
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Olusola Samuel Jolayemi, Caleb Iyanu Alagbe2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1565-1575
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIndustrial application of castor oil is anchored on both agronomical and technological variables that intrinsically influence its quality properties. Therefore, castor oils of two varieties (Gibsoni and Carmenicita), extracted by screw press, solvent and traditional methods were compared in terms of oxidative stability indices, quality parameters and fatty acid distributions. General factorial analyses showed the significance of both factors on the oil yield, color intensity, moisture content, oxidative stability indices, most of the oil’s fatty acids and other quality parameters. Gibsoni variety yielded more oil at the range of 40.12 - 53.51%, especially in solvent extraction. The two oxidative stability indicators; peroxide value (PeV) and free fatty acids (FFA) favored traditional extraction and were significantly higher in oils of Carmenicita variety, at 4.26 - 7.21 meqO2/kg and 2.55 - 3.94%, respectively. In addition to ricinoleic acid (85.93 - 89.19%), other fatty acids characterized in the oils include, oleic (4.73 - 5.84%), stearic (1.41 - 2.50%), linoleic (1.08 - 3.41%), and palmitic acids (0.60 - 1.29%). Saponification (SaV) and iodine values (IoV) of the oils were unaffected by varietal differences or extraction processes and the ranges recorded in both varieties were within ASTM (175 - 187 mgKOH/g) and EN 14214 (120-140 g I2/100 g) acceptable limits. Principal component analysis (PCA) model built on the data of the oils further emphasized the significance of these two factors in quality characterization of castor oil.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (741K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (741K) -
Yu-yao Chen, Xing-yu Zhou, Shan-hua Qian, Jing-hu Yu2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1577-1589
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn order to investigate how the addition of two common ingredients in chocolate, sugar and milk powder, affects the mechanical properties of solid chocolate, uniaxial compression tests and wedge fracture tests were carried out using four ratios of chocolate as the experimental material. Mechanical properties such as Young’s modulus and fracture toughness were directly correlated with textural properties such as hardness, elasticity, and brittleness. The results show that adding sugar increases Young’s modulus and fracture toughness of chocolate, while milk powder is the opposite. In equal amounts of both, sugar played a more substantial role. In combination with the properties exhibited by chocolate in the above tests, data from creep tests were collected to improve the classical Bingham model and develop a new constitutive model for predicting the mechanical behaviour of solid chocolate with different ratios of added sugar and milk powder. The new four-component constitutive model allows for a more accurate fit to the creep test data and this work provides some suggestions for making different tasting chocolates by adjusting the addition of ingredients.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (863K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (863K) -
Wuttisan Khiowthong, Prachasanti Thaiyasuit2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1591-1603
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe continuous production of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) from waste cooking oil (WCO) via transesterification was carried out under theoretical methanol to oil molar ratio using a high-performance bumpy surface rotor reactor (BSRR). Three types of rotors with different area fractions (AF) of 6.9%, 13.8% and 27.6% were used to equip the BSRR. The selection of the highest performance rotor was compared by factorial experiments. Absolute methanol with 99.9 vol% purity was used as the reactant and potassium hydroxide with 90 wt% purity was used as the base catalyst. Response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to design the experiments and predict the optimal conditions. The three variables in RSM were 0.58-1.43 wt% potassium hydroxide concentration [KOH], 2160-3840 rpm rotor speed, and 1.38-4.74 L/min flow rate. The performance was the specific energy consumption (SEC). The highest performance rotor was AF27.6%. In the first step, the transesterification process was performed using [KOH] 1.5 wt%, a rotor speed of 3000 rpm and a flow rate of 2.027 L/min to produce 98.6 wt% FAME and using SEC at 12.5 W h/kg. In the second step, RSM predicted the optimal condition of [KOH] 1.016 wt%, rotor speed 2910 rpm, flow rate 2.134 L/min and FAME content 97.3 wt%. The actual FAME content averaged 97.16 wt%. The biodiesel properties complied with the EN 14214 standard. This biodiesel production can reduce the cost of methanol by one-half and the cost of KOH by one-third. The energy consumption is only 0.012 kW・h/kg, so the methanol recovery process is not necessary. It has low KOH residue, so washing with water is superfluous and uses minimal energy, which can reduce a lot of costs. The high flow rate of 128 L/h can be used to scale up commercial production.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1034K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1034K) -
Salwa Ali Mohamed Ali, Ali Mahmoud Muddathir, Amro B. Hassan2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1605-1612
