
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Febri Odel Nitbani, Putra Jiwamurwa Pama Tjitda, Beta Achromi Nurohmah ...2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 277-295
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLFatty acid and monoglyceride are examples of lipid compounds that can be founded in vegetable oils. The fatty acid has an important role in the human diet, lubricants, detergents, cosmetics, plastics, coatings, and resin. Monoglyceride has a wide function in the food industry in particular as natural emulsifier, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, antioxidant, and antibacterial. Therefore, isolation and preparation of fatty acid and monoglyceride are the crucial step. This article focuses on providing the chemical reaction paths of isolation fatty acid and synthesis of monoglyceride from vegetable oils. Fatty acids could be isolated by Colgate-Emery steam hydrolysis, hydrolysis of vegetable oils using inorganic base catalyst or lipase, and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of pure fatty acid methyl ester. There are three steps in the synthesis of pure fatty acid methyl ester which are neutralization, transesterification, and fractional distillation. There are four reactions paths in preparing monoglyceride from vegetable oils. They are glycerolysis, ethanolysis using lipase enzyme (sn-1,3), esterification of fatty acid with glycerol in the presence of inorganic acid catalyst or lipase, transesterification of fatty acid methyl ester with glycerol, transesterification of fatty acid methyl ester with protected glycerol (1,2-O-isopropylidene glycerol), and deprotection using an acid resin (Amberlyst-15).
View full abstractDownload PDF (1060K) Full view HTML
-
Teik Siun Ong, Chee Chin Chu, Chin Ping Tan, Kar Lin Nyam2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 297-306
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSPlant seed oil is often incorporated into the cream emulsions to provide multifunctional effects on the skin. In the current study, pumpkin seed oil (PSO) was used to develop a stable oil-in-water emulsion. The study aimed to optimise PSO cream formulation and determine the synergistic effect of the PSO with vitamin E oil added. The physical properties, antioxidant activities and storage stability of the formulations were analysed. Besides, the synergistic effect of the best formulation was analysed based on α-tocopherol content using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC). The storage stability test was assessed upon storing at 25 ± 2°C and 40 ± 2°C for 12 weeks. The best formulation (20% PSO, vitamin E oil and beeswax) selected showed physically and microbiologically stable. The incorporation of vitamin E oil into the formulation produced with PSO was found to be compatible, as it showed a synergistic effect in the amount of α-tocopherol content (combination index (CI) = 0.98). Thus, PSO had shown its potency to be incorporated into the topical products with a promising potential in delivering additional properties that can nourish the skin.
View full abstractDownload PDF (318K) -
Kashif Ghafoor, Mehmet Musa Özcan, Fahad Al Juhaimi, Elfadıl E Babiker ...2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 307-315
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
Advance online publication: March 03, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe acidity values changed between 1.03 mgKOH/100g (control) and 1.11 mgKOH/100g (0.1% extract) for orange oil, 1.06 mgKOH/100g (0.5% extract) and 1.13 mgKOH/100g (0.1% extract) and 1.25 mgKOH/100g (0.5% extract) and 1.31 mgKOH/100g (control) for mandarin oil. The peroxide values were determined between1.37 meqO2/kg (0.5% extract) and 1.43 meqO2/kg (0.1% extract) for orange oil, between 1.24 meqO2/kg (control) and 1.27 meqO2/kg (0.1% extract) for lemon and 1.60 meqO2/kg (0.5% extract) and 1.71 meqO2/kg (control) in mandarin oil samples. The viscosity values of samples changed between 0.051 Pa.S (control) and 0.065 Pa.S (0.5% extract) for orange, 0.051 Pa.S (control) and 0.067 Pa.S (0.5% extract) lemon and 0.044 Pa.S (control) and 0.057 Pa.S (0.5% extract) in mandarin oil samples. At the end of storage study (28th day), the acidity values significantly changed, and their values ranged between 2.28 mgKOH/100g (0.5% extract) and 3.64 mgKOH/100g (control) in orange, 1.67 mgKOH/100g (0.5% extract) and 2.28 mgKOH/100g (control) in lemon and 1.74 mgKOH/100g (0.5% extract) and 2.36 mgKOH/100g (control) in mandarin oil samples. While peroxide values vary between 11.68 meqO2/kg (0.5% extract) and 32.57 meqO2/kg (control) for orange, 12.55 meqO2/kg (0.5% extract) and 34.63 meqO2/kg (control) for lemon and between 17.56 meqO2/kg (0.5% extract) and 37.81 meqO2/kg (control) for mandarin oils, viscosity values after 28 day storage changed between 0.123 Pa.S (0.5% extract) and 0.675 Pa.S (control) in orange, 0.257 Pa.S (0.5% extract) and 0.697 Pa.S (control) in lemon and 0.215 Pa.S (0.5% extract) and 0.728 Pa.S (control) in mandarin oil samples.
