caused significant reductions in human pancreatic cancer cell viability. IC50 results (IC50: 10-50 µM) were better than control. In the otherwords, the docking results suggest that both compounds tend to have lower efficacy on the main protease targets of SARS-CoV-2 than standard compounds, (NL-1 and NL-2). The reason for this is that the standard compounds interact strongly and more frequently with the target proteins, and the surface areas they cover on the active surface are much larger than the small ligand molecules studied.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1883K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1883K) -
Qiulian He, Peng Ma, Ramin Torshizi2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 863-873
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, some phenolic compounds including 4-Hexylresorcinol, 5-Pentadecylresorcinol, 5-Tricosylresorcinol, Bilobol, and Urushiol were tested against α-glycosidase enzyme from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and sorbitol dehydrogenase enzymes from sheep liver. These compounds determined good inhibition properties against α-glycosidase and sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH) enzymes. IC50 values were record in the range of 1.45±0.20-24.532±3.83 μM for α-glycosidase and 6.20±0.96-108.22±18.02 μM for SDH. These inhibitor compounds can be selective drug candidates as anti-diabetic agents, because of they have inhibition properties against both enzymes. In this study, the anti-oxidant activities of the molecules were compared with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Comparison was made with the experimental enzymes by molecular modeling calculations. In the cellular and molecular part of the recent study, the treated cells with some phenolic compounds were assessed by molecularly targeted therapy (MTT) assay for cytotoxicity and anti-acute lymphoblastic leukemia potentials on Clone 15 HL-60, HL-60, HL-60/MX1, and HL-60/MX2 cell lines. The IC50 of these compounds were µg/mL level against these cell lines.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3059K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3059K) -
Mehwish Saleem, Farzana Rashid, Iram Liaqat, Irfana Liaqat, Mobina Ulf ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 875-879
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSOne of the principal mechanisms that contribute resistance to antibiotics is the production of extended spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) in Gram negative bacteria. In the present study, molecular methods were used to evaluate the prevalence of the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-encoding CTX-M gene among Gram negative bacterial strains. In total, 148 clinical samples were collected from different tertiary care hospitals of Lahore, Pakistan. Disc synergy diffusion method was used to detect the presence of ESBL production. Moreover, antibiotic resistance patterns and molecular detection of bla CTX-M ESBLs, were also studied. The pathogens isolated from the 148 samples included Escherichia coli (43%) followed by Klebsiella sp. (28%), Proteus sp. (18%) and Pseudomonas sp. (11%). In all 148 strains, 95 (64%) were ESBL producers while 53 (36%) were non ESBL producers. The strains which were phenotypically ESBL producers, bla CTX-M were found in 46% E. coli strains, while 50% Klebsiella sp. were harboring the gene. A high resistance rate was observed against cephalosporins (cefopodoxime 67%, cefoperazone 73%, cephalexin 63% sparaxin 61%). Lower resistance was observed against meropenem among all isolated bacterial strains. Genotypic detection of bla CTX-M genes by PCR revealed 46% of E. coli and 50% of Klebsiella strains harbored bla CTX-M gene. The present study showed that ESBLs producers were resistant to commonly used antibiotics. Similarly, bla CTX-M ESBL production is more prevalent in our clinical isolates.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (535K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (535K)
-
Yingjun Song, Xu Li, Xiaozhou Liu, Zhaozhong Yu, Guofu Zhang2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 881-887
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
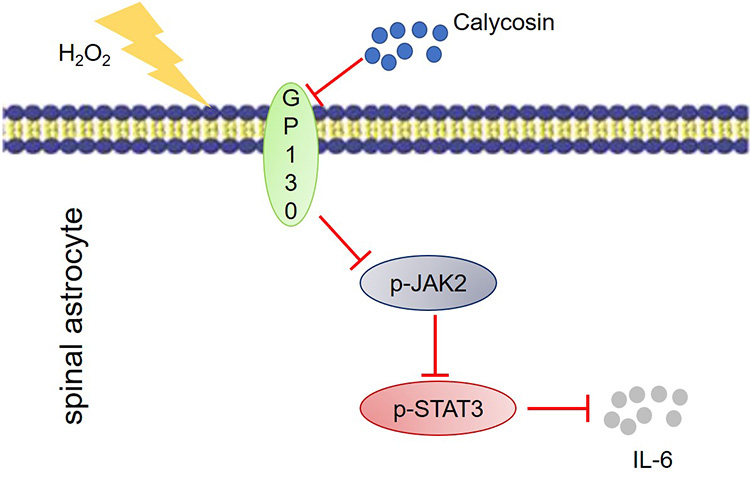
