
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages Contents5
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (123K)
-
Kazuya Nishimura, Xiannan Huang, Aya Yoshinaga-Kiriake, Yuna Yahata, S ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 637-644
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSEpoxy fatty acid formation during heating was estimated using triolein (OOO) and trilinolein (LLL). Epoxy octadecanoic acids were found in heated OOO, while epoxy octadecenoic acids were found in heated LLL. The content of epoxy fatty acids increased with heating time, and trans-epoxy fatty acids were formed significantly more than cis-epoxy fatty acids. A comparison between OOO and LLL indicated that epoxy fatty acid formation was higher in the OOO than that in the LLL. Heating tests in the presence of α- tocopherol suggested that the formation of epoxy fatty acids could be suppressed by antioxidants.
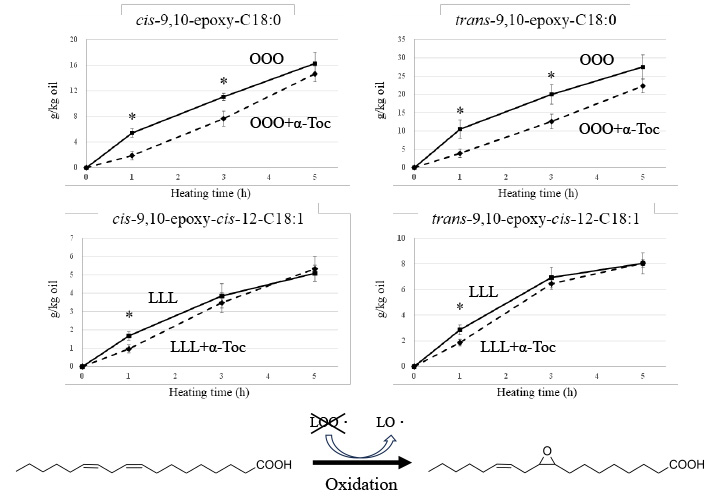 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (457K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (457K) -
Bingkai Wang, Lixia Hou, Ming Yang, Lei Jin, Huamin Liu, Xuede Wang2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 645-655
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: April 05, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe physicochemical characteristics and general food quality were greatly impacted by milling. In order to investigate the effect of milling technique for physicochemical properties of sesame paste of sesame paste, samples were prepared using ball mill and colloid mill by varying grinding times. The samples prepared by ball milling had the higher moisture contents (0.07% - 0.14%) than colloid milling (p < 0.05), except for colloid milling for one cycle (0.11%). The particle size curves showed the multimodal distributions. Compared to colloid milled samples, ball milled samples have smaller particle sizes and more uniform particle distribution. The L* values of samples prepared by ball milling were higher than colloid milling. The ball mill produced sesame paste with a wider range of hardness and silkier texture, and the samples made by ball milling for 30 min had the highest hardness. And the hardness of both CMS and BMS showed a decreasing trend with increasing grinding time. During ball milling, high-speed cutting and collision caused breakage of disulfide bonds, and the sesame proteins were decomposed to their subunits. In conclusions, ball milling may be an alternative and promising process for the preparation of sesame paste.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1701K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1701K) -
Yue Zhao, Xiangyu Kong, Xiaoqian Hu, Yang Sun, Ningning Jiang2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 657-664
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialThis present work investigated the influence of black rice anthocyanins as antioxidants on the oxidation stability of oil. Malonic acid, succinic acid and succinic anhydride were grafted on black rice anthocyanins through acylation method to improve their antioxidant activity in oil. The results from fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed new absorption peaks near 1744 cm –1 and 1514 cm –1 , which implied that malonic acid, succinic acid and succinic anhydride grafted on the -OH of glucoside and rutinoside through esterification reaction and resulted that the polarity of these were reduced. Total content of anthocyanin (TAC) decreased to 166. 3 mg/g, 163.7 mg/g and 150.2 mg/g, respectively after modification with succinic acid, malonic acid and succinic anhydride. Compared with native anthocyanins, the acylation of black rice anthocyanins partially reduced its antioxidant activity. In addition, DPPH clearance of molecular modified anthocyanins decreased to 62.6% (San-An). As revealed in the oil stability through the determination of primary oxidation products (PV) and secondary oxidation products (p-AV), Sa-An, Ma-An and San-An showed stronger antioxidant activity in Schaal oven accelerated oxidation test during 12 days than native black rice anthocyanin in both corn oil and flaxseed oil. Molecular modified black rice anthocyanins are expected to be used as colorants, antioxidants, etc. in oil-rich food.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (351K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (351K) -
Alexandra Valencia, Ana María Muñoz, Monica Ramos-Escudero, Keidy Canc ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 665-674
