
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Shigesaburo Ogawa2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 489-499
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
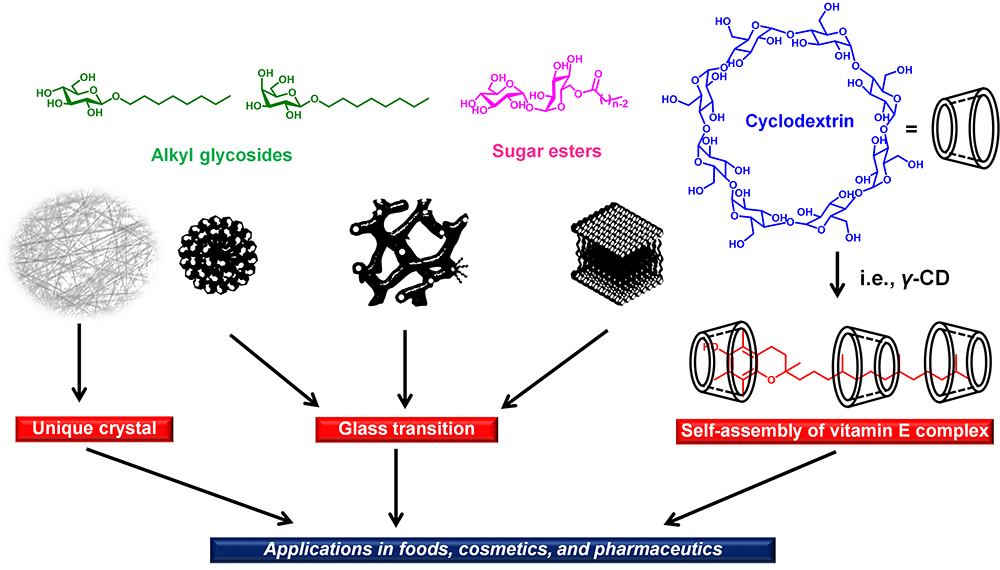
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLCurrently, numerous fascinating molecular assemblies are used in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Sugar-based amphiphiles are representative constituents of these molecular assemblies. Despite numerous studies on these generic compounds, many aspects remain unexplored even in aqueous systems. In this review, molecular assembly studies of sugar-based amphiphiles in aqueous systems are summarized. First, recent advances in molecular assembly studies, including the glassy state of lyotropic and thermotropic liquid crystalline (LC) phases, modulated crystal phases, and coagels consisting of nanofibers of alkyl β-D-glycosides, are presented. Second, research on thermotropic LC phases under desiccated conditions of trehalose fatty acid monoesters to clarify the fundamental behaviors of the glassy state and their use as stabilizers of glass-forming surfactants for pharmaceutical applications are discussed. Several effective X-ray analytical approaches are included to identify or clarify these phenomena, unknown or unsolved for a long time. Third, a comprehensive analysis of vitamin E (tocopherol)-cyclodextrin in aqueous systems is presented. Along with these topics, the importance of investigating stabilizer-free functional components, considered minor components, is highlighted. These unveiled phenomena or concepts will contribute to the development of nanoarchitectonics covering the self-assembly and selforganization of soft molecules.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3775K) Full view HTML
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3775K) Full view HTML
-
Carla del Carpio-Jiménez, Ruth Sara Molleda-Gutierrez, Profeta Tapia-D ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 501-509
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
Advance online publication: April 11, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, Chenopodium pallidicaule (Cañihua) oilseed was investigated to determine the composition, and main physico-chemical properties to establish its potential cosmetic applications. The results were compared with well-known vegetable oils. The extraction yield was 2.14±0.01 g of extracted oil/100 g of dry-weight seeds. Unsaturated fatty acids were the most abundant in Cañihua oil. The major unsaturated fatty acid was linoleic acid (42.1%), followed by oleic acid (24.7%) and linolenic acid (3.0%). The specific gravity was 0.897±0.01 (20°C), the average acid value was 0.48±0.14 mg / KOH, the peroxide value was 5.0±1.34 mEqO2/kg, the iodine value was 175.3±18.63 g I2/100 g, and the saponification number was 190.0±0.01 mg KOH / g oil. Other properties for use in cosmetic formulations like surface tension, viscosity, spreadability, and pour and cloud points were similar to those of other vegetable oils used in these formulations. A stable cosmetic emulsion was formulated using Cañihua oil (5%). All results demonstrated the potential of Cañihua oil as an ingredient for cosmetic emulsions for skin treatment.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1454K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1454K) -
Soek Sin Teh, Harrison Lik Nang Lau, Nur Sulihatimarsyila binti Abd. W ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 511-520
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSRed palm-pressed mesocarp olein (PPMO) contains plenty of naturally occurring phytonutrients. However, the application of PPMO in food is limited due to the lack of scientific data. In the study, stability and degradation kinetics of carotenoid and vitamin E in PPMO under two storage temperature, 23°C (with and without light) and 35℃ (without light), for a period of twelve months were performed. Amber bottles were used for optimum protection against damaging UV light. Both temperature and light conditions significantly influenced the total carotenoid and vitamin E contents of PPMO, as well as oil quality in terms of peroxide value and anisidine value to a different extent. Correlation analysis showed that oil quality was significantly but negatively correlated with phytonutrients. In addition, both zero- and first-order kinetic models were able to describe the degradation kinetics of the phytonutrients in PPMO. Zero-order was the best fit with higher correlation coefficients (R2) for both carotenoid and vitamin E contents, except for carotenoid that was kept at 23°C whereby first-order displayed the best fit. The half-life of carotenoid and vitamin E in PPMO were 40.8 months and 21.6 months, respectively under the optimised storage condition (23°C in amber bottles). In conclusion, storage of PPMO at lower temperature and in light-limited environment could effectively lower its oxidation rate and degradation rate of carotenoid and vitamin E, postulating its shelf life to be prolonged.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (981K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (981K) -