View full abstractDownload PDF (353K) -
Zubair Rehman Nengroo, Abdul Rauf2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 317-326
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSSeed extracts of Nymphia alba Linn. and Lupinus polyphyllus Lindl. were analyzed for fatty acid composition, functional group analysis and antioxidant activity. The petroleum ether extract of seeds were found dominant in unsaturated fatty acids with oleic acid (39.9%) and linoleic acid (29.6%) in L. polyphyllus and linoleic (37.5%) and oleic acid (10.9%) in N. alba. All the defatted seed extracts of N. alba and L. polyphyllus found to have powerful DPPH, ABTS, H2O2 and NBT antioxidant radical scavenging activity with reference to butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT). The defatted seed extracts were further analyzed with functional group analysis through FTIR found to contain numerous functional groups which may be responsible for their antioxidant activity.
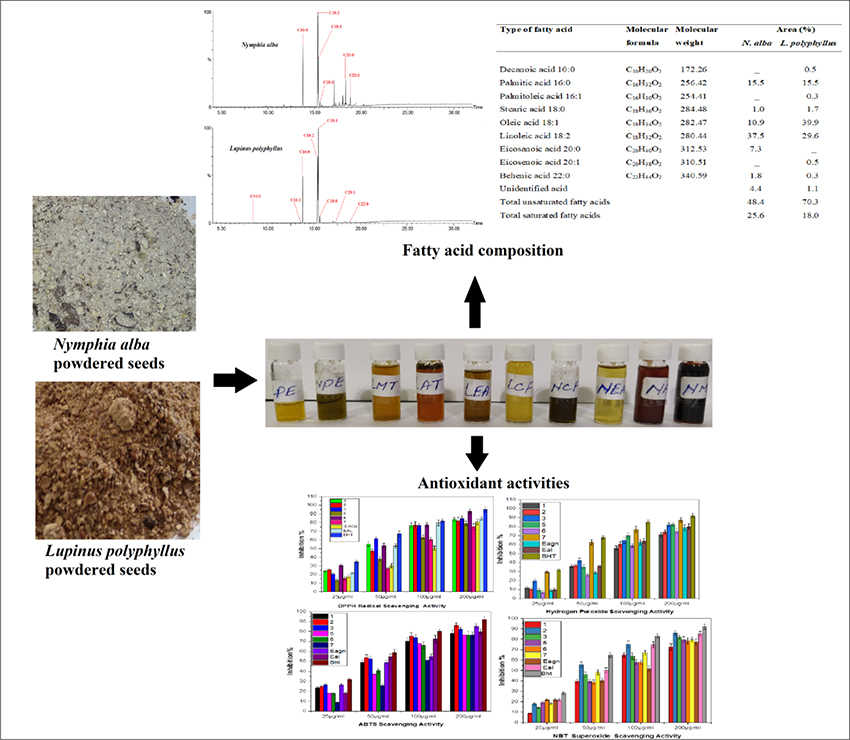 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (632K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (632K)
-
Aggregation Behavior of Antipsychotic Drug under the Influence of Bile Salt in Aqueous/Urea SolutionNaved Azum, Malik Abdul Rub, Abdullah M. Asiri2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 327-335
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe self-assembly of pharmaceutical amphiphiles is an important area of research because of the involvement of these amphiphiles in physiological processes. The mixed micellization behavior of antipsychotic drug (chlorpromazine hydrochloride, CPZ) in the presence of bile salt (sodium cholate, SC) was studied by surface tension and fluorescence techniques in aqueous/urea solution. The output of the study has been analyzed by using different models (Clint, Rubingh, and Motomura) for mixed amphiphilic systems. The attractive or synergistic interactions between these two amphiphiles in water/urea were confirmed by the obtained data. Various thermodynamic parameters for the mixed micellization process have been computed and discussed.