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSSacha inchi seed oil is a food matrix rich in bioactive constituents, mainly polyunsaturated fatty acids. In this study, the characteristics of color, carotenoid content, tocopherols, and volatile aroma compounds in eight sacha inchi seed (Plukenetia volubilis L.) oil accessions were evaluated. Results showed that the oil obtained from the accessions presented a lightness and chroma of 91 to 98 units and 6 to 10 units respectively, while the hue angle ranged between 93 to 97 units. The total carotenoid content in the different accessions ranged from 0.6 to 1.5 mg/kg, while γ- and δ-tocopherol ranged from 861.6 to 1142 mg/kg and 587 to 717.1 mg/kg. In addition, the total content of tocopherols varied between 1450 and 1856 mg/kg and the δ/γ ratio ranged between 0.58 and 0.70. The oils from the accessions PER000408 (861 µg/kg) and PER000411 (896 µg/kg) were those with the higher volatile concentration, especially 1-hepten-3-ol, 2-nonanol, (E)-3-hexen- 1-ol, (E)-2-hexenal, and 1-hexanol. In this study, the variability of the oil obtained from 8 accessions were observed, from which promising accessions can be selected for continuous investigations of the new sacha inchi seed genotypes.
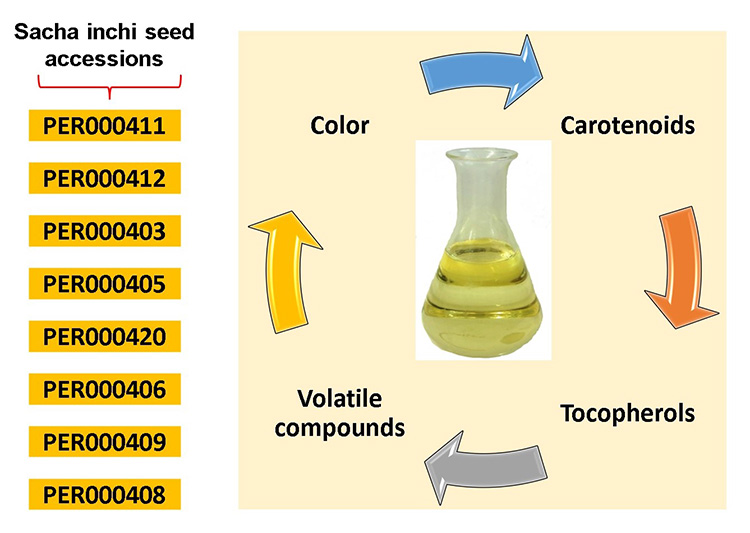 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (329K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (329K)
-
Akinori Inoue, Takashi Kameya, Masaru Oya2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 675-681
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSProtein soils must be removed for both appearance and hygienic reasons. They are denatured by heat treatment or bleaching and cleaned using enzymes. Among the various types of protein soils, blood soils are the most noticeable and known to be denatured by heat and bleaching by oxidation. We verified herein that the detergency of heat and oxidatively denatured hemoglobin is greatly improved by the enzyme immersing treatment in the detergency with SDS and can be analyzed using the probability density functional method. The probability density functional method evaluates the cleaning power by assuming that the adhesion and cleaning force of soils are not uniquely determined, but instead have a distribution in intensity, with a usefulness that had recently been demonstrated. This analytical method showed that the cleaning power of the enzyme immersing treatment improved when the soil adhesive force was decreased due to denatured protein degradation, even though the cleaning power of the SDS remained unchanged, and the values were consistent with those in the cleaning test. In conclusion, the probability density functional method can be used to analyze enzymatic degradation of denatured protein soils and the resulting changes in their detergency.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1178K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1178K)
-
Guiqin Fan, Jing Yu, Zhengzheng Tao, Xingjia Qian, Qinghong Qian, Jun ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 683-693
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: March 25, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, we outlined the green synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) using the plant-mediated method. Employing the nitrate derivative of Zinc and the extract from the native medicinal plant, Ottonia anisum, the nanoparticles were effectively produced. After obtaining a yellow-colored paste, it was meticulously dried, gathered, and set aside for subsequent examination. The UV-visible spectrometry analysis indicated an absorption peak at 320 nm, which is indicative of ZnO NPs. Characterization techniques, such as XRD and HR-TEM, confirmed the existence of agglomerated ZnO NPs with an average diameter of 40 nm. Through EDS analysis, distinct energy signals for both Zinc and Oxygen were observed, confirming their composition. Furthermore, FT-IR spectroscopy highlighted an absorption peak for Zn–O bonding in the range of 400 to 600 cm −1 . Further, we employed three distinct pain models in mice to evaluate the influence of ZnO NPs on the nociceptive threshold. Our findings revealed that, when orally administered, ZnO NPs at concentrations ranging from 5-20 mg/kg exerted a dose-dependent analgesic effect in both the hot-plate and the acetic acid-induced writhing tests. Moreover, when ZnO NPs were administered at doses between 2.5-10 mg/kg, there was a notable reduction in pain responses during both the initial and subsequent phases of the formalin test, but no change in PGE 2 production within the mice's hind paw was found. On the other hand, acute lung injury studies revealed that the administration of ZnO NPs orally 90 minutes prior to HCl instillation decreased the neutrophil infiltration into the lungs in a doseresponsive manner. This reduction in pulmonary inflammation was paralleled by a significant decrease in lung edema, as evidenced by the reduced total protein content in the BALF. Additionally, the ZnO NPs appeared to recalibrate the lung's redox equilibrium following HCl exposure, which was determined through measurements of ROS, malondialdehyde, glutathione, and catalase activity. All these results further indicated the potential of biofabricated ZnO NPs for future applications in analgesics and acute lung injury treatments.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1788K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1788K) -
