All issues

Volume 79, Issue 4
Displaying 1-11 of 11 articles from this issue
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
Overview
-
Akira Takeuchi2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 157-168
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis paper describes high-entropy alloys (HEAs), bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) and high-entropy bulk metallic glasses (HE-BMGs) for their alloy design based on the quantities corresponding to the difference in atomic size and heat of mixing. The contents started with describing the differences between HEAs and BMGs, followed by the features of HE-BMGs by focusing on the universalities underlying these three alloys. The significance of thermodynamics with ability to describe the necessary quantities for designing these alloys as a function of alloy composition was argued by referring to the early studies. Furthermore, future prospects of these alloys in terms of alloy design are described for their further progress in researches.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5508K)
Regular Article
-
Ryutaro Hara, Masahiro Yamamoto, Gen Ito, Kazunori Kamimiyada, Ichihit ...2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 169-175
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSInfluence of nitrogen addition as one of the alloying element on the formation of solidification structure and the improvement of hardness after thermal treatments was investigated for high-speed steel type alloys (Fe-1.7~2.3%C-5%Cr-5%Mo-5%V). Nitrogen content was successively varied from 48 ppm to 1542 ppm by the mixing of Cr2N into the molten alloy. Analysis of diffraction pattern reveals the formation of M2CN carbonitride at N-containing specimen, whereas the eutectic MC carbides containing mainly V solidifies at N-free specimen. The macrohardness of the quenched specimens gradually increases with increasing quenching temperature. Nitrogen addition helps to improve the hardness as carbon does. Macrohardness of the quenched specimen depends on both the amount and hardness of martensite matrix. The specimen, which contains high volume fraction of retained austenite, shows the superior secondary hardening after the optimized twice tempering. Furthermore, the hardening of specimens is enhanced by nitrogen addition. The precipitation of nano-size carbonitride is observed around primary micro-size carbonitride, which indicated that M2CN carbonitride diffuses nitrogen, causes carbonitride precipitation, and finally develops macrohardness at N-containing specimen.
View full abstractDownload PDF (5134K) -
Yuichi Higashi, Chihiro Iwamoto, Yoshihito Kawamura2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 176-182
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
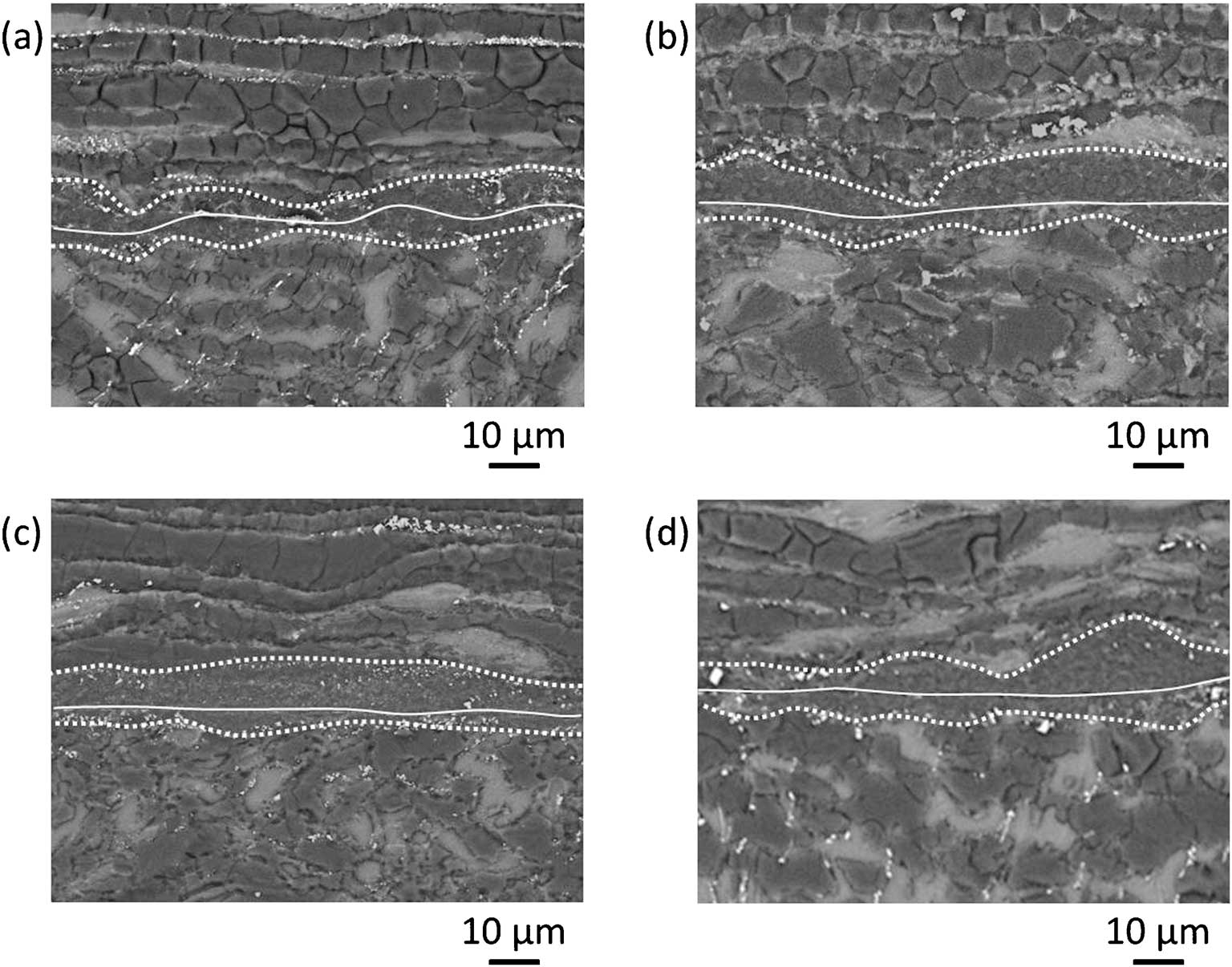
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSExtruded Mg96Zn2Y2 alloys have excellent mechanical properties and are two-phase alloys consisting of an Mg-matrix and a long-period stacking ordered (LPSO) structure phase extended along the extrusion direction. Developing the welding process of the advanced Mg/LPSO alloys is indispensable for expanding applications. This study evaluated microstructure evolution of the extruded Mg96Zn2Y2 alloy joints which were welded by ultrasonic welding.
Specimens were welded so that extrusion directions could be orthogonal to each other. The extrusion direction and the direction in which the LPSO phases extended are parallel, thus the extrusion direction of the top plate is 90° orientation to the ultrasonic vibration. The bottom plate is 0° orientation.
