
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Kouichi Nakagawa2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 1-6
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
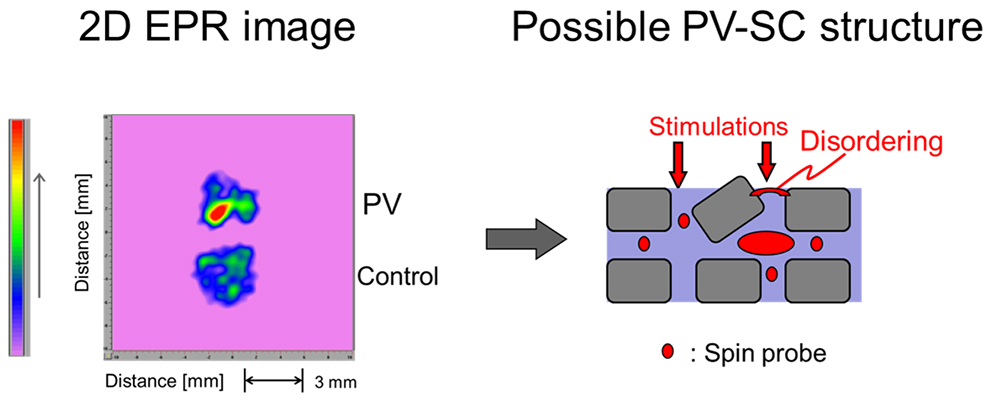
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLX-band (9.4 GHz) electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and electron paramagnetic resonance imaging (EPRI) were used for elucidating structural aspects of the stratum corneum (SC). We found that psoriasis vulgaris (PV)-SC has a less-ordered structure than that of the control SC, indicating the abnormal architecture of PV-SC. Different spectra were observed for the PV-SC. The three-line spectral pattern suggests that the 5-doxylstearic acid (5-DSA) is mobile or less rigid in the SC. The simulated order parameter (S0) value obtained for 5-DSA in the SC was approximately 0.20. The statistical analysis suggests that the value of the PV-SC is significantly smaller than that of the control (p < 0.01). Thus, we suggest that this EPR assay is of great use for evaluating SC function. In addition, the EPRI of various SC samples provides a useful image concerning SC status. A strong red image was observed for the PV skin. No red lesion region was observed in the control. The EPR images differentiated various sizes and number distribution concerning the disordered states in the SC.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (679K) Full view HTML
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (679K) Full view HTML
-
Kazuo Mukai, Masayuki Hirata, Junya Ito, Taiki Shiomi, Kiyotaka Nakaga ...2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 7-22
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialRecently, singlet-oxygen (1O2) quenching and aroxyl-radical (ArO·) scavenging rates (kQ and kS, respectively) of eight vegetable oils were measured in the ethanol/chloroform/D2O solution. Furthermore, the kQ and kS values and concentrations of four tocopherols and four tocotrienols contained in the vegetable oils were measured. In this study, the concentrations of nine fatty acids (including stearic, oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acids) comprising the above-mentioned eight vegetable oils were determined by gas chromatography. The kQ and kS values for ethyl stearate, ethyl oleate, ethyl linoleate, methyl linolenate, and glyceryl trioleate in the ethanol/chloroform/D2O solution were measured by UV-vis spectrophotometry. Based on the results obtained for the above-mentioned fatty acid esters, the kQ and kS values were estimated for nine fatty acids. Furthermore, comparisons of kQ values observed for the vegetable oils with the sum of the product {∑kQAO-i [AO-i]} of the kQAO-i values obtained for each antioxidant-i (AO-i) and the concentrations ([AO-i]) of AO-i (i.e., four tocopherols (& four tocotrienols) and nine fatty acids) contained in vegetable oils were performed. Based on the results, a detailed comparison of the contributions of the tocopherols (and tocotrienols) and the fatty acids to the 1O2-quenching rate constants (kQ) was performed. This indicated that both the tocopherols (and tocotrienols) and the fatty acids contribute to the 1O2- quenching. A similar comparison was conducted for the ArO· -scavenging rate constants (kS). The results suggested that only the tocopherols (and tocotrienols) contained in the oils contributed to the ArO· -scavenging, with negligible contribution from the fatty acids.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1700K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1700K)
-
Akshita Mehta, Chetna Grover, Kamal Kumar Bhardwaj, Reena Gupta2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 23-29
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSMicrobial lipases are used for the synthesis of various short chain esters such as octyl acetate, methyl salicylate, ethyl acetate and ethyl lactate. In this study, a purified lipase of Aspergillus fumigatus was utilized for the synthesis of two esters i.e. ethyl acetate and ethyl lactate. The purified lipase from Aspergillus fumigatus performed esterification of ethanol and acetic acid (at a molar ratio of 1:1) when incubated at 40℃ under shaking (130 min−1) for 12 h resulting in the formation of ethyl acetate (89%). In case of ethyl lactate maximum esterification (87.32%) was achieved when ethanol and lactic acid (500:100 mM ) was used in heptane resulting in the synthesis of ethyl lactate at 40°C under shaking (120 rpm) after 12 h of reaction time. These esters of short chain carboxylic acid and alcohols belong to the highly important natural aroma compounds and are used as green solvents in food and pharmaceutical industry.