Cuiyu Li, Bin Fang, Yuanyuan Wei, Rou Mo, Xing Lin, Quanfang Huang2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 695-708
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThis study was to investigate the effects of Smilax China L. saponins (SCS) on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Rats were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 weeks to induce NAFLD, followed by SCS treatment for 8 weeks. The effect of SCS on liver injury was observed by H&E staining and the regulative mechanism of SCS on lipid formation was exposed by detecting Oil red O, insulin resistance (IR), and fatty acids synthesis (FAS). Furthermore, transcriptomics and metabolomics were performed to analyze the potential targets. The experimental results indicated that SCS exerted a positive curative effect in alleviating HFD-induced overweight, hepatic injury, steatosis, and lipid formation and accumulation in rats, and the preliminary mechanism studies showed that SCS could alleviate IR, inhibit FAS expression, and reduce Acetyl-CoA levels. Besides, the integrative analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics exposed the targets of SCS to regulate lipid production likely being the sphingolipid metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism pathways. This study demonstrates that SCS significantly ameliorates lipid metabolic disturbance in rats with NAFLD by relieving insulin resistance, inhibiting the FAS enzymes, and regulating the sphingolipid and glycerophospholipid metabolism pathways.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (10162K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (10162K) -
Ana Paula Dias Moreno, Priscyla Daniely Marcato, Letícia Bueno Silva, ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 709-716
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSEpigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a polyphenol derived from Green Tea, is one of the sources of natural bioactive compounds which are currently being developed as medicinal ingredients. Besides other biological activities, this natural compound exhibits anti-cariogenic effects. However, EGCG has low physical-chemical stability and poor bioavailability. Thus, the purpose of this study was to develop and characterize lipid-chitosan hybrid nanoparticle with EGCG and to evaluate its in vitro activity against cariogenic planktonic microorganisms. Lipid-chitosan hybrid nanoparticle (LCHNP-EGCG) were prepared by emulsion and sonication method in one step and characterized according to diameter, polydispersity index (PdI), zeta potential (ZP), encapsulation efficiency (EE), mucoadhesion capacity and morphology. Strains of Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus sobrinus and Lactobacillus casei were treated with LCHNP- EGCG, and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) were evaluated. LCHNP-EGCG exhibited a size of 217.3 ± 5.1 nm with a low polydispersity index (0.17) and positive zeta potential indicating the presence of chitosan on the lipid nanoparticle surface (+33.7 mV). The LCHNP-EGCG showed a spherical morphology, high stability and a mucoadhesive property due to the presence of chitosan coating. In addition, the EGCG encapsulation efficiency was 96%. A reduction of almost 15-fold in the MIC and MBC against the strains was observed when EGCG was encapsulated in LCHNP, indicating the potential of EGCG encapsulation in lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Taking the results together, the LCHNP-EGCG could be an interesting system to use in dental care due to their nanometric size, mucoadhesive properties high antibacterial activity against relevant planktonic microorganisms.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (524K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (524K)
-
Handan Mert, Nihan Mert, Salih Cibuk, Serkan Yildirim, Nihat Mert2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 717-727
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe anti-diabetic effect of Ficus carica (Fig) seed oil was investigated. 4 groups with 6 rats in each group were used in the experiment as control, diabetes (45 mg/kg streptozotocin), fig seed oil (FSO) (6 mL/ kg/day/rat by gavage) and diabetes+FSO groups. Glucose, urea, creatinine, ALT, AST, GSH, AOPP and MDA analyses were done. Pancreatic tissues were examined histopathologically. When fig seed oil was given to the diabetic group, the blood glucose level decreased. In the diabetes+FSO group, serum urea, creatinine, AOPP, MDA levels and ALT and AST activities decreased statistically significantly compared to the diabetes group, while GSH levels increased significantly, histopathological, immunohistochemical, and immunofluorescent improvements were observed. It has been shown for the first time that FSO has positive effects on blood glucose level and pancreatic health. It can be said that the protective effect of fig seed oil on tissues may be due to its antioxidant activity.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2027K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2027K) -
