
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|
-
Yukio Kobayashi, Akio NishimotoArticle type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 5 Pages 167-173
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2021
Advance online publication: March 08, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLIn this study, multilayer diamond-like carbon films 1 µm thick with different numbers of multilayer repetitions were deposited onto austenitic stainless steel SUS304 substrates using different source gases. The influence of the gas and the difference in the number of multilayer repetitions on the adhesion strength and wear resistance of the films was subsequently investigated. The samples were subjected to cross-sectional microstructure observations, elemental analysis by glow-discharge optical emission spectroscopy, nano-indentation tests, Rockwell indentation tests, friction and wear tests, and delamination tests. The nano-indentation tests showed that the films prepared using C2H2 gas were harder than those prepared using CH4 gas. In addition, irrespective of the gas used, the film hardness was improved when four layers rather than two layers were deposited. However, the hardness of the eight layers film decreased. The Rockwell indentation tests showed no improvement in adhesiveness when the gas or the number of multilayer repetitions was varied. The wear tests revealed that the friction coefficient of the films prepared using C2H2 gas was smaller than that of films prepared using CH4 gas. No difference was observed with increasing number of multilayer repetitions. The delamination tests showed that the distance until delamination of the films prepared using C2H2 gas was longer than that of the films prepared using CH4 gas. In addition, the distance until delamination was improved by changing the number of multilayer repetitions from two layers to four layers for both gases but decreased when the number of repetitions was extended to eight layers. In this study, the value of H/E (hardness/Young’s modulus) increased and various characteristics improved with increasing number of multilayer repetitions.
Mater. Trans. 62 (2021) 271-277に掲載.文献12)を追加.
 View full abstractDownload PDF (3082K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (3082K) Full view HTML -
Yutaro Sako, Takashi Kurose, Akira Ishigami, Hiroshi ItoArticle type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 5 Pages 174-181
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2021
Advance online publication: March 08, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLAluminum (Al) flake filled epoxy resin composites were fabricated, and the effect of flake surface treatment on the mechanical properties of the composites was investigated. The tensile shear test between the Al plate and epoxy resin displayed the highest interfacial shear strength of 12.1 MPa when the Al plate surface was treated with a silane coupling agent after cleaning with a degreasing agent. The highest tensile modulus 8.5 GPa in Al flake filled epoxy resin composite was obtained when the same treatment was applied to Al flake. However, the tensile strength of the composite was not improved. The aggregate structure of Al flakes was observed on the fracture surface of the specimen. The reason why the tensile strength of the composite was not improved was deduced that the shear force enough to deform Al flakes was not transferred from the epoxy resin to each flake due to the formation of Al flake aggregation.
 Fig. 9 Tensile modulus of various composites. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6993K) Full view HTML
Fig. 9 Tensile modulus of various composites. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6993K) Full view HTML -
Yutaka Shimauchi, Sachi Ikemoto, Shigekazu Ohmori, Takaomi ItoiArticle type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 5 Pages 182-189
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2021
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLSilicon (Si) has attracted considerable interest as a negative electrode material for next-generation lithium (Li)-ion batteries because of its high capacity density. In this study, ex situ electron microscopy was applied to observe Si negative electrodes under different charge states within an actual battery structure to reveal the Li intrusion direction and the effects of Li concentration on the electrode structure. All of the processes from disassembly of the charged battery and preparation of specimens for use in electron microscopy observation to specimen transport to the electron microscopes were performed under non-atmospheric exposure conditions. The orientation of the single-crystal Si powder in the charged state was observed by electron backscatter diffraction, indicating that lithiation occurred preferentially along the (110) plane of Si. The initial stage of amorphization was observed by high-angle annular dark field-scanning transmission electron microscopy, demonstrating that the Li atoms occupied the tetrahedral sites of Si crystals, and that the crystal structure was destroyed via the severing of Si-Si bonds between the {111} planes. During the charge reaction, Li occupied the tetrahedral sites via intrusion along the <110> direction of Si, and amorphization proceeded as the Li concentration increased. Thus, the amorphous region grew preferentially in the <110> direction of Si.
