
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Priyanka Kumari Singh, Rajni Chopra, Meenakshi Garg, Aishwarya Dhiman, ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1697-1709
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn recent years, scientists and technologists have become increasingly interested in producing modified lipids with enhanced nutritional and functional properties. The application and functional properties of fats and oil depend on the composition and structure of triacylglycerols (TAG). As a result, lipid TAG changes can be used to synthesize tailored lipids with a broader range of applications. However, no natural edible oil is available with appropriate dietary and functional properties to meet the human recommended dietary allowances (RDA). On the other hand, the arising health concern is the transfat consumption produced during the chemical modification of vegetable oil through the partial hydrogenation process. Therefore, innovative technologies are shifting toward modifying fat and oil to improve their functionality. Enzymatic interesterification (EIE) is one of the emerging and novel technology to modify the technological traits of naturally available edible oil. It helps in modifying physicochemical, functional, oxidative, and nutritional characteristics of fats and oil due to the rearrangement of the fatty acid positions in the glycerol backbone after interesterification. Enzymatic interesterification utilizes lipase as a biocatalyst with specificity and selectivity to produce desired lipids. Alternation in the molecular structure of triacylglycerol results in changes in melting/dropping point, thermal properties, crystallization behavior, solid fat content, and oxidative stability. Because of its high acyl exchange reaction efficiency, simple reaction process, flexibility, eco-friendly, and generation of fewer by-products, (EIE) is gaining more attention as a substitute lipid modification approach. This review paper discusses the uses of EIE in developing modified fat with desirable physicochemical and nutritional properties. EIE is one of the potential techniques to modify vegetable oil’s physicochemical, functional, and nutritional characteristics without producing any undesirable reaction products. EIE produces different modified lipids such as trans fat-free margarine, plastic fat, bakery, confectionery fat, therapeutic oil, infant food, cocoa butter substitute, and equivalent.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (970K) Full view HTML
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (970K) Full view HTML
-
Zixuan Liu, Meichu Liu, Chunmao Lyu, Bin Li, Xianjun Meng, Xu Si, Chi ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1711-1723
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThermal processing, a common processing method of vegetable oil in daily life, is accompanied by the formation of some harmful substances. This study determined the peroxide value, anisidine value, total peroxide value, polar compound content, fatty acid content, and core aldehyde content of hazelnut oil under different thermal processing conditions. The oxidation kinetics equation of fatty acid and temperature of hazelnut oil was established, and the correlation between the contents of fatty acid and core aldehyde and four oxidation indexes was analyzed. The results showed that the TPC of hazelnut oil exceeds 24% when heated for 10 min at 210ºC, indicating that hazelnut oil is not suitable for high temperature and long-time heating. The contents of linoleic acid and oleic acid in hazelnut oil varied significantly at different thermal processing temperatures (p ≤ 0.01). The change of linoleic acid was more consistent with the first-order oxidation kinetics model. Two core aldehydes were detected in hazelnut oil, aldehyde 9-oxo and aldehyde 10- oxo-8. The core aldehyde 9-oxo content changed most obviously with the heating temperature, and it was the main non-volatile aldehydes of hazelnut oil thermal oxidation. Correlation analysis showed that the heating temperature of hazelnut oil had a significant effect on the oxidation index (p ≤ 0.01), and linoleic acid had the strongest correlation with the oxidation index, which could reflect the overall oxidation of hazelnut oil. The total amount of core aldehyde and the content of core aldehyde 9-oxo strongly correlated with the oxidation index (p ≤ 0.01), which can be used as one of the indicators to evaluate the oxidation degree of hazelnut oil. This study is of great significance for promoting the application of hazelnut oil in daily cooking and processing.