Yuling Zhang, Chunhao Gao, Mengjia Zhu, Fangtian Chen, Yongye Sun, Yu ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 729-742
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSAstaxanthin is a keto-based carotenoid mainly obtained from marine organisms, like Haematococcus pluvialis (H. pluvialis). Previous studies indicated the protective effects of Astaxanthin and H. pluvialis on aging related oxidative injury in liver, while the potential mechanisms are largely unknown. In addition, H. pluvialis residue is a by-product after astaxanthin extraction, which is rarely studied and utilized. The present study aimed to compare the effects of astaxanthin, H. pluvialis and H. pluvialis residue on the oxidant injury of liver in D-galactose-induced aging mice and explore the potential mechanisms through gut-liver axis. The results showed that all the three supplements prevented D-galactose-induced tissue injury, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in liver and improved liver function. Gut microbiota analysis indicated that astaxanthin notably increased fecal levels of Bacteroidetes, unclassified_f__ Lachnospiraceae, norank_f__Lachnospiraceae, norank_f__norank_o__Clostridia_UCG-014, Prevotellaceae_ UCG-001, unclassified_f__Prevotellaceae in D-galactose-fed mice (p < 0.05). Compared to aging mice, H. pluvialis group had higher fecal levels of norank_f__Lachnospiraceae and Lachnospiraceae_UCG-006 (p < 0.05). H. pluvialis residue group displayed higher relative levels of Bacteroidetes, Streptococcus, and Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (p < 0.05). Moreover, the production of fecal microbial metabolites, like SCFAs and LPS was also differently restored by the three supplements. Overall, our results suggest astaxanthin, H. pluvialis and H. pluvialis residue could prevent aging related hepatic injury through gutliver axis and provide evidence for exploiting of H. pluvialis residue as a functional ingredient for the treatment of liver diseases. Future studies are needed to further clarify the effect and mechanism of dominant components of H. pluvialis residue on liver injury, which is expected to provide a reference for the high-value utilization of H. pluvialis resources.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4346K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (4346K) -
Hisaaki Ito, Taro Honma, Hidetsugu Tabata, Tomoyuki Koyama, Shigeaki U ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 743-749
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialConjugated fatty acids have anticancer effects. Therefore, the establishment of a synthetic method for conjugated fatty acids is important for overcoming cancer. Here, we attempted to synthesize conjugated fatty acids using enzymes extracted from seaweeds containing these fatty acids. Lipids from 12 species of seaweeds from the seas around Japan were analyzed, and Padina arborescens Holmes was found to contain conjugated fatty acids. Then, we synthesized parinaric acid, a conjugated tetraenoic acid, from α-linolenic acid using the enzyme of P. arborescens. This method is expected to have a variety of potential applications for overcoming cancer.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (722K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (722K) -
Naoki Kawada, Hideaki Kobayashi, Akifumi Mikami, Kenta Susaki, Ryosuke ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 751-760
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSA double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial was performed to analyze the effects of a small amount of lysolecithin and canola oil on blood glucose levels after consuming japonica rice. Overall, 17 Japanese adult men were assigned to consume 150 g of normally cooked japonica rice (placebo group) and 150 g of japonica rice cooked with 18 mg of lysolecithin and 1.8 g of canola oil (treatment group); these lipids were added as emulsified formulation (EMF) for stability and uniformity. Subsequently, blood samples were collected before and 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 min after consuming test foods. There was no significant difference in blood glucose, insulin, and triglyceride levels between the groups. However, a stratified analysis of 11 subjects with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 22 revealed that blood glucose levels were significantly lower after 30 min in the treatment group than in the placebo group (p = 0.041). Through in vitro digestibility test, the rice sample of the treatment group was observed to release significantly less glucose within 20 min than that in the placebo group rice. These results suggest that the combination of a small amount of lysolecithin and canola oil modulated the increase in postprandial blood glucose levels induced by the intake of cooked japonica rice in adult men with BMI ≥ 22. This clinical trial was registered with the University Hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN) Center, (UMIN000045744; registered on 15/10/2021).