View full abstractDownload PDF (596K)
-
Soodeh Shaghaghi, Mohammad Ghahderijani, Mohammad hadi Dehrouyeh2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 337-346
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
Advance online publication: March 03, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe growing global demand for fossil fuels and considerable environmental threats and risks have prompted researchers to launch investigations over some renewable energy sources in recent years. Especially biodiesel and ethanol have been considered as major alternative fuels as they are derived from renewable sources. These fuels are well oxygenated and therefore have a great potential to reduce emissions. Biodiesel, which is chemically derived from edible oils or animal fats by transesterification reaction, is esters of long-chain saturated/unsaturated fatty acids and can be an important alternative fuel source to consider for the vehicle. It can offer desirable features to diesel engines, and internal combustion engines (ICEs) in particular. The present study aims at determining and assessing the effect of the engine’s load and speed as well as various ratios of diesel and biodiesel fuels blending on the emissions of pollutants from the OM 314 diesel engine. Design Expert 11 statistical software was used. Second-order models obtained using response surface methodology (RSM) to predict the effect of input variables on response surfaces were statistically significant at an alpha level of 1. Following an increase in the percentage of biodiesel compared to pure diesel fuel, the HC (Hydrocarbons) emission rate decreased. According to the optimization results, the lowest HC emission rate (33.52 ppm), and the least NOX emission rate occurs when using 8.82% biodiesel. The lowest HC emission rate was observed after using pure biodiesel fuel. Following an increase in the percentage of biodiesel in the blended fuel, the NOX emission rate increased, while the lowest emission rate was observed after using pure diesel fuel. Engine smoke flow rate decreased after increasing the percentages of biodiesel in blended fuel compared to diesel fuel. A higher percentage of biodiesel was considered as the most effective way to reduce the rate of smoke opacity. According to the multi-objective optimization (MOO) results, the lowest HC, and NOX emission rates and the rate of smoke opacity was observed for blended fuel “D32.47B67.53” with the Desirability of 60% under applying a load of 41.36% and rotational speed of 1383 rpm.
View full abstractDownload PDF (877K) -
Maomao Kou, Siting Feng, Nanjing Zhong2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 347-358
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS
Supplementary materialIn this study, Lecitase® Ultra (LU) was immobilized onto the parent and the amino-functionalized SBA-15. The immobilization conditions were studied and the activity of the parent SBA-15 supported LU (SBA-15-LU) was found to be at 2177.78 ± 101.84 U/g. After 3-aminopropyl and n-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl groups functionalization, enzymatic activity was increased to 3555.56 ± 200.21 and 3444.44 ± 346.41 U/g respectively. The immobilized LU samples were then used to catalyze glycerolysis. The possibility for diacylglycerols (DAG) and monoacylglycerols (MAG) production was evaluated and it was found only suitable for DAG production. In addition, the glycerolysis activity of the immobilized LU was impaired by the tert-pentanol and solvent-free was found suitable. Similar DAG content over 50 wt% could be obtained from glycerolysis by the three immobilized LU samples. The reusability in glycerolysis was evaluated, and 9.79 % of the initial glycerolysis activity was remained from the SBA-15-LU after 5 cycles of reuse. Encouragingly, after 3-aminopropyl and n-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyl groups functionalization, 62.93 and 83.91% of their initial activity was respectively remained after 5 cycles of reuse.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1651K) -
Chonlada Yaisamlee, Anchalee Sirikhachornkit2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 359-368
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSBiodiesel production from microalgae is still not commercially realized due to the high cost of production. High light-tolerance has been suggested as a desirable phenotype for efficient cultivation in large scale production systems under fluctuating outdoor conditions. Nevertheless, it has not been shown if algae with such a phenotype would have better efficiency for lipid production. To determine lipid productivity in high light-tolerant mutants, and to understand the pathways involved in high light-tolerant phenotype, two very high light-tolerant mutants of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii - CAL028_01_28 and CAL034_01_48 - were selected from eighteen high light-tolerant mutants from the CAL collection. Under high light intensity conditions, and the presence of reactive oxygen species, which are conditions constantly experienced by algae growing in open-pond environments, these strains exhibited higher photosynthetic efficiency and improved survival. The physiological characterization of these mutants revealed that the detoxification of ROS by carotenoids and antioxidant enzymes is crucial for their growth under high light conditions. Neither mutant was affected in terms of its ability to accumulate lipid under nitrogen-depleted condition. More importantly, lipid productivity under high light conditions increased twofold in these mutants compared to that of the wild-type. Taken together, very high light-tolerant mutants confer a high potential for biofuel production under outdoor conditions, and their improved ability to survive under oxidative stress is an important key for efficient growth under outdoor conditions.
