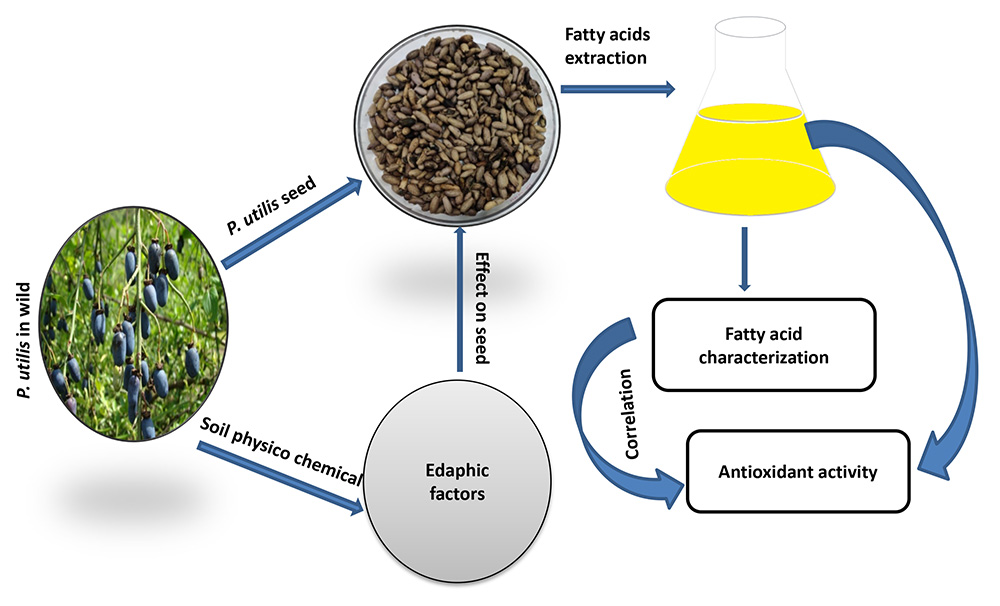
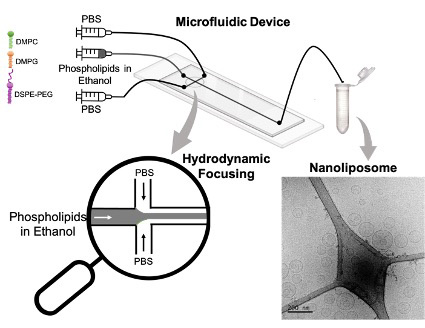
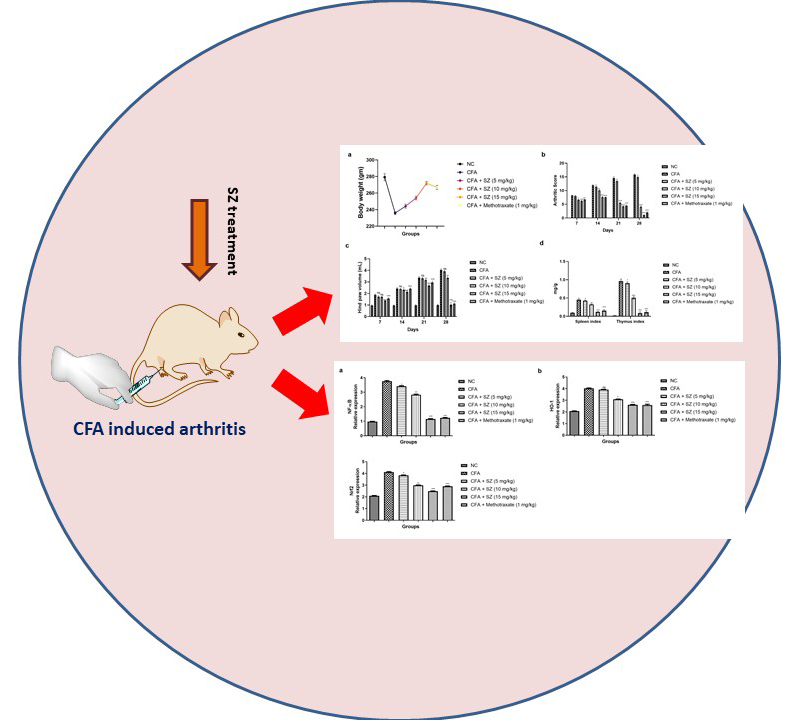
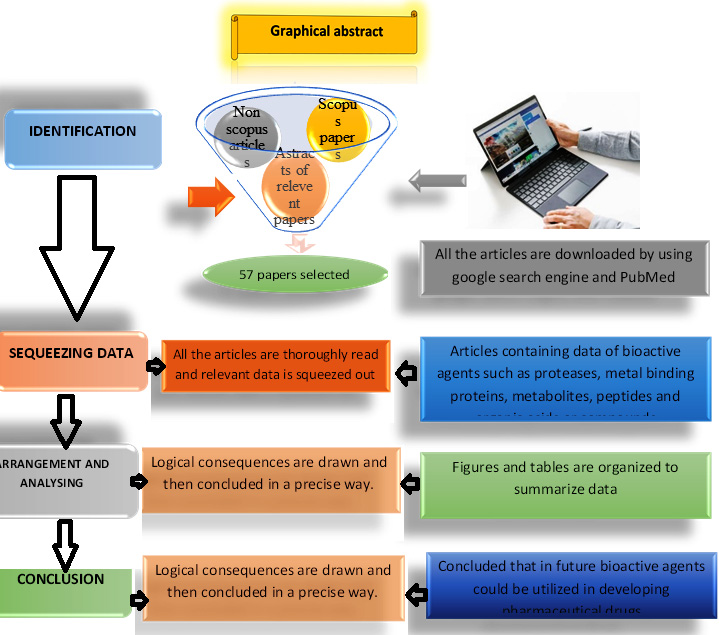
Volume 71, Issue 4
Displaying 1-19 of 19 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Oils and Fats
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 469-479
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (443K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 481-491
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (1351K)
Detergents, Surfactants, Interface and Colloid
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 493-504
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (2215K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 505-514
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (3426K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 515-522
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (2127K)
Biochemistry and Biotechnology
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 523-533
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (1035K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 535-540
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (308K) -
Bacteriocin Production by Lactobacilli and Their Role as Antibacterial Tool against Common Pathogens2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 541-550
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (1675K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 551-561
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (1542K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 563-573
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (827K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 575-585
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (1110K)
Medical Chemistry
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 587-597
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (2843K)
Nutrition and Health Function
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 599-607
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (628K)
General Subjects
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 609-618
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (737K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 619-626
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Advance online publication: March 14, 2022Download PDF (3629K)
Errata
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 627
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (273K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 628
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 15, 2022
Download PDF (111K)
Retraction
-
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 629
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2022
Download PDF (95K) -
2022Volume 71Issue 4 Pages 630
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: April 15, 2022
Download PDF (98K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|