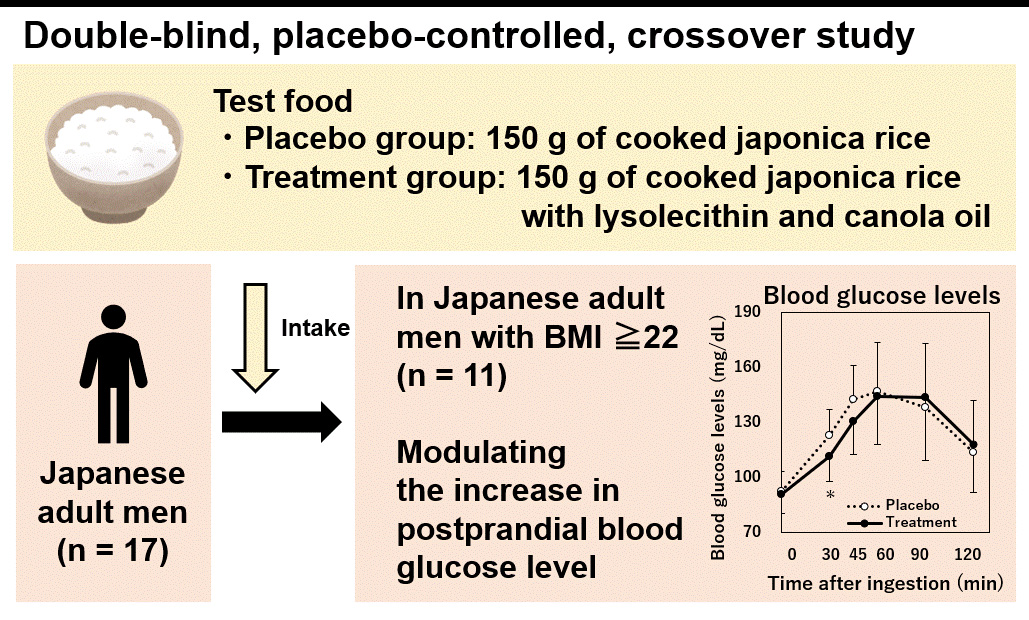 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (407K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (407K)
-
Yi-Xi Feng, Xin-Xin Lu, Jia-Wei Zhang, Yue-Shen Du, Yu Zheng, Shu-Shan ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 761-772
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialVolatile secondary metabolites of plants interact with environments heavily. In this work, characteristic components of Michelia yunnanensis essential oils (EOs) were isolated, purified and identified by column chromatography, GC-MS and NMR. Leaves of M. yunnanensis were collected monthly and extracted for EOs to investigate chemical and insecticidal activity variations as well as potential influencing environments. Different organs were employed to reveal distribution strategies of characteristic components. Results of insecticidal activities showed that all EOs samples exerted stronger contact activity to Lasioderma serricorne, but repellent effect was more efficient on Tribolium castaneum. One oxygenated sesquiterpene was isolated from EOs, basically it could be confirmed as (+)-cyclocolorenone (1). It exerted contact toxicity to L. serricorne (LD 50 = 28.8 μg/adult). Chemical analysis showed that M. yunnanensis leaves in reproductive period would produce and accumulate more 1 than in vegetative period. Moreover, reproductive organs (flowers and fruits) contained more 1 than vegetative organs (leaves and twigs). Partial correlation analysis indicated that temperature-related elements positively correlated with the relative content of 1.