View full abstractDownload PDF (380K) -
Hadeel Hosney, Ahmad Mustafa2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 31-41
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe aim of this work was to investigate the technical as well as the economic feasibility of producing 2-ethyl hexyl oleate (2-EHO), a non-phthalate plasticizer in a solvent free medium. The esterification reaction between oleic acid and 2-ethyl hexyl alcohol was carried out in a packed bed reactor (PBR) using Candida antarctica lipase B (Novozym 435; Novozymes; Copenhagen-Denmark) as biocatalyst. RSM was employed to optimize the esterification reaction conditions. The optimum reaction conditions were found to be flow rate of 1.5 mL/min, No. of cycles of 12 and molar ratio of 4:1 2-ethyl hexanol to oleic acid. The maximum experimental and predicated conversions were found to be 95.8% and 95.61% respectively. Formation of 2-EHO was approved by FTIR, 1HNMR and 13CNMR. From the economic prospective, PBR was capable of producing 2-EHO with a purity of more than 94% over 480 h without remarkable reduction of enzyme activity. This revealed an economic production of 2-EHO at a yield of 2 tons kg–1 lipase. The manufacturing cost was found to be $ 1.88 /kg 2-EHO, this contributed to a profit of about 30% compared to the commercial price of 2-EHO. Such results approve the technical and economic feasibility for this sustainable method in esters production.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3367K) -
Ning Yao, Shangde Sun2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 43-53
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSFerulic acid (FA), 4-hydroxyl-3-methoxy-2-benzylacrylic acid, has antioxidant, anticancer and ultraviolet absorption activities. However, the low hydrophilicity of FA has limited its application. Glyceryl ferulate (FG), which is an all-natural hydrophilic derivative of FA, can be used as an antioxidant and UV filter in food and cosmetic formulations. However, the applications of FG in these fields are limited due to its low content in nature. In this work, free liquid lipase was firstly used as a catalyst for FG preparation. Several different free liquid lipases (Candida antartica lipase-B, Candida antartica lipase-A, Thermomyces lanuginosus (Lipozyme TL 100L)) were screened and compared. The effects of the transesterification parameters (time, temperature, enzyme load and substrate ratio) were optimized and evaluated by response surface methodology. A reaction thermodynamic investigation was also performed. The results showed that, among the tested free lipases, the maximum FG yield (84.8±1.5%) was achieved using free Candida antartica lipase-B. Under the optimized conditions (an atmospheric system, an enzyme load of 11.1% and a 20:1 molar ratio of glycerol to EF at 70°C for 39.5 h), the FG yield and EF conversion were 84.8±1.5% and 95.7±1.2%, respectively. The activation energies of FG formation and EF conversion were 56.4 and 58.0kJ/mol, respectively.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2038K)
-
Yan Hao, Hou-Zhi Yu, Hai-Tao Yuan2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 55-63
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSBy employment of a rigid tripodal nitrogen-containing heterotopic ligand tris(1-imidazolyl) benzene (Htib), a new fluorescent Zn(II)-containing coordination polymer {[Zn(tib)2](NO3)2(H2O)3}n (1) with a rare two-fold interpenetrating (3,6)-connected pyr network topology has been successfully prepared under the solvothermal reaction conditions. Under the condition of visible light irradiation, rhodamine B (RhB) and methylene blue (MB) could be degraded with good performance. In the biological function study, the cytotoxicity of the synthetic was evaluated with CCK-8 detection kit on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). The inhibitory effect of compound on vcam-1 expression in the vascular endothelial cells was evaluated by RT-PCR. The effect of the complex on the inflammatory response in the vascular endothelial cells was determined via ELISA test of IL-1β and TNF-α. The results of pose scoring software as well as molecular docking was conducted to explore the interaction between compounds and VCAM, which might provide latent regulatory mechanisms along with binding sites for compounds.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2281K)