A band with fine grains around the weld interface was generated and the grain growth occurred outside of the band. Inside of the band indicated the basal texture and outside of the band kept the extruded texture. The width of the band with fine grains expanded in the top plate side with increasing the welding energy. The grown grains outside of the band were also large in the top plate side. In addition, the grown grains of Mg matrix were estimated to be morphology that extended to the extrusion direction. In ultrasonic welding process, the expansion of the band width and the grain size of the grown grains in the top plate side were found that the direction of ultrasonic vibration and the orientation of the extruded texture were contributed.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3891K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (3891K) -
Kaho Tomita, Toko Tokunaga, Munekazu Ohno, Kiyotaka Matsuura2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 183-190
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSIt has been shown using an Al-4.0 mass%Cu alloy as a demonstration material that hot extrusion with the use of a specially-designed die, which is called a heteromorphic die, leads to grain refinement and improvement in ductility. The heteromorphic die consists of two plates and one spacer. One plate is called a strain-giving die and has six holes of 5 mm in diameter, while the other plate is called a shape-giving die and has one rectangular hole of 9 mm×15 mm in side length. The spacer separates these plates at a distance of 10 mm and gives a space between them. The Al-Cu alloy billet was hot-extruded from the strain-giving die into the space between the two dies to produce six thin bars, and all the six bars passed together through the shape-giving die to become a thick rectangular bar. The rectangular bar produced by the present extrusion was tensile-tested at room temperature and the results were compared with those of the un-extruded billet and the bar produced by a conventional hot extrusion using only the shape-giving die. The elongation of the specimens made of the billet, the bar extruded by the conventional method and the one extruded using the present heteromorphic die were 21, 35 and 57%, respectively. The largest elongation found in the sample extruded using the present heteromorphic die should be due to the fine recrystallized grain structure in that sample. It is suggested that the recrystallization is induced by a large strain generated in the present heteromorphic die due to the friction at the large contact area between the die hole wall and the alloy.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (5746K)
View full abstractDownload PDF (5746K) -
Masayuki Koshiyama, Hazuki Sako, Munekazu Ohno, Kiyotaka Matsuura2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 191-194
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCombustion-synthesized Y-α-SiAlON and Ca-α-SiAlON powders have been consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) at 1300-1450℃ for 10 min, and the mechanical properties of the consolidated bulk samples were investigated. XRD analysis revealed that α-SiAlON partially transforms into β-SiAlON during the SPS and a bulk of α/β-SiAlON mixture was obtained. The fraction of β-SiAlON increases with the increase in sintering temperature and the α to β transformation ratio is high for Y-α-SiAlON compared with Ca-α-SiAlON. The hardness of the consolidated bulk increases