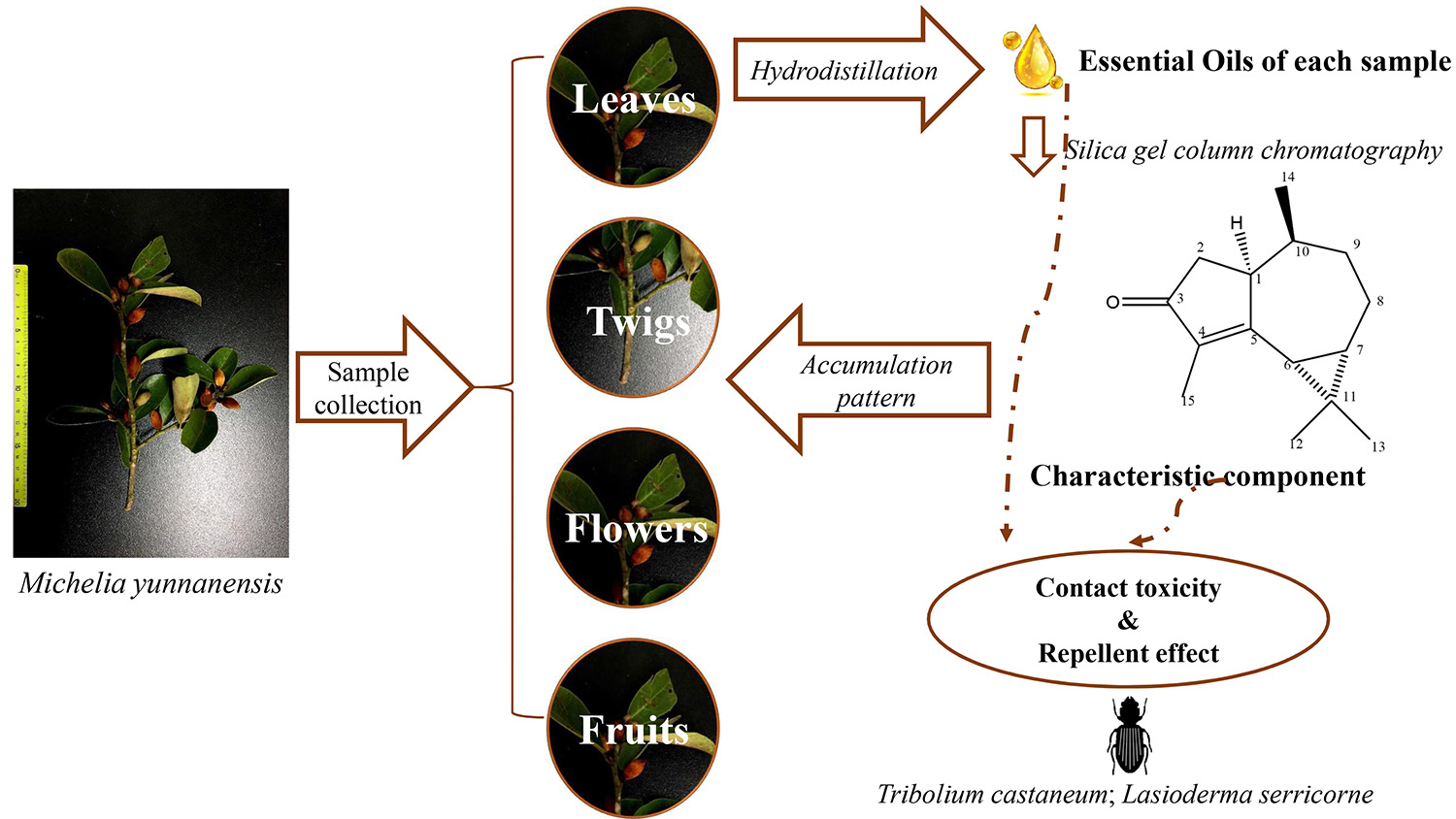 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1694K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1694K) -
Xinliang Jiang, Qing Liu, Fei Fei, Ziwei Chen, Chang Shu, Xiaolu Jie, ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 773-786
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSTo overcome the defects of Citrus aurantium L. var. amara Engl. essential oil (CAEO), such as high volatility and poor stability, supercritical fluid-extracted CAEO nanoemulsion (SFE-CAEO-NE) was prepared by the microemulsification method. Emulsifiers comprising Tween 80, polyoxyethylenated castor oil (EL-40), and 1,2-hexanediol, and an oil phase containing SFE-CAEO were used for microemulsification. We examined the physicochemical properties of SFE-CAEO-NE and steam distillation-extracted CAEO nanoemulsion (SDE-CAEO-NE), which were prepared using different concentrations of the emulsifiers. The mean particle size and zeta potential were 21.52 nm and –9.82 mV, respectively, for SFE-CAEO-NE, and 30.58 nm and –6.28 mV, respectively, for SDE-CAEO-NE, at an emulsifier concentration of 15% (w/w). SFE-CAEO-NE displayed better physicochemical properties compared with SDE-CAEO-NE. Moreover, its physicochemical properties were generally stable at different temperatures (–20–60℃), pH (3–8), and ionic strengths (0–400 mM). No obvious variations in particle size, zeta potential, and Ke were observed after storing this nanoemulsion for 30 days at 4℃, 25℃, and 40℃, suggesting that it had good stability. The sleep-promoting effect of SFE-CAEO-NE was evaluated using a mouse model of insomnia. The results of behavioral tests indicated that SFE-CAEO-NE ameliorated insomnia-like behavior. Moreover, SFE-CAEO- NE administration increased the serum concentrations of neurotransmitters such as 5-hydroxytryptamine and γ-aminobutyric acid, and decreased that of noradrenaline in mice. It also exerted a reparative effect on the function of damaged neurons. Overall, SFE-CAEO-NE displayed a good sleep-promoting effect.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3495K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3495K) -
Ty Viet Pham, Thao Xuan Hoang, Hoai-Nguyen Nguyen, Bich Hang Do, Huy-H ...2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 787-799