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis study aimed to evaluate the physical and chemical properties of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duchesne) seed oil obtained from local Sudanese pumpkins. Three different genotypes of the pumpkin fruits as round, elongated and bell shapes were collected from Elgadarif State, Sudan. The oil’s seeds’ physical and chemical characteristics were determined by viscosity, specific gravity, refractive index, oil content peroxide value, acid value, saponification, unsaponifiable, pH, iodine value, total polyphenols and fatty acid content. The results revealed that there were significant (p < 0.05) differences in the oil content and chemical characteristics (except acid value and pH) of oil among the different pumpkin fruit genotypes. Linoleic and oleic acids were the primary fatty acids among the different pumpkin fruit genotypes. However, there were no significant (p < 0.05) differences in the fatty acid content and physical properties of the seed’s oil. The high oil content, phenolic content and essential fatty acids indicated that the obtained oil from different local Sudanese pumpkins might impart health and nutritional benefit when involved in the food industry as a natural resource.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (801K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (801K) -
Bo Qiao, Xiaoya Li, Yi Wu, Tan Guo, Zhoujin Tan2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1613-1624
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDiet is the most direct and rapid contributor to the gut microbiome. Oils and fats are important nutrients in the human body. The effects of lard or vegetable blend oil on gut microbiota were investigated. Kunming mice were given lard or vegetable blend oil for six weeks. Changes in microbiota composition and abundance in lard or vegetable blend oil diets were analyzed by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Our study shows that the gut microbiota of mice changed significantly after ingestion of lard or vegetable blend oil. Lard may synergize with Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002. Vegetable blend oil has synergistic effects with Akkermansia, Roseburia, and Enteractinococcus. Coriobacteriaceae_UCG-002 showed a significant negative correlation with Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis. Roseburia was most strongly associated with Starch and sucrose metabolism. According to bacterial function prediction and correlation analysis, long-term consumption of lard or vegetable oil may affect glycolipid metabolism, but lard has a greater impact on human health and consequently host health.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3902K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3902K)
-
Makoto Uyama, Atsushi Takahara, Yuji Higaki, Norifumi L. Yamada, Hirok ...2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1625-1637
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSPolyethyleneglycol 12 mol / polydimethylsiloxane co-polymer (PEG-12 dimethicone) is a type of polyether modified silicone (PEMS), which can form a lamellar liquid crystalline phase, and is widely used in cosmetics. The structural changes of PEG-12 dimethicone caused by water contents as well as shear flow were evaluated using simultaneous measurements of rheology and small angle neutron scattering (Rheo-SANS) and neutron reflectometry (NR). At high PEG-12 dimethicone concentrations (≥ 36 wt%), a reorientation of plate-like lamellar structures were observed and the neutral orientation was the most favorable. However, lamella-to-vesicle transitions were hardly observed. PEG-12 dimethicone turned out to form a bi-layer on a hydrophilized Si-wafer in a similar manner to that in bulk though the structure had a certain level of roughness.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1413K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1413K) -
Shigekazu Yano, Senri Terada, Misaki Fukushi, Yuitsu Otsuka, Satomi Mi ...2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1639-1645
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialConsidering that iodine is highly volatile and has low solubility in water, it is utilized as an antiseptic in its complex form (iodophor) with a carrier material. Herein, we prepared the polysorbate 80-iodine complex and investigated its properties. In the presence of 0%, 0.01%, 0.1%, and 1% polysorbate, Pseudomonas putida NBRC 100650 growth was inhibited at 75, 75, 50, and 25 ppm iodine, respectively, indicating that high concentrations of polysorbate 80 enhanced the antibacterial activity of iodine. Absorption spectra of the mixtures of polysorbate 80 and iodine were analyzed; we observed that two peaks at 287 and 350 nm, derived from triiodide ions, shifted to the longer wavelength side in the presence of 0.1% and 1% polysorbate 80. Further, when 1% polysorbate 80 was added to the mixture of soluble starch and iodine, the peak around 580 nm arising from the amylose-iodine complex disappeared, indicating that polysorbate 80 captured iodine from the starch-iodine complex. We also found that polysorbate 80 retained iodine for approximately 4 months and prevented its volatilization; moreover, the mixture did not lose its growth inhibitory activity upon storage for approximately 4 months. Collectively, our data indicated that polysorbate 80 firmly retains low concentrations of iodine and that the polysorbate 80-iodine complex can serve as an antiseptic that can be stably stored for a long time.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
-
Rieko Tanaka-Yachi, Rena Otsu, Chie Takahashi-Muto, Chikako Kiyose2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1647-1653
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialBrown adipose tissue (BAT) functions as a radiator for thermogenesis and helps maintain body temperature and regulate metabolism. Inflammatory signals have been reported to inhibit PGC-1α activation and UCP1-mediated thermogenesis in brown adipocytes. Inflammation is mainly caused by cell hypertrophy and macrophage invasion due to obesity, and invading macrophages secrete inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL1β, and IL6, which suppress the thermogenesis in BAT. Tocopherol is a lipid-soluble vitamin with anti-inflammatory effects is expected to contribute to the suppression of inflammation in adipose tissue. In this study, we investigated the protective effect of tocopherols, α-tocopherol (α-toc) and δ-tocopherol (δ-toc), against brown adipocyte inflammation and thermogenesis dysfunction.