Chang Liu, Weining Wang, Hairong Zhang, Shunian Luo, Xue Wang, Liqi Wa ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 521-531
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
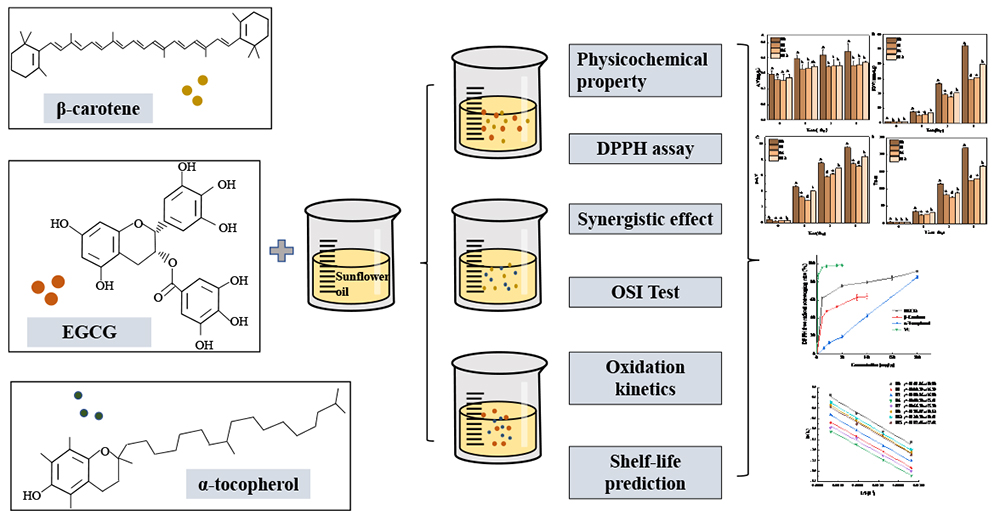
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSUsing sunflower oil as the oil matrix, the antioxidant effects and types of interactions of three natural components, α-tocopherol, β-carotene and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), were investigated and the kinetic model of oxidation reaction was established. The results showed that the ability of the three antioxidants to scavenge DPPH radicals was ranked as EGCG > β-carotene > α-tocopherol in the concentration range of 0~100 mg/kg. 15 samples were obtained by combining two of three natural components. When the concentration ratios of β-carotene and EGCG were 1:20 and 1:7.5, α-tocopherol and EGCG were 1:13.3, 1:6, and 1:2, and α-tocopherol and β-carotene were 1:0.2 and 1:0.05, the type of interaction was synergistic, while the rest of the samples showed antagonistic effects. The sample with a 1:13.3 concentration of α-tocopherol and EGCG showed the longest induction period, the lowest oxidation rate constant, the highest activation energy, the best oxidative stability, and the longest shelf life at different temperatures. This compounded natural antioxidant was the most favorable for the stability of sunflower oil. This provides some theoretical basis for the development and application of compounded natural antioxidants in vegetable oils.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (842K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (842K) -
Yi Jane Lee, Yih Phing Khor, Nur Shafika Abdul Kadir, Dongming Lan, Yo ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 533-541
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSAbstract: Diacylglycerol (DAG) is commonly known as one of the precursors for the 3-monochloro-1,2-propanediol esters (3-MCPDE) and glycidyl esters (GE) formation. However, due to its health-promoting effects, its potential as alternative frying medium was examined. This study aimed to assess the frying performance of soybean oil-based diacylglycerol oil (DO) and its oil blends with palm olein (PO), in comparison with PO. Four different oil types (DO, PO, OB I (DO:PO, 1:1, w/w) and OB II (DO:PO, 1:2, w/w)) were used to fry potato chips for five consecutive days at 180℃. The formation of oxidation compounds, acylglycerol composition, 3-MCPDE and GE changes throughout the frying study were investigated. Both OB I and OB II exhibited lower oxidation compounds’ formation rates than PO. Besides, significant (p < 0.05) reductions of 3-MCPDE and increments of GE levels were observed in all frying systems throughout the frying study. After 25 frying cycles, the 3-MCPDE levels in all frying oils were below 0.13 mg/kg, while the GE levels ranged from 1.51 mg/kg to 1.89 mg/kg. Despite the poorer oxidative stability of DO, its 3-MCPDE and GE levels were much lower compared to PO. In comparison to DO, the 3-MCPDE degradation and GE formation rates were enhanced and reduced, respectively with the blending of PO and DO. This study showed the potential of DO:PO oil blend in deep-fat frying application. With appropriate blending ratio of DO and PO, an alternative frying medium with enhanced nutritional value and oxidative stability could be developed.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (300K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (300K)
-
Keisuke Matsuoka, Daichi Asamoto2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 543-548
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThe selectivity of adsorption between alkali metal ions (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+) based on the ionic functional groups of the surfactants was studied using two types of surfactants, dodecanoic acid (DA) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), in the foam separation system. The results showed that Li+ was preferably removed by foam separation using DA. The removal rates of other alkali metal ions were relatively low, and there were no significant differences among other alkali metal ions (Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+). However, Cs+ exhibited the highest removal rate among the mixed alkali metals by foam separation using SDS. From these results, the selectivity of the alkali metal in foam separation was dependent on the type of surfactant.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1199K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1199K)