with sintering temperature and after reaching the peak at 1350℃ the hardness gradually decreases with temperature in both the cases of Y-α-SiAlON and Ca-α-SiAlON. The increase in hardness with temperature arises from increase in density of the sintered body, while the decrease in hardness results from grain growth due to high temperatures. The fracture toughness monotonically increases with temperature and does not show a peak for both SiAlONs, although Y-α-SiAlON always exhibits higher toughness than Ca-α-SiAlON. The higher toughness of the Y-α-SiAlON is attributable to its higher fraction of transformed β-SiAlON, because the elongated shape of β-SiAlON leads to prevention of crack propagation.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1477K) -
Chika Tsuda, Tatsuro Morita, Shota Kariya, Chuji Kagaya2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 195-202
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThis study was conducted to comprehensively investigate the effect of combination treatment on the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, mechanical properties and fatigue strength of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The combination treatment was composed of plasma nitriding, short-time heat treatment and fine-particle bombarding (hereafter, FPB). Plasma nitriding was performed at 1123 K. The obtained results were compared with those of the previous study concerning the combination treatment in which plasma nitriding was performed at 1023 K. A thick hardened layer (thickness: 200 μm) was formed by plasma nitriding. The substrate was strengthened by short-time heat treatment. The surface brittle compound layer was eliminated by FPB, and high compressive residual stress was introduced at the same time. The combination treatment improved wear resistance without the deterioration of corrosion resistance. Moreover, the combination treatment improved tensile strength and fatigue strength although it markedly reduced ductility. The comparison with the results obtained in the previous study showed that the combination treatment in which plasma nitriding was performed at 1023 K was more effective to improve the functionalities and strength of Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
View full abstractDownload PDF (15170K) -
Takaoki Takeshita, Yoshinori Murata, Nobuhiro Miura, Yoshihiro Kondo, ...2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 203-209
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSNKH71 is a Re free nickel-based single crystal superalloy. The long-term creep strength of this alloy is superior to that of the practical used 2nd generation superalloy, CMSX-4, containing Re but the short-term creep strength is inferior to that of CMSX-4. This may be caused by the initial microstructure before creep. In order to arrange the initial morphology of the γ′ phase in NKH71, eight kinds of processes in heat treatment are carried out. After a series of heat treatments, each specimen is examined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). From SEM, it is found that the initial morphology of the γ′ phase is different by the cooling rate after solution treatment and temperatures of 1st step aging. It is also found by TEM that dislocation density at the interface between the γ and γ′ phase is different. In order to make clear the origin of the morphological difference in the each heat treatment, the phase field simulation is carried out on the basis of Gibbs free energy calculated using thermodynamic date of Ni-Al binary system.
