All issues

Volume 64, Issue 3
Displaying 1-13 of 13 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Review
-
Motoo Tori2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 193-206
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLA chemical analysis of 30 samples of Ligularia virgaurea (Asteraceae) collected in Sichuan province and its adjacent territories in China was reviewed. These samples afforded 146 compounds, 73 of which were novel, and the chemical constituents were classified into 8 categories: (1) simple eremophilanes (without ring C) and eudesmanes including nor-derivatives, (2) furanoeremophilanes and lactones with a 1(10)-saturated bond, (3) furanoeremophilanes and lactones with a 1(10)-unsaturated bond, 1,10-epoxide, or 10-ol, (4) furanoeremophilanes and lactones with 1(10)-en-2-one, 1(10)-en-2-ol, or 1-en-3-one, (5) furanoeremophilanes and lactones with 1(10)-en-9-one, 1(10)-en-9-ol, or 1,10-epoxy-9-one, (6) cacalol and their derivatives, (7) bakkanes and their derivatives, and (8) others, as shown in Tables 1–7. In these studies, five chemotypes were identified in addition to three clades from the DNA sequences of L. virgaurea. The structural determination of some compounds was also discussed and a comment on how to express the real structure was proposed, particularly for spiro compounds. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2563K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2563K) Full view HTML
Regular Articles
-
Mio Tange, Miyako Yoshida, Yuka Nakai, Takahiro Uchida2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 207-214
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialCeftriaxone sodium preparation for injection is known to form insoluble microparticles with calcium. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of an impurity in the ceftriaxone sodium preparation on this incompatibility. Firstly, using HPLC, two impurities were identified in the ceftriaxone sodium solution. The major impurity (impurity 1) was identified as tetrahydro-2-methyl-3-thioxo-1,2,4-triazine-5,6-dione by LC/MS. Secondly, the role played by this impurity in the incompatibility with calcium was examined. Using seven different ceftriaxone preparations for injection, the effect of adding impurity 1 to mixed solutions of ceftriaxone sodium and calcium chloride on the appearance of insoluble microparticles, was examined using a light obscuration particle counter. Although incompatibility was not completely suppressed by the addition of impurity 1, the number of insoluble microparticles formed with calcium chloride solution was decreased in proportion to the concentration of impurity 1, and the concentration of calcium ion decreased as the concentration of added impurity 1 increased. These results show that impurity 1 plays a concentration-dependent role in incompatibility between ceftriaxone sodium preparation for injection and calcium-containing solutions. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1186K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1186K) Full view HTML -
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Tatsuya Suzuki, Hidemi Minami, Katsuhide Terada2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 215-221
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn the pharmaceutical tablet film coating process, we clarified that a difference in exhaust air relative humidity can be used to detect differences in process parameters values, the relative humidity of exhaust air was different under different atmospheric air humidity conditions even though all setting values of the manufacturing process parameters were the same, and the water content of tablets was correlated with the exhaust air relative humidity. Based on this experimental data, the exhaust air relative humidity index (EHI), which is an empirical equation that includes as functional parameters the pan coater type, heated air flow rate, spray rate of coating suspension, saturated water vapor pressure at heated air temperature, and partial water vapor pressure at atmospheric air pressure, was developed. The predictive values of exhaust relative humidity using EHI were in good correlation with the experimental data (correlation coefficient of 0.966) in all datasets. EHI was verified using the date of seven different drug products of different manufacturing scales. The EHI model will support formulation researchers by enabling them to set film coating process parameters when the batch size or pan coater type changes, and without the time and expense of further extensive testing.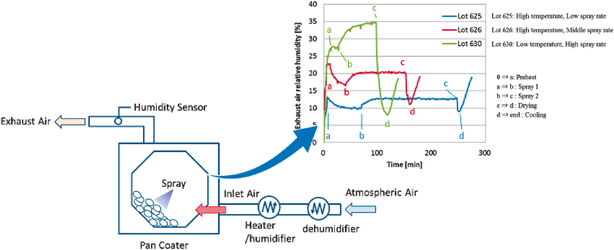 Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1125K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1125K) Full view HTML -
Yasuhiro Suzuki, Chihiro Yokohama, Hidemi Minami, Katsuhide Terada2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 222-227
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThe purpose of this study was to measure the tablet velocity in pan coating machines during the film coating process in order to understand the impact of the batch size (laboratory to commercial scale), coating machine type (DRIACOATER, HICOATER® and AQUA COATER®) and manufacturing conditions on tablet velocity. We used a high speed camera and particle image velocimetry to measure the tablet velocity in the coating pans. It was observed that increasing batch sizes resulted in increased tablet velocities under the same rotation number because of the differences in circumferential rotation speeds. We also observed the tendency that increase in the filling ratio of tablets resulted in an increased tablet velocity for all coating machines. Statistical analysis was used to make a tablet velocity predictive equation by employing the filling ratio and rotation speed as the parameters from these measured values. The correlation coefficients of predicted value and experimental value were more than 0.959 in each machine. Using the predictive equation to determine tablet velocities, the manufacturing conditions of previous products were reviewed, and it was found that the tablet velocities of commercial scales, in which tablet chipping and breakage problems had occurred, were higher than those of pilot scales or laboratory scales. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (903K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (903K) Full view HTML -