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialLaunaea sarmentosa, also known as Sa Sam Nam, is a widely used remedy in Vietnamese traditional medicine and cuisine. However, the chemical composition and bioactivity of its essential oil have not been elucidated yet. In this study, we identified 40 compounds (98.6% of total peak area) in the essential oil via GC-MS analysis at the first time. Among them, five main compounds including Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (52.4%), (E)-α-Atlantone (9.0%), Neryl isovalerate (6.6%), Davanol D2 (isomer 2) (3.9%), and trans-Sesquisabinene hydrate (3.9%) have accounted for 75.8% of total peak area. The anti-bacterial activity of the essential oil against 4 microorganisms including Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa has also investigated via agar well diffusion assay. The results showed that the essential oil exhibited a strong antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis with the inhibition zones ranging from 8.2 to 18.7 mm. To elucidate the anti-bacterial effect mechanism of the essential oil, docking study of five main compounds of the essential oil (Thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether, (E)-α-Atlantone, Neryl isovalerate, Davanol D2 (isomer 2), and trans-Sesquisabinene hydrate) against some key proteins for bacterial growth such as DNA gyrase B, penicillin binding protein 2A, tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase, and dihydrofolate reductase were performed. The results showed that the main constituents of essential oil were highly bound with penicillin binding protein 2A with the free energies ranging –27.7 to –44.8 kcal/mol, which suggests the relationship between the antibacterial effect of essential oil and the affinity of main compounds with penicillin binding protein. In addition, the free energies of main compounds of the essential oil with human cyclooxygenase 1, cyclooxygenase 2, and phospholipase A2, the crucial proteins related with inflammatory response were less than diclofenac, a non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug. These findings propose the essential oil as a novel and promising anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory medicine or cosmetic products.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (9728K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (9728K)
-
Shuko Konno, Koji Asanuma, Yoshimune Nonomura2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 801-811
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
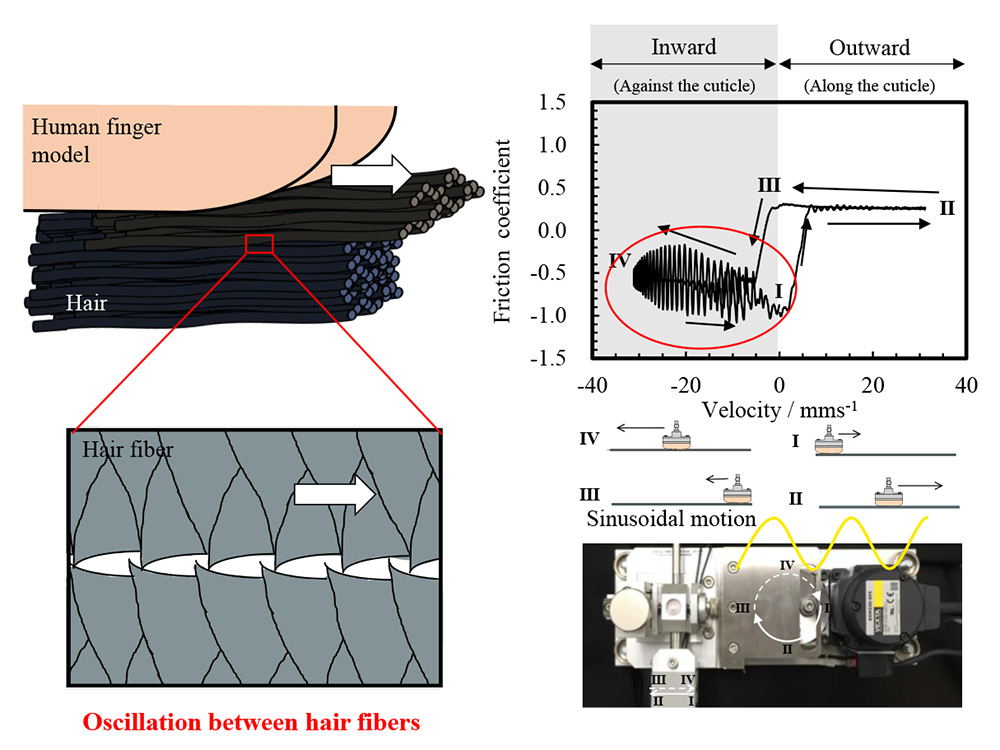
Supplementary materialHair shape affects the frictional properties and tactile sensation of hair. In this study, we evaluated the friction associated with the rubbing of straight, curly, or wavy hair by a contact probe equipped in a sinusoidal motion friction evaluation system. This system provides dynamic information such as the velocity dependence and hysteresis of the frictional force. In the case of hair fibers fixed at 1 mm intervals on a glass plate, a stable friction