Inflammatory stimulation by TNF-α, a major inflammatory cytokine, significantly decreased the protein expression levels of UCP1 and PGC-1α in rat primary brown adipocytes. The pre-incubation of α-toc or δ-toc significantly suppressed the decrease in UCP1 and PGC-1α expression and lipid accumulation. Additionally, α-toc and δ-toc suppress the induction of ERK1/2 gene expression, implying that an antiinflammatory effect is involved in this protective effect. We fed mice a high-fat diet for 16 weeks and investigated the effects of α-toc and δ-toc in the diet. Intake of α-toc and δ-toc significantly suppressed weight gain and hypertrophy of brown adipocytes. Our results suggest that α-toc and δ-toc suppress the dysfunction of thermogenesis in brown adipocytes due to inflammation and contribute to the treatment of obesity and obesity-related metabolic diseases.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1147K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1147K)
-
Yun Feng, Yiding Ma, Tao Yu, Jingjiao Li2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1655-1661
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
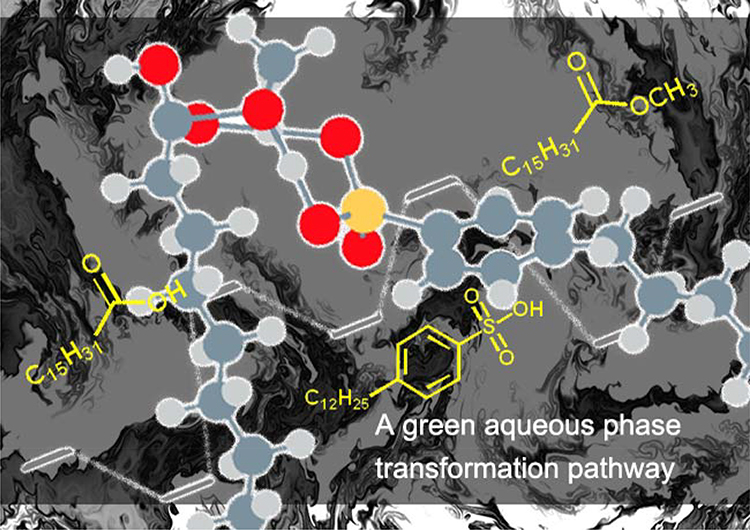
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis work provides quantified explanations for the thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics of esterification in aqueous phase, and how phase transfer catalysts improve water phase esterification of fatty acids in a computational-experimental way. Self-catalyzed reaction mode with or without solvation effects, water participated reaction mode, and catalytic reaction mode (catalyzed by p-dodecyl benzene sulfonic acid, DBSA) are discussed. Our results show that the initial self-catalytic reaction mode undergoes the energy barrier of 100.1 kJ/mol, and rises to 148.9 kJ/mol when water molecule is involved, which hinders the esterification reaction. With the DBSA catalyst, this energy barrier will drop to 97.5 kJ/mol and the water phase esterification is successfully promoted with the yield of 81%. The key kinetic factor of binding energy is discussed as that water molecule has a strong reactant binding competitiveness (with the binding energy of -57.9 kJ/mol, and the value for the non-aqueous phase mode is 3.0 kJ/mol) and DBSA has the binding energy with the value of -45.3 kJ/mol, so it can compete with water to form reactant complexes. This work is a successful practice of a computation-experiment combined scheme, and provides a quantitative basis for the improvement of phase transfer catalysts on water phase esterification reactions. The calculation mode and method of aqueous esterification make it possible to convert bio-based fatty acids into fatty acid esters in fermentation broth.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1597K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1597K)
-
Mami Hayasaki, Minami Iwakiri, Akane Shikata, Machi Oyama, Noe Souda, ...2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1663-1668