Mater. Trans. 60 (2019) 2328-2335に掲載
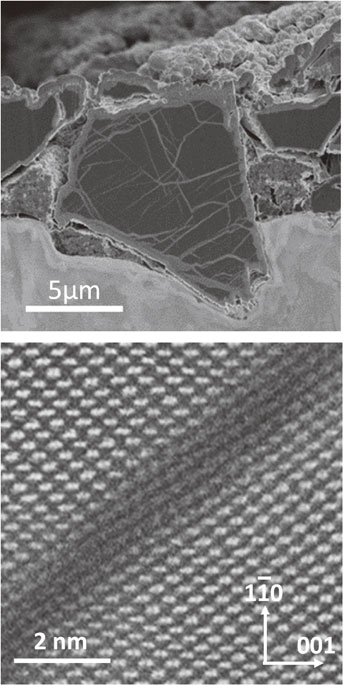 View full abstractDownload PDF (6523K) Full view HTML
View full abstractDownload PDF (6523K) Full view HTML -
Kana Inoue, Koji KakehiArticle type: Regular Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 5 Pages 190-197
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2021
Advance online publication: March 12, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLThis study was conducted to reveal the relationship between the oriented microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM). The microstructure observation in EBM sample showed that duplex structure/γ band layers fabricated by EBM process.
Tensile and creep tests were conducted for two kinds of samples fabricated by EBM. One was a sample in which loading direction was parallel to the building direction (vertical sample) and another was sample in which the loading direction was normal (horizontal sample). The tensile test showed anisotropic tensile properties at room temperature, 650℃ and 750℃. The tensile strengths of the vertical samples were inferior to the horizontal samples due to the oriented duplex structure with γ band layers. The creep lives were 206 h tested at 650℃/450 MPa and 298 h tested at 750℃/200 MPa in the vertical sample, whereas they were 332 h tested at 650℃/450 MPa and 326 h tested at 750℃/200 MPa in the horizontal sample; i.e., the creep test also showed the anisotropy of creep rupture life due to the oriented microstructure.
 As-built sample fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM) showed the anisotropy in tensile and creep properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy. Fig. (a) and Fig. (b) show the tensile properties of vertical and horizontal samples tested at room temperature, 650℃ and 750℃, and the creep curves tested at 650℃/450 MPa, respectively. The creep-ruptured surface showed the fine facets in the vertical sample (Fig. (c)) and the dimples in the horizontal sample (Fig. (d)). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8897K) Full view HTML
As-built sample fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM) showed the anisotropy in tensile and creep properties of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy. Fig. (a) and Fig. (b) show the tensile properties of vertical and horizontal samples tested at room temperature, 650℃ and 750℃, and the creep curves tested at 650℃/450 MPa, respectively. The creep-ruptured surface showed the fine facets in the vertical sample (Fig. (c)) and the dimples in the horizontal sample (Fig. (d)). Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (8897K) Full view HTML
-
Tomohisa Kanazawa, Masao Hayakawa, Mitsuhiro Yoshimoto, Yuuki Tahara, ...Article type: Technical Article
2021 Volume 85 Issue 5 Pages 198-206
Published: May 01, 2021
Released on J-STAGE: April 25, 2021
Advance online publication: March 26, 2021JOURNAL FREE ACCESS FULL-TEXT HTMLTo investigate the microstructure and damage of friction-fatigued carburized martensitic steels for the reliability of remanufacturing parts, the retained austenite (γ) phase and residual stress were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). We evaluated their changes before and after roller pitching tests, and before and after the operation of the gear parts.
In the roller pitching tests, the retained γ phase decreased with increasing load and number of cycles, presumably due to martensitic transformation caused by the cyclic load. The residual stress ratio (after/before the test) was significantly lower at high loads than that before testing, which was ascribed to the appearance of surface microcracks and the resultant release of internal stress. From SEM observations of the cross-section of the friction surface, we confirmed that the changes in the retained γ phase and residual stress ratio reflect the process of formation of multiple microcracks in the 10 µm surface layer. The decreases in both the retained γ phase ratio and the residual stress ratio would therefore appear to rule out reuse. A decision on the potential for gear reuse can be made by means of non-destructive testing, i.e., investigating the relationship between the retained γ phase ratio and the residual stress ratio.
 Fig. 8 Residual stress ratio versus retained austenite ratio. As the retained austenite ratio decreased, the residual stress ratio of used gears and 2.0 GPa without pitching increased, but that of 3.7 GPa with pitching was very low. The internal stress appears to be released by the surface microcracks. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6149K) Full view HTML
Fig. 8 Residual stress ratio versus retained austenite ratio. As the retained austenite ratio decreased, the residual stress ratio of used gears and 2.0 GPa without pitching increased, but that of 3.7 GPa with pitching was very low. The internal stress appears to be released by the surface microcracks. Fullsize ImageView full abstractDownload PDF (6149K) Full view HTML
- |<
- <
- 1
- >
- >|