pattern was observed, in which the friction coefficient was almost constant during the dynamic friction process. The friction coefficients in the inward direction toward the hair root for straight, curly, and wavy hair were 0.47 ± 0.04, 0.51 ± 0.02, and 0.54 ± 0.04, respectively. As wavy hair is thick and has a larger true contact area with the contact probe, the friction coefficient was larger. When the finger model rubbed the straight or curly hair bundle in the inward direction, an oscillation pattern was observed, with the friction coefficient fluctuating at 20 ms intervals and the kinetic friction coefficient evaluated at 0.67 and 0.64, respectively. For the surface of straight hair, containing densely arranged cuticles, a large oscillation was observed in the direction against the cuticles. Meanwhile, no oscillation phenomenon was observed in wavy hair, which is characterized by a smooth cuticle and complex hair flow. Because wavy hair, which is frizzy, has fewer points of contact between hairs, impeding the occurrence of cooperative fluctuations in the frictional force.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3735K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3735K)
-
Ming Yang, Lixia Hou, Yifan Dong, Bingkai Wang, Huamin Liu, Xuede Wang2024 Volume 73 Issue 5 Pages 813-821
Published: 2024
Released on J-STAGE: May 01, 2024
Advance online publication: April 05, 2024JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS
Supplementary materialGas chromatography-olfactory-mass spectrometry (GC-O-MS) combined with Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis (AEDA) were employed to characterize the key odor-active compounds in sesame paste (SP) and dehulled sesame paste (DSP). The AEDA results revealed the presence of 32 and 22 odor-active compounds in SP and DSP, respectively. Furthermore, 13 aroma compounds with FD ≥ 2, OAV ≥ 1, and VIP ≥ 1 were identified as key differential aroma compounds between SP and DSP. Specifically, compounds such as 3-methylbutyraldehyde (OAV = 100.70-442.57; fruity), 2-methylbutyraldehyde (OAV = 106.89-170.31; almond), m-xylene (FD = 16; salty pastry), and 2,5-dimethylpyrazine (FD = 8-16; roasted, salty pastry) played an important role in this differentiation. Additionally, the dehulling process led to increased fermented, sweet, green, and nutty aroma notes in DSP compared to the more pronounced burnt and roasted sesame aroma notes in SP. Our findings offer a theoretical foundation for the regulation of sesame paste aroma profiles.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2194K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2194K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|