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe aim of this study was to identify and characterize the aroma components of absolute oil from natsudaidai (Citrus natsudaidai Hayata) flowers. A total of 43 aroma components were detected in the absolute oil of natsudaidai flowers using a headspace solid phase microextraction (SPME)-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The most abundant components from the absolute oil was linalool (31.14%), followed by methyl anthranilate, γ-terpinene, p-cymene, (E)-β-ocimene, limonene, indole and α-terpineol. The configuration of linalool from the absolute oil was assigned as (S)-form and its optical purities were determined as 89.36±0.36% enantiomeric excess using a SPME-chiral GC. These results indicated that the composition of aroma components in the absolute oil would influence the overall aroma qualities of natsudaidai flowers and the physiological effects on human.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (300K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (300K)
-
Iram Liaqat, Rabbia Ali, Uzma Hanif, Asma Latif, Asia Bibi, Sadiah Sal ...2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1669-1677
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSBiogenic synthesis of cobalt (Co) and copper (Cu) nanoparticles (NPs) was performed using the bacterial strains Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Prepared NPs were confirmed by a color change to maroon for CoNPs and green for CuNPs. The NPs characterization using FTIR showed the presence of functional groups, i.e., phenols, acids, protein, and aromatics present in the Co and CuNPs. UV-vis spectroscopy of E. coli and B. subtilis CuNPs showed peaks at 550 and 625 nm, respectively. For E. coli and B. subtilis CoNPs, peaks were observed at 300 nm and 350 nm, respectively. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of B. subtilis and E. coli Co and CuNPs was determined at 100 mg/mL concentration against two bacterial strains at 5, 2.5, and 1.5 mg/mL against fungal two strains F. oxysporum and T. viridi, respectively. B. subtilis CuNPs showed significantly higher inhibition zones (ZOI=25.7-29.7 mm) against E. coli and B. subtilis compared to other biogenic NPs. Likewise, B. Subtilis CuNPs showed lower MIC (4.3 ± 6.3) and MBC (5.3 mg/mL) values against both tested isolates. Antifungal activity of B. subtilis and E. coli CuNPs and CoNPs showed a concentration-dependent decrease in ZOI. Among all biogenic NPs, B. subtilis CoNPs showed the highest ZOI (25-30 mm) against F. oxysporum followed by E. coli CuNPs with maximum ZOI (20-27 mm) against T. viridi. Again, B. subtilis CoNPs and E. coli CuNPs showed lowest MIC and MFC values against both fungal isolates. In conclusion, the current study showed that biogenically synthesized B. subtilis Cu or CoNPs can be used as effective antimicrobial agents due to their potential antibacterial and antifungal potential.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (818K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (818K) -
Changhwan Ju, Yu Jin Lee, Hui Su Yoon, Byung Hee Kim, In-Hwan Kim2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1679-1688
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
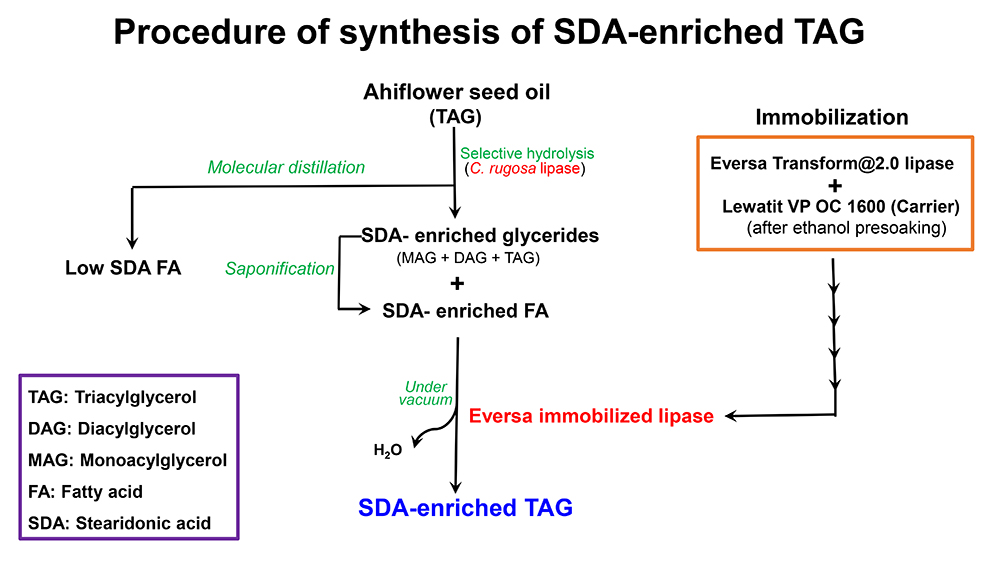