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSpinal injury is a complicated disease and is reported to be associated with damages on spinal astrocytes induced by oxidative injury. Astragali Radi, a famous traditional Chinese medicine, is reported to have promising efficacy in protecting injuries in the central nervous system. This study aims to investigate the effect of calycosin, an isoflavone phytoestrogens isolated from Astragali Radi, on oxidative injury in spinal astrocytes induced by H2O2 and the underlying mechanism. Primary rat spinal astrocytes were pretreated with 5, 10, and 20 μM calycosin and subjected to H2O2 treatment for 24 h to establish an oxidative injury model. Cell viability was detected using the CCK-8 assay to screen the optimized concentration of calycosin. Flow cytometry was used to evaluate the apoptotic rate and cell cycle. The expression level of Brdu was visualized using the immunofluorescence assay. Western blotting was used to measure the expression levels of p-JAK2, p-STAT3, p-AKT, GP130, and IL-6 in spinal astrocytes. We found that proliferation was inhibited and that apoptosis was induced by the stimulation of H2O2. The expression levels of p-JAK2, p-STAT3, p-AKT, GP130, and IL-6 were significantly elevated in H2O2-treated astrocytes. After the treatment of calycosin, proliferation was facilitated, and apoptosis was suppressed. These phenomena were accompanied by the downregulation of p-JAK2, p-STAT3, p-AKT, GP130, and IL-6, which were abolished by the co-administration of PI3K (ly294002) or STAT3 (stattic) inhibitor. Overall, calycosin alleviated oxidative injury in spinal astrocytes by mediating the GP130/JAK/STAT pathway.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3036K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3036K)
-
Kento Miyamoto, Sakura Hasuike, Hirona Kugo, Wanida Sukketsiri, Tatsuy ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 889-896
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
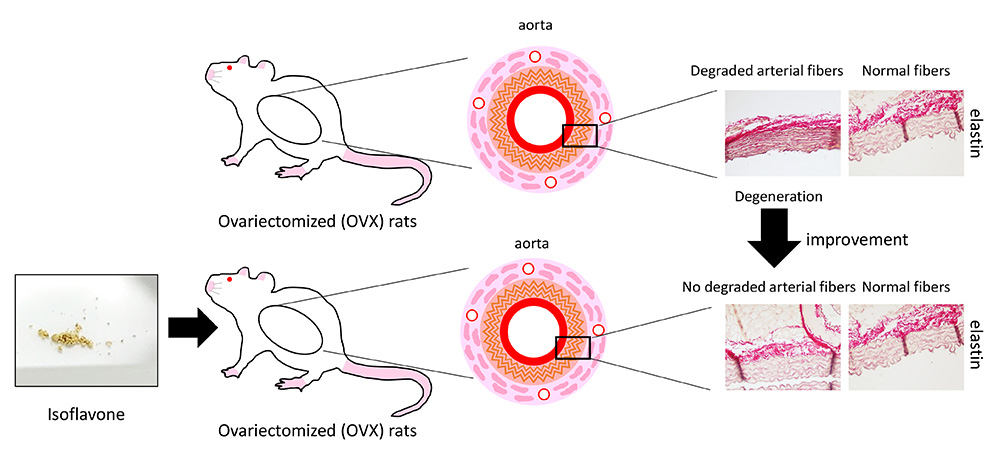
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWomen are more resistant to vascular diseases; however, the resistance is reduced after menopause. It has been reported that the risk of vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis and abdominal aortic aneurysm is increased in postmenopausal women. Currently, methods to prevent vascular disease in postmenopausal women have not been established. Isoflavones are promising functional food factors that have a chemical structure similar to estrogen. In this study, we investigated the effects of isoflavones on ovariectomized (OVX)-induced degeneration of the aortic wall in mice. Increased destruction of elastic fibers in the thoracic and abdominal aorta was observed in the OVX group, and isoflavones attenuated the destruction of elastic fibers. The positive areas of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in the OVX group were higher than those in the control group. Isoflavones decreased the positive areas of MMP-2 and MMP-9 compared to those in the OVX group. These data suggest that isoflavones have a suppressive effect on OVX-induced degeneration of the aortic wall by inhibiting the increase in MMP-2 and MMP-9.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1601K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1601K)
-
Kento Iwai, Khimiya Wada, Feiyue Hao, Haruyasu Asahara, Nagatoshi Nish ...2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 897-903
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
J-STAGE DataDirect aziridination of a nitrostyrene is achieved upon treatment with an alkylamine and N-chlorosuccinimide. The reaction is initiated by the Michael addition of amine to nitroalkene. Subsequent N-chlorination and nucleophilic substitution at the nitrogen atom afford 1-alkyl-2-nitroaziridine diastereoselectively. This reaction mechanism was clarified by NMR studies.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (558K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (558K)
-
Minoru Yoshimoto, Shigeru Kurosawa, Mutsuo Tanaka2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 905-913