View full abstractDownload PDF (3046K) -
Koki Shimosakaida, Shinpei Fujii2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 210-214
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSRecently, new compounds Mn2RuSn and Mn2RuSi were synthesized and their crystal structures were studied by X-ray diffraction measurements. The measurements showed that they have a Heusler-like cubic structure, but the details have been unclear so far. Therefore, to clarify their atomic and magnetic order, we have carried out first-principles total-energy calculations for several different atomic arrangements, together with ferrimagnetic and ferromagnetic orders. The comparison among total energies shows that the most stable structure is ferrimagnetic Hg2CuTi one in both Mn2RuSn and Mn2RuSi. It is also found that the compound Mn2RuSi with a Hg2CuTi structure could be a half-metallic ferrimagnet.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1491K) -
Hiroki Asami, Kohei Matsumoto, Koji Takazawa, Yu Iwahashi, Shinichi Ik ...2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 215-219
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSCr1−x-Mgx-N-O powders, with Mg content in metallic elements (x=Mg/Cr+Mg) ranging from 0 to 0.5, were synthesized from CrN and MgO powders using mechanical alloying under nitrogen atmosphere. Densification of these original powders is carried out by the spark plasma sintering is performed under a 70 MPa pressure and at 1200℃. The result of X-ray diffraction (XRD) indicated that (Cr, Mg)(N, O) phase with NaCl (B1) structure was synthesized in all the Cr-Mg-N-O powders. The MgO phase exists in the Cr-Mg-N-O ceramics for the higher Mg content of x=0.2, whereas the diffraction peaks attributed to MgO were not observed in the ceramics with x=0.1. The maximum Vickers hardness of HV 2050 was obtained for Cr1−x-Mgx-N-O ceramics with x=0.1, and was HV of approximately 500 higher than CrN ceramics (x=0). Moreover, the result of nano-indentation test showed that the Young's modulus of Cr1−x-Mgx-N-O ceramics increase from 398 GPa to 418 GPa in the x range 0 to 0.1.
View full abstractDownload PDF (1825K) -
Toshiaki Toyoda, Yuji Sutou, Shoko Komiyama, Daisuke Ando, Junichi Koi ...2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 220-226
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSThe hardness and wear properties of Ti-Mo-C-N films were investigated by nanoindentation and ball-on-disc measurements, respectively. Ti-Mo-C-N films were deposited onto a stainless steel substrate by a reactive RF magnetron sputtering in the mixture of argon (7.5 ccm) and nitrogen (0-6.0 ccm) gases using Ti25Mo25C50 target. Ti-Mo-C film deposited without nitrogen gas flow showed a hardness of 34.8 GPa. The hardness drastically decreased with increasing nitrogen gas flow rate (fN2) and reached to a minimum hardness of 16.4 GPa at fN2=2.0 ccm. Contrarily, at over fN2=3.0 ccm, the hardness drastically increased with increasing fN2 and reached a maximal value of 32 GPa, and then slightly decreased again with further increase of fN2. It was found by TEM observation that the drastic decrease in hardness is caused by the formation of nanocrystalline microstructure, while the increase in hardness is due to the microstructural change from nanocrystalline to columner structure. The friction coefficient decreased with increasing fN2 and the film deposited at fN2=5.0 ccm showed a minimum value of 0.27. The simple oxidation test in air indicated that lubricious MoO3 is easy to be formed in the film deposited at a high fN2, which should cause the reduction of friction coefficient.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2859K) -
Yuki Takebe, Tadaharu Yokokawa, Toshiharu Kobayashi, Kyoko Kawagishi, ...2015 Volume 79 Issue 4 Pages 227-231
Published: 2015
Released on J-STAGE: April 01, 2015
JOURNAL FREE ACCESSAlloy development for turbine blade materials with higher temperature capabilities is crucial in order to improve the thermal efficiency in jet engines and gas turbine systems. The 6th generation Ni-base single crystal (SC) superalloy, TMS-238, developed by NIMS has a good microstructure stability and 1120℃ temperature capability (1000 hours creep rupture life under stress of 137 MPa). In the previous studies, we investigated the influence of alloying elements on microstructure and creep strength of TMS-238 to improve the temperature capability of this alloy. The rupture life of TMS-238+ReRu alloy which had increased Re and Ru concentrations based on TMS-238 was three times longer than TMS-238 under the condition of 1150℃-137 MPa. In the case of 1000℃ and 900℃ and at higher stresses conditions, however, rupture lives of TMS-238+ReRu alloy were shorter than TMS-238 due to fine TCP phase precipitation during creep test. In this study, we examined effect of substituting Ru with Ir in TMS-238+ReRu to improve the stability of γ-γ′ two-phases microstructure and the creep strengths. As a result, the rupture life of TMS-238+ReIr was longer than TMS-238+ReRu under the condition of 900℃-392 MPa. This is due to suppression of fine TCP phase precipitation and the solution strengthening of Ir. In the case of 1150℃-137 MPa, the rupture life of TMS-238+ReIr was shorter than TMS-238+ReRu but longer than TMS-238.
View full abstractDownload PDF (2615K)
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|