-
Linghui Meng, Guoliang Shen, Shengnan Zhang, Chao Zhou, Yaojie Han, Ru ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 549-556
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSHerein, a new approach for glycerol monooleate (GMO) was developed. GMO was synthesized via the esterification method using self-made sodium oleate and 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol as reactants, tetrabutylammonium bromide as the catalyst, and toluene as the solvent. The effects of the reaction molar ratio, type and amount of catalyst, and reaction temperature and time on the yield were investigated. Results showed that the optimal process conditions for synthesizing GMO were as follows. The molar ratio of sodium oleate to 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol was 1:2, the reaction temperature was 115°C, the reaction time was 6 h, weight of toluene was 25 g, and the catalyst dosage was 3.5%. Under these conditions, high-purity GMO was synthesized with a yield of 89.02%.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1124K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1124K)
-
Binfeng Yang, Kaisheng Yuan, Ming Lu, Attalla F. El-Kott, Sally Negm, ...2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 557-570
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe anti-cancer activities of the compounds were evaluated against KYSE-150, KYSE-30, and KYSE-270 cell lines and also on investigated esophageal line HET 1 A as a standard. Modified inhibitory impact on enzymes of collagenase and elastase were used Thring and Moon methods, respectively. Among both compounds, both of them recorded impact on cancer cells being neutral against the control, both had IC50 lower than 100 µM and acted as a potential anticancer drug. The chemical activities of Skullcapflavone I and Skullcapflavone II against elastase and collagenase were investigated utilizing the molecular modeling study. IC50 values of Skullcapflavone I and Skullcapflavone II on collagenase enzyme were obtained 106.74 and 92.04 µM and for elastase enzyme were 186.70 and 123.52 µM, respectively. Anticancer effects of these compounds on KYSE 150, KYSE 30, and KYSE 270 esophageal cancer cell lines studied in this work. For Skullcapflavone I, IC50 values for these cell lines were obtained 14.25, 19.03, 25.10 µM, respectively. Also, for Skullcapflavone II were recorded 20.42, 34.17, 22.40 µM, respectively. The chemical activities of Skullcapflavone I and Skullcapflavone II against some of the expressed surface receptor proteins (CD44, EGFR, and PPARγ) in the mentioned cell lines were assessed using the molecular docking calculations. The calculations showed the possible interactions and their characteristics at an atomic level.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6638K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6638K) -
Lokadi Pierre Luhata, Zixin Deng, Eri Tanaka, Toyonobu Usuki2023Volume 72Issue 5 Pages 571-576
Published: 2023
Released on J-STAGE: April 28, 2023
Advance online publication: April 11, 2023JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialAn ethyl acetate leaf extract from Odontonema strictum has been reported to have potent antihypertensive activity by inhibiting coronary artery contractions in porcine heart. However, the phytochemistry of the active fraction was unknown. Here we report, for the first time, the isolation and characterization of four known α-pyrones from the active fraction. The antioxidant activity of umuravumbolide (IC50 = 55.7±0.027 µg/mL), deacetylumuravumbolide (IC50 = 0.24±0.0002 µg/mL), dideacetylboronolide (IC50 = 149±0 µg/mL) and deacetylboronolide (IC50 = 24±0 µg/mL) was evaluated in vitro against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals. Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control (IC50 = 1.73×10-3±0.3 µg/mL). The presence of 6-substituted 5,6-dihydro-α-pyrones and phenylpropanoid glucosides in the active fraction was suggested to be responsible for the antihypertensive activity. This is the first time that the antioxidant potential of these phytochemicals has been evaluated, and the results indicate that O. strictum has potential as an herbal medicine. Thus, further chemotaxonomic studies among the genera Odontonema and Tetradenia, a known source of α-pyrones, are recommended.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1018K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1018K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|