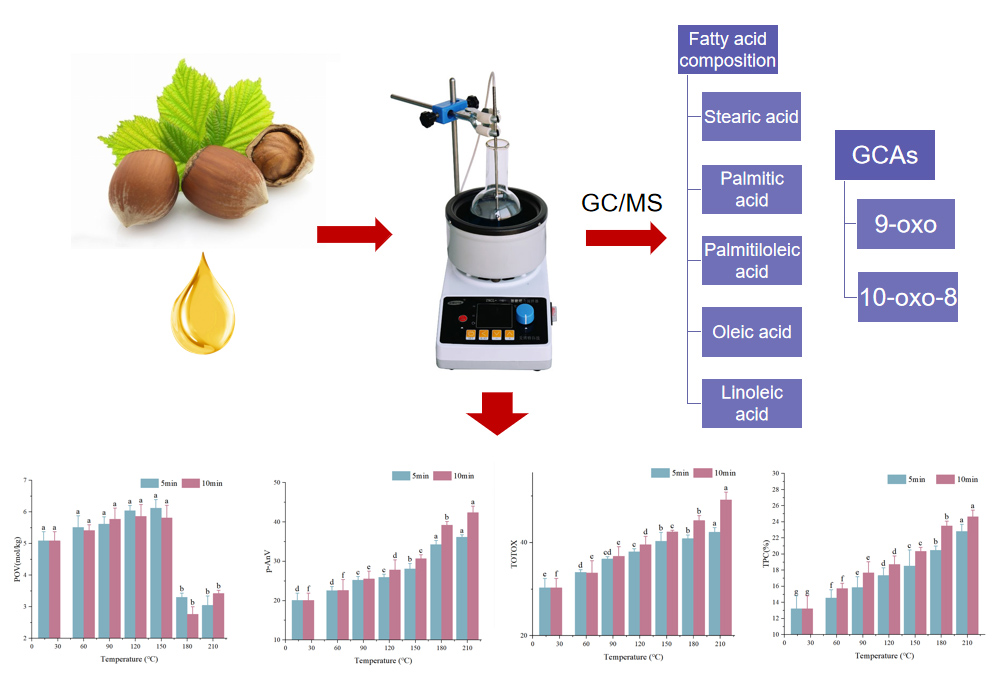 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1380K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1380K) -
Taiki Shimizu, Takaya Tanabe, Hisanori Kachi, Masashi Shibata2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1725-1733
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSCandelilla wax (CW) is used as an oil-gelling agent in cosmetic sticks. However, its hardness is inadequate compared to those of hydrocarbon waxes such as paraffin. In this study, behenyl behenate (BB), an additive plant-derived wax ester with a high melting point, was shown to improve the oil-gel hardness of CW.
Although the gel with BB alone had a relatively low gel hardness, when BB was mixed with CW at a ratio of 70:30 (CW:BB), the gel hardness significantly increased to four times that of the CW gel. The hardness of the CW and BB mixtures was higher than that of paraffin wax, which is used to solidify cosmetic oils. An increase in gel hardness was not observed when additives with chemical structures similar to those of BB, such as stearyl stearate (which has a lower molecular weight than BB) and behenic acid or behenyl alcohol (which are components of BB), were blended.
Scanning electron microscopy indicated the presence of many spherical clusters comprising fine crystallites in the CW gel. This morphology was in contrast to that of paraffin wax gel, in which only plate crystals were observed. It was concluded that this heterogeneous structure led to the low gel hardness of CW. When BB was added to CW, the spherical clusters disappeared, and the internal structure changed to a homogeneous card-house structure composed of plate crystals.