Tsuyoshi Busujima, Hiroaki Tanaka, Kanako Iwakiri, Yoshihisa Shirasaki ...2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 228-238
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLWe previously reported 2-[2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)ethyl]-N-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6-sulfonamide 2 as on orally available monoacylglycerol acyltransferase 2 (MGAT2) inhibitor which exhibited an in vivo efficacy at an oral dose of 100 mg/kg in a mouse oral lipid tolerance test. Further optimization of compound 2 to improve the intrinsic potency culminated in the identification of compound 11. Compound 11 showed a >50-fold lower IC50 against human MGAT2 enzyme than 2. Oral administration of 11 at a dose of 3 mg/kg in the oral lipid tolerance test resulted in significant suppression of triglyceride synthesis. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (786K) Full view HTML -
Hiroko Otake, Tomoyuki Okuda, Hirokazu Okamoto2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 239-245
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
Advance online publication: December 25, 2015JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSpray-freeze-drying (SFD) is a unique powderization technique to produce highly porous dry powders with a low density. The characteristic morphology can markedly contribute to the superior inhalation performances of SFD powders. Due to the increased specific surface area of the powders, however, moisture adsorption may readily occur, subsequently leading to losses of their inhalation potentials. In this study, hydrophobic amino acids were newly applied as pharmaceutical excipients to obtain SFD powders with both a favorable inhalation performance and antihygroscopic property. SFD powders composed of several hydrophobic amino acids were prepared. The morphology, particle size distribution, and crystallinity of the prepared powders were evaluated by scanning electron micrography, laser diffraction, and X-ray powder diffraction, respectively. The inhalation characteristics of the SFD powders were examined using a twin-stage liquid impinger equipped with an inspiratory pattern simulator and devices. To investigate their antihygroscopicity, moreover, the SFD powders were stored under a humidified condition to assess the morphology, crystallinity, and inhalation performance as described above. It was demonstrated that a SFD powder composed of L-leucine, L-isoleucine, or L-phenylalanine showed a superior inhalation performance, which was sufficiently maintained after storage under the humidified condition, strongly indicating their antihygroscopicity. These results indicated that the hygroscopicity of SFD powders can be effectively improved by the application of hydrophobic amino acids as excipients. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2541K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (2541K) Full view HTML -
Hirofumi Yamamoto, Masataka Oda, Marina Kanno, Shota Tamashiro, Ikuko ...2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 246-257
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
Advance online publication: December 26, 2015JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialLipopolysaccharide (LPS) antagonists have attracted considerable interest as promising candidates for the treatment of severe sepsis triggered by Gram-negative bacteria. In this article, we describe the development of a novel LPS antagonist based on chemical hybridization of vizantin and the hydrophobic molecular unit of LPS (lipid A). Vizantin, 6,6′-bis-O-(3-nonyldodecanoyl)-α,α′-trehalose, was designed as an immunostimulator from a structure–activity relationship (SAR) study with trehalose 6,6′-dicorynomycolate (TDCM). Our recent study indicated that vizantin displays adjuvant activity by specifically binding to the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/MD2 protein complex. Because lipid A unit (or LPS) is also known to trigger an inflammatory response via the same TLR4/MD2 complex as vizantin, we designed a hybrid compound of vizantin and lipid A with the aim of developing a novel biofunctional glycolipid. Focusing on the antagonism to Escherichia coli LPS in an in vitro model with human macrophages (THP-1 cells), we identified a potent LPS antagonist among the synthesized hybrid compounds. The novel LPS antagonist effectively inhibited LPS-induced release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 value of 3.8 nM, making it a candidate for the treatment drug of Gram-negative sepsis and/or septic shock. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3733K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (3733K) Full view HTML -
Nachanun Sirimangkalakitti, Masashi Yokoya, Supakarn Chamni, Pithi Cha ...2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 258-262