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe temperature dependence of the resonant length, molecular weight, and rheology (shear viscosity and shear modulus) of chemisorbed soft matter on a solid-liquid interface oscillating at a megahertz frequency was studied using a quartz crystal microbalance. As a form of chemisorbed soft matter, self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) formed from six types of mercapto oligo(ethylene oxide) methyl ethers were used. A systematic analysis using the Voigt model showed that the variation in effective hydrated thickness (sensed mass), which is related to the resonant length, was classified into three types based on the molecular weight. As a result, a 2.2-nm change in the resonant length occurred in the studied temperature range from 10 to 35℃. Moreover, the variation in the effective hydrated thickness was dependent on the shear viscosity and shear modulus of the SAMs. A further investigation revealed that the relationships η 1∝M n 0.13 and μ 1∝M n 0.30 could be estimated regardless of the temperature, where η 1 and μ 1 are the shear viscosity and shear modulus of the SAM, and M n is the molecular weight of mercapto oligo(ethylene oxide) methyl ether. As a result, we revealed that the experimental results followed the polymer formula irrespective of temperature.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (596K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (596K) -
Chao Ju, Weimin Li, Qin Zhao, Xiaobo Wang2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 915-925
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, bio-based ionic liquid prepared from ricinoleic acid and choline was firstly used as additive in lithium base grease. The characterization and tribological performance of the prepared ionic liquid ([cho][ricinoleic]) as additive in grease were studied compared with the traditional ionic liquid such as L-P104. All the concentrations showed promising friction-reducing and anti-wear properties, though a 3% concentration has superior lubricating properties than others. Furthermore, [cho][ricinoleic]) can greatly enhance the lubrication capability of lithium base greaseunder different frequency and load at room temperature. Although L-P104 showed good lubricating performance than [cho][ricinoleic] at 150°C, the chosen formulation (1.5% [cho][ricinoleic] + 1.5% L-P104) could have better synergism at high and room temperature, which could be a good supplement to ionic liquid as grease additive. Thin films formed according to the results of SEM and XPS were attributed to be the main account for the preferable tribological properties of [cho][ricinoleic] in lithium base grease.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4120K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4120K) -
Masato Amano, Kazuaki Hashimoto, Hirobumi Shibata2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 927-932
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
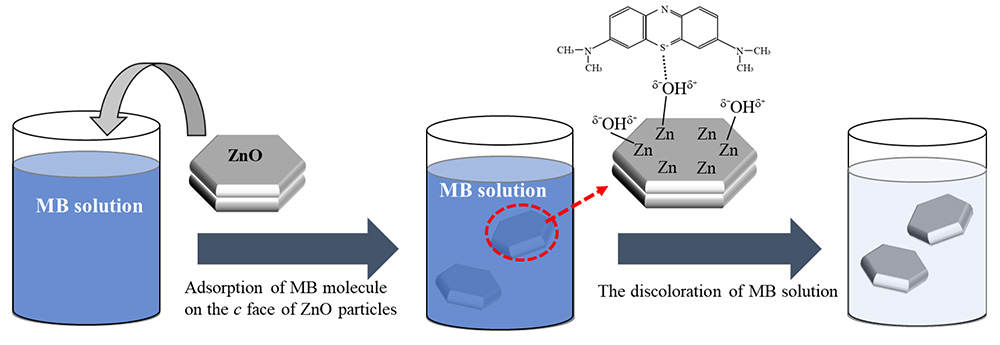
Advance online publication: May 18, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSHexagonal plate-like ZnO particles with a high degree of c-face orientation have been synthesized using hydrothermal method in the presence of various anionic surfactants bearing different hydrocarbon chains. The c-face of the ZnO particles increased upon increasing the surfactant alkyl chain length. The photocatalytic activity of the as-obtained hexagonal plate-like ZnO particles was evaluated using the degradation of methylene blue (MB). Although the specific surface area of hexagonal rod-like particles is higher than that of hexagonal plate-like particles, the amount of MB adsorption on the ZnO particle surface was different for the hexagonal plate-like and rod-like particles. In addition, the hexagonal plate-like ZnO particles showed a significantly higher decrease in the MB concentration with the duration of ultraviolet light irradiation when compared to the hexagonal rod-like ZnO particles obtained in the absence of a surfactant. These results indicate that crystal-face-controlled ZnO with a high degree of c-face orientation exhibits high photocatalytic activity.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (917K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (917K)
-
2022Volume 71Issue 6 Pages 933
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: June 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (110K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|