-
Yoshiko Moriyama, Kunio Takeda2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 65-72
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe secondary structures of human serum albumin (HSA) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were disrupted in the solution of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), while being hardly damaged in the solution of the bile salt, sodium cholate (NaCho). In the present work, the removal of dodecyl sulfate (DS) ions bound to these proteins was attempted by adding various amounts of NaCho. The extent of removal was estimated by the restoration of α-helical structure of each protein disrupted by SDS. Increases and decreases in α-helical structure were examined using the mean residue ellipticity at 222 nm, [θ]222, which was frequently used as a measure of α-helical structure content. The magnitudes of [θ]222 of HSA and BSA, weakened by SDS, were restrengthened upon the addition of NaCho. This indicated that the α-helical structures of HSA and BSA that were disrupted by the binding of DS ions were nearly reformed by the addition of NaCho. The NaCho concentration at which the maximum restoration of [θ]222 of each protein was attained increased nearly linearly with SDS concentration. These results indicated that most of the bound DS ions were removed from the proteins but the removal was incomplete. The removal of DS ions, examined by means of the equilibrium dialysis, was also incomplete. The α-helical structure restoration and the DS ion removal by NaCho were considered to be due to the ability of cholate anions to strip the surfactant ions bound to HSA and BSA. These stripped DS ions appeared to be more likely to form SDS-NaCho mixed micelles in bulk rather than SDS-NaCho mixed aggregates on the proteins.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (728K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (728K) -
Kitkanya Benjatikul, Hansa Mahamongkol, Paveena Wongtrakul2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages 73-82
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: January 01, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe physicochemical and sunscreen properties of marl as a function of particle size were investigated. The research findings established that the marl under investigation consisted of more than 95% calcium carbonate (CaCO3). The particles of marl inspected under a scanning electron microscope were calcite, which is the stable polymorph of CaCO3, with a rhombohedral structure. The particle size classification by the sieving method showed that grinding using a ball mill could downsize the marl particles by 2 to 3 times, reaching below 15 µm on average. Marl particles showed a tendency to reflect ultraviolet A (UVA) rays rather than UVB rays and a possibility to steadily absorb both UVAII and UVAI. Finer particles obtained after a longer grinding process demonstrated higher efficacy regarding UV reflection and absorption properties. The 3 wt.% marl displayed a sun protection factor (SPF) value of 1 to 2. However, marl demonstrated a good ability to protect against radiation over a broad spectrum range with a critical wavelength above 370 nm. The addition of marl in the formulation containing avobenzone and octinoxate had a positive synergistic effect because the marl was able to increase the UV absorbance efficacy (based on the area under the curve (AUC) value) and SPF value of the cream. Furthermore, it was also discovered that the added marl powder could slow the decrease in UV protection efficacy of the products in terms of the AUC calculated from the absorbance profile after exposure to simulated UV rays with an amplitude range of 10 J/cm2 to 40 J/cm2 for 30 min, which was similar to the results obtained from octocrylene and bemotrizinol.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1682K)
-
2020Volume 69Issue 1 Pages e1
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: August 08, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSDownload PDF (26K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|