View full abstractDownload PDF (710K)
-
Chenbo Yang, Shenkun Wang, Wei Liu, Zhiyuan Ma, Mengmeng Dou, Wentao L ...2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 369-376
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe aim of this work was to analyze the expression of Ki-67 in ovary, testis of aging mice with anthocyanidin extract from Summer-black-grape. ICR mice (the aging group and the anthocyanidin-groups (50 mg/kg/D-group, 75 mg/kg/D-group and 100 mg/kg/D-group) were employed to evaluate the effect of grape anthocyanidin on reproductive system. The results showed that the anthocyanidin had strong scavenging ability for free radicals, the level of oxidation in serum of mice treated with anthocyanidin was low, and the pathological changes were not obvious. In the anthocyanidin group, the Ki-67 positive particles in the testis and ovary tissue were significantly decreased. The anthocyanidin of Summer-black-grape reduces the expression of Ki-67 protein in the testis or ovary of aging mice. In gonadal cells of aging mice, the anthocyanidin were shown protective effect in the proliferation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2018K)
-
Somaieh Hosseni, Jahanshir Amini, Javad Nazemi Rafei, Jalal Khorshidi2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 377-390
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSColletotrichum nymphaeae is the causal agent of strawberry anthracnose, which is one of the most important disease affecting strawberry plant in Iran. This research aimed to apply the selected plant essential oils (EOs) such as Achillea millefolium, Mentha longifolia, and Ferula kuma to the management of strawberry anthracnose disease under in vitro, in vivo, and greenhouse conditions. In vitro tests indicated that all the EOs and fungicide were able to inhibit mycelial growth and conidial germination of the pathogen. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed that EOs significantly suppressed the mycelia growth and caused a change in morphology of fungal mycelia. The severity of strawberry anthracnose disease was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) reduced by all EOs under in vivo and greenhouse conditions. Results of all experiments showed that M. longifolia EO was the best EO to control C. nymphaeae. Also, EOs almost reduced weight loss and preserved firmness, ascorbic acid, total phenol, antioxidant activity (DPPH), and enzyme peroxidase activity in treated fruit. Moreover, EOs preserved the sensory quality of strawberry fruit during the storage period so that there were no significant differences between treatments (EOs) in their appearance, flavor, odor attributes, and overall evaluation compared to the control. Our results indicate that EOs are excellent bio-fungicides for the management of strawberry anthracnose.
View full abstractDownload PDF (899K)
-
Hua-Min Liu, Ya-Fei Han, Nan-Nan Wang, Yong-Zhan Zheng, Xue-De Wang2020 Volume 69 Issue 4 Pages 391-401
Published: 2020
Released on J-STAGE: April 03, 2020
Advance online publication: March 03, 2020JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis investigation was carried out to offer insight into the formation and antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products (MRPs) derived from various sugar-amino acid model systems active in the roasting of sesame seeds. Reducing sugars (glucose, fructose, and xylose) and amino acids (serine, cystine, arginine, and lysine) present in sesame seeds were used to prepare the MRPs at various reaction times, and then the effect of reaction time on the MRPs derived from the various model systems was investigated. Within the first 15 min, the amounts of free amino groups decreased around 40% remaining amino groups of Lys-sugar model and around 75% remaining amino groups of Arg-sugar model. Results indicated that reducing sugar and free amino groups decreased obviously in Lys- and Arg-model systems. Based on correlation coefficient of antioxidant activities assessment and MRP formation in the Lys- and Arg-model systems above 0.978 and an extremely significant correlation in Pearson test exists, a conclusion could be made that these model systems are critical contributing factors in MRP formation during the roasting of sesame seeds. These findings offer insight into the formation and antioxidation of MRPs during the sesame seeds roasting.
View full abstractDownload PDF (777K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|