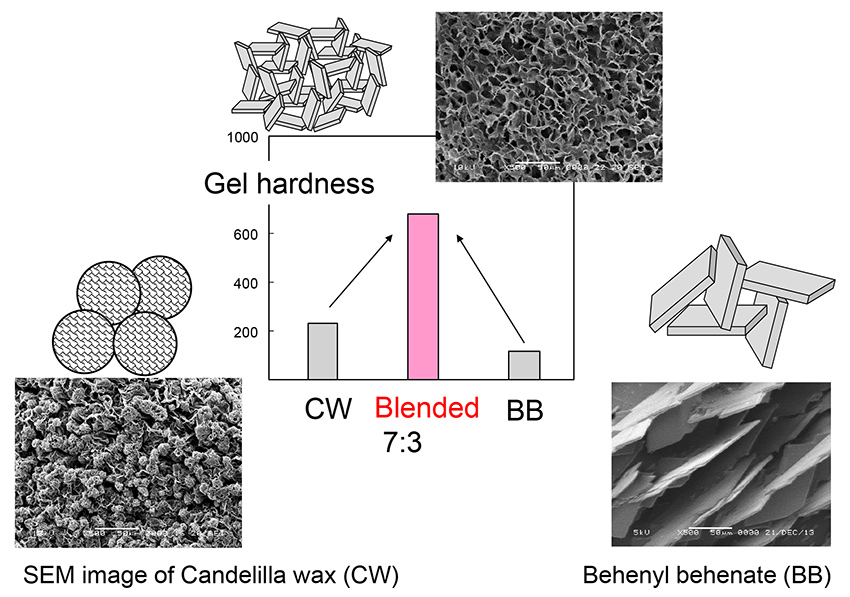 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3080K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3080K) -
Liyan Liu, Lin Li, Ni He, Bing Li, Xia Zhang2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1735-1741
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe quality and processing characters of shortening are strongly influenced by the temperature fluctuation during storage and handling. Some chemical components, especially the presence of emulsifiers in shortening formula might be attributed to the quality change of shortening in response to temperature fluctuation. In this work, the effect of emulsifiers on the mechanical properties, crystalline structure, and crystalline transformation of fat was investigated with a palm oil-based shortening under varied storage temperature (4°C, 12 h - 28°C, 12 h, cycle reciprocating). Results show that the shortening without emulsifiers deteriorated easily with a severe separation of liquid oil and reduction of hardness, which was owing to the aggregation of crystals, and the appearance to high proportion of β crystals at the later stage in storage (day 7 and day 14). However, the addition of the emulsifiers such as sorbitan monopalmitate (SMP), Glyceryl monostearate (GMS), and Glycerol monopalmitate (GMP) ameliorated the production of β crystals effectively. Among the tested emulsifiers, the shortening adding GMS showed the best quality, which remained stable in multiple cycles up to 14 times. The findings will guide the use of emulsifiers in palm fat processing.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1692K) -
Aya Yoshinaga-Kiriake, Daisuke Takata, Takashi Norito, Masayasu Maki, ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1743-1748
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSWe investigated the fatty acid composition and regiospecific distribution of triacylglycerol in Juglans mandshurica Maxim. var. sachalinensis (Komatsu) Kitam and Juglans regia L. oils. Significant differences are observed in the fatty acid compositions and regiospecific distribution of triacylglycerol in both oils. In addition, we measured volatile compounds and tocopherol content in two walnut oils. In results of volatile compound analysis, vanillin is specifically detected from J. mandshurica var. sachalinensis oil, and was not detected in J. regia L. oil. Notably, γ-tocopherol content in the J. mandshurica var. sachalinensis oil was significantly higher than J. regia L. oil.
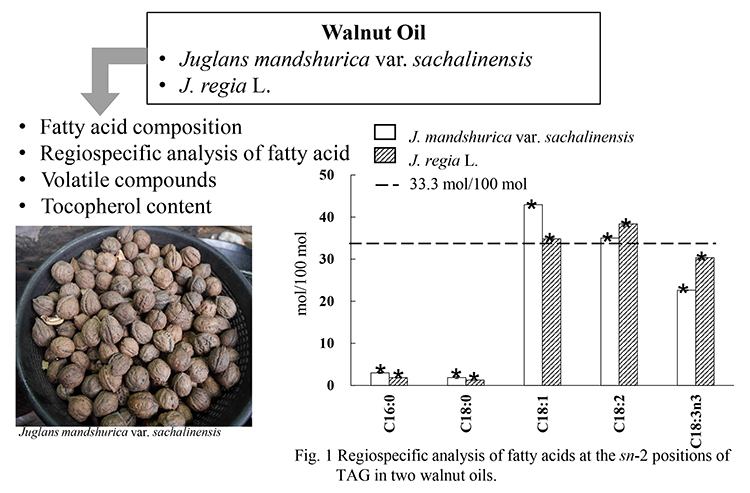 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (316K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (316K)
-
Anning Liu, Huijuan Jing, Xiaojing Du, Chaoyang Ma, Hongxin Wang2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1749-1760
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, the recovery of pecan nut kernel oil (PNKO) obtained by mechanical pressing (MP) was compared with that obtained by ultrasonic-assisted aqueous enzymatic extraction (UAAEE). At the same time, contents of substances with proven bioactivity, fatty acid compositions, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of PNKO were also assessed. Obviously, the oil yield obtained by UAAEE (71.32%) was higher than that obtained by MP (56.81%). Therefore, Plackett-Burman design (PBD), as well as Box-Behnken design (BBD), further optimized the UAAEE process, and the highest oil yield of 78.83% was acquired under the following conditions: incubation time of 2 h, the mixed enzyme (cell ulase+hemicellulase+pectinase+neutrase, w/w/w/w=1/1/1/1) concentration of 2.9%, liquid-solid ratio of 4 mL/g, pH of 4, particle size of 300 μm, ultrasonic time of 20 min, ultrasonic power of 432 W and reaction temperature of 53°C. The PNKO obtained by the two methods possessed similar fatty acid composition, but that obtained by UAAEE had comparatively low acid value and peroxide value. Moreover, rich content of total phenolics, squalene and phytosterols, as well as strong scavenging activities against DPPH and ABTS+ free radicals, were also contained in the PNKO obtained by UAAEE. These results demonstrated that UAAEE was an efficient method to acquire pecan nut kernel oil with excellent quality and high recovery.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1616K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1616K) -
Chikara Kato, Isabella Supardi Parida, Satoshi Maeda, Tsuyoshi Mikekad ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1761-1767
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSFollowing a growing interest in the physiological effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), more cell culture experiments have begun to elucidate its mechanism of action. However, to our knowledge, no reports have used instrumental analysis, such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), to study cellular uptake of PQQ. In addition, despite the propensity of PQQ to react with amino acids and other compounds, only a handful of cell culture experiments have been conducted on PQQ derivatives. In the present study, we prepared PQQ derivatives by reacting PQQ with various amino acids and used them as reference standards for optimizing the LC-MS/MS analysis conditions to detect PQQ and its derivatives. Using this method, we evaluated the uptake of PQQ into mouse 3T3-L1 cells and found that most PQQ added to the medium was taken up by the cells in its unchanged form, while some PQQ reacted with amino acids in the medium and was taken up by the cells as PQQ derivatives. These results suggest that PQQ derivatives may contribute to the physiological effects of PQQ. To further elucidate the function of PQQ, it is necessary for future studies to clarify the activity of PQQ derivatives and to evaluate the types of PQQ present in food, animal, and cell samples in more detail.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (800K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (800K)
-
Shiro Ezoe, Kenji Ueda, Hirotake Matsuo, Hiroyuki Nagaoka, Yoshihiko A ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1769-1775
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSThe aim of this study was to propose an alternative route for preparing chiral β- and α-ionols by asymmetric oxidation with a heme acquisition system A (HasA) derived from symbiotic fluorescent bacteria as a biocatalyst. The HasA (6 g) in distilled water (300 mL) was stirred at 1150 rpm for 1 day at 40°C. Subsequently, a secondary alcohol (0.77 mmol) as a substrate in 2% 2-propanol was added to the catalyst solution. After verifying that the oxidation proceeded to ca 50% using gas chromatography (GC), the reaction mixture was filtered, extracted, washed, and dried over. The extract was concentrated in vacuo and purified using silica gel column chromatography to yield the oxidized product and recover the unreacted alcohol. β-Ionol was oxidized into β-ionone in a conversion of ca. 50% in the presence of the HasA for three days, and the remaining alcohol was recovered and analyzed using chiral GC after acetylation. The HasA selectively catalyzed the asymmetric oxidation of β-ionol with a preference for the (R)- form to recover (S)-β-ionol with 96.4 ±1.6% enantiomeric excess (ee). In addition, α-ionol was similarly oxidized into α-ionone in a conversion of ca. 50% for seven days, preferentially remaining (9S)-α-ionol with 97.9 ± 0.2% ee. The characteristic aroma of (S)-β-ionol obtained by the asymmetric oxidation with the HasA showed floral and fruity like, while the aroma of (9S)-α-ionol described as violet and sweet. In this study, we successfully developed a new approach to prepare enantiomerically pure (S)-β- and α-ionols by the asymmetric oxidation with the HasA.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (459K)
-
Hamdoon A. Mohammed, Salman A. A. Mohammed, Omar Khan, Hussein M. Ali2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1777-1788
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSEucalyptol is a major volatile constituent among well-known wound healing medicinal plants. The current study evaluated eucalyptol wound healing activity in the rat’s third-degree skin-burn model. The parameters, i.e., skin-healing, oxidative/antioxidant markers, pro-/anti-inflammatory markers, were evaluated after 1- and 2-weeks of treatment regimens with 5% eucalyptol ointment. Eucalyptol-loaded ointment base of 5% w/w strength was formulated using fusion method and physically evaluated for consistency, stability, and homogeneity. A 25-rats were divided randomly into intact, negative control (untreated), silver sulfadiazine (SS, positive control), 1-week, and 2-weeks treated eucalyptol groups. Using an aluminum cylinder (120℃, 10 second duration), 3rd-degree skin burns were created on the rat’s dorsum. Skin biopsies were collected at the end of the experiment for biochemical and histological investigations. Compared to the negative group; time-dependent wound size reduction and decreased edema were observed in eucalyptol-treated animals. Histopathological examinations demonstrated epidermis integrity, decreased neutrophil, and increased capillaries number in the 2-weeks and SS groups, compared to the negative and 1-week treated eucalyptol groups. Compared to the untreated animals, the 1- and 2-weeks eucalyptol treated groups’ demonstrated significantly increased antioxidant superoxide dismutase (SOD, p=0.002 and p=0.003, respectively) and reduced lipid peroxide (LP, p=0.005 and p=0.0006, respectively). However, a significant increment of catalase (CAT, p=0.0009) was found only in the 2-weeks of eucalyptol group at a level of 2.42 ± 0.39 ng/g compared to 1.14 ± 0.04 ng/g in the untreated animals. Also, significant reductions in the cytokines, IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-α (p < 0.05); and increase in the pro-angiogenic marker, IL-10, were detected in the 2-weeks (p=0.001) and SS (p=0.002) treated animals compared to the negative and 1-week eucalyptol treated groups. The study concluded that eucalyptol induced significant duration-based wound healing properties attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1665K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1665K) -
Yang Yu, Ran Wei, Xinru Jia, Xiaoxu Zhang, Hongqin Liu, Bo Xu, Baocai ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1789-1797
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSTo overcome the problems of incomplete flavor components from Piper nigrum extract and the Piper nigrum product easy deterioration in the storage process, microcapsules of the whole Piper nigrum were prepared by spray-drying combined with enzymatic hydrolysis. Under the best conditions for the microencapsulation obtained by the response surface methodology, which have been determined as the ratio of core and wall material (1:0.2, w/w), proportion of wall materials (starch sodium octenyl succinate : maltodextrin : xanthan gum) (1:1:0.2, w/w/w), wall material concentration (11%, w/v) and inlet air temperature (180°C), the embedding rate of the prepared Piper nigrum microcapsules reached 90.21%. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and particle size distribution studies established that the Piper nigrum powder was entrapped within the microcapsules, which had intact morphology and uniform particle size distribution. Besides, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis demonstrated that the prepared Piper nigrum microcapsules could preserve the major of the volatile aroma components of Piper nigrum, carene, D-limonene, α-phellandrene, and (-)-β-pinene. The obtained results showed that the microcapsules might contribute to the development of preserving original flavor from Piper nigrum and have potential applications in the commodity market.
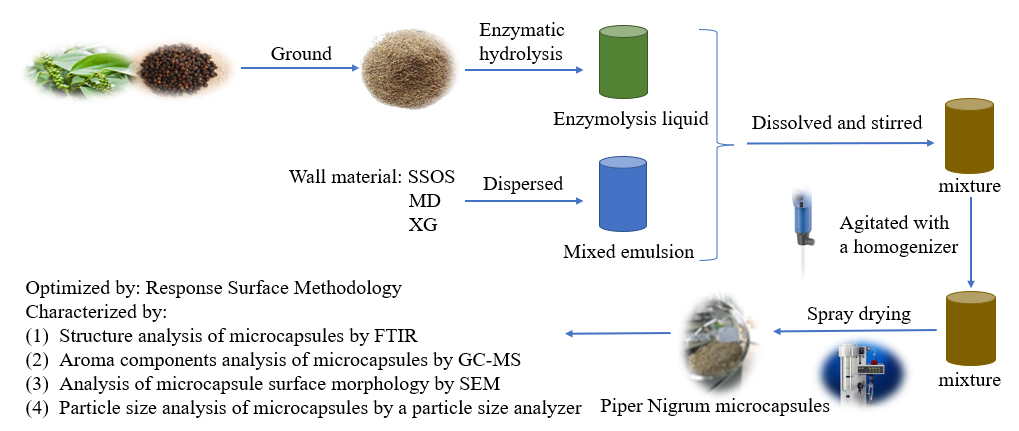 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (754K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (754K)
-
Xiaoshuang Cai, Xiaojuan Zhao, Wenbo Miao, Zhongwei Wu, Hua-Min Liu, X ...2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1799-1811
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
Advance online publication: November 07, 2022JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSIn this study, tigernut oil was extracted from tigernut meal by subcritical n-butane extraction with the assistance of microwave pretreatment. Effects of microwave pulse duration, particle size of tigernut meal, and subcritical extraction variables (temperature, time, solid-liquid ratio, number of extraction cycles) on extraction efficiency were examined by single-factor experiments and Response Surface Methodology (RSM) modeling. The results indicate that microwaving (560 W, 6 min) significantly increased the subcritical extraction efficiency. The variation of extraction yield could be interpreted as a nonlinear function of extraction time, temperature and liquid-solid ratio. Changing the independent variables could affect the oil extraction efficiency. The subcritical extraction of tigernut oil with a liquid-solid ratio of 3.62 kg/(kg of tigernut meal) at a temperature of 52°C for 32 min after three extraction cycles produced the most oil, and a maximum yield (24.736%) of tigernut oil was achieved. The ratio of unsaturated to saturated fatty acids (4.68 UFA/SFA), low acid value (3.30 mg KOH/g oil), low peroxide value (0.28 meq.kg-1), and preponderance of oleic acid indicate a high-quality oil. To describe the extraction kinetics, a modified Brunner’s mathematical model was used. The model fit the experimental data well over the entire operating range, and the explanation coefficient exceeds 96%. Our results can be used to develop an optimized method for subcritical fluid extraction of tigernut oil and can move industry further toward implementing microwave-assisted subcritical extraction in oil processing.
 graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1895K)
graphical abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1895K)
-
2022 Volume 71 Issue 12 Pages 1813-1814
Published: 2022
Released on J-STAGE: December 03, 2022
JOURNAL OPEN ACCESSDownload PDF (375K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|