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialAcanthodendrilline (1), a new bromotyrosine alkaloid, was isolated from the Thai marine sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. The structure of 1 was fully characterized by spectroscopic analysis, in agreement with the synthesized compound used to resolve the single chiral center at C-11. Total synthesis of the enantiomers of 1 allowed for the comparison of specific rotation values and hence the determination of the absolute configuration as 11-S. Cytotoxicity evaluation revealed that (S)-1 exhibited approximately three-fold more potent cytotoxicity against the human non-small cell lung cancer H292 cell line than (R)-1. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (546K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (546K) Full view HTML -
Maher Abd El-Aziz El-Hashash, Mohammad Emad Azab, Rasha Abd El-Aziz Fa ...2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 263-271
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
Advance online publication: December 22, 2015JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLBenzoxazinones and quinazolinones have a wide spectrum of biological activity. In this paper we focused on studying the antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities of some newly synthesized benzoxazinone and quinazolinone derivatives. Thus we prepared 2-[α-benzoylaminostyryl]-6,8-dibromo-3,1-benzoxazin-4(H)-one 2 which underwent a reaction with primary and secondary amines, and hydrazine hydrate to give compounds 3, 4 and 5, respectively. Treatment of 2 with hydroxylamine hydrochloride, formamide and/or NaN3/AcOH afforded compounds 7, 8, 11 and 12, respectively. Also, compound 2 reacted with maleic anhydride, aromatic hydrocarbons and/or active methylene compounds to produce compounds 13, 15a–c and 16, respectively. Most of the newly synthesized compounds showed significant antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities comparable to ampicillin, mycostatine and indomethacin positive controls. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (720K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (720K) Full view HTML
Notes
-
Mika Shingaki, Tsuyoshi Wauke, Peni Ahmadi, Junichi Tanaka2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 272-275
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialChemical analysis of the sponge Dysidea cf. arenaria from Irabu Island provided four new diterpenes 1–4. Their structures were elucidated by NMR and other spectroscopic analyses. All the metabolites retained the spongian skeleton and an isovalerate ester, but were different from those previously isolated from a specimen of Okinawa Island, implying geographic variation. The cytotoxicity of compounds 1–4 to NBT-T2 cells was evaluated and their IC50 values were 3.1, 1.9, 8.4, and 3.1 µM, respectively. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (359K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (359K) Full view HTML -
Donggen Piao, Taein Kim, Hai Yan Zhang, Hyun Gyu Choi, Chong Soon Lee, ...2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 276-281
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTML
Supplementary materialFourteen compounds were isolated from the flowers of Inula japonica THUNB. (Asteraceae), including two new compounds, (1S,2S,4S,5S,8S,10R)-2-acetoxy-4,3-dihydroxy-pseudoguai-7(11)-en-12,8-olide (1) and (1S,2S,4S,5S,8S,10R)-2,4,13-trihydroxy-pseudoguai-7(11)-en-12,8-olide (2), and twelve known compounds, budlein B (3), 6β-hydroxytomentosin (4), 6-deacetoxybritanin (5), 4-epipulchellin (6), britanin (7), tomentosin (8), (+)-dihydroquercetin (9), (−)-syringaresinol (10), quercetagetin 3,4′-dimethyl ether (11), luteolin (12), britanin G (13) and inuchinenolide C (14). Structures of 1 and 2 were determined based on one and two dimensional (1D)- and (2D)-NMR data and Mosher’s esterification method. Compounds 9 and 12 showed inhibitory activities toward DNA topoisomerase I with IC50 values of 55.7 and 37.0 µM, respectively, compared to camptothecin (CPT) with an IC50 of 24.5 µM. Compounds 7–9 and 11–14 exhibited more potent inhibitory activity against topoisomerases II with IC50 values of 6.9, 3.8, 3.0, 6.9, 10.0, 14.7 and 13.8 µM, respectively, than that of etoposide (VP-16) with an IC50 of 26.9 µM. Compounds 4–7 and 10–14 exhibited weak cytotoxicities to the selected cancer cell lines. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1204K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (1204K) Full view HTML -
Takahiro Matsui, Hiroshi Sugiyama, Misaki Nakai, Yasuo Nakabayashi2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 282-286
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo evaluate the anticancer activity of the cyclometalated ruthenium(II) complexes [Ru(bpy)2(C^N)]Cl, we have studied the interaction of these complexes using calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) and cytotoxicity assays with two tumor (L1210 and HeLa) and a non-tumor (BALB/3T3 clone A31) cell lines. It is suggested that the complexes act as intercalators and/or DNA minor groove binders. Moreover, the complexes display favorable cytotoxicity activities with L1210 and HeLa, which in all cases were significantly more favorable than cisplatin. In contrast, the complexes exhibit appreciably lower cytotoxicity toward BALB/3T3 clone A31. Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (668K) Full view HTML
Graphical Abstract Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (668K) Full view HTML
Errata
-
2016Volume 64Issue 3 Pages 287
Published: March 01, 2016
Released on J-STAGE: March 01, 2016
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLDownload PDF (62K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|