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSStearidonic acid (SDA) is a plant-based n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid with multiple biological activities. The enrichment of SDA and synthesis of triacylglycerol (TAG) were carried out consecutively via two lipase-catalyzed reactions, hydrolysis, and esterification. First, SDA was enriched into a glyceride fraction from ahiflower seed oil by Candida rugosa lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Under the optimum conditions of 35°C, 0.1% lipase powder of Lipase OF, and 50% buffer solution (based on the weight of total substrate), SDA was enriched from 21.6 to 40.7 wt% in glyceride fraction. SDA-enriched TAG was then synthesized from the SDA-enriched glyceride and the SDA-enriched fatty acid via esterification using an in-house immobilized lipase as a biocatalyst. The SDA-enriched fatty acid was obtained from part of the SDA-enriched glyceride by saponification and the in-house immobilized lipase was prepared from Eversa® Transform 2.0 using Lewatit VP OC 1600 as a carrier. The optimum reaction conditions for the synthesis of TAG were a temperature of 50°C, an enzyme loading of 10%, and a vacuum of 10 mmHg. A maximum conversion to TAG of ca. 94% was achieved after 12 h under the optimum conditions.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (536K)
-
Chikara Kato, Yuuri Suzuki, Isabella Supardi Parida, Shunji Kato, Hiro ...2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1689-1694
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
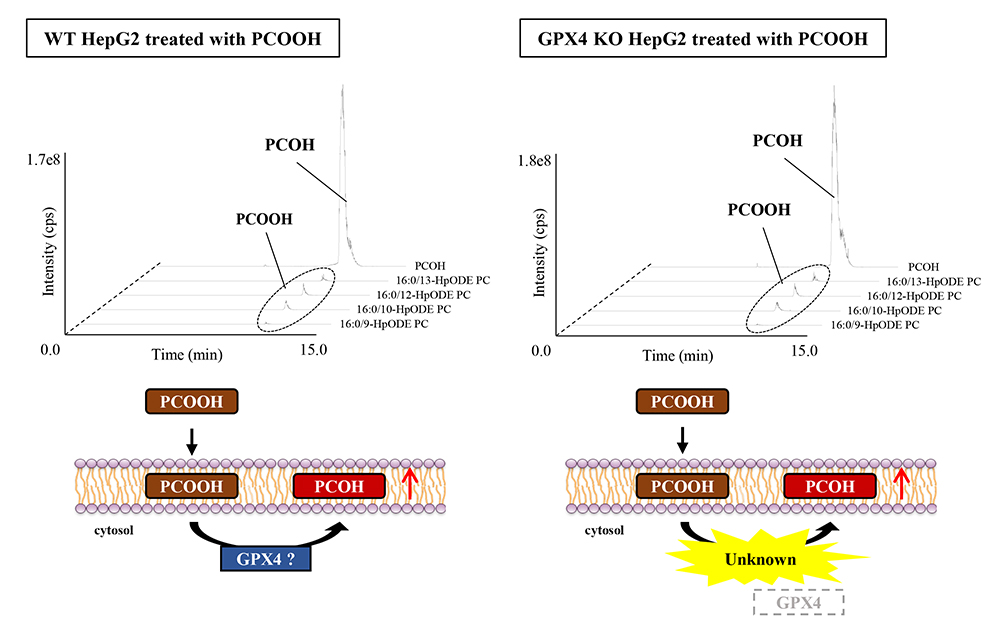
Advance online publication: October 05, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFerroptosis is mainly caused by iron-mediated peroxidation of phospholipids and has recently attracted attention due to its involvement in various diseases. At the center of it is supposedly the inability of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) to reduce excess peroxidized phospholipids (e.g., phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide (PCOOH)) that trigger ferroptosis. However, the involvement of enzymes other than GPX4 in ferroptosis is scarcely known. To elucidate this matter, we evaluated the uptake of PCOOH in a GPX4 knockout (KO) human hepatoma cell line HepG2 generated using CRISPR-Cas9. After confirming that GPX4 expression in the KO cells was below the detection limit, we cultured both wild-type (WT) and GPX4 KO HepG2 cells in a medium containing 50 μM PCOOH for 1-8 hours. By analyzing the level of PCOOH and its reduction product (phosphatidylcholine hydroxide, PCOH) in cells using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, we detected the cellular uptake of PCOOH. On top of this, we detected a large amount of PCOH not only in WT HepG2 but also in GPX4 KO HepG2, thus indicating the notable involvement of enzymes other than GPX4 (e.g., other GPX family, glutathione S-transferase, thioredoxin, or peroxiredoxin) in reducing PCOOH. Further corroboration of these findings hopefully leads to the development of novel methods to prevent ferroptosis-related diseases by targeting enzymes other than GPX4.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (453K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (453K)
-
2022Volume 71Issue 11 Pages 1695
